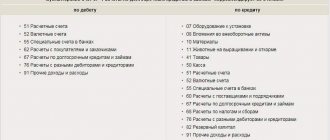
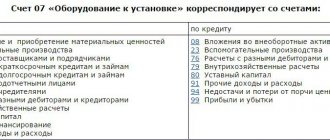
Main characteristics of 66 accounts
According to the Chart of Accounts for the financial and economic activities of organizations and the Instructions for its application (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n), account 66 in accounting is called “Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings.”
Reflect on account 66 business transactions showing the status of short-term (for a period of no more than 12 months) loans and borrowings received by the organization.
Now about the score 66. It is active-passive:
- passive - because it takes into account debts to counterparties who lent funds to the organization, i.e. there is always a credit balance;
- active - there may be a balance of 66 debit accounts when borrowed funds are repaid in a larger amount or interest has been overpaid.
Also see “Short-term loans and borrowings: line item on the balance sheet.”
What about the credit of account 66
The amounts of short-term credits and loans received by the organization are shown in the credit of account 66 and the debit of accounts:
- 50 "Cashier";
- 51 “Current accounts”;
- 52 “Currency accounts”;
- 55 “Special bank accounts”;
- 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”, etc.
Interest payable on loans and borrowings received is reflected in the credit of account 66 in correspondence with the debit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”. In this case, accrued interest amounts are taken into account separately.
Analytical accounting on account 66 is carried out according to:
- types of credits and loans;
- credit institutions;
- other lenders who provided them.
The Ministry of Finance does not list possible subaccounts for account 66 in the Chart of Accounts. That is, organizations act here at their own discretion (also see below about bills).
https://youtu.be/aH6gWoiRYF0
Topic 16. Accounting for expenses on loans and credits
1. Interest on a short-term loan received by an organization is included in other expenses:
a) on the date of payment;
b) on the date of accrual of interest in accordance with the terms of the loan agreement;
c) always at the reporting date of the annual financial statements.
2. A long-term liability is:
a) an obligation whose maturity date has passed;
b) a liability that will mature within 12 months after the reporting date;
c) an obligation that will mature within a period exceeding 12 months.
3. The accrual of interest on a loan received by an organization includes:
a) the cost of products sold;
b) for current production costs;
c) for other expenses of the reporting period.
4. Interest on loans received for the purchase of fixed assets before the objects are put into operation includes:
a) for investments in non-current assets;
b) for general business expenses;
c) for other expenses of the reporting period.
5. Accounting for received loans and borrowings is reflected by the following entries:
a) D51 K60; b) D67 K51; c) D51 K67; d) D60 K67.
6. The opening of a letter of credit account using a short-term bank loan is reflected by the posting:
a) D51 K66;
b) D55 K66;
c) D52 K66;
d) D57 K66.
7. Accounting for interest on loans and borrowings is reflected by the following entries:
a) D67 K51;
b) D51 K66;
c) D62 K90;
d) D66 K51;
e) D51 Kt 67.
8. Repayment of loans and borrowings is reflected by the following entries:
a) D67 K51;
b) D66 K51;
c) D51 K66;
d) D51 K67.
9. Bonds placed by the organization with a circulation period of 12 months are recorded in the account:
a) 58 “Financial investments”;
b) 66 “Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings”;
c) 67 “Calculations for long-term loans and borrowings.”
10. The costs of servicing loans and borrowings include:
a) interest due on received loans and borrowings;
b) the borrower's costs for consulting and information services related to obtaining a loan;
c) bank commission for banking services.
11. The organization places bonds at a price exceeding the par value; the maturity period of the bonds is 12 months:
a) on account 67 reflects the amount actually received upon placement;
b) on account 66 the nominal value is reflected, and the excess amount is recorded in the account. 98;
c) on account 67 the nominal value is reflected. cost, and the excess amount is taken into account on account99.
