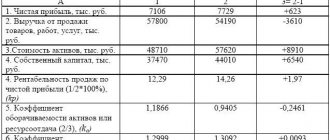
2020-03-18 20592
Financial statement consolidation is the process of combining and subsequently synchronizing reporting data from a group of enterprises. This is done in order to present information on the financial position of consolidated companies in one single reporting package.
Financial statement consolidation is the process of combining and subsequently synchronizing reporting data from a group of enterprises. This is done in order to present information on the financial position of consolidated companies in one single reporting package.
Such a group is created during the merger of several enterprises into a holding company or at the moment when one company acquires a large stake in the capital of another, which gives it the right to act as a controlling participant. In this case, the parent company exercises control over one or more companies and directly influences their financial policies.
Definition of the concept
Consolidated financial statements are data on the economic and property status of the merged companies, the results of their activities, as well as regarding projects for further development.
This documentation is created uniformly for all subjects of the group and determines the pace of development of the association as a whole; it is not documentation for presentation to the tax or other government authorities and carries information on the external activities of the participants.
In the process of its compilation, IFRS standards are adhered to in compliance with the information style. It is used to provide information about the group to outsiders who have an interest in the company in order to increase their level of trust, as well as to summarize the company’s activities at the end of the year for the meeting of directors and founders.
Moreover, this concept is closely related to the definition of a group of enterprises and their characteristics, since these are several legal entities that are united to achieve one goal, but are not subordinate to one legal entity.
Representatives of these associations are holding companies or concerns, which are headed by a parent entity that exercises economic and economic control.
https://youtu.be/I3Ar6Bqu2tw
What is consolidated reporting and why is it needed?
The definition of consolidated financial statements is related to the definition of a group of companies.
A group of companies is two or more enterprises that have legal status and are united into one group, which as an economic unit is not considered a legal entity.
Control over enterprises (subsidiaries) is exercised by the parent (parent or management) company, which determines the financial and economic activities of its subsidiaries to obtain financial benefits. The most common forms of creating groups of enterprises are holding companies and concerns.
Consolidated financial statements (KFO) are a type of reporting that contains reliable information about the property and financial condition of a group of companies, the economic results of its activities, and the prospects for future development.
The CFO is compiled independently of the financial statements and is not submitted to the tax service or other government bodies. The document gives only a general idea of the affairs of the entire interconnected group as one whole, but not for each enterprise separately.
The CFR must comply with IFRS standards and be for informational purposes only. It is provided to third party users interested in the group of companies and is aimed at increasing their trust. Based on such a report, users make decisions regarding a group of enterprises.
REFERENCE. To improve the level of accounting and reporting, the Government of the Russian Federation carried out a corresponding reform that brought Russian accounting and reporting standards closer to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
Regulatory regulation
Regarding the rules and features of the application of one reporting for the entire group, as well as its formation standards, Federal Law No. 208 was published in 2010. According to this act, a number of commercial enterprises must necessarily use consolidated statements using IFRS standards.
This innovation is revolutionary for domestic legislation and is designed to bring accounting reporting to a new level in order to awaken investor confidence.
There is also Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 112 of 1996 regarding the use of methods for the formation and provision of reporting documents of similar importance, to which summary documentation is also relevant. According to the legislative act, consolidated documentation for one object is taken into account in consolidated documentation if the following circumstances exist:
- the parent company owns over 50% of the total capital or voting shares
- The parent company makes the main decisions and influences the effectiveness of decisions made by other companies
- if possible, influence decisions made by subsidiaries
In addition, on the basis of another Federal Law No. 317 of 2007, such reporting must also be prepared by the state enterprise Rosatom.
At the same time, Federal Law No. 145 of 2009 obliges another state enterprise to submit a report of the consolidated version “Russian Highways”.
When registering a prospectus, issuers must also submit consolidated reporting documentation on the basis of Federal Law No. 39.
According to Federal Law No. 208, such documentation must be prepared in compliance with deadlines, namely before the general meeting of all participants, but no later than 120 days from the last day of the reporting year and 2 months for the interim report.
