Terminology
The volume of product sales on the balance sheet is the amount of revenue received for the sale of goods in the reporting period. In this case, the form of calculations does not matter. Products can be sold on credit, for cash, with deferred payment or at a discount. Therefore, for a more accurate calculation, the formula for calculating net sales in the balance sheet is used, when the revenue received is adjusted by the amount of goods shipped on credit.
Sales volume reflects the amount of funds received by the company. Therefore, it should be calculated by all organizations. The indicator can be expressed in the quantity of goods sold, the amount of funds received, the monetary value of goods sold, etc.
https://youtu.be/jcObl35A5Wk
LET'S SUM UP
1. The larger the share in the cost structure of high-margin products (products with the maximum ratio of marginal income to price), the higher the level of marginal income for the company as a whole. Structural restructuring in favor of increasing the share of high-margin products contributes to the growth of sales profits.
2. To improve the sales structure and increase the profit of a company with limited resources, the priority of production of a particular type of product must be assessed based on the marginal income per unit of the limiting factor (for example, by the processing time of a unit of production in machine hours).
3. The company's acceptance of an additional order depends on the influence of the operating leverage effect, that is, on the ratio of variable and fixed costs. The influence can be positive and negative.
The positive impact of the operating leverage effect appears only after reaching a sales volume at which fixed costs are covered. Thus, the critical sales volume in the company is blocked.
4. To quantify the coverage of all current cash expenses of an enterprise due to sales growth, you can use a formula similar to that used to determine the critical sales volume. In this case, expenses that are not accompanied by an outflow of cash, primarily depreciation charges, are excluded from fixed expenses. This formula must take into account changes in the composition of current assets (inventories) and investments in long-term assets.
Inventory turnover in days
– annual production costs;
– average annual value of reserves (usually defined as the amount at the beginning and end of the year, divided in half, although a more detailed study of their changes during the year is possible)
The higher the company's inventory turnover, the more efficient production is and the lower the need for working capital to organize it.
When using income statement data for a period other than the year, the cost of sales value must be adjusted accordingly.
– annual turnover of the company;
Avg. accounts receivable - the average annual value of accounts receivable (usually defined as the amount at the beginning and end of the year, divided in half, although a more detailed study of its changes during the year is possible)
RT shows how effectively the company organized the collection of payments for its products. A decrease in this indicator may signal an increase in the number of insolvent customers and other sales problems, but it may also be associated with the company’s transition to a softer policy of customer relations aimed at expanding market share. The lower the accounts receivable turnover, the higher will be the company's working capital needs to expand sales.
When using income statement data for a period other than the year, the sales volume value must be adjusted accordingly. See accounts receivable turnover in the marketer's dictionary.
Sales volume = Revenue
All data necessary to calculate this indicator is taken from the income statement. The return on sales ratio reflects the company's income for each ruble earned and can be useful both for the correct interpretation of turnover data and for economic forecasts in conditions of limited market volume, which constrains sales growth. Also, return on sales is an important indicator for comparing the efficiency of business organization in companies operating in the same industry.
Despite the fact that the most common version of this ratio is the calculation based on the use of net profit, other options are often used. When calculating ROS, instead of a company's net profit, the following can be used:
- gross margin;
- Operating profit;
- earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT);
- profit before taxes
The choice of calculation option depends on the purposes of the analysis and the operating conditions of a particular company.
The efficiency of the enterprise in the reporting period is calculated by correlating various indicators of profitability and costs. There are several profitability indicators. Let's look at the main ones.
Sales efficiency is determined by the ratio of profit to revenue. If gross profit is used in the numerator of the fraction, then this indicator is called gross return on sales. =:
- GPM = Gross Profit : Revenue = (Sales Volume – Total Profit) : (Price x Number of Products).
Operating return on sales is calculated as follows:
- ROS = EBIT: Revenue = line 2300 2330: (2110 – (2120 2210 2220)).
Balance sheet return on sales:
- RP = Profit: Revenue = line 050: line 010 (form No. 2).
- RP (from form No. 2) = 2200: 2110.
Most often, to determine sales efficiency, the net profitability indicator is calculated:
- NPM = Net Profit : Revenue.
These formulas are used to determine the share of different types of profit in revenue. By analyzing the value of the coefficient over time, you can determine what changes have occurred in the organization’s activities.
Production volume calculation formula in economics
Suppose that the enterprise sold 1000 units of some product “A” during the year, and the costs of production and sales of this product in the period under review amounted to 25,000.