12. On June 1, the organization received a loan in the amount of 300,000 rubles. for a period of 3 months at 20% per annum. Interest is calculated and transferred to the lender monthly at the end of each month. The principal amount is returned on August 31. Prepare accounting entries.
| No. | Contents of operation | Sum | Postings |
| Debit | Credit |
The organization issued its own promissory note with a nominal value of 300,000 rubles to secure the loan received. The loan amount is 270,000 rubles, the discount is taken into account as part of deferred expenses. Prepare accounting entries.
| No. | Contents of operation | Sum | Postings |
| Debit | Credit |
The organization raises borrowed funds by issuing short-term interest-free bonds with a maturity of 6 months. The nominal value of the bonds is 400,000 rubles, bonds are placed at a price of 380,000 rubles. The accounting policy provides for the one-time inclusion of the discount amount in operating expenses. Prepare accounting entries.
| No. | Sum | D | TO |
15. The organization placed bonds with a par value of 1,000,000 rubles on January 1, 2008. at a price of RUB 1,200,000. The maturity date of the bonds is December 25, 2011, interest is paid quarterly, the rate is 15% per annum. Make accounting entries for 2008.
| No. | Contents of operation | Sum | Postings |
| Debit | Credit |
16. Debt on credits and loans, the repayment period of which has not come, is called:
a) short-term;
b) expired;
c) long-term;
d) urgent.
17. Receipt of a short-term loan at the cash desk of an organization is reflected in accounting:
a) D 50 K 66;
b) D 50 K 67;
c) D51 K 66;
d) D 51 K 67.
18. Add. expenses incurred in connection with obtaining loans and borrowings do not include:
a) payment for intermediary services;
b) expenses for communication services;
c) depreciation of fixed assets;
d) payment for consulting services.
19. Accounting entry D 51 K 66 reflects:
a) obtaining a short-term loan or loan;
b) transfer of interest;
c) calculation of interest;
d) loan repayment.
20. The return of loans previously issued to another organization is reflected by the entry:
a) D 51 K 57;
b) D 51 K 58;
c) D51 K 58;
d) D 55 K 76.
Topic 17. Accounting for settlements
1. The limit on the cash balance at the organization’s cash desk is established:
a) the head of the organization;
b) Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
c) approved by the servicing bank based on the organization’s calculations.
2. The form of settlements between organizations is established:
a) contracts concluded by organizations;
b) tax authorities;
c) the servicing bank.
3. The cash limit may be exceeded:
a) by order of the head of the organization;
b) only on the days of payment of wages;
c) in accordance with the schedule approved jointly with the bank;
d) only in emergency cases.
4. Receipt of money from the current account to the cash desk for payment of wages is reflected in accounting:
a) Dt 50 Kt 51;
b) Dt 70 Kt 52;
c) Dt 50 Kt 57.
5. Payment to the supplier for materials is reflected in accounting:
a) D60 K51;
b) D60 K52;
c) D60 K57.
6. Receipt of money to the current account from product buyers:
a) D51 K60;
b) D51 K62;
c) D51 K76.
7. When cash is received for sold products, the following entry is made in accounting:
a) D51 K76;
b) D51 K99;
c) D50 K62;
d) D51 K90.
8. When issuing wages from the organization’s cash desk, the following entry is made in accounting:
a) D70 K51;
b) D51 K70;
c) D50 K70;
d) D70 K50.
9. Funds are issued from the organization’s cash desk to the accountable person:
a) by decision of the cashier;
b) at the request of the accountable person;
c) by order of the head of the organization.
10. Accounting entry Dt 50 Kt 71 means:
a) receipt of money by an accountable person for travel expenses;
b) return of unused accountable amounts;
c) payment of wages;
d) submission of an advance report to the accounting department.
11. Depositing funds into the organization’s cash desk is formalized:
a) receipt order;
b) cash receipt order;
c) advance report;
d) account.