Also, taking into account the same legislative document, this reporting must be audited and published.
Consolidated Financial Reporting Law
Legislation regulates this area using Federal Law No. 208-FZ. Based on this regulatory act, consolidated reporting is data calculated, selected and systematized on the principles of reliability and unity to display the financial condition of the structure and the financial performance of its work in the reporting period.
The preparation of such reports is strictly regulated by this and other legislative acts. Among the most important requirements are the following:
- Consolidated accounting statements (KBO) and consolidated financial statements (KFO) are drawn up exclusively on the basis of the federal law “On Accounting”.
- When preparing reports, preparers take into account international documentation requirements adopted in this area.
- Documents are drawn up in Russian, the Russian ruble is used in calculations, all papers are signed by the general director.
- Reporting is received by shareholders and founders, the Central Bank.
- The annual CFO is published in publicly available media within 30 days.
- Subject to mandatory audit, the results of which are published along with the KFO.
- Does not include duplicate information, such as information about financial transactions between the parent company and subsidiaries. All data on assets and financial liabilities of several independent business units are combined into a common system.
- Preparation of documentation ends on the same day at all enterprises.
- The information is reliable, consistent, not duplicated, not distorted.
KFO is regulated by Federal Law No. 208-FZ and international standards
. Such reporting is provided by all organizations that:
- have a structure of dependent organizations and are responsible for implementing strategic policies in them;
- have more than 51% of the shares of a joint stock company or 51% of the authorized capital of an LLC;
- have foreign branches (their reporting is also prepared in Russian, in calculations - Russian ruble).
Also, to correctly prepare reports, you need to know the labor, tax and civil codes, thematic orders of the Ministry of Finance, in particular No. 112 of December 30, 1996. It is important to know that rules and regulations are updated regularly, so it is important to keep track of the latest versions of documents. The application of a number of international standards in the preparation of documentation is aimed at improving its quality.
The reporting contains:
- balance sheet, with all summaries and explanations;
- loss and profit report;
- information about all participants in the system, chain of command (full list, registration addresses, share of the main organization in shares or authorized capital).
Nuances of consolidated reporting
The CFO, unlike a standard accounting report, has certain nuances:
- it is rented out to several companies at once
- intended for a narrow circle of users
- differs in format and purpose from the summary
The documentation consists of the following data:
- Form 1 – the entire accounting balance, accompanied by applications and summaries
- part 2 – a full report on the income and expenses of the association
- information regarding the participants of the association - full details, names, share of participation in the authorized capital of each entity of the association
As a result, all reports for enterprises are combined together without reflecting financial and settlement transactions between participants, since the essence of creating consolidated reporting lies in displaying the external activities of the group.
For all companies, information on financial activity is permissible for inclusion in reporting only if a controlling stake or 51% of the share is in the hands of the main entity. Otherwise, this information is not provided individually.
Methods for forming CFO
In order to process a large amount of data, several methods for generating CFOs are used. The choice of method is made by the parent organization, which is influenced by the nature of the enterprise’s activities and the share of the company that it owns.
Full consolidation
The method is used when consolidating reports by the parent organization from dependent (subsidiary) enterprises. This approach requires a clear definition of the structure of the group of companies. Here, the method of adding up the indicators of the balance sheet items of the same name minus intragroup settlement transactions is used.
Share
The method is relevant if the investor has a share of the capital of the organization, but is not its member. Consequently, profit and loss are determined based on the actual cost of the share, followed by an adjustment to the share of the organization's profit.
Interest pooling method
When several firms equally own an enterprise, but there is no parent organization in the structure, the pooling of interests method is used. In this case, when preparing reports, each owner must reflect information regarding all subsidiaries.
Combined reporting
Combined reporting is formed in cases where there is a group of companies without a parent company, but essentially owned by one owner without any legal connection. As a result, reports are first compiled for each organization, after which all indicators (including capital) are summarized in one document, after which intra-group calculations are subtracted.