Determine the cost of products produced by all departments of the enterprise for the analyzed period (gross product turnover). For calculations, use the accounting data. Find the cost of manufactured and sold products for the period on line 020 “Product cost” of the Profit and Loss Statement.
To make accounting entries for the receipt of revenue, it is necessary to comply with the principles of income recognition laid down by the Ministry of Finance in the Accounting Regulations “Organizational Income” PBU 9/99:
- the company has the right to funds from sales, which is supported by documents. In this case, the counterparty accepted the service or received the rights to the product sold to him;
- the volume of income and expenses associated with sales can be calculated;
- the firm has confidence that the transaction will take place and will bring economic benefits through the receipt of money or other property.
You will need
- Accounting data for the period under review (Balance Sheet, Profit and Loss Statement).
To carry out account assignment confirming the fact of sale, documents must correspond to standard samples or be drawn up according to a form developed and approved by the company.
The rhythm of product release is the release of products in accordance with the planned target for certain periods of time. Characterization of the degree of plan in terms of rhythm is carried out using the rhythm coefficient, which is determined by the method of least numbers.
Net profit (or simply Profit)
Gross profit (accounting profit) is the difference between the sales amount (sales income) and expenses (costs). Accounting profit (dirty profit) does not take into account taxes and deductions.
Gross profit = Net sales income − Costs (Cost Operating expenses)
Operating expenses are the day-to-day costs a company costs to run its business and produce products and services.
Profit is the remainder of total income after deducting all costs, the difference between gross profit and additional expenses, such as: uncompensated own costs of the entrepreneur, not included in the cost, including lost profits, costs of “stimulating” officials, additional bonuses to employees.
Profit is one of the performance indicators. Therefore, when analyzing the work of an organization, one should correlate the level of profit received with the costs incurred. There are several types of profits.
1. Income received from sales is called revenue or sales volume.
2. Gross profit is sales volume adjusted by the amount of production costs incurred:
- VP = Sales volume – Cost.
QUESTIONS AND SOLUTIONS
One of the most important factors in managing production and sales processes is the division of costs into variable and fixed.
This division makes it possible to predict profits based on how costs change depending on the growth or decline in sales volume, and to determine for each specific situation the volume of sales that ensures the break-even operation of the enterprise. This, in turn, allows you to avoid erroneous decisions made in the case of calculating the cost in the amount of full expenses. The key indicator in the sales profit management system is marginal income , which is the difference between sales revenue and variable costs. The economic significance of marginal income is that it covers fixed costs. Any excess of marginal income over fixed costs forms the company's profit .
Marginal income characterizes the contribution of each product sold to the profit of the enterprise. Thanks to this indicator, the company's management receives information about the profitability of each type of product in the overall financial result .
Sales growth entails an increase in working capital and requires an increase in sources of financing. Consequently, any forecast of an increase in sales requires a forecast analysis of the enterprise's cash flows, during which it is possible to assess the risk of a cash deficit (negative net cash from current activities).
Costs, production and sales volumes, and profits are closely interrelated, and many questions related to these indicators arise. We will consider the solution to many of them in this article.
Gross Margin
S = (FC EBIT)/MPed
It is deciphered as follows: FC are conditionally fixed costs that are of a production nature; EBIT is profit until interest is subtracted from it; MPed is marginal profit, which is calculated per unit of production, which in turn is calculated as an increase in the selling price per unit of goods (p) over variable costs per unit of goods (v): MPed = p – v
So, thanks to this formula, you can easily solve all your questions, and calculate and analyze all the necessary nuances with indescribable ease.
In this matter, an important issue is the ability to calculate gross sales volume. It should be said that the calculation of gross income occurs over a certain period of time, and is also based on the structure of trade turnover, which operates within certain standards of trade markups, including those regulated by the state.
The calculation of gross income for the planned period is based on the projected structure of trade turnover and the current norms of trade markups, including those regulated by the state for socially important goods. Gross income is calculated using the TN formula.
ROS = (Net Profit x 100%) / Net Sales
After the questions with the formulas are resolved, it is necessary to move on to the next question, namely, what is the break-even point. It is worth saying that the break-even point, which is often referred to as the profitability threshold (more about profitability of sales), implies that this is an economic indicator that characterizes a certain sales volume, where revenue from the sale of goods equals the costs of producing these goods .
