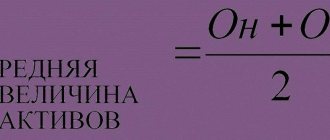Composition of assets and where to look
Any specialist who has ever dealt with accounting knows the words “balance sheet” and “organizational assets.” If we explain their meaning in accessible language, it turns out that the book value of assets is a certain number of funds and benefits that can be expressed in monetary terms.
If we speak in the language of accountants about what the book value of an enterprise's assets is, then this is the amount of all the company's assets in cash, which is clearly shown in the accounting. balance.
https://www.youtube.com/watch{q}v=OfHuns4bqcM
Assets can be:
- non-current - they are summarized in line 1100 of the balance sheet;
- negotiable – written in line 1200.
All main types of property and intangible assets are classified as non-current. They appear on the balance sheet at their residual value (at which they were received/purchased, taking into account subsequent aging, wear and tear and revaluation carried out by the company).
Working capital includes assets, the use of which in the activities of an enterprise to achieve financial success is quite frequent. They are involved for 12 months or another established cycle. These include:
- materials needed for production;
- debts of debtors to the company;
- monetary assets and the like;
- VAT on property acquired by the enterprise;
- financial investments, etc.
It is not at all difficult to find the book value of assets: this is line 1600 in the balance sheet. It shows the amount of both current and non-current assets.
Thus, there is only one option where to look at the book value of assets in the balance sheet: it is written in line 1600 of the balance sheet.
Net assets and net profit
Net assets are also analyzed with other economic and financial indicators of the organization. So the dynamics of growth of net assets is compared with the dynamics of changes in sales revenue and. Sales revenue is an indicator reflecting the efficiency of an enterprise's sales and production systems. Net profit is the most important indicator of the profitability of a business; it is through it that the assets of the enterprise are primarily financed. As can be seen from the figure below, net profit decreased in 2014, which in turn affected the value of net assets and financial condition.
Balance calculation rules
The balance sheet is the main financial reporting document of a business entity. It must be filled out by budgetary and private institutions. Document data is used within the company and by regulatory authorities during reconciliation work and inspections. To simplify the work of an accountant, it is better to use the 1C software product, which, when used correctly, fills out the report automatically. When filling out a balance sheet, it is necessary to take into account the regulated sample reporting form and the rules defined by regulations:
- All data is generated as of the last day of the annual reporting period.
- The document displays similar parameters with values for two years, one of which is the reporting year, and the second is the one preceding it and taken into account in the previous report.
- Information for calculations is taken from the balance sheet.
- When calculating, all indicators are taken into account as a whole number, rounded according to standard rules.
- Negative indicators are subtracted when determining the total values.
- The net numeric values of assets and liabilities in the “total” section must be the same.
- All information must be compiled on the basis of supporting documents and certificates.
All assets on the balance sheet are divided into two groups: current and non-current. The latter should be reflected at residual value. The total value of assets is displayed in line 1600 of the balance sheet and is the sum of lines 1100 and 1200. Calculations can also be made based on their component parts.
How to calculate net working capital
N 84n “On approval of the Procedure for determining the value of net assets.” This procedure is used by joint-stock companies, limited liability companies, state unitary enterprises, municipal unitary enterprises, production cooperatives, housing savings cooperatives, and economic partnerships.
Calculation (formula)
The calculation comes down to determining the difference between assets and liabilities (liabilities), which are determined as follows.
The assets accepted for calculation include all assets of the organization, with the exception of receivables of the founders (participants, shareholders, owners, members) for contributions (contributions) to the authorized capital (authorized fund, mutual fund, share capital), for payment of shares.
The liabilities accepted for calculation include all liabilities, except for deferred income.
.
But not all future income, but those recognized by the organization in connection with the receipt of government assistance, as well as in connection with the gratuitous receipt of property
. These incomes are actually the organization's own capital, therefore, for the purposes of calculating the value of net assets, they are excluded from the short-term liabilities section of the balance sheet (line 1530).
Those. The formula for calculating net assets on the Balance Sheet of an enterprise is as follows:
Net assets = (line 1600 - ZU) - (line 1400 + line 1500 - DBP)
where ZU is the debt of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital (it is not separately allocated in the Balance Sheet and is reflected as part of short-term receivables);
DBP – deferred income recognized by the organization in connection with the receipt of government assistance, as well as in connection with the gratuitous receipt of property.
An alternative way to calculate the net asset value, giving exactly the same result as the formula above would be:
Net assets = line 1300 - ZU + DBP
Normal value
The net asset indicator, known in Western practice as net assets or net worth, is a key indicator of the activity of any commercial organization. The organization's net assets must be at least positive. Negative net assets are a sign of the insolvency of an organization, indicating that the company is completely dependent on creditors and does not have its own funds.
Net assets must not only be positive, but also exceed the authorized capital of the organization. This means that in the course of its activities, the organization not only did not waste the funds initially contributed by the owner, but also ensured their growth. Net assets less than the authorized capital are permissible only in the first year of operation of newly created enterprises. In subsequent years, if net assets become less than the authorized capital, the civil code and legislation on joint stock companies require that the authorized capital be reduced to the amount of net assets. If the organization's authorized capital is already at a minimum level, the question of its further existence is raised.
Net asset method
In valuation activities, the net asset method is used as one of the methods for assessing the value of a business. With this method, the appraiser uses data on the organization's net assets according to the financial statements, previously adjusted based on its own estimated values of the market value of property and liabilities.
Why do the calculations?
The book value of assets also helps businesses determine how large a transaction is. This follows from Article 46 of the Law
If this amount is 25% of the value of all assets or more, then the transaction will be considered large. In this case, to confirm it, it is necessary to hold a meeting of participants (shareholders).