12. Bukh. posting Dt 52 “Currency accounts” Kt 75 “Settlements with founders” means:
a) opening a foreign currency account in a bank;
b) receipt of dividends by the founders in foreign currency;
c) transfer of money in foreign currency to the supplier;
d) contribution of foreign currency by the founders to the authorized capital.
13. The accountable person was given an advance for travel expenses:
a) accounts payable is recognized for the amount of the advance issued;
b) expenses for current activities are recognized for the amount of the advance issued;
c) for the amount of the advance issued, before the approval of the advance report, receivables are recognized.
14. The buyer transferred the delivery amount specified in the contract to the seller’s bank account before shipping the products. In the seller's accounting:
a) revenue from the sale of products should be recognized, because the funds have actually been received;
b) accounts payable are recognized for the amount of payment received;
c) other income is recognized in the amount of payment received.
15. Amounts of accounts payable written off the balance sheet for which the statute of limitations has expired include:
a) on other income of the organization in the reporting period;
b) on income from ordinary activities;
c) for other expenses of the reporting period.
16. Write-off from the reserve for doubtful debts of receivables from customers that are unrealistic for collection is reflected by the following entries:
a) Dt 99 “Profits and losses” Kt 63 “Provisions for doubtful debts”;
b) Dt 63 “Provisions for doubtful debts” Kt 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”;
c) Dt 63 “Provisions for doubtful debts” Kt 91 “Other income and expenses”;
d) Dt 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” Kt 63 “Provisions for doubtful debts”.
17. At the end of the reporting year, the amount of accounts receivable in settlements with customers amounted to 1,000,000 rubles; The amount of the reserve for doubtful debts at the end of the year is 150,000 rubles. In the balance sheet, accounts receivable will be reflected in the amount of:
a) 1,000,000 rubles;
b) 1,150,000 rubles;
c) 850,000 rub.
18. The manufacturing organization entered into an agreement with the buyer of the products in the amount of 354,000 rubles, incl. VAT. The contract provides for advance payment for products in the amount of 50% of its cost. The buyer made an advance payment, the products were shipped, and the final payment was made. Prepare accounting entries.
| No. | Sum | D | TO |
The organization’s balance sheet includes accounts receivable in the amount of 22,800 rubles, which arose under a product supply agreement, the statute of limitations for which has expired. Prepare accounting records for debt write-off; no reserve for doubtful debts was created.
| No. | Sum | D | TO |
20. An organization purchases a consignment of goods in the amount of 90,034 rubles, including VAT. According to the supply agreement, the goods are shipped to the buyer only after making an advance payment in the amount of 80% of the contract value. After receiving the goods, the organization transfers the remaining amount. Prepare accounting entries.
| No. | Sum | D | TO |
During the inventory of accounts payable, a debt for delivered goods was identified in the amount of 9,440 rubles, including VAT, the statute of limitations for which had expired. Prepare entries for debt write-off.
| No. | Sum | D | TO |
22. The debt of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital is included in the debt:
a) accounts receivable;
b) urgent;
c) doubtful;
d) creditor.
23. Repayment by the founders of debt on contributions to the authorized capital by transferring funds to the current account is reflected in the accounting entry:
a) Dt 75 Kt 51;
b) Dt 58 Kt 75;
c) Dt 51 Kt 75;
d) Dt 75 Kt 80.
24. Transfer of taxes to the budget is reflected in accounting:
a) Dt 68 Kt51;
b) Dt 68 Kt52;
c) Dt 68 Kt 50.
25. Property tax has been assessed, which is reflected in accounting:
a) Dt68 Kt51;
b) Dt99 Kt68;
c) Dt91 Kt68.
26. Establish a correspondence between business transactions for the purpose of various taxes and correspondence accounts:
1. income tax accrued a) D 91 K 68
2. property tax accrued b) D 68 K 51
3. land tax is transferred c) D 99 K 68
27. The debt of the founders for contributions to the management company is included in the _________ debt of the organization:
a) urgent;
b) doubtful;
c) creditor;
d) accounts receivable.