As for the break-even analysis, it is extremely necessary in order to be able to analyze the success of the enterprise, as well as assess its level. Therefore, break-even analysis solves the following problems:
- analyzes commercial enterprises, in particular analyzes trends and decisions, according to a system such as “costs - production volume - profit”;
- deals with state-owned enterprises, where he presents financial indicators and analyzes higher structures;
- analyzes the work of potential contractors and shareholders of the enterprise, with a view to the financial stability of the enterprise.
represents the percentage of total sales revenue that a company retains after incurring direct expenses associated with the production of the goods and services sold by the company. The higher the share, the greater the company’s income per ruble from the sale of goods, services and obligations.
Gross Margin (%) = (Revenue – Cost of Goods) / Revenue)
There is an inverse relationship between gross margin and inventory turnover: the lower the inventory turnover, the higher the gross margin; The higher the inventory turnover, the lower the gross margin.
Cost of goods sold includes variable costs and fixed costs directly associated with the product, such as materials and labor, and does not include indirect fixed costs, such as office expenses, rent, administrative costs, etc.
How to calculate gross margin: The price per unit of goods is 150 rubles, with a cost of 100 rubles. Gross Margin = (150-100)/150 = 33%
Manufacturers must ensure higher gross margins compared to trade because their product spends more time in the production process. Gross margin is determined by pricing policy.
Understanding what net sales is follows from its name. It is no secret that everyday business activity, unfortunately, is not always without costs and unforeseen situations. Life can make adjustments even to a perfectly formed project. These include product returns associated with detected defects or other unplanned costs and expenses associated, for example, with the human factor.
Another reason for the decrease in net sales is, dictated by competition, without which it is difficult to imagine modern market relations, the need to provide customers with discounts or installment plans, which is sometimes necessary not only to attract new customers, but also to prevent the loss of regular ones. Therefore, net sales volume is only the amount received from sales, minus all the costs listed above.
Namely, net sales volume is the main evaluation indicator that allows us to identify the degree of efficiency of the organization and predict the prospects for its development.
INFLUENCE OF SALES STRUCTURE
All company expenses can be divided into two parts:
- variable expenses - change in proportion to the scale of the company’s activities;
- Fixed expenses - remain unchanged when the scale of the enterprise’s activities changes.
Variable costs include direct material costs and wages of production personnel with deductions (piecework wages). Fixed expenses usually include administrative and management costs, depreciation, and selling and general expenses.
The meaning of dividing costs into variable and constant is that they behave differently in the process of managing production at an enterprise.
Variable costs per unit of output considered to be a constant value, often called unit variable costs or variable cost rate. Variable costs grow almost in proportion to the growth in production volume.
Fixed costs per unit of output decrease as the quantity of output increases. Thus, total unit costs decrease as production and sales volumes increase.
This economic representation of these costs simplifies the analysis of the influence of individual factors of production at the stage of preliminary aggregated calculations. First of all, this concerns the influence of the structure of production and sales on the company's profit. After all, most enterprises produce a wide range of products.
In this case, the question arises: how rational is the current structure of sales of individual products? It is possible that the production and sale of products of the same types, but in different volumes and ratios, are more profitable for the company. The choice of criterion for assessing the optimal sales structure becomes of paramount importance under these conditions.
EXAMPLE 1
The company's manufacturing business segment produces three types of products - A, B and C (Table 1). Currently, the segment's activities are unprofitable. The amount of loss is 4 million rubles.
The current sales structure is determined by the following data:
- product A - 10.87%;
- product B - 34.78%;
- product C - 54.35%.
If there is demand for products, the solution to the issue of improving the sales structure depends on the profitability of individual types of products (goods). By increasing the share of the most profitable products in total sales, it is possible to increase the overall profitability of sales and increase the company’s marginal income.
| Table 1. Manufacturing business segment of the company | |||||
| No. | Index | Product type | Total | ||
| A | B | C | |||
| 1 | Price per unit of production, rub. | 200 | 800 | 2500 | — |
| 2 | Variable costs per unit, rub. | 120 | 500 | 2000 | — |
| 3 | Marginal income per unit, rub. (item 1 – item 2) | 80 | 300 | 500 | — |
| 4 | Marginal income to product price, % (item 3 / item 1) | 40 | 37,5 | 20,0 | — |
| 5 | Sales volume, thousand units | 50 | 40 | 20 | — |
| 6 | Revenue, thousand rubles (item 1 × item 5) | 10 000 | 32 000 | 50 000 | 92 000 |
| 7 | Revenue for each type of product to total revenue, % | 10,87 | 34,78 | 54,35 | 100,0 |
| 8 | Variable expenses, thousand rubles. (item 2 × item 5) | 6000 | 20 000 | 40 000 | 66 000 |
| 9 | Fixed expenses, thousand rubles. | 30 000 | |||
| 10 | Financial result, thousand rubles. (clause 6 – clause 8 – clause 9) | –4000 | |||
Before we begin the calculations, we will analyze the profitability of all types of products presented in table. 1.