If it turns out that the calculation of the book value of assets was made incorrectly, the validity of the transaction that has already taken place is jeopardized.
How to determine the average price of assets
Any balance sheet is designed in such a way that it allows you to calculate not only the book value of assets, but also its average. It gives a clearer understanding of the value and size of assets. It seems to neutralize the circumstances that distort the real amount.
A c – average cost for the year; A n – assets on the balance sheet at the beginning of the year; A k – value of assets at the end of the year.
Note that the amount of assets in the balance sheet is shown as of the last day of the calendar year. That's why:
- the indicator at the beginning of the year is the balance of line 1600 at the end of December of the year before the previous one;
- book value at the end of the year - the balance at the end of December of the previous year.
As a result, the book value of assets is the price of property owned by the enterprise according to accounting data. Key information about it can be found in line 1600 of the balance sheet. This indicator is very important for analyzing the company's performance.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and press Ctrl Enter.
It is not uncommon for an accountant, when paying a certain amount to an employee, to ask the question: is this payment subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions{q} And is it taken into account for tax purposes{q}
We talked about them in separate consultations, brought them up, and also considered the issue. In this material we will dwell in more detail on the book value of assets.
The form of the balance sheet allows you not only to answer the question of how to determine the book value of assets on the balance sheet, but also to calculate their average value.
The average net asset value indicator can give a more realistic idea of the value of assets, smoothing out possible sharp fluctuations that arose on one of the reporting dates.
A SG = (A NG A KG) / 2,
where A NG is the value of assets on the balance sheet at the beginning of the year;
And KG is the value of assets on the balance sheet at the end of the year.
Considering that assets are shown in the balance sheet as of December 31, the value of assets at the beginning of the year corresponds to the balance of line 1600 as of December 31 of the year preceding the previous one, and the value of assets at the end of the year corresponds to the balance of line 1600 as of December 31 of the previous year.
Let's show this with an example.
Thus, the average annual value of the organization’s assets for 2016 will be calculated in the amount of 115,455 thousand rubles. ((127,234,103,676) / 2).
Company assets are resources expressed in value that support the production process. These include non-current assets (buildings, structures, work equipment, machines, vehicles, as well as business reputation, software products that are intangible assets) and current assets, i.e.
money in cash and in bank accounts, inventories, accounts receivable, short-term investments and others. Our publication is devoted to such a concept as the book value of assets. Where to look in the balance sheet, as well as find out how the book value and average annual value of assets are calculated is the topic of this article.
▪ in the first section of the balance sheet (total line 1100) non-current – fixed assets and intangible assets, accounted for at residual value, i.e. minus depreciation;
▪ in the second (total line 1200) – current inventories, finances, liabilities, investments participating in the production process.
Accounting amount of assets The balance sheet is only an absolute indicator that determines the total value of the company's property assets.
- Ang – book price of funds at the beginning of the reporting period;
- Akg is the book price of funds at the end of the reporting period.
Average assets on balance sheet
The average annual value of assets in the balance sheet (A SG) is determined by the formula (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n):
A SG = (line 1600 NG + line 1600 KG) / 2,
where line 1600 NG is the amount on line 1600 as of December 31 of the previous year;
line 1600 KG - the amount on line 1600 as of December 31 of the reporting year.
At the same time, the average value of individual groups or types of assets can be separately calculated from the balance sheet. For example, the average value of non-current assets or the average value of inventories, etc.
Exercise
Based on financial statements 1, 2, 5, calculate:
1) indicators of the efficiency of use of production resources (fixed assets, working capital, material resources);
2) indicators of turnover of working capital;
3) indicators of profitability of activities;
4) solvency indicators;
5) indicators of financial stability;
6) indicators of net assets and net working capital.
Arrange in tables and write a conclusion about the financial condition in the analyzed period.
1)
ANALYSIS OF THE EFFICIENCY OF USE OF PRODUCTION RESOURCES
| Indicator name | Previous Year (2003) | Reporting year (2004) |
| Profit (loss) before tax | ||
| Average annual cost of fixed assets | ||
| Capital productivity | ||
| Capital intensity | ||
| Average annual cost of working capital | ||
| Average annual cost of material resources | ||
| Material efficiency | ||
| Material consumption | ||
| Profit (loss) from sales | ||
| Profit per 1 rub. mat. costs |
Average annual cost of fixed assets
= sum of indicators p. 190 for the reporting year /2
a) for 2003: (162840+68718)/2 = 115779
b) for 2004: (68718+66030)/2 = 67374
Capital productivity
= Revenue (net) from the sale of goods / Average annual cost of fixed assets
a) for 2003: 197832/115779 = 1.71
b) for 2004: 181494/67374 = 2.69
Capital intensity
= Average annual cost of fixed assets / Revenue (net) from the sale of goods
a) for 2003: 115779/197832 = 0.59
b) for 2004: 67374/181494 = 0.37
Average annual cost of working capital
= sum of indicators p. 290 for the reporting year /2
a) for 2003: (28610+38160)/2 = 33385
b) for 2004: (38160+54648)/2 = 46404
Average annual cost of material resources
= inventory + VAT on purchases. values/ 2
a) for 2003: ((20200+ 1526)+(20552+1880))/2 = 22079
b) for 2004: ((20552+1880)+(34480+2080))/2 = 29496
Material efficiency
= Revenue (net) from the sale of goods / Average annual cost of material resources;
a) for 2003: 197832/ 22079 = 8.96
b) for 2004: 181494/ 29496 = 6.15
Material consumption
= Average annual cost of material resources / Revenue (net) from the sale of goods.
a) for 2003: 22079/197832 = 0.11
b) for 2004: 29496/181494 = 0.16
Profit per 1 rub. material costs
= Revenue (net) from the sale of goods / Profit (loss) from sales
a) for 2003: 197832/ 12860 = 15.38
b) for 2004: 181494/ 13944 = 13.02
The efficiency of using materials has decreased, as can be seen from the table:
Material intensity increased by 0.05, it shows how many material resources are needed to produce units. products.