Bonds on the books. account 66
Separate entries in account 66 are made in relation to short-term loans raised by issuing and placing bonds.
| Situation | Solution |
| Bonds are placed at a price exceeding their face value | Make entries according to Dt 51 “Current accounts”, etc. in correspondence with the accounts:
The amount allocated to account 98 is written off evenly during the circulation period of the bonds to account 91 “Other income and expenses”. |
| Bonds are placed at a price below their face value | The difference between the placement price and the nominal value of the bonds is added evenly during the period of circulation of the bonds from the credit of account 66 to the debit of account 91. |
Dt 60 and kt 60, 50, 51, 76, 62 in accounting (nuances)
Important
Dt 19 Kt 60 - reflected input VAT of RUB 23,796.61. Dt 68 Kt 19 - VAT is accepted for deduction in the amount of RUB 23,796.61. March 31: Dt 62 Kt 90 - return of goods 156,000 rubles. Dt 90 Kt 68 - VAT charged RUB 23,796.61. Dt 90 Kt 41 - the cost of goods is written off 132,203.39 rubles. Dt 60 Kt 62 - offset of obligations in the amount of 156,000 rubles was carried out.
IMPORTANT! Tax officials consider the return of a quality product as a reverse sale (letter from the Ministry of Finance dated February 18, 2013 No. 03-03-06/1/4213). Example for wiring Dt 60 Kt 76 Let's look at another situation.
Attention
When transferring an advance, its amount is credited to the debit of account 60/2 by posting D60/2 K50 (51, 52). After which the supplier delivers, provides services or performs work.
Bills of exchange on account 66 in the accounting department
A separate sub-account to account 66 reflects settlements with credit institutions for accounting (discounting) bills and other debt obligations with a maturity of no more than 12 months.
| Situation | Solution |
| Accounting (discount) operation for bills and other debt obligations | The organization-bill holder reflects according to Kt 66 (face value of the bill) and Dt 51 “Settlement accounts” or 52 “Currency accounts” (actually received amount of funds) and 91 “Other income and expenses” (account interest paid to the bank). |
| Closing the accounting (discount) operation of bills and other debt obligations | Based on the bank’s notification of payment by reflecting the amount of the bill under Dt 66 and the credit of the corresponding accounts receivable accounts |
| Return by the organization-bill holder of funds received from the bank as a result of discounting (discounting) bills or other debt obligations due to failure by the drawer or other payer of the bill to fulfill its payment obligations on time | Make an entry according to Dt 66 in correspondence with cash accounts. At the same time, the debt for settlements with buyers, customers and other debtors, secured by overdue bills of exchange, continues to be reflected in the accounts receivable. |
Analytical accounting of discounted bills is carried out according to:
- credit institutions that have discounted bills of exchange or other debt obligations;
- drawers;
- separate bills.
Accounting for settlements with credit institutions, lenders and bill drawers within a group of interconnected companies, the activities of which are compiled under consolidated accounting records, is kept separately on account 66.
Display of receipts and return of credit/borrowed resources in accounting records for item 66
As you can see, the designated position is used when attracting short-term resources not only in national, but also in foreign currency. In the second case, the funds received are displayed in the equivalent of the national currency at the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the day the resources were received.
The financing received is recorded in credit 66 of the correspondence account with items 50, 51, 52 and 55.
For the financing received, the company will at some point in time incur certain cost items in the form of interest expenses on loan funds, commissions of the lending institution and exchange rate differences. All these costs and income (if we are talking about a positive exchange rate difference) are taken into account in account 91.1 in the structure of operating costs.
With regard to the return of the received financing and the payment of interest on it, these amounts are reflected in the debit part of position 66 in combination with 50, 51 or 52 accounts.