Product C has a maximum marginal income per unit of production - 500 rubles/unit. It is followed by product B - 300 rub./unit, and closes the row with product A - 80 rub./unit.
It is a mistake to believe that product C is the most profitable in the sales structure, since the relative measure of profitability should not be the marginal income per unit, but the ratio of marginal income to price .
Then it turns out that the share of marginal income in the price of product C is minimal (20%), and the most profitable from this point of view is product A (40%). Accordingly, product B occupies an intermediate place (37.5%).
Therefore, the level of marginal income for the company as a whole is higher, the larger the share in the cost structure is occupied by types of products with the maximum ratio of marginal income to price (or the maximum value of the MD/P ratio ). It follows that an increase in the share of high-margin products (MD/C ratio) will lead to an increase in sales profits.
EXAMPLE 2
Suppose the management of an enterprise (example 1) raises the question of increasing the output of products A and B by reducing product C. The new and old sales structure is presented in table. 2.
Let's evaluate how the change in structure will affect the financial result of the company's activities.
| Table 2. Old and new sales structure of the company | ||||
| Product type | Marginal income per unit of production, rub. | MD/C ratio | Sales structure, % | |
| former | new | |||
| A | 80 | 0,4 | 10,87 | 30,0 |
| B | 300 | 0,375 | 34,78 | 45,0 |
| C | 500 | 0,2 | 54,35 | 25,0 |
First, let's solve the problem in general form. To do this, we calculate the weighted average MD/C ratios for both sales structures by multiplying this coefficient by the sales structure (in percentage).
Previous structure:
- product A :
0,4 × 0,1087 = 0,04348;
- product B :
0,375 × 0,3478 = 0,13042;
- product C :
0,2 × 0,5435 = 0,1087.
Total coefficient MD/C — 0,2826.
New structure:
- product A :
0,4 × 0,30 = 0,12;
- product B :
0,375 × 0,45 = 0,16875;
- product C :
0,2 × 0,25 = 0,05.
Total coefficient MD/C — 0,33875.
As we can see, the new sales structure led to an increase in the weighted average ratio (MA/C). This also means increased profits, since fixed costs have not changed.
Let's calculate the amount of marginal income relative to revenue, taking into account the weighted average MD/C ratio. For the old sales structure it would be:
92,000 thousand rubles. × 0.2826 = 26,000 thousand . rub .
The amount of loss for the old structure will be:
26,000 thousand rubles. – 30,000 thousand rubles. = –4000 thousand rub.
This completely coincides with the financial result from example 1 (see Table 1).
The amount of marginal income for the new sales structure:
92,000 thousand rubles. × 0.33875 = 31,165 thousand . rub .
With constant fixed costs, the profit for the new structure will be:
RUB 31,165 thousand – 30,000 thousand rubles. = 1165 thousand rub .
That this is so can be shown by fully calculating the company’s economic indicators (Table 3).
| Table 3. Manufacturing business segment of the company for the new sales structure | |||||
| No. | Index | Product type | Total | ||
| A | B | C | |||
| 1 | Price per unit of production, rub. | 200 | 800 | 2500 | — |
| 2 | Variable costs per unit, rub. | 120 | 500 | 2000 | — |
| 3 | Marginal income per unit, rub. (item 1 – item 2) | 80 | 300 | 500 | — |
| 4 | Marginal income to product price, % (item 3 / item 1) | 40 | 37,5 | 20,0 | — |
| 5 | Sales volume, thousand units | 138 | 51,75 | 9,2 | — |
| 6 | Revenue, thousand rubles (item 1 × item 5) | 27 600 | 41 400 | 23 000 | 92 000 |
| 7 | Revenue for each type of product to total revenue, % | 30,0 | 45,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| 8 | Variable expenses, thousand rubles. (item 2 × item 5) | 16 560 | 25 875 | 18 400 | 60 835 |
| 9 | Fixed expenses, thousand rubles. | 30 000 | |||
| 10 | Financial result, thousand rubles. (clause 6 – clause 8 – clause 9) | 1165 | |||
In Table 3, sales volume in physical units is calculated by dividing revenue for each sales position (type of product) by the corresponding unit price. Sales volume will be:
- for product A :
RUB 27,600 / 200 rub./pcs. = 138 thousand units;
- for product B :
RUB 41,400 / 800 rub./pcs. = 51.75 thousand units;
- for product C :
23,000 rub. / 2500 rub./pcs. = 9.2 thousand pcs.
