Break even
“How many products need to be produced and sold? What price should I set for it to start making a profit?” — these questions concern every entrepreneur. The answer can be given by calculating the break-even point (the situation in which expenses will equal income).
After this point has been found, you can begin to optimize the enterprise’s activities: produce more or less products, or change prices.
At the moment when revenue exceeds the break-even point, we can say that the company is making a profit. Otherwise, it suffers losses.
Methods for calculating the break-even point
The main indicators that will have to be used when determining the break-even point are:
P – product price;
X – volume of manufactured products required for sale;
FC – fixed costs (do not depend on the quantity of products produced, for example, wages of employees);
VC(X) – variable costs (increase with each unit of production);
S – revenue for a certain period;
R – profitability.
You can find the break-even point in various ways, depending on the available information.
First method: costs and sales volume are known
Having information about costs, as well as the quantity of products that need to be sold, it is possible to determine the minimum price for a product that allows the enterprise to work “to break even.”
The formula itself looks like this:
P = (FC + VC(X)) / X.
Second method: price and costs are known
Here, knowing the price and costs, the volume of product sales is determined, which will allow you to get zero profit.
Formula:
X = FC / (P – VC).
The absence of the variable “(X)” is explained by the fact that the formula takes into account only the cost of producing 1 unit of output.
In practice, the price of a product is set in advance based on costs and market realities, so determining quantity is the most common task facing management.
Calculation of the break-even point for the service and trade sectors
The method of determining the break-even point for the service and trade sectors is characterized by complexity and uncertainty in calculating the cost of 1 unit of production. The number of goods in trade can reach several thousand and calculating the cost of each product turns out to be impossible.
In the service industry, costs cannot be accurately determined due to the uniqueness of each service provided. In these cases, it is preferable to use profitability indicators. Profitability is the difference between price and cost of production.
Formula:
S = FC/R.
Calculation formulas in monetary and physical terms
The break-even point formula exists in two main versions: in physical and monetary terms.
To calculate BEP in physical terms, the following indicators are needed:
- FC - fixed cost, that is, the sum of fixed costs per volume;
- AVC - average variable cost, the value of variable costs per unit of production;
- P - price, unit price of a product or service, work.
To calculate the break-even point, that is, the critical sales volume, in physical terms, use this formula:
BEP = FC/( P-AVC )
Similar calculations of BEP in monetary terms are made using the following indicators:
- FC — fixed cost, the amount of fixed costs;
- VC - variable cost, the sum of variable costs per volume or AVC - average variable cost, the value of variable costs per unit of production;
- P - price, price or TR - total revenue, income (revenue).
The formula for the break-even point in monetary terms also requires the calculation of the marginal income coefficient, that is, its share in revenue. First you need to find the value of marginal revenue itself (MR - marginal revenue), and this is the amount of revenue minus variable costs.
MR = TR - VC
But there is one nuance: revenue per unit of production is precisely the price of the product, it can be expressed by the formula: P = TR/Q, where TR, as we already know, is the amount of revenue, and Q is the sales volume. It turns out that marginal income is the difference between price and variable costs, only per unit of production: MR = P - AVC
Then we calculate the marginal income coefficient as follows:
Kmr = MR/TR
Or, if we calculate MR based on price:
Kmr = MR/P
You can count it both ways, the result will be the same.
The break-even point is also calculated in monetary terms: BEP = FC/ Kmr
As a result of the calculation, you will get a critical amount of revenue, that is, its level at which the profit is zero.
Calculation of break-even point in Excel
To perform the calculation, you must determine the main indicators.
Let's assume that:
- Fixed costs = 100;
- Variable costs = 50;
- Price = 75;
Next, you should calculate the change in net profit depending on the volume of production and determine when the break-even point will be reached.
You need to create and fill out a table:
- Fixed costs = C2
- Variable costs = A9*$C$3
- Total costs = B9+C9
- Income = A9*$C$4
- Net profit = E9 – D9
Based on this table, it can be seen that the break-even point is reached with the release of the 4th product, and subsequent release increases the organization’s profit.
What indicators are taken into account in the break-even point formula
How to determine the break-even point? To do this, you need to know the components of the calculations, first of all, the specific costs of the enterprise. They are divided into constants and variables, and it is important to be able to distinguish one from the other.
Fixed costs include rent for premises, depreciation, as well as salaries of management and other managers (both basic and additional), taking into account deductions.
Variable costs are fuel and energy for technological needs, materials (main and auxiliary), components, and semi-finished products. This also includes workers’ wages, also basic and additional (with deductions).
Fixed costs are called that way because they are slightly susceptible to fluctuations and changes. It is generally accepted that they practically do not depend on the volume of production and sales. Changes in fixed costs can occur under the influence of such factors as growth or decline in enterprise capacity, changes in the level of labor productivity, expansion due to the opening of new workshops or a reverse phenomenon, inflation, rent adjustments, etc.
But variable costs are precisely tied to production volumes, and accordingly, they change with them. The dependence is directly proportional: with an increase in production and sales volume, the amount of variable costs also increases.
But please note: we are talking specifically about the total amount of this indicator. At the same time, variable costs per unit of production do not change significantly with increasing production volumes. Experts say that variable costs per unit of production are conditionally constant.
Practical benefits of using the break-even point
Determining the break-even point is one of the main tasks facing the managers and employees of the enterprise.
Thus, determining the equilibrium level of income and expenses will allow startup entrepreneurs who enter the market with a unique product to set the optimal price for their product.
