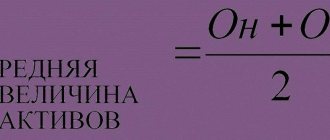No investor invests money blindly without doing preliminary research: he must be confident that it will pay off or, at a minimum, be returned. To do this, the potential profitability of the investment project is assessed. Of course, this cannot be done except comprehensively, using a number of specially developed indicators, the most important of which is the internal rate of return.
Let's consider what are the features of the investment research method based on calculating the internal rate of return - IRR.
What is internal rate of return?
No one can calculate with 100% probability what income will be received from the invested funds. There are too many variable factors that can affect the implementation of a business project financed by an investor. However, you can minimize the risk of inaccuracy if you use a relative rather than an absolute assessment.
The interest rate at which the investor is guaranteed to recoup his investment, but will not receive a profit, is called the internal rate of return (IRR). The norm is that all cash flows of a given investment project will be offset in total. In other words, the costs of an investment project at some point in time are balanced by the income received (they say that the project “broke to zero”).
IMPORTANT! The word “internal” in the definition of this investment rate means its dependence on the properties of the project itself, and not on external factors.
Experts may call the internal rate of return differently. The following names :
- VND is a Russian abbreviation;
- IRR is an English abbreviation for “Internal Rate of Return” - “internal rate of return”;
- internal rate of return;
- internal rate of return;
- internal rate of return on investment;
- maximum efficiency of capital investments;
- percentage rate of return;
- discounted flow of real money;
- financial rate of return;
- own rate of return.
ATTENTION! This norm can be considered the limit, since going beyond its limits already means a loss for the investor.
https://youtu.be/q—hjGUnF-k
Why do you need a calculation?
The economic meaning of the indicator is that it characterizes the following points:
- Profitability of a possible investment . When an enterprise chooses which project to invest in, it is guided by the value of this indicator. The larger the IRR, the higher the return on investment.
- Optimal loan rate . IRR is the maximum price at which an investment breaks even. If the company plans to obtain a loan for this investment, then you should pay attention to the annual rate. If the interest on the loan is greater than the received value, then the project will generate a loss.
When using an indicator to evaluate future investments, you need to consider the advantages and disadvantages of this method.
The positive aspects of using VND include:
- Comparison of possible investments with each other based on the efficiency of capital use. The company will prefer to choose the investment that, with an equal interest rate, has a higher rate.
- Comparison of projects with different investment horizons, that is, the time period for which the investment is made. In this case, when comparing the IRR of different possible deposits, the one that will bring the greatest income in the long term is identified.
This is interesting: Business on coffee machines
The main disadvantages and negative features include:
- Difficulty in predicting payments. By calculating this value, it is impossible to predict what the size of the next deposit receipt will be. The amount of profit is influenced by many different factors, risks, situations at the micro and macroeconomic level, which are not taken into account in the calculation.
- It is impossible to determine the absolute value of the influx of money. IRR is a relative indicator; it specifies only the percentage at which the contribution still breaks even.
- Reinvestment is not taken into account. Some deposits require the inclusion of interest payments. That is, there is a process of increasing the amount of investment due to profit from it. The IRR calculation does not provide for this possibility, so the indicator does not reflect the real profitability of these costs.
Indicators for calculating IRR
Mathematically, calculating the internal rate of return is not that complicated, but the formula includes many additional indicators that must be taken into account. Among them:
- NPV – from the first letters of the expression “Net Present Value” (“net present value”) – the sum of all cash flows of a given project, reduced to a general indicator when netting income and costs;
- CF – cash flows (from “Cash Flows”) – the values of various inflows and outflows of finance, including invested funds, in a selected period of time t (usually a year). For an investment project, the first cash flow - the investment itself - will naturally have a negative value (this is a cost).
- R is the discount rate, that is, the percentage at which an investor can receive funds for investments (take a bank loan, sell their shares or use internal funds).
- WACC - weighted average cost of capital (from Weighted Average Cost of Capital) - if several sources of raising money are used at once, then the interest rate will represent the average value, calculated proportionally.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION! It would be very simple to calculate the internal rate of return if we knew all the necessary indicators. However, in practice it is impossible to determine the exact values of cash flows and unambiguously calculate the discount rate. Therefore, for each individual project, the degree of dependence of NPV on the interest rate is assessed.
Analysis of the result
The indicator is used to analyze the effectiveness of potential investments. To determine the feasibility of investing money, GNI is compared with a certain level of profitability. Often this is done using the weighted average cost of capital (CAC).