As we can see, the financial results of the general assessment and more complete calculations made in table. 3, completely coincided.
IT IS IMPORTANT
To ensure that the required (planned) amount of profit is obtained, it is necessary to maintain a certain ratio of marginal income (contribution) to revenue.
Conclusion: if production conditions and demand allow, then the previous sales structure should be replaced with a new one, in which the share of high-margin products is much higher. In this case, factors such as market share and the ability to offer customers the range of goods they need must be taken into account.
Example No. 2
In April, the company sold goods worth 200 thousand rubles. The cost of production amounted to 90 thousand rubles. Overhead expenses in the form of salaries, rent, taxes amounted to another 30 thousand rubles. We count:
- VP = OP – S/S = 200 – 90 = 110 thousand rubles.
- PE = VP – Expenses = 110 – 30 = 90 thousand rubles.
Let's look further at how you can determine net sales on the balance sheet.
Based on the results of a month of work, the company received 1.32 million rubles. arrived. The product is sold at a price of 250 rubles. a piece. Variable costs per unit are 98 rubles, and constant costs for the entire production volume are 0.38 million rubles. Let's determine the sales volume in the balance sheet.
MP = Price – Variable costs = 250 – 98 = 152 rubles.
OP = (Fixed costs Profit before interest): Marginal profit = (380,000 1,320,000) : 152 = 11,250 pcs.
Extra charge
should not be confused with gross margin. Yes, yes... in Russia, not in the accounting community (among managers, and sometimes directors), the markup is traditionally and erroneously called “margin”.
The markup is the percentage that must be added to the cost per unit of production to get the selling price.
Markup (%) = (Revenue – Cost of products sold) / Cost of products sold x 100
In other words, with a cost of 100 rubles and a markup of 50%, the revenue will be 150 rubles.
The markup, in addition to being calculated in % (see Markup), is also calculated in money, as a simple addition to the cost, which forms the selling price.
Markup (in money) = Sales price – Cost
Product sales volume: formula
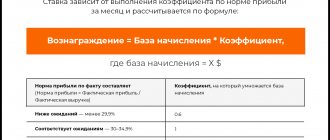
Sales volume is equal to the amount of profit, without calculating interest and the level of expenses from it, divided by marginal profit.
Sales volume can be calculated as follows:
- OP = (Fixed costs Profit) : (Price per unit – Variable costs per unit).
To determine your target sales volume, use the following formula:
- OP = (Fixed costs Earnings before interest) : Marginal profit.
- MP = Price – Variable costs per unit.
As mentioned earlier, in order to determine the efficiency of the enterprise, it is more appropriate to calculate the net sales volume in the balance sheet. How to calculate? It is necessary to adjust the OP for the amount of returned goods, as well as those that were sold at a discount and provided by the consumer. The formula looks like this:
- OPC = (Net profit x 100%) : (OP – Returnable products).
Traditionally, the formula for calculating product sales volume looks like this:
- Vрп – volume of products sold;
- Кn – quantity of products of the corresponding type;
- Цn – price per unit of product of the corresponding type.
The main indicators characterizing the volume of production are the gross and commodity value of the product. Gross value is the monetary value of all company products and services provided during the reporting period. It takes into account the total cost of manufactured products, semi-finished products, services provided, changes in work in progress balances and intra-system turnover.
Commodity value refers to the cost of products produced by an enterprise and intended for sale. Fluctuations in the value of “work in progress” and intra-farm turnover are not included in the commodity value. In many enterprises, the values of gross and marketable output are identical if there are no indicators of internal turnover and work in progress.
VP = TP (NPk/g – NPn/g), where
VP and TP – gross and marketable products,
NPk/g and NPn/g – work in progress at the end and beginning of the year.
Def = K x C, where K is the number of units of goods produced, C is the price of the product.
For example, if during the period under review 100 parts were produced at a price of 200 rubles. and 500 parts at a price of 300 rubles, then the total production volume will be 170,000 rubles. (100 x 200 500 x 300).
