The implementation of any economic activity is impossible without the movement of financial resources. Cash is involved in all processes implemented in enterprises of various forms of ownership.
Acquiring working capital, investing capital in production assets, making settlements with budgets of all levels, employees and founders - all production and administrative actions are carried out with the help of cash to increase income.
Calculations and their types
In practice, two main types of payments are used - non-cash and cash. The latter is typically used for small cash flows.
We are talking about one-time payments that can be made through the company’s cash desk.
This is the best option for small businesses with low turnover and low income. Large enterprises often prefer a cashless system due to the reduction of cash in circulation and the acceleration of the payment process. That is why today almost 98% of payments go through the banking system, launching the non-cash payment mechanism.
How is the cashless system reflected in accounting?
For accounting, planning, analysis and movement of non-cash flows on accounts opened in banking institutions, the enterprise resorts to opening a synthetic 51st accounting account.
“Current accounts” is an active account, which implies recording receipts by debit and expenditure of resources by credit. Its purpose is related to taking into account the most mobile assets of the enterprise, commensurate with non-cash funds. Reflection in the balance sheet is expressed in general terms; the balance is determined daily for operational purposes of capital management.
The balance is formed according to the formula: balance at the beginning plus debit turnover minus credit turnover.
The resulting value represents the amount of funds available at the current moment. It is credited to account 51 as the initial debit balance for the next period. Analytical accounting is carried out for each current account.
An enterprise may have accounts opened with one or more credit institutions. However, all information on the movement of non-cash funds must be summed up and assigned to the 51st account without taking into account the number of accounts.
How are transactions carried out on a current account?
As a rule, the implementation of all settlement and payment transactions is entrusted to a certain credit organization with which the company has entered into an agreement for servicing accounts. The basis for withdrawal, transfer or write-off of funds is usually a written notification from the owner, previously verified by bank employees for compliance with legal regulations and approved forms.
The right to choose the form of settlement with counterparties belongs to the account owner, who himself makes the decision based on contractual obligations. Somewhat less commonly used are unconditional write-offs, which do not require confirmation from the owner of the assets.
Cash intended for its own needs is written off by the enterprise using the number of checks previously declared to the bank. A checkbook can also be used as an enterprise’s settlements with suppliers, contractors, etc. A check issued to an individual or organization is cashed at a banking institution upon presentation by the payer.
Account document flow
The 51st account is maintained on the basis of a statement from a credit institution, to which documents must be attached that serve as instructions for the movement of resources through a specific account of the enterprise. All write-offs and transfers made by the owner of the assets within the statement period are evidenced by payment orders. The counterfoil of the check is used as justification for the cash withdrawal.
Recording of receipts, for example, revenue from an enterprise, is reflected through a bank order.
Confirmation of funds received from debtors in accordance with contractual obligations is recorded by a payment order of the paying company. All documents related to the movement of non-cash funds are drawn up in accordance with the requirements of the bank and are subject to certification by the signatures of authorized persons and the corresponding seals.
Accounting for settlements with founders (postings)
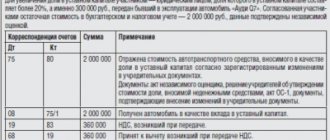
Contributions to the authorized capital in money: before registering a legal entity, i.e. before making an entry in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, no postings need to be made. After registration, accounts 75 and 80 “Authorized capital” are opened for each founder and the following entries are made:
- Dt 75-1 Kt 80 - reflects the debt of the participant on the contribution to the management company in the amount according to the Charter;
- Dt 51, 50 Kt 75-1 - reflects the receipt of money from participants to pay for the management company.
For income tax purposes, money received is not included in income, in accordance with paragraphs. 3 p. 1 art. 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation on the general system and paragraphs. 1 clause 1.1 art. 346.15 for simplified taxation system. VAT is also not charged on receipts to the management company.
The capital may be deposited in foreign currency, which results in an exchange rate difference that must be taken into account as part of the additional capital on the account. 83 with the following entries: Dt 75-1 Kt 83 - a positive exchange rate difference is reflected.
Making a contribution to the management company with property is carried out according to OS-1 for fixed assets, acts M-15 or others for inventories. If the participant is an organization, the act must contain the following information:
- value of property according to tax records. For fixed assets this is the residual value, for other property - the cost of its acquisition. For depreciated fixed assets and inventories previously written off as expenses, the cost is indicated as zero;
- VAT restored on property;
- the period of use of the property by the participant for the operating system.
If the participant is an individual, it is possible to indicate in the act his costs for the acquisition of property and attach supporting documents (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated November 2, 2016 No. 03-04-05/64313).
Postings:
- Dt 75-1 Kt 80 - reflects the debt of the participant on the contribution to the management company;
- Dt 08, 10, 43 Kt 75-1 - reflects the receipt of property in payment for the management company at the cost specified in the decision of the participants;
- Dt 19 Kt 83 - VAT recovered by the depositor is taken into account;
- Dt 68 Kt 19 - VAT is accepted for deduction.
There will be no income for income tax. Property is accounted for at its value from the deed if the investor was an organization. If the property was contributed by an individual, it must be assessed by an independent appraiser (Letter dated November 2, 2016 No. 03-04-05/64313). For tax accounting purposes, the value of such property is taken as the lesser of the acquisition costs from the act of the individual founder or the market value from the appraiser's report. Received inventories are taken into account in expenses in the general manner, depreciation on fixed assets is calculated based on the remaining period of use by the previous owner. The useful life of fixed assets received from an individual does not decrease.