The SSC indicator characterizes the minimum amount of enterprise income that can provide the founders with a return on funds spent on capital contributions. Most investment decisions are made based on this figure.
Also, the interest rate on loans is often taken as an indicator of profitability. This method allows you to find out whether raising borrowed funds is effective for a given project.
The feasibility of the company’s deposits is determined based on the ratio of IRR and profitability indicator (P):
- VSD=P . This means that the investment is at the maximum permissible level. To ensure cost efficiency, the initial cost of investments should be reconsidered, flows and timing should be adjusted. Also, when analyzing investments, their comparative analysis is used.
- VSD>P . This ratio indicates that the investment will cover the costs of its provision. This investment can be considered as a possibility, the final decision should be made after further financial analysis.
- VSD. This means that the analyzed project has a lower profitability than the cost of capital, loans, etc. The organization is advised to abandon investments, as they will not bring profit.
- VSD1. This ratio shows that one of the proposed investments is more profitable than the other.
Methods for calculating GNI
It is not possible to calculate the internal rate of return manually, since if you derive the IRR value from it, it will turn out to be a 4th power multiplier. This indicator can be calculated in several ways:
- use a special financial calculator;
- use the Excel program, in which this function is built into the “Financial Formulas” section called IRR (“internal rate of return”);
- use one of the online calculators;
- apply a graphical method (used before the widespread use of personal computers).
Calculation in Excel
The easiest way to calculate an indicator is to use automated tools, such as Excel. This program has built-in financial formulas that allow you to make calculations very quickly.
To calculate the value there is a VSD function . However, this formula will work correctly only if there is at least one positive and one negative value in the table.
Here you can download a free Excel file with an example calculation
The formula in the final cell looks like this: =VSD(E3:E12) .
You can see the calculation procedure in this program in the following video:
Advantages and disadvantages of the IRR method
To evaluate investment opportunities, two methods are mainly used - calculating NPV and IRR. The method for determining the internal rate of return is relative, so it cannot claim high accuracy, but it has a number of advantages :
- helps to easily assess the profitability of an investment project;
- shows the maximum allowable cost for investment in the project;
- allows you to compare different projects in terms of profitability, even if they differ in scale and duration over time.
Disadvantages of the IRR method:
- it is impossible to calculate the absolute return on an investment (that is, exactly how much money – rubles, foreign currency – it can bring to the investor);
- it is possible that the investment effect may be overstated if the IRR is very different from the company's level of reinvestment (that is, positive cash flows are “returned” to the investor at an interest rate that does not coincide with the IRR);
- when calculating, the sequence of cash flows is neglected (for the formula it does not matter in what order the costs occur and the profit comes, whereas in practice this can be of decisive importance);
- distortions are possible when assessing mutually exclusive investment projects.
Interpretation of internal rate of return
The main rule by which the possibility of investing is assessed by the IRR indicator: a project can be accepted if the IRR is higher than the weighted average cost of capital for the company (WACC). This means that it is worthwhile for an investor to borrow money for an investment, and it is more likely to generate incremental returns.
FOR EXAMPLE . The bank can provide the investor with money at 12% per annum. An investor is going to take out a loan and invest in a project whose IRR is 16%. This means that 16% per annum is the upper limit at which you can borrow money for this project. If the project really brings 16% profit, 4% will remain in favor of the investor; in any case, he will be able to return the borrowed funds without loss to himself.
Example of application of VND
Let's give a real-life example of assessing internal profitability that an ordinary citizen, and not just an entrepreneur, can understand.
Renting out an apartment seems to be a profitable undertaking. But it all depends on whether this apartment is owned. If this is so, then the initial investment is zero, so the project is certainly profitable. But what if you plan to invest in buying an apartment, rent it out, and then sell it in order to repay the loan taken for it?
Let's consider whether this project will be profitable. Let the apartment cost 5 million rubles, and the rental amount for the year will be 25,000 rubles. per month. Let's neglect tax expenses for registering the purchase of an apartment and rent. Over 3 years, rental income will be 25,000 x 3 = 75,000 rubles. Let’s imagine that the real estate market conditions have not changed in 3 years and the apartment can be sold for the purchase price. This means that after three years the investment will bring an income of 75,000 + 5 million rubles. The IRR of such a project will be approximately 6%.