Differences between consolidated and consolidated forms
In addition to reporting documentation on the merger of organizations, there is also a summary document, the purpose of which is also to indicate information on the company’s activity for a specific time period. However, these two indicators have certain differences, indicated in Table 1.
| Consolidated | Summary |
| Formed by the association of entities that are separate legal entities | Formation within one enterprise, according to information from all divisions related to it |
| Designation not of amounts, but of total data regarding the activities of an enterprise as an economic complex - a feature of its formation, elimination of indicators | Line-by-line addition of numerical values reflected in the organization’s reporting forms for a separate object |
| Formation in relation to a group of legal entities | Reporting is generated based on industry or target settings |
| Reflection of data for a group of interrelated indicators | Indications for a specific object |
| In the reporting process, the moment at which the subsidiary becomes dependent on the parent is taken into account. |
How IFRS reveals the concept of consolidated statements
Dedicated to consolidated reporting, IFRS 10 provides a set of definitions that describe the basic principles and approaches to compiling CFRs. For example, among such definitions are the following:
- Consolidated reporting is the reporting of a group in which the reporting indicators of MC and DF are presented together as indicators of a single economic entity.
- MK is a company that controls one or more companies.
- DF is a company controlled by another company.
- Other terms (investment entity, non-controlling interest, etc.).
Another set of concepts related to CFD is disclosed in the standards:
- IFRS 3 (on business combinations);
- IFRS 11 (on joint arrangements);
- IFRS 12 (on disclosure of interests in other entities),
- IAS 24 (related parties).
Without disclosing the terminology of these standards, it is difficult to understand the principles of formation of the CFO. For example, in order to compile a CFO, the following concepts require decoding:
- A business combination is an event in which an acquirer gains control of one or more businesses;
- a related party is an individual or company associated with the reporting firm;
- key management personnel - directors and other persons of the company authorized and responsible for planning, managing and controlling its activities;
- other terms and definitions necessary for understanding the procedure for registering a CFO.
Read about some standards that may be in demand when compiling the CFO in the articles:
- “IFRS No. 3 Business Combinations - Application Features”;
- “IFRS No. 31 Financial statements of interests in joint ventures”.
Who should apply it mandatory?
According to the law, the use of consolidated accounting reporting documents is mandatory for certain state-owned enterprises, which are regulated in their activities by separate legislative acts.
As well as companies that have subsidiaries and are engaged in activities in the field of:
- lending
- insurance, excluding medicine
- clearing
- non-state pension funds
- bidders
- investment funds, with the exception of mutual funds
- other enterprises designated by legislative acts
Consolidation of financial statements
Financial statement consolidation is the process of combining and subsequently synchronizing reporting data from a group of enterprises. This is done in order to present information on the financial position of consolidated companies in one single reporting package.
Such a group is created during the merger of several enterprises into a holding company or at the moment when one company acquires a large stake in the capital of another, which gives it the right to act as a controlling participant. In this case, the parent company exercises control over one or more companies and directly influences their financial policies.
Substance and composition of consolidated financial statements
The parent company prepares consolidated financial statements. This reporting format provides objective and truthful information to managers about their investments, control and ownership of net assets. This is a justified requirement, since the individual reporting of the parent company does not display information regarding investments in controlled structures.
Consolidated financial statements, which are prepared in accordance with IFRS requirements, reflect the activities of a group of companies as a whole and include the following reports:
- Balance sheet;
- Profit and Loss Statement;
- Statement of changes in equity;
- Cash flow statement;
- Notes.
Benefits of Consolidating Financial Statements
- favorable conditions for involving finance;
- improving the company's manageability through increased solidity of financial results;
- attracting foreign investors and partners;
- increasing the value of the company by reducing uncertainty in the financial position.