Material productivity for the reporting period decreased by 2.81, this indicator characterizes the number of products produced per 1 ruble. consumed material resources.
Capital productivity shows how many products are produced using 1 ruble. fixed assets. During the analyzed period, there was an increase in indicators.
The value of the capital intensity indicator decreased. Capital intensity characterizes the amount of fixed assets necessary to produce products worth 1 ruble.
2)
ANALYSIS OF WORKING CAPITAL TURNOVER INDICATORS
Average annual cost of total capital
= balance amount at the beginning and end of the period
a) for 2003: (191450+106878)/2=149164
b) for 2004: (106878+120678)/2=113778
Average annual cost of working capital
= amount line 290 at the beginning and end of the period
a) for 2003: (28610+38160)/2=33385
b) for 2004: (38160+54648)/2=46404
Capital turnover ratio
=revenue /avg. cost of capital;
a) for 2003: 197832/149164=1.33
b) for 2004: 181494/113778=1.60
The working capital ratio is calculated in a similar way.
Turnover in days
= (average cost of working capital / sales revenue) X360;
The total capital turnover ratio increased by 0.27;
The duration of turnover of total capital decreased by 45.76;
The duration of working capital turnover increased by 31.29
The indicators of the enterprise's capital turnover give grounds to conclude that its use is deteriorating, however, the indicators of working capital turnover are growing.
3) PROFITABILITY INDICATORS
| Indicator name | Previous Year (2003) | Reporting year (2004) | Deviation |
| Revenue (net) from the sale of goods | |||
| Profit (loss) from sales | |||
| Return on sales in % | |||
| Average annual cost of capital | |||
| Return on equity in % | |||
| Average annual cost of working capital | |||
| Return on working capital in % | |||
| Average annual cost of fixed assets | |||
| Return on fixed assets in % |
Return on sales
= Profit (loss) from sales / Revenue (net) from sales of goods
a) for 2003: 12860/197832=0.065
b) for 2004: 13944/181494=0.077
Return on Equity
= Profit (loss) before tax / Average annual cost of capital
a) for 2003: 11426/149164=0.077
b) for 2004: 9170/113778=0.08
Return on working capital
= Profit (loss) before tax / Average annual cost of working capital
a) for 2003: 11426/33385=0.342
b) for 2004: 9170/46404=0.198
Return on fixed assets
= Profit (loss) before tax / Average annual cost of fixed assets
a) for 2003: 11426/115779=0.098
b) for 2004: 9170/67374=0.136
The return on sales indicator, which characterizes how much profit a company has from 1 ruble. sales grew by 1.2% in the reporting period. Return on equity increased by 0.3% compared to the previous period. Return on equity, which characterizes the return on equity, decreased by 45.4%. from 159.3 in 2003 up to 114.0. Return on working capital decreased by 14.4% from 34.2 in 2003. up to 19.8% in 2004
The profitability of fixed assets characterizes the profit before tax per 1. rub. fixed assets, it grew by 3.7%.
4) SOLVENT ASSESSMENT
Absolute liquidity ratio
= cash(260) + short-term financial. investments (250) / short-term liabilities;
Quick
ratio = (Cash + Short-term financial investments + Accounts receivable) / Current liabilities;
Current
ratio = (Current assets - Deferred expenses) / Current liabilities;
The absolute liquidity ratio shows what part of short-term liabilities can be repaid using available cash.
The quick liquidity ratio shows the degree of repayment of short-term obligations with cash; short-term financial investments and accounts receivable increased this indicator by 1.75;
The current liquidity ratio shows the degree to which short-term debt is covered by current assets; an increase of 0.03 was noted in this indicator.
Due to the fact that liquidity indicators do not correspond to standard values (Current liquidity ratio is norm -2, Quick liquidity ratio is norm -07.-1), we will calculate the coefficient of recovery and loss of solvency:
Recovery and loss of solvency ratio = Current liquidity ratio (2004) + 6/12 (Current liquidity ratio (2004) - Current liquidity ratio (2003)) / 2
Coefficient of recovery and loss of solvency = (1.33 + 6/12 (1.33-1.36)) / 2 = 0.66
Since the coefficient of restoration and loss of solvency is less than 1, the company cannot restore its solvency within 6 months.
5) FINANCIAL STABILITY RATIO
| Indicator name | Deviation |
| Equity | |
| long term duties | |
| Short-term liabilities | |
| Borrowed capital (line 590+610+620+630) | |
| Balance currency | |
| Financial autonomy ratio | |
| Financial dependency ratio | |
| Current debt ratio | |
| Financial risk ratio | |
| Debt coverage ratio with own funds |
Financial autonomy ratio
= Own capital/Balance sheet currency;
Financial dependency ratio
= Borrowed capital / Balance sheet currency;
Current debt ratio
= Current liabilities/ Balance sheet currency;
Debt coverage ratio with own funds
=Equity capital/Debt capital;
Financial risk ratio
= Debt capital/Equity capital.
The enterprise's financial dependence on external sources decreased - the share of equity capital increased by 146, but borrowed capital increased by 13,654, and the financial risk coefficient increased accordingly by 0.18. The financial autonomy coefficient decreased by 0.08, the current debt ratio increased by 0.06, and the debt coverage ratio with own funds decreased by 0.81.