As you know, the bank lending rate is approximately 9%, which means that if you have free funds at your disposal (for example, having received them as an inheritance), it is more profitable to put them on deposit than to buy an apartment for rent.
But if the cost of the apartment increases significantly over the years, the GNI of the project will also change for the better.
Examples of IRR calculations
Not only professional investors, but also almost any person who wants to profitably invest their accumulated funds are faced with the need to calculate the IRR indicator.
An example of calculating IRR for business investing
Let us give an example of using the method of calculating the internal rate of return under the condition of a constant barrier rate.
Project characteristics:
- The size of the planned investment is $114,500.
- Investment income:
- in the first year: $30,000;
- in the second year: $42,000;
- in the third year: $43,000;
- in the fourth year: $39,500.
- The size of the compared effective barrier rate is 9.2%.
This calculation example uses the successive approximation method. “Types” of barrier rates are selected so as to obtain the minimum NPV values modulo. Then approximation is carried out.
How to calculate the IRR for the barrier rate r(a) = 10.0%?
Let's recalculate cash flows in the form of current values:
- PV1 = 30000 / (1 + 0.1) = $27272.73
- PV2 = 42000 / (1 + 0.1)2 = $34710.74
- PV3 = 43000 / (1 + 0.1)3 = $32306.54
- PV4 = 39500 / (1 + 0.1)4 = $26979.03
NPV(10.0%) = (27272.73 + 34710.74 + 32306.54 + 26979.03) - 114500 = $6769.04
Before calculating the IRR for the barrier rate r(b) = 15.0%, we will again recalculate the cash flows in the form of current values:
- PV1 = 30000 / (1 + 0.15)1 = $22684.31
- PV2 = 42000 / (1 + 0.15)2 = $31758.03
- PV3 = 43000 / (1 + 0.15)3 = $28273.20
- PV4 = 39500 / (1 + 0.15)4 = $22584.25
NPV(15.0%) = (22684.31 + 31758.03 + 28273.20 + 22584.25) - 114500 = -$9200.21
Assuming that on the segment a-b the NPV(r) function is rectilinear, we use the equation for approximation on this section of the line:
IRR calculation:
IRR = ra + (rb - ra) * NPVa /(NPVa - NPVb) = 10 + (15 - 10)* 6769.04/ (6769.04 - (-9200.21)) = 12.12%
Since a certain dependency must be preserved, we check the result against it. The calculation formula is considered fair if the following conditions are met: NPV(a) > 0 > NPV(b) and r(a) < IRR < r(b).
The calculated IRR shows that the internal payback ratio is 12.12%, which exceeds 9.2% (the effective barrier rate), which means that the project can be accepted.
To eliminate the problem of multiple determination of IRR and avoid (with alternating cash flows) incorrect calculation, an NPV(r) graph is most often constructed.
An example of such a graph is presented above for two conditional projects A and B with different interest rates. The IRR value for each of them is determined by the intersection with the X-axis, since this level corresponds to NPV=0. So in the example you can see that for project A the intersection with the scale will be at the point marked 14.5 (IRR=14.5%), and for project B the intersection will be at the point marked 11.8 (IRR=11.8%) ).
Comparative Case Study of Private Investment
Another example of the need to determine IRR can be an illustration from the life of an ordinary person who does not plan to launch any business project, but simply wants to make the most profitable use of accumulated funds.
Let’s say that having 6 million rubles requires either taking it to the bank at interest, or purchasing an apartment to rent it out for 3 years, and then sell it, returning the main capital. Here the IRR will be calculated separately for each solution.
- In the case of a bank deposit, it is possible to place funds for 3 years at 9% per annum. Under the conditions offered by the bank, you can withdraw 540 thousand rubles at the end of the year, and after 3 years you can withdraw all 6 million plus interest for the last year. Since a deposit is also an investment project, the internal rate of return is calculated for it. Here it will coincide with the percentage offered by the bank - 9%. If the starting 6 million rubles are already available (that is, you do not need to borrow them and pay interest on using the money), then such investments will be profitable at any deposit rate.
- In the case of buying an apartment, renting it out and selling it, the situation is similar - funds are also invested at the beginning, then income is taken and, by selling the apartment, the capital is returned. If the cost of the apartment and rent do not change, then the rent at the rate of 40 thousand per month for the year will be equal to 480 thousand rubles. Calculation of the IRR indicator for the “Apartment” project will show 8% per annum (subject to uninterrupted delivery of the apartment during the entire investment period and a return of capital in the amount of 6 million.