Orp = VP Ogpng – Ogpkg, where
VP – gross product,
Ogpng and Ogpkg – GP balances at the beginning and end of the year.
Orp =0 – 35,000 = 285,000 rub.
Buy in the online store, best prices, inexpensive delivery
It is customary to talk about annual production output at both micro and macro levels. In the first case, we are talking about the annual production volumes of individual economic entities (enterprises, organizations, firms), and in the second case, we are talking about the volumes of production activity of the national economic system as a whole.
The planned volume of annual production is calculated for the future, based on current production capabilities, and the actual volume reflects the actual production output over the past year. Often these two indicators are subject to comparison, during which relative and absolute deviations in output are determined, as well as the reasons and factors that influenced them.
https://youtu.be/d-GWeJuMPvM
Semi-finished products (castings) were produced in the amount of 120 tons, the wholesale price for one ton of castings was 100 rubles. Of the total amount of casting, 30 tons will be consumed for our own needs.
But be careful: the procedure for paying for “children’s” sick leave remains the same! Annual output of products with formula
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Degree of development of new types of products. To survive in market conditions, enterprise managers need to constantly master the production of new consumer products. This allows you to avoid double counting, because the company produces intermediate products, which are then recycled.
Sales volume in balance
In the financial statements, in the “Sales Volume” section, the receipt of funds is entered exclusively from operations that are carried out by the enterprise on a regular basis. Other cash transfers are recorded in the income statement in the “Other income” column.
Sales volume on the balance sheet is divided into the following types:
- Current - products or services that are the specialization of a given enterprise;
- Remains – goods available, but already discontinued;
- Non-core - not related to the main specialization of the company.
The sale of goods or services is the final stage of the circulation of funds in the cycle of economic activity of an enterprise. When recording the fact of sale, it is necessary, firstly, to record the shipment in fact, and secondly, to determine whether the funds received from the buyer cover the company’s costs for its production and sale.
Having the financial statements data, you can calculate all the main financial indicators. You can, for example, determine sales volume. There is no balance formula as such. Since this data is reflected in the “Profit and Loss Statement”. Line 2110 indicates the amount of products sold in monetary terms after deducting VAT.
Line 2400 = 2110 – (2120 2210 2220) 2340 – 2350 – 2410, where 2410 is the amount of income tax.
Net sales on the balance sheet can be calculated by subtracting retained earnings (uncovered loss) at the end of the period from the value at the beginning of the period. A positive difference indicates a net profit, and a negative difference indicates losses.
Market capacity varies
In global practice, there are 3 types of market capacity: actual, potential and available. Each type of market capacity can be calculated in different units of measurement: TV in physical terms (in pieces), in value terms (in rubles), in volume of goods (in liters, kilograms, etc.).
Let us give a brief description of each type of market capacity.
Potential
Potential market capacity is the size of the market based on the maximum level of development of demand for a product or service among consumers. The maximum level of demand means that the culture of using the product has reached its maximum: consumers consume the product as often as possible and constantly use it. Potential market capacity is the maximum possible market volume, which is determined on the basis that all potential consumers know and use the product category.
Actual
Actual or real market capacity is the size of the market based on the current level of development of demand for a product or service among the population. The actual market capacity is determined based on the current level of knowledge, consumption and use of the product among consumers.
Available
Available market capacity is the size of the market that a company can claim with its existing product and its characteristics (distribution, price, audience) or the level of demand that a company with its available resources can satisfy. In other words, when calculating the available market capacity, the company narrows the actual market volume, considering not all market consumers as potential buyers, but only those who meet its target audience criteria.
A small example of different types of market volume
Let's imagine that a company operates in the electric toothbrush market. How to determine the criteria by which companies calculate the size of the potential, actual and available market volume? Let's look at it in detail.
The company should calculate the potential market size based on the following assumptions (the following are the assumptions from the manufacturer that will form the basis for calculating the potential market size; you can include your own assumptions in the calculation that reflect your current assessment objectives):
- All potential toothbrush consumers use “electric toothbrushes” as opposed to regular manual brushes.
- All consumers buy brushes in accordance with the frequency recommended by the manufacturer: that is, they change them regularly, after 1 month of use.
- The average price per brush corresponds to the current average price of the manufacturer.