6) ANALYSIS OF INDICATORS NET ASSETS
Net assets
= Current assets - (Loans and credits + Accounts payable + Debt to founders for payment of income + Other short-term liabilities);
Own working capital
= Current assets - Non-current assets.
In the analyzed period, the net assets of the enterprise increased by 5360, which indicates an improvement in financial stability, however, the enterprise cannot finance its activities itself through working capital because The indicator Own working capital has a negative value.
At the end of winter and beginning of spring, all organizations are actively preparing financial statements for 2016. Let's talk about one of the key indicators of any enterprise - the book value of assets. Where can I see it on my balance sheet?
for 2016 and how it will help.
Average annual value of assets on balance sheet
The amount of assets on the balance sheet is only an absolute indicator that states the value of existing property, but for a more detailed analysis of changes in the composition of assets and the calculation of many necessary values, the average annual value of assets will be required.
A av = (A n A k) / 2,
where A n is property at the beginning, A k is at the end of the period, 2 is the number of reporting dates.
Let's take the values from the balance sheet presented above.
And avg = (696,098,730,605)/2 = 713,351.5 tr., i.e., the average annual value of assets (line 1600 in the balance sheet) amounted to 713,351.5 tr.
▪ OS – (689,500,721,000)/2 = 705,250 tr.
▪ reserves (3420 5421)/2 = 4420.5 tr.6
The average value of assets, calculated for the year, is used by analysts to calculate ratios characterizing the financial condition of the company, determine the reasons that led to changes and make decisions on further resource management.
A av = (An Ak) / 2,
where An is the property at the beginning, Ak is the end of the period, 2 is the number of reporting dates.
Asr = (696,098,730,605)/2 = 713,351.5 tr., i.e., the average annual value of assets (line 1600 in the balance sheet) amounted to 713,351.5 tr.
▪ OS – (689,500,721,000)/2 = 705,250 tr.
The average annual value of assets is defined as the value of resources, the parameters of which are determined at the beginning and end of the reporting period. All information is taken from the balance sheet. When calculating a parameter, it is necessary to find the sum of indicators for which the average value can be found, and then divide the resulting figure by 2.
SSA = (A1 A2)/2,
A1 – cost at the beginning of the year;
A2 – cost at the end of the year.
How to reflect in accounting and reporting
The coefficient allows you to determine the number of transfers of mobile assets into cash and vice versa.
The development of an enterprise is impossible without a detailed analysis of the results of its activities, including an assessment of the dynamics, composition and structure of the organization’s resources used. One of the most important elements of this process is the study of asset turnover ratios.
The indicators must be used in a similar way by finding the average value of assets and comparing balance sheet data for the corresponding years.
The total assets of the organization consist of:
- working capital - they are consumed in one production cycle or written off from the balance sheet during the year;
- non-current - part of the resources with a service life (consumption) of more than a year.
The ratio is the ratio between revenue and average annual assets. The value of the indicator indicates how many goods and services were sold during the period under study for each ruble of assets used.
Take revenue from the income statement for the analyzed period. Dividing it by the average value of current assets, multiply the resulting figure by the number of days in the reporting period.
For example, if during the year the current asset turnover ratio increased from 1.4 to 2, this is a positive trend. However, it is difficult to say whether a value equal to 2 is an optimal, acceptable or critical turnover indicator for an enterprise. At2 - current assets of the enterprise at the end of the period. You can then analyze the effectiveness of their use.
Book value of assets: how to calculate and where to view this indicator in the balance sheet{q}
- Sat – balance sheet value of the company’s capital
- Co – balance sheet value expression of working capital
- St – balance sheet value of non-current assets
How to earn real money on Instagram{q} Step-by-step instructions are contained in the publication at the link.
Example 1
Sat – balance sheet value of the company’s assets
Co – cost of current assets
St – value of non-current assets.
A sample certificate of the book value of a company's fixed assets.
Example 2
Thus, the balance sheet value of the funds of enterprise “B” will be equal to 700,000 rubles.
The first indicator (line 1100 of the balance sheet) includes fixed assets and intangible assets valued at their residual value.
The second indicator (line 1200) includes values that are used in a year or in one full cycle. This:
- inventories;
- receivable;
- money;
- VAT accrued by suppliers (such tax amounts, although not directly, are included in the assets of the enterprise);
- financial investments that are short-term in nature.
After summing up all the given values, an indicator such as the book value of assets (BSA) is obtained. This is balance line number 1600.
An enterprise can calculate the size of each asset separately, or it can determine the value of the entire property complex. It all depends on the tasks assigned to the specialist who determines these indicators.
For interested parties, the company prepares a certificate containing this calculation.
IMPORTANT! In accounting terms, there is also the book value of net assets, which is calculated minus the liabilities that the company has.
The value of assets on the balance sheet is the sum of all the assets of the company in monetary terms, reflected in the accounting book. balance. The balance sheet asset consists of two parts:
- Non-current assets – line 1100;
- Current assets – line 1200.
The total value of assets on the balance sheet is line 1600.
Non-current assets include fixed assets and intangible assets. They are accounted for on the balance sheet at their residual value, that is, at the purchase price minus the amount of accumulated depreciation.
Current assets are funds that are completely consumed in one year or one production cycle. These include: debts of debtors, money, materials, short-term investments and VAT.
What is the book value of an enterprise's assets{q}
The total amount of balance sheet assets is the book value, i.e. the amount at which assets are reflected in the balance sheet.
In relation to the approved form of the balance sheet (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n), the book value of assets is balance sheet line 1600 “Balance”. This is the answer to the question of how to calculate the book value of assets on the balance sheet.