In large organizations, it is very important to establish the process of production and sales of products. The long-term nature of the activity requires careful attention to planning production and sales of products.
For example, a beverage manufacturer must determine the price and production volume that will best satisfy demand and maximize profits. Excess production leads to unnecessary costs, and insufficient supply leads to lost profits.
In addition to the organizations themselves, this indicator is used by investors, banks, and business incubators to decide on the provision of funds or premises.
Break-even point: what is it?
The break-even point (formula) shows the required level of production and subsequent sales of products to cover all waste and costs.
In other words, this is the volume of products sold at which the firm's profit is zero.
The coefficient is measured in monetary and natural equivalents.
In practical terms, the indicator serves as an excellent indicator of the size of production and sales of products (services), where the initial costs of the company are fully covered by incoming cash flow. The coefficient is used by company managers in the process of creating and analyzing a future project.
The higher the company's break-even level, the higher the indicator of its solvency and, as a result, financial stability. If the break-even ratio increases, this indicates the presence of structural problems within the company that have a negative impact on profit making.
Features and benefits of use
- The ability to calculate how much revenue can be reduced so as not to be at a loss in the future. It is especially important if there is an increase in actual revenue over estimated revenue.
- Ability to identify structural problems of the company associated with temporary changes in the break-even level.
- The ability to determine the prospects of a new investment project, as well as the time frame within which it can fully pay off.
- Ease of use.
- Calculation of the break-even level allows us to identify the interdependence of the cost of products with the volume of their sales to end consumers. Makes it possible to calculate the most favorable price threshold for the products offered.
The use of the break-even point formula is most effective in markets characterized by a low level of competition, as well as stable demand from consumers. Globalization of all levels of markets creates variable demand for domestic products.
Strengths and weaknesses of the break-even point model
This model allows you to quickly calculate approximate indicators at which the enterprise will begin to make a profit. Based on these formulas, this method can determine the approximate price of a product or production volume.
Despite this, this model has serious disadvantages:
- The linearity of the function does not allow us to take into account changes occurring in the market. Characteristics such as seasonality, inflation, increased competition are not displayed in any way on the graph;
- An enterprise's costs may change over time , which is also not taken into account when calculating the break-even point;
- The limitation of demand only by price in the model does not reflect the real situation on the market. Demand is also influenced by other important characteristics of the product, such as quality or fashion.
Determining the break-even point
You can use a chart to determine the break-even point. To build it, you need to have information about fixed and variable costs, as well as prices for 1 unit of production.
The graph displays 2 straight lines:
- Expenses;
- Quantity of products (note: tables);
At the point where they intersect there will be a break-even point. The higher the direct revenue relative to it, the greater the profit the organization will receive.
Graphic expression for calculating the break-even point
The most obvious way to visualize the break-even point is using a graph. To do this, we draw a revenue line, then a line of variable costs (sloping) and fixed costs (straight line). We get the value of production volume (sales) on the horizontal axis, and on the vertical axis we see the result of costs and income in monetary terms. Example in the picture:
Having calculated the sum of variable and fixed costs, we will derive a line of gross costs. Where will the desired break-even point be on the chart? At the intersection of the revenue and gross cost lines. in the example given, this point represents 40% of sales volume.
At the break-even point, revenue is called threshold (critical), and the same term is used to describe sales volume.
Plotting the break-even point
Calculating the break-even point for a grocery store (example)
To calculate a store's break-even point, it is necessary to determine its fixed costs. Let's take a grocery store as an example.
Let's assume that:
- Rent of premises – 80,000 rubles;
- Salary for sellers – 60,000 rubles;
- Insurance premiums (30%) – 18,000 rubles;
- Utility costs - 10,000 rubles.
- Purchase of food products - 800,000
The total costs will be 968,000 rubles. The rate of return will be set at 50%.
According to the formula, we get:
S = 968000 / 50% = 1936000 rub.
With an average check of 500 rubles. the store will need to serve 3,872 customers per month.
Calculation of the break-even point for an enterprise (example)
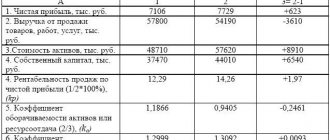
Let’s say an enterprise produces 1 type of product, the cost of 1 unit of which is 50,000 rubles. The price is 100,000 rubles. Fixed costs - 2,000,000 rubles.
It is necessary to calculate the minimum volume of output to reach the break-even point.
It turns out:
X = 2000000 / (100000 - 50000) = 40 units of production.
We make calculations for the enterprise
The break-even point of an enterprise is calculated differently; here the formula in physical terms is most often used.
Fixed costs in our example:
- depreciation charges - 100,000 rubles;
- general plant expenses - 80,000;
- AUP salary - 100,000;
- utility costs - 20,000.
The total amount is 300,000 rubles of fixed expenses.
Variable costs:
- wages of main workers - 60 rubles. — per one unit of production;
- deductions from wages (insurance contributions - 30% of the total wages) - 20 rubles. per unit of production;
- materials costs (for the entire production volume) - 150 rubles.
- costs for semi-finished products (for the entire volume) - 90 rubles.
Total 320 rubles with a product price of 400 rubles.
Break-even point: BEP = 300000/(400 - 320) = 3750 pcs.
This means that this enterprise will have to produce 3,750 units of product in order to break even. Profit will be made when this volume is exceeded.