The increase in the capital is reflected by the following transactions:
- Dt 75-1 Kt 80 - for the amount of the additional deposit;
- Dt 84 Kt 80 - The capital is increased due to retained earnings.
What is reflected in the debit of the account
The debit of the 51st account is used to reflect cash receipts.
As a rule, crediting to the current account is made from the following sources:
- cash register of the enterprise - compiled by posting D 51 / K 50;
- settlements with counterparties (buyers, suppliers, other debtors), expressed in the form of a return of advance payment, settlements on claims made, excessively transferred funds - compiled by posting D 51, K 62, K 60, K 76;
- credits, borrowings, advances - borrowed funds, respectively, are reflected by entry D 51 / K 66;
- settlements with shareholders, founders - funds are contributed as working capital/in the event of an increase in the authorized capital and are reflected by posting D 51 / K 75;
- settlements with budgets and extra-budgetary financing organizations - we are talking about transfers of overpaid taxes, amounts of social security for citizens (sick leave, various benefits, etc.). Reflected by wiring D 51, K 68, 69.
The summation of turnover by debit is carried out for the reporting period and represents a generalized indicator indicating the receipt of funds into the current account of the enterprise. The use of a balance sheet is used to analyze receipts by item.
Calculation of dividends
The founders have the right to receive profits in the form of dividends. The terms of payments are stipulated by the constituent documents. The decision on the distribution of funds is made by the management structure. For example, this could be a shareholders meeting. The founders are paid dividends in the amount of the initial contribution. For example, the creator contributed 50% of the authorized capital. Consequently, he becomes entitled to half of the organization's profits. To account for dividend payments, subaccount 2 is opened to account 75.
The accrual of funds to the founder is reflected in these entries:
- DT84 KT75/2. Payment of dividends to persons who are not employees of the organization.
- DT84 KT70. Transfer of dividends to company employees.
Funds must be paid to the founders within 2 months from the date of the decision on profit distribution. The corresponding rule is given in paragraph 3 of Article 28 of the Federal Law “On LLC” No. 14 of February 8, 1998. If this instruction is violated, the founders can recover from the LLC a percentage in the amount of 1/360 of the refinancing rate on the basis of Article 395 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The following taxes are charged on dividends:
- For FL income.
- For the profit of the legal entity.
The tax agent will be the company itself. The rate for residents of the country will be 13%. The tax base for dividends is determined separately. For example, if a person receives a salary and dividends, the base must be calculated separately from these forms of income.
IMPORTANT! A resident is a person who stays in the country for at least 183 days throughout the year. The period must be continuous.
The income tax rate is 0% when one resident receives funds from another resident. However, the following conditions must be met:
- The dividend recipient's contribution is 50% or more of the authorized capital.
- The recipient holds the deposit for at least a year.
In other cases, the rates will be as follows:
- 13% if dividends are issued by a company that does not meet the conditions given above.
- 15% if funds are paid to non-residents.
These entries will appear in the accounting:
- DT75/2 KT68. Withholding personal income tax on dividends paid to persons who are not employees of the organization.
- DT70 KT68. Withholding personal income tax from amounts transferred to employees of the subject.
- DT75/2 KT68. Withholding tax on payments to legal entities.
At this stage, funds are only credited. Preparations for payment are in progress.
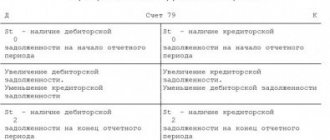
What is reflected in the account credit
The formation of a loan for the fifty-first account of an enterprise is carried out by writing off non-cash funds.
Loan turnover reflects the total amount of cash withdrawals, transfers and debits from the account.
Let's look at the loan transactions:
- D 50 / K 51 – funds were withdrawn from the current account. The expense item is indicated in advance. Cashing out is subject to a limited procedure. Often used by enterprises when paying wages or for business needs;
- D 51/55, K 51 – part of the funds was transferred from the current account to another account or a special letter of credit was opened for settlements with the counterparty;
- D 60/62/76, K 51 – the amount is transferred from the current account to contractors, suppliers, other creditors (for example, for services, goods, return of products);
- D 66, K 51 – interest for the use of borrowed funds is transferred to the current account or the loan debt is closed;
- D 68/69, K 51 – speaks of the fulfillment of obligations to extra-budgetary funds, budgets of all levels (the designation of a sub-account in correspondence takes into account the specific fund/tax);
- D 70, K 51 – salaries of employees were transferred;
- D 75, K 51 – payments were made to the founders based on performance results.
Payments to founders
Payments may be made in the form of money or property. If the founder receives money, this posting is made: DT75/2 (70) KT50, 51, 52. Payment of funds minus tax.
If the founder receives income in the form of property, this posting is made:
- DT75/2 KT90/1. Dividends were transferred in the form of services, goods, and property.
- DT75/2, 70 KT90/1. Dividends were transferred in the form of other property (materials).
- DT90/2 (91/2) KT43, 41, 20. Write-off of the cost of property.
- DT90/3 KT68. VAT accrual.
The cost of property paid to the founders as dividends includes the amount of VAT on the basis of Article 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. If taxes on personal income are withheld, the amount of dividends is not reduced by tax deductions.