The value of assets on the balance sheet is the main indicator that characterizes the financial position of the organization at the reporting date.
Asset turnover: calculation formula
The value of the resource efficiency indicator directly depends on sales volume. If there is a downward trend in the value of the ratio, this means that financial activity is declining. And, conversely, its increase indicates that sales volumes have increased and capital is turning over faster.
The quality of work with debtors is analyzed based on the receivables turnover ratio. It characterizes how quickly debtors pay for products provided on credit. The higher the indicator, the more effective the pricing policy is considered.
27 Jun 2020 stopurist 412
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Amendments to Article 228 2020
- Procedure for registering a land plot in cadastral register
- How to apply for maternity capital for the purchase of an apartment
- When Buying an Apartment With a Young Family Certificate What is the Minimum Area
What is the book value of fixed assets{q}
In accounting, the book value of a fixed asset is the residual value of the fixed asset, which is defined as the difference between the original cost and the amount of accrued depreciation.
When accounting for fixed assets at a revalued cost (revaluation), the book value of fixed assets is equal to the difference between its current (replacement) cost and the amount of accrued depreciation.
Information on the status of the book value of fixed assets can be obtained by looking at line 1600 of the balance sheet (BB).
All assets are divided into 2 types: current and non-current.
- Working capital is all the company’s property, which completely transfers its value to the produced goods in one turnover.
- Non-current assets are all the company’s property that generates profit and is involved in production during several turnovers of current assets. By the way, fixed assets are part of the company's assets.
Thus, the book value of a firm's fixed assets is equivalent to the sum of current and non-current assets.
Sample certificate of the book value of the company's assets.
The book value of fixed assets is the monetary value of all fixed assets according to accounting. Why is the phrase “accounting” present here?
You can find out how much you earn on YouTube for and how to earn real money on your channel in our new article at the link.
Scheme: What is book value{q}
In accounting, an object can be valued in different ways. For this reason, it is important that equipment on the company's balance sheet, for example, is displayed in accordance with some accounting method. This is due to the specifics of entrepreneurship.
The initial value expression of fixed capital is the totality of the costs incurred by the entrepreneur, which contains the costs of:
- Acquisition of a fixed asset
- Its transportation
- Its installation
- Other goals related to the operation of the means of production.
What is profitability and how to calculate the profitability of an enterprise yourself, you can read at the link.
Basic concepts of accounting.
There are a number of types of accounting policies (methodologies for accounting for enterprise assets). With an accounting policy based on the initial price of the accounting object, it is assumed that throughout the accounting period the asset will be accounted for as the difference from the original cost and the amount of depreciation of the fixed asset (depreciation).
The next category, which must be introduced to fully understand what the book value expression of fixed capital is, is closely intertwined with the type of accounting valuation based on regular revaluation of fixed capital.
What is the responsibility of the chief accountant since 2016 and what changes have occurred in the legislation this year, you can read here.
The book value of fixed assets can be calculated based on historical cost and replacement cost. The choice of method depends on when the revaluation of fixed assets was carried out.
Scheme for calculating the average annual book value of fixed assets.
If the revaluation was carried out after the commissioning of the main asset, then it is accounted for at its replacement cost, if before - at its original cost. What to do if the fixed asset has already been used, but it appears on the company’s balance sheet for the first time{q}
The balance sheet value of fixed capital is equal to the sum of all initial and replacement costs of fixed assets of the enterprise.
Sometimes replacement cost is calculated not on the basis of original cost (a figure is calculated to show how the price of an asset has changed and then multiplied by the original cost of the asset), but on the residual value. When choosing, they rely on the specifics of a particular company and current tax standards.
A sample business plan with calculations and step-by-step instructions for its preparation are contained in this article.
Example 1
Let the enterprise “Advantage” have machine A, purchased for 100,000 rubles. (including profit tax). Transportation costs amounted to 8,000 rubles, installation costs – 6,000 rubles, other costs – 3,000 rubles. Fixed assets were revalued.
Since the purchase of machine A, its value has dropped by 20%. Abstracting from the details, let's calculate the book value of fixed assets for this situation. Machine A was put into operation before the revaluation, so it must be accounted for on the balance sheet at its replacement cost.
St = (Zp Zper Zm Id)*Kmi;
- St – replacement cost
- Salary – purchase costs
- Zper – costs of transporting means of production
- Zm – installation costs
- Id – other costs;
- Kmi – obsolescence coefficient (the obsolescence coefficient in this case is the reduction in the cost of the machine, as a monetary expression of obsolescence)
(RUR 100,000 RUR 8,000 RUR 6,000 RUR 3,000) *0.8 = RUR 93,600 (since the cost has fallen by 20%, the current price is equal to: 1 minus 0.2 – 0.8 of the original cost).
- First - initial cost
- Salary – costs of purchasing a machine
- Zt – costs of transporting the machine
- Zu – costs of installing the machine
- Zpr – other costs;
equal to: 60,000 rub. 7,000 rub. 5,000 rub. 1,500 rub. = 73,500 rub.
RUB 93,600 RUB 73,500 = 167 100
Sample calculation of the book value of fixed assets in the OS program.
Example 2
Let enterprise “G” have machine A, purchased for 250,000 rubles. (including profit tax). The cost of transporting the machine amounted to 7,000 rubles, installation - 5,000 rubles, other costs amounted to 2,500. Since the purchase of the machine, its cost has increased by 15%. Fixed assets were revalued.