To assess the actual market share, the company must take into account the prevailing culture of consumption of the product (electric toothbrushes) in the target market. To do this, she conducts a survey among all potential market consumers and clarifies the following indicators:
- Current level of consumption of the category “electric toothbrushes” among the population or What % of all potential market consumers use this type of brush? This indicator is called “category penetration”.
- Current purchase frequency of electric toothbrushes or How many times per year do customers who use electric toothbrushes buy them?
- The current average purchase price of electric toothbrushes.
To assess the available market capacity, the company clarifies the indicators not for the entire market audience, but only for its target segment, which, for example, are young consumers aged 20-40 years.
Explanations for reporting
Each type of accounting report is accompanied by an explanatory note. It contains information:
- about the chosen method of accounting for fixed assets, inventory items;
- description of some balance sheet items (terms of debt repayment, rent payments, etc.);
- information about shareholders, capital structure;
- data on mergers, acquisitions, liquidations;
- off-balance sheet items.
Often an explanatory note provides more information about the financial position than statements. According to data from the balance sheet and f. No. 2 you can obtain information about the current state of affairs and performance efficiency. Having false information is worse than not having it. Therefore, it is important that financial statements are prepared correctly.
Unfortunately, even accountants make mistakes. The use of technical means allows you to avoid arithmetic errors, but not methodological ones. Also, reporting may be distorted due to the low skills of a specialist.
It is important to understand that the data in the balance sheet reflects the state of affairs at the reporting date. The very next day these indicators change. In the last weeks of the reporting period, the organization tries to defer payments, but in the first days of the new year, funds will be used to pay off the debt. Therefore, reporting is always done “with a reserve”.
According to accounting rules, all transactions must be reflected at historical cost. But assets and liabilities arrive on the balance sheet at different periods of time. Therefore, on-balance sheet acquisition costs do not reflect the true value of the assets. You should also consider currency fluctuations if you have assets or liabilities denominated in foreign currencies.
Proceeds from the sale of goods what line in the balance sheet
It is impossible to give a resigning employee a copy of SZV-M. According to the law on personal accounting, when dismissing an employee, the employer is obliged to give him copies of personalized reports (in particular, SZV-M and SZV-STAZH). However, these reporting forms are list-based, i.e. contain information about all employees.
This means transferring a copy of such a report to one employee means disclosing the personal data of other employees.
Volume of production in the balance sheet
Important Moreover, this indicator will not give an understanding of the amount of profit from sales over the entire history of the company. Line 1370 of the “Capital and Reserves” section reflects the balance of account 84.
This means that the indicator is equal to the amount of accumulated loss or profit received (not only from sales, but also taking into account non-operating income and expenses, taxes) minus expenses that were incurred at the expense of profit (this could be, for example, accrued dividends, formation of reserve capital and other expenses). To learn about the principles by which accounting statements are compiled, read the article “Accounting statements for LLCs - features and nuances.”
Financial results report for the analysis of economic activities It is the financial results report that will make it possible to analyze the structure of the enterprise's profit, its dynamics in comparison with previous reporting periods.
Which line shows profit from sales in the balance sheet?
Attention Depending on the type of activity and the specifics of the organization's work, the entries to reflect the receipt of revenue and write-off of expenses may differ.
But the reflection of profit or loss from sales will be the same regardless of what activity the company conducts.
To properly understand how profit from sales is formed, it is best to analyze which turnovers fall into the 90th account:
- Revenue is reflected by posting Dt 62 Kt 90.1. But in retail trade, the wiring will look like Dt 50 Kt 90.1 or Dt 57 Kt 90.1.
- The cost of services and work is written off with such entries as Dt 90.2 Kt 20 (23, 26, 25, etc.).
In wholesale trade, the cost of goods will be written off by operation Dt 90.2 Kt 41, and sales expenses - Dt 90.2 Kt 44. In retail, you additionally need to take into account the markup Dt 90.2 Kt 42.
Reflection of revenue in the balance sheet
So, for such persons you need to take both SZV-M and SZV-STAZH!
But be careful: the procedure for paying for “children’s” sick leave remains the same!
However, for the application of this deferment there are a number of conditions (tax regime, type of activity, presence/absence of employees). So who has the right to work without a cash register until the middle of next year?
Net sales in the balance sheet: line. sales volume on the balance sheet: how to calculate?
- VP = OP - S/S = 200 - 90 = 110 thousand rubles.
- PE = VP - Expenses = 110 - 30 = 90 thousand.
rub.
Let's look further at how you can determine net sales on the balance sheet. The formula Sales Volume can be calculated as follows:
- OP = (Fixed costs + Profit): (Price per unit – Variable costs per unit).