Principles of consolidation of financial statements
- The principle of completeness
requires a complete reflection of information about the assets, liabilities, deferred expenses, and deferred income of the combined group of companies, regardless of the size of the parent company. - The principle of fair and reliable assessment
- consolidated financial statements must be transparent, intelligible, easily understandable and provide meaningful and objective information about the assets, liabilities and financial condition of the organizations that are part of the group of companies. - The principle of equity capital
- the equity capital, financial results of operations and reserves of the group are consolidated, since the parent company and its structural divisions are perceived as a single whole. - The principle of constant application of consolidation methods and the principle of a going concern
oblige the use of selected consolidation methods over a long period, subject to the effective functioning of the group of companies. - Materiality principle
— only if the information is important to users, it is disclosed in the consolidated statements.Only those items that have a direct impact on investment or other management decisions are considered material and should be shown in the financial statements.
- The principle of uniform valuation methods
- the parent company undertakes to use uniform valuation methods when consolidating financial statements and when preparing its own. - The principle of a single date of preparation of consolidated financial statements
- the consolidated financial statements are prepared as of the date of preparation of the parent statements. - The principle of a single accounting policy
- when preparing consolidated statements, a single accounting policy is used for parent and subsidiaries, applicable to similar transactions and other events under similar circumstances.
Methods of consolidating financial statements
There are certain methods for consolidating financial statements:
Full consolidation method
— a group of companies is a single whole economic entity. The assets of structural divisions fall under consolidation, while the liabilities demonstrate the rights of minorities. This method is applicable for subsidiaries that are formed through a merger or acquisition.
Proportional consolidation method
— provides for the reflection in reporting only of those assets that a structural unit of a group of companies actually owns and exercises use and control over them.
Equity method
- a method that takes into account investments in associated organizations. Investments are reflected at par value with the creation of goodwill.
Stages of consolidation of financial statements
- The process of preparing financial statements separately for each company that is part of the group for the consolidation itself:
- identification and exclusion of all intra-group transactions that lead to the formation of profits and losses that cannot be realized;
- determining the amount of unrealized gains and losses.
- Consolidation of goodwill.
- Consolidation of accumulated capital.
- Determination and separation of the minority interest in the net assets and net profit (or loss) of business units, consisting of:
- amounts at the date of merger;
- part of the minority in the amount of the change in the equity capital of the structural unit after the merger.
- Formation of consolidated financial statements by item-by-line summation of elements of the financial statements of structural divisions with similar elements of the financial statements of the parent company.
Methods for preparing primary consolidated statements:
- method of acquisition (purchase);
- method of association (merging).
The difficulty in preparing consolidated financial statements is the need to eliminate (exclude) items to prevent re-counting and artificially inflating the amount of capital and financial results.
PS You can watch the full recording here
Source: https://finacademy.net/materials/article/konsolidaciya-finansovoi-otchetnosti
For whom and in what way is it compiled?
According to Art. 4 Federal Law No. 208, consolidated reporting is prepared by the parent organization of the association for specific recipients, namely:
- participants and owners of fixed assets - shareholders, founders, directors, it is for their meeting that it is necessary to comply with the deadlines for the formation of interim or annual reporting
- The Central Bank must also receive the reporting document
- for interested individuals, the report is provided within a month, through the media
Reporting must be prepared in compliance with the following requirements:
- In the process of document generation, it is necessary to comply with all reporting principles.
- The document must be drawn up using one language, and indicators must be reflected in one currency.
- Information must only be reliable and accurate; the head of the parent company is responsible for this.
- Compliance with reporting deadlines.
- Report summaries must be prepared by all group members.
- The KFO has an audit report required to be submitted along with the reporting.
If there are foreign branches, data on their financial activities must be indicated in the main report, in the language of general preparation.