- St – replacement cost
- Salary – costs of purchasing a machine
- Zt – costs of transporting the machine
- Zu – costs of installing the machine
- Zpr – other costs
- Kmi – coefficient of obsolescence of the machine;
(250,000 rub. 7,000 rub. 5,000 rub. 2,500 rub.) * 1.15= 304,175 rub. (In this case, the price increase exceeded the amount of obsolescence, so the obsolescence coefficient, according to the rules of proportion, was: 1 0.15 = 1.15).
- First - initial cost
- Salary – purchase costs
- Zper – transportation costs
- Zm – installation costs
- Id – other costs;
The book value of fixed assets, which in this situation is equivalent to the sum of the replacement cost of machine A and the initial cost of machine B, is: 304,175 rubles. 160,000 rub. = 464,175 rub.
Find out what liability is provided for non-payment of taxes by a legal entity here.
Fixed assets of a company are defined as part of the company's property that is used to meet production needs for more than one year. They are not goods and are used for commercial purposes. Their acquisition occurs in large transactions. For an objective assessment, three types of cost are used:
- balance sheet;
- residual;
- restorative.
The total book value is determined by the purchase price plus expenses. Residual value is calculated as the difference between the original price and depreciation. Replacement cost is determined based on the current market price. In the balance sheet, the cost of fixed assets is reflected in line 1130.
Book value of assets: how to calculate and where to view this indicator in the balance sheet{q}
Let's look at a specific example of how to calculate net assets on a balance sheet.
Vesna LLC prepared annual financial statements, including a balance sheet in the OKUD form 0710001.
NA = (13,800 19,283 – 0) – (12,930 – 0) = 20,153 rubles.
Example 2
The total balance sheet assets is an indicator that reflects the total book value of all types of assets of the organization. The procedure for determining the book value of assets is disclosed in the relevant regulatory documents governing accounting. At the same time, it is important to take into account the main requirement for reflecting assets on the balance sheet: they are reflected in a net valuation, that is, minus regulatory values (clause 35 of PBU 4/99).
S OST = D 01 – K 02,
where D 01 is the debit balance of account 01 “Fixed assets”;
To 02 - credit balance of account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets”.
Similarly, intangible assets are reflected in the balance sheet at their residual value.
The balance sheet amount of accounts receivable is shown minus the created reserves for doubtful debts, and inventories - minus the reserve for reduction in the value of material assets.
Calculation procedure and examples
The procedure for calculating the value is approved by legal documents and instructions. The calculation is made quarterly and annually on the reporting date with the results obtained being recorded in the relevant documents.
The following are used in the calculations:
- Non-current assets are fixed and intangible assets, long-term financial investments.
- Current assets are cash, accounts receivable, securities, production, inventory, etc.
When adding up assets, the company's costs for purchasing its own shares from co-owners of the business and the debt of participants for investments in the authorized capital are excluded.
Liabilities involved in the calculation include:
- debt to co-owners for payment of dividends;
- targeted funding and revenues;
- other long-term liabilities, including deferred tax payments;
- loans, loans, etc.
When adding up liabilities, future income is not taken into account. Moreover, only those that are recognized by the company in connection with the receipt of gratuitous property or assistance from the state.
The formula looks like this:
NA = (A - ZU - ZVA) - (P - DBP) , where:
- NA - net assets;
- A - assets;
- ZU - debt of business participants on contributions to the authorized capital;
- ZBA - costs of purchasing the company's own shares from co-owners;
- P - liabilities;
- DBP - deferred income.
The amounts for calculation are taken from the enterprise’s balance sheet, where liabilities are accounted for in lines 1400 and 1500, assets - in line 1600. You will also need the debit value of account 75, reflecting the debts of participants on contributions to the authorized capital, and the data in line 1530 - deferred income.
The calculation algorithm for the balance sheet looks like this:
NA = (line 1600 - line 75) - (line 1400 + line 1500 - line 1530)
Example
The balance sheet of Sibiryak LLC as of November 1, 2015 is presented in the following table:
| Balance indicators | Balance data |
| ASSETS | |
| 1. Non-current assets (1st part) | 1 599 500 |
| residual value of fixed assets | 999 300 |
| capital investments in unfinished construction | 455 150 |
| long-term financial investments | |
| 2. Current assets (2nd part) | |
| stocks | 145 200 |
| accounts receivable | 525 600 |
| including debts of co-owners in the authorized capital | 35 850 |
| cash | 630 250 |
| PASSIVE | |
| 3. Capital and reserves (3rd part) | |
| authorized capital | 125 300 |
| retained earnings | 1 250 300 |
| 4. Long-term liabilities (4th part) | |
| long-term loans | 745 300 |
| 5. Short-term liabilities (5th part) | |
| short-term loans | 268 300 |
| debts to the budget | 95 600 |
| other current liabilities | 1 520 600 |
- Value of assets: 3,919,150 = 1,599,500 + 999,300 + 455,150 + 145,200 + 525,600 + 630,250 - 35850.
- The amount of liabilities: 2,629,800 = 745,300 + 268,300 + 95,600 + 1,520,600, the calculation does not include data from the 3rd part of the report.
- NA = 3,919,150 – 2,629,800 = 1,289,350.
Based on the calculation, the net asset value of Sibiryak LLC as of November 1, 2015 is 1,289,350 rubles.
You can get detailed information about this indicator from the following video:
Calculation based on current assets
Current assets are identified as the organization's resources not intended for long-term storage and are reflected in the balance sheet in line 1200. Their category includes liquid assets that can be converted into cash over a short period of time, as well as inventories and short-term receivables .
Important! To calculate the value of total current assets, you can also find the difference between the sum of long-term liabilities and equity with non-current assets.
To calculate the size of current assets, you need to look at line 1200 of the balance sheet and analyze the values of the parameters that were relevant at the beginning and end of the period in order to determine the dynamics of change. The average value is calculated using the formula Ats = (At1 At2)/2, which sums up current assets at the beginning and end of the period and then divides by 2.