To determine your target sales volume, use the following formula:
- OP = (Fixed costs + Profit before interest) : Marginal profit.
- MP = Price - Variable costs per unit.
As mentioned earlier, in order to determine the efficiency of the enterprise, it is more appropriate to calculate the net sales volume in the balance sheet.
What is revenue from product sales?
You can, for example, determine sales volume. There is no balance formula as such. Since this data is reflected in the “Profit and Loss Statement”. Line 2110 indicates the amount of products sold in monetary terms after deducting VAT. All costs for the production and delivery of products are reflected here: line 2120 + line 2210 + line 2220.
The organization may have other unforeseen expenses (p. 2350) and income (p. 2340). This way you can calculate net profit or net sales in the balance sheet: Line 2400 = 2110 – (2120 + 2210 + 2220) + 2340 – 2350 – 2410, where 2410 is the amount of income tax.
Net sales on the balance sheet can be calculated by subtracting retained earnings (uncovered loss) at the end of the period from the value at the beginning of the period. A positive difference indicates a net profit, and a negative difference indicates losses.
General business expenses include:
- administrative and management expenses;
- maintenance of general business personnel not related to the production process;
- depreciation charges and expenses for repairs of fixed assets for management and general economic purposes;
- rent for general business premises;
- expenses for payment of information, audit, consulting and other similar services;
- other administrative expenses similar in purpose.
An organization that is a professional participant in the securities market reflects the amount of costs associated with its activities under the item “Administrative expenses”. The amount on line 040 is equal to the amount of costs written off in the reporting period from the credit of account 26 to the debit of account 90.2 “Cost”.
- amounts received under commission agreements, agency agreements and other similar agreements in favor of the principal, principal, etc.;
- amounts of advances received as advance payment for products, goods, works, services;
- receipts as collateral, if the agreement provides for the transfer of the pledged property to the pledgee;
- amounts received to repay a loan provided to the borrower.
Income recognized in accounting as income from ordinary activities, if it is significant or without knowledge of which it is impossible for interested users to assess the financial results of the organization's activities, must be reflected separately in the form of a transcript to line 010 or in an appendix to the profit and loss statement (in if it is developed and adopted by the organization independently). Every year, companies prepare financial statements. Using data from the balance sheet and profit and loss report, you can determine the effectiveness of the organization’s activities, as well as calculate the main planned indicators. Provided that management and the finance department understand the meaning of terms such as profit, revenue and sales on the balance sheet. Terminology The volume of product sales on the balance sheet is the amount of revenue received for the sale of goods in the reporting period.
In this case, the form of calculations does not matter. Products can be sold on credit, for cash, with deferred payment or at a discount. Therefore, for a more accurate calculation, the formula for calculating net sales in the balance sheet is used, when the revenue received is adjusted by the amount of goods shipped on credit.
Sales volume reflects the amount of funds received by the company. Therefore, it should be calculated by all organizations.
Revenue from sales of products which line in the balance sheet
Having false information is worse than not having it. Therefore, it is important that financial statements are prepared correctly.
Unfortunately, even accountants make mistakes. The use of technical means allows you to avoid arithmetic errors, but not methodological ones. Also, reporting may be distorted due to the low skills of a specialist. It is important to understand that the data in the balance sheet reflects the state of affairs at the reporting date. The very next day these indicators change.
In the last weeks of the reporting period, the organization tries to defer payments, but in the first days of the new year, funds will be used to pay off the debt. Therefore, reporting is always done “with a reserve”. In the registers you can always find costs that will reduce the profitability indicator. For example, write off more inventory, non-current assets or bad debts.
After all, it is always easier to lose profit than to increase it.
Source: https://advocatus54.ru/vyruchka-ot-realizatsii-tovarov-kakaya-stroka-v-balanse/
Gross Sales
Gross sales are total sales (including credit sales) for the reporting period, valued at full prices (invoice prices) without taking into account discounts, returns of sold products, price reductions and other adjustments.
Gross sales are considered to be all sales in aggregate (this also includes those made on credit) for the specific accounting period under consideration. It should be noted that sales are calculated at prices, excluding:
- Discounts;
- Returns;
- Other forced, unpredictable expenses.
A very interesting indicator, gross sales, is for retail businesses, as it allows you to calculate the size of a company's product in comparison with its competitors. Studying this performance indicator also helps to identify consumer preferences and habits.