In addition, you can use the formation methods indicated in Table 2.
| Types | Explanations |
| Full consolidation | In this case, it is necessary to clearly structure the data according to the documents of the same name for each enterprise. |
| Share | The presence of an investor's share in an enterprise without his direct participation. Determination of profit and loss based on the actual value of the share with further adjustment of the share participation |
| Interest pooling method | When a company is managed by several organizations without identifying the parent one, in this case information on subsidiaries is indicated by each owner |
| Combined | This case is relevant to companies that essentially have a main owner without his official separation into a management company. In this case, reporting is initially generated for each organization, and then one report is generated based on the received documentation |
| Proportional | Drawing up a joint activity agreement between enterprises indicating rights and obligations, and choosing by agreement any method of consolidation |
The reporting must include the following data:
- relative to the financial position at the end of the reporting period
- regarding profit and loss for the reporting period
- in relation to total financial receipts for a given period
- summaries of cash flows for this period
- explanations of the group's accounting policies used in the preparation of financial statements and other data
After this, it is necessary to transform the financial statements generated according to Russian standards into international parameters. This possibility exists, for example, in the 1C program, thanks to which input data can be transformed into final data, taking into account all the required points.
The adjustment will provide an opportunity for foreign investors to study the group’s potential using their own methodology and determine its opportunities for development in the future.
By whom and for whom are consolidated statements prepared?
The KFO is compiled by the parent company of the group and determines the categories of reporting recipients. These are:
- Participants and owners of enterprise property - shareholders, founders, board of directors. They are the first to receive annual/interim reporting within the deadlines established by law: 120 and 60 days, respectively, from the end of the reporting period.
- The Central Bank of the Russian Federation receives the CFO in the manner and within the time limits established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
- Users of interest are suppliers, investors and others. For them, reporting is posted on public resources such as media and Internet portals for 30 days.
What information is not taken into account in the process of compiling it?
When preparing consolidated statements, amounts for settlement transactions carried out within the group during the past period are not taken into account, since there should be no distortion of external indicators for the general activities of the group.
Consolidated statements are important for displaying the overall activities of the group, taking into account the option of its formation - purchase or merger, while purchase means the acquisition of a majority stake in the share of subsidiaries.
Top
Write your question in the form below
Translation from functional currencies to reporting currency
Our companies operate in different countries with different currencies. The group's reporting currency is EUR. Therefore, for companies from countries where the main currency is not EUR, it is necessary to convert all financial transaction amounts into EUR.
In NAV, in the table of financial transactions there are separate fields for amounts in an additional reporting currency (this is standard functionality of the system). For example, the primary reporting currency for a US company is USD, and all amounts in financial transactions are in USD, and the secondary reporting currency is EUR, and all amounts in additional fields are in EUR.
NAV takes the exchange rate on the transaction date and calculates the amount at that rate. Naturally, he makes sure that the balance of the financial transaction converges, and in some cases adds additional lines with zero amounts in the local currency and one or two EUR cents to compensate for discrepancies due to rounding.
At the end of the year, the balances of the asset and liability accounts by measurement are recalculated at the end of the year exchange rate (refinement of the standard functionality).
Reflection of indicators when using the acquisition method
The acquisition method is used for groups of companies that include dependent enterprises. Accounting must be carried out on identical conditions. When implementing the acquisition method, the following are excluded:
- Summation of share capital. The article indicates only the size of the parent enterprise;
- The value of the parent company's investment. The share of participation in the net assets of the dependent company is indicated. When the cost of investments is higher than the share in the NA, the reporting reflects the overpayment (goodwill), less than the NA - the amount of income from the transaction;
- Indicators of transactions (income, expenses, balances) made between the parent and dependent enterprises.
Retained earnings in the acquisition method of the parent company are added to the share due in the subsidiary company that arose after the transaction.
Consolidated reporting requirements
When drawing up a CFO, a number of requirements must be met:
- KFO reporting is presented along with standard financial statements;
- When preparing reports, the provisions of standards adopted within the framework of IFRS approved in the Russian Federation are used;
- The reporting currency is the Russian ruble;
- The formation of an MFO is preceded by a mandatory audit;
- Before submitting reports to the control authorities, the MFO must be presented to the founders and shareholders of the company.
Financial statements submitted by companies included in a consolidated group must be presented as of the same date. Enterprises must have the same type of accounting rules, enshrining them in the accounting policies of each legal entity. In the event of significant influence over the activities of a subsidiary, the accounting procedure of the parent company is adopted.