Return on current assets and its calculation formulas
Particular attention is often paid to the profitability of the enterprise's assets. This is a percentage that shows how profitable the company's activities are. In other words, return on assets reflects the amount of income received from each ruble spent by the enterprise.
The concept of return on current assets reflects the effectiveness of the production process. With its help, you can safely judge the nature of the implementation of economic and financial plans. Increasing the volume of production and sales of goods, conquering new markets, must constantly be guaranteed by working capital.
Meaning of book value calculation
Assets are the resources of an enterprise that bring it profit. Analysis of their size, structure and dynamics allows us to draw conclusions about the current state of the company and predict its further existence.
The balance sheet clearly presents the most important values, which can be used to quickly perform simple calculations. In the future, when identifying problems, it is necessary to go deeper into the analysis of the causes and factors of cost and structural changes, which will make it possible to correctly adjust management policies and increase the profitability of the organization.
Indicator analysis
NA must be calculated to record the current financial condition of the enterprise. By studying their value, the owners draw conclusions about the efficiency and productivity of the business and make decisions on further investment or withdrawal of their funds. Net assets in the balance sheet, line 3600, demonstrate to the owners how profitable their cash investments and the institution's equity capital are.
NA is extremely necessary for analyzing financial and economic activities. They are also taken into account when paying dividends. NA must be positive, and their indicator must exceed the size of the authorized capital. When their value grows, management can conclude that the organization’s profits are growing. Negative net assets can be observed in the first year of the enterprise’s operation - the most difficult period for operation, when the NAV can decrease and be significantly lower than the invested capital. In the case when an enterprise has been operating for a long period of time, and the NAV is negative, this indicates that the organization is operating ineffectively and investments are not profitable.
An increase in net assets is associated either with a change in their value (for example, revaluation of fixed assets) or with a change in the value of liabilities. Also, the increase in the NAV is made due to additional investments of the founders when additional capital is used.
| Home » Accountant » Net assets calculation form 2017 download |
What is the book value of an enterprise's assets
Book value of assets is the sum of all the company's assets that are reflected in the balance sheet.
The book value of assets is the sum of non-current and current assets.
Fixed assets and intangible assets are classified as non-current assets and are indicated in the balance sheet at their residual value, that is, at the purchase price minus accumulated depreciation and taking into account revaluation, if it was carried out at the enterprise.
Current assets are assets that are involved in the activities of the enterprise and are consumed within one year or one full cycle.
Current assets include assets such as:
- materials/supplies;
- accounts receivable;
- cash;
- VAT on acquired values, which indirectly, but also, is the property of the enterprise;
- short-term financial investments.
According to the laws of the balance sheet, both of its first sections, combined together, make up the full value of the company's property. Their sum is the book value of the assets. Where can I look at this indicator in the balance sheet{q} Line 1600 is the final value showing the balance of assets in value equivalent as of the reporting date.
Page B 1100 Page B 1200.
According to the laws of the balance sheet, both of its first sections, combined together, make up the full value of the company's property. Their sum is the book value of the assets. Where can I look at this indicator in the balance sheet{q} Line 1600 is the final value showing the balance of assets in value equivalent as of the reporting date.
What formula is used to calculate the return on assets of an enterprise?
The total cost (TC) can be found by adding up all the costs of the enterprise: materials, components, wages of workers and administrative and management personnel, depreciation charges, utility costs, safety and security, general shop and plant expenses, etc.
In the financial and economic analysis of an enterprise, there are two main groups - absolute and relative indicators. Absolute indicators include revenue, sales volume and profit. Analysis of these indicators does not allow a comprehensive assessment of the economic activity of the enterprise.
Why is it necessary to determine the book value of assets?
Economic services calculate the value of assets for various purposes. In particular, find out the absolute value of the property as a whole or by its constituent elements, for example, exclusively fixed assets, intangible assets or liabilities. Informing partners and users - investors, founders, insurers - is the responsibility of the enterprise, and they have the right to request various information, and first of all, about the condition of assets.
▪ return on property, which determines the amount of profit that the company receives from each ruble invested in the purchase of raw materials and production of the product.
▪ asset turnover demonstrating the effectiveness of their use.
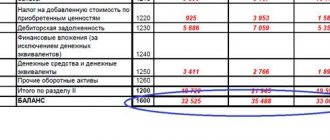
| Indicator name | Line code | as of 12/31/16 | as of 12/31/15 |
| 1. Non-current assets: | |||
| NMA | 1110 | 35 | 48 |
| OS | 1150 | 689 500 | 721 000 |
| Total for 1 section | 1100 | 689 535 | 721 048 |
| 2. Current assets: | |||
| Reserves | 1210 | 3420 | 5421 |
| VAT on purchased assets | 1220 | 241 | 459 |
| Accounts receivable | 1230 | 451 | 623 |
| Cash | 1250 | 2 451 | 3 054 |
| Total for section 2 | 1200 | 6 563 | 9 557 |
| BALANCE | 1600 | 696 098 | 730 605 |
From the universal form of the balance sheet, which already contains the calculation formula, it is easy to understand how to calculate the book value of assets on the balance sheet: line 1600 accumulates the values of lines 1100 and 1200, i.e.
689,535 tr. 6,563 tr. = 696,098 tr. – book value of assets at the end of 2020, and 721,048 tr. RUB 9,559 = 730,605 tr. – amount of assets as of December 31, 2015.
In turn, lines 1100 and 1200 are the sum of the lines included in the corresponding sections. Each line contains information about the availability of the corresponding assets.
For example, as of December 31, 2020, the company has intangible assets in the amount of 35 tr, fixed assets - 689,500 tr, inventories - 3,420 tr. etc.
By analyzing line-by-line values, for example, comparing the values of line 1210, the economist builds the dynamics of changes in the availability of an asset over control periods of time. In the course of analytical work, the economist is faced with such a concept as the market value of assets, which is the price of property at which it can be sold at the moment. This value cannot be seen on the balance sheet and is used only as a marker that determines the value of existing assets.
The value of assets on the balance sheet is what{q} The answer is contained in the same letter dated October 16, 2001 No. IK-07/703. The book value of assets is a line of the balance sheet containing the inscription “BALANCE”, that is, it is a figure that is the sum of the currency of this report.
In fact, the BSA of an organization is the sum of its balance sheet assets: this is the sum of its non-current and current assets or the sum of the results of sections I and II of this report. It should be remembered that fixed assets and intangible assets are shown in the report at their residual value, that is, minus accumulated depreciation.
Economic services calculate the value of assets for various purposes. In particular, find out the absolute value of the property as a whole or by its constituent elements, for example, exclusively fixed assets, intangible assets or liabilities. Informing partners and users - investors, founders, insurers - is the responsibility of the enterprise, and they have the right to request various information, and first of all, about the condition of assets.
▪ return on property, which determines the amount of profit that the company receives from each ruble invested in the purchase of raw materials and production of the product.
▪ asset turnover demonstrating the effectiveness of their use.
| Indicator name | Line code | as of 12/31/16 | as of 12/31/15 |
| 1. Non-current assets: | |||
| Total for 1 section | |||
| 2. Current assets: | |||
| VAT on purchased assets | |||
| Accounts receivable | |||
| Cash | |||
| Total for section 2 | |||
| BALANCE |
From the universal form of the balance sheet, which already contains the calculation formula, it is easy to understand how to calculate the book value of assets on the balance sheet: line 1600 accumulates the values of lines 1100 and 1200, i.e.
689,535 tr. 6,563 tr. = 696,098 tr. – book value of assets at the end of 2020, and 721,048 tr. RUB 9,559 = 730,605 tr. – amount of assets as of December 31, 2015.
For example, as of December 31, 2020, the company has intangible assets in the amount of 35 tr, fixed assets - 689,500 tr, inventories - 3,420 tr. etc.
https://www.youtube.com/watch{q}v=lQVzmq5_CQo
By analyzing line-by-line values, for example, comparing the values of line 1210, the economist builds the dynamics of changes in the availability of an asset over control periods of time. In the course of analytical work, the economist is faced with such a concept as the market value of assets, which is the price of property at which it can be sold at the moment. This value cannot be seen on the balance sheet and is used only as a marker that determines the value of existing assets.
About assets in simple words
Assets are the totality of all property, property rights that are the property of the enterprise, which have undergone appropriate assessment and are put on the balance sheet. This includes means of production and fixed assets (fixed assets), accounts receivable and everything that may constitute the overall property picture of the organization.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Work for Russians in the UK
An asset cannot be negative, since these are real available funds for conducting business activities. They can be counted, measured or weighed because they have a quantitative basis.
The most reliable assets are those that can easily be converted into cash without a serious loss of value. Therefore, these assets are called liquid:
- cash,
- finished product inventories,
- short-term investments and more.
Accordingly, illiquid assets can be called those property that acquires a monetary form with a very significant loss of current value or can be repaid only after a long time:
- means of production,
- fixed assets,
- overdue debts of debtors, etc.
Using assets, the management of an enterprise can receive benefits, control them, and direct them in the right direction in order to increase the level of financial flows.
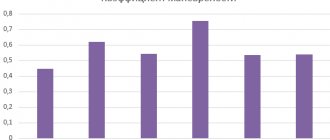
Solvency is the ability of an enterprise to pay for its obligations on time and in full. To assess solvency, firstly, a comparison is made of the amount of net assets with the size of the authorized capital and, secondly, an assessment of the trend of change. The figure below shows the dynamics of changes in net assets by quarter.
Analysis of the dynamics of changes in net assets
Solvency and creditworthiness should be distinguished, since creditworthiness shows the ability of an enterprise to pay off its obligations using the most liquid types of assets (see → How to assess the creditworthiness of a company). Whereas solvency reflects the ability to repay debts both with the help of the most liquid assets and those that are slowly sold: machines, equipment, buildings, etc. As a result, this may affect the sustainability of the long-term development of the entire enterprise as a whole.
Based on an analysis of the nature of changes in net assets, the level of financial condition is assessed. The table below shows the relationship between the trend in net assets and the level of financial health.
| Trend in net assets | Financial analysis |
| CHA ↗ | Improving the financial condition of the enterprise and the solvency of the enterprise, reducing the risk of bankruptcy |
| Cha ↘ | Deterioration of the financial condition of the enterprise, decrease in solvency, which leads to an increase in the risk of bankruptcy |
In addition to the dynamic assessment, the amount of net assets for an OJSC is compared with the size of the authorized capital. This allows you to assess the risk of bankruptcy of an enterprise (see → 4 bankruptcy assessment models). This comparison criterion is defined in the law of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (clause 4, article 99 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation; clause 4, article 35 of the Law on Joint Stock Companies).
In the scientific work of Zhdanov I.Yu. shows that there is a close connection between the rate of change in the net assets of an enterprise and the value of the international credit rating of such agencies as Moody's, S{amp}amp;P and Fitch. A decrease in the economic growth rate of net assets leads to a decrease in the credit rating. This in turn leads to a decrease in the investment attractiveness of enterprises for strategic investors.
Summary