When paying for “children’s” sick leave, you will have to be more careful. A certificate of incapacity for caring for a sick child under 7 years of age will be issued for the entire period of illness without any time limits. But be careful: the procedure for paying for “children’s” sick leave remains the same! < ... Home → Accounting consultations → Accounting Current as of: February 1, 2020 Land is a type of real estate that, along with other things, can be the object of purchase and sale, with the exception of certain cases (Articles 128, 130, paragraph. 1, Article 549 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Articles 6, 27, 35, 37 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). We will tell you about accounting for land in accounting in our consultation. Land accounting: on what account? The procedure for accounting for a land plot depends on the purpose for which this plot is acquired.
Accounting for agricultural land
The complexity of accounting for agricultural land is due to the need to maintain extensive analytical records.
They are a means and a subject of labor at the same time. It is necessary to determine the effectiveness of their use. Primary accounting of land is carried out in cards, lists, registration acts, inventory lists, etc.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpressru
The site is included in fixed assets (FPE) subject to a number of requirements:
- The object is used in the production process, for management needs or for rental;
- The land is used for a long time (more than 12 months);
- Resale of land is not implied;
- Subsequently, the object will bring economic benefits.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from Scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) purchased by {amp}gt; 8000 books |
| Number (Account, subaccount, analytics) | Name |
| Owned land use objects | |
| 01-6 | “OS”, “Land plots and environmental management facilities” |
| 01-6-1 | “OS”, “Land plots and environmental management facilities owned” |
| 01-6-1-1 | "Arable land" |
| 01-6-1-2 | "Perennial plantings" |
| 01-6-1-3 | "Deposits" |
| 01-6-1-4 | "Hayfields and pastures" |
| 01-6-1-5 | "Irrigated lands" |
| Leased facilities (including land shares of employees) | |
| 001 | "Leased assets", "Land" |
| Farm lands in circulation for other reasons (for lease) | |
| 01-6-2 | "OS", "Plots leased" |
| 01-6-2-1 | "Arable land", etc. |
Analytics is carried out in hectares by type of land. These indicators are reflected in the register - the land cadastral book of the enterprise. To fill it out, title documents for the land are used: boundary plan, acts of transfer of plots, etc.
| Contents of operation | Account correspondence | |
| Debit | Credit | |
| Purchased a plot of land | 08 | 60 |
| State duty for registration and registration is taken into account | 08 | 76 |
| Services for surveying, assessment, etc. are taken into account. | 08 | 76 |
| The site was put into operation | 01-6 | 08 |
| The land was contributed as a contribution to the authorized capital | 08 | 75 |
| Leased land use objects | 001 | – |
| Land rent accrued | 20, 26 | 76 |
| The land was received free of charge | 08 | 98 |
| Payment for land acquisition reflected | 60, 76 | 51 |
| Land tax accrued | 20, 25, 26, 44 | 68 |
| Land tax paid | 68 | 51 |
Dt 75 Kt 80 - the founder’s debt on contribution to the management company is taken into account;
Dt 08 Kt 75 - the plot was received from the founder as a contribution to the management company;
Dt 01 Kt 08 - land is accounted for as an asset.
Dt 08 Kt 83 - land was received from the founder, the company has no income;
Dt 08 Kt 98 - land donated by third parties;
Dt 08 Kt 01 - the site was put into operation;
Dt 98 Kt 91 - income from land received free of charge is taken into account.
Dt 91 Kt 01 - reflects the cost of the land donated.
The actual costs at which a plot of land is taken into account may include:
- the cost of the plot paid to the seller;
- real estate, consulting services;
- payments to the intermediary;
- the amount of state duty for land registration;
- other costs associated with the acquisition of land.
On a note! When borrowed funds are used to purchase a plot, the interest on them is gradually included in the cost of the land until the moment when it moves from non-current assets to fixed assets (PBU 15/2008 “Accounting for expenses on loans and credits”).
Transactions with land plots may include: receiving as a gift, under an exchange agreement, receiving as a contribution to the authorized capital, as well as purchase, sale, lease, sale of part of the plot, etc.
Let's look at the most common land transactions that an accountant has to take into account.
Purchase
Land is included in accounting as fixed assets:
- Dt 08/1 Kt 60 - purchase of memory from a counterparty;
- Dt 08/1 Kt 10, 60.76 - acquisition costs (real estate, consulting, material);
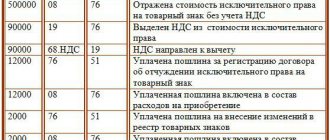
- Dt 08/1 Kt 76 (68/invoice “State duty”) - the state duty for registering a land plot is reflected;
- Dt 01 Kt 08/1 - ZU is included in fixed assets.
Land is included in accounting as an object of subsequent resale:
- Dt 41 Kt 60 - purchase of memory from a counterparty;
- Dt 41 Kt 10, 60, 76 - acquisition costs (real estate, consulting, material);
- Dt 41 Kt 76 (68/invoice “State duty”) - reflects the state duty for registering a land plot.
We invite you to read Article 38. The procedure for providing a vacant room in a communal apartment
On a note! Despite the fact that there are no clear distinctions between the use of accounts 76 and 68 when accounting for state duties, the tax authorities recommend that the duty for registration of a site be taken into account in account 68, since it is a federal tax (Article 13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Sale
Land sold as OS:
- Dt 62 Kt 91 - income from the sale of storage units is recorded;
- Dt 91 Kt 01 - fixed asset deregistered at its cost;
- Dt 91 Kt 10, 70, 60, etc. - the costs of selling the storage unit are taken into account.
Land sold as a commodity:
- Dt 62 Kt 90 - income from the sale of storage units is recorded;
- Dt 90 Kt 41 - the storage unit is written off as a product from the register, at its cost;
- Dt 44 Kt 10, 70, 60, etc.
- Dt 90 Kt 44 - expenses for the sale of storage units as goods are taken into account and written off.
Let's look at an example of how to correctly account for the sale of part of a plot. Let the memory be listed on account 01 as a fixed asset, a single object. Its cost is approximately 100,000 rubles. After the cadastral work was completed, the land was divided into two parts. One remains in the organization (60,000 rubles), and the other is sold (40,000 rubles). 50,000 rubles were received from the sale.
Let's divide the area in accounting:
- Dt 01 “for sale” Kt 01 “initial” - 40,000 rubles. — a part has been allocated for sale;
- Dt 01 “remaining in the organization” Kt 01 “initial” - 60,000 rubles. – the part remaining in the organization is allocated;
- Debit 91 Credit 01 “for sale” - written off from the register of a loan subject to sale at its cost of 40,000 rubles;
- Debit 62 Credit 91 - 50,000 rub. income from sales.
Next, we take into account the costs of sales, according to the above correspondence: Dt 91 Kt expense account, and reflect the profit (loss) from the transaction Dt 91 (99) Kt 99 (91).
In this case, it would be correct to divide the plots, and not write off the land plots and register two newly formed objects.
Rent
Initially, expenses for concluding a lease agreement are charged to account 97 “Deferred expenses”, and then in equal shares are written off to accounts for ordinary activities:
- Dt 97 Kt 76 - costs of acquiring the right to lease;
- Dt 19 Kt 76 - VAT accrual on the value of the rental right;
- Dt 68 Kt 19 - VAT is presented for deduction;
- Dt 20, 25, 26, etc. Kt 97 - write-off of a share of expenses during the lease term.
The rent is calculated by posting Dt 20, 25, 26, etc. Kt 76. If the rental conditions allow, VAT can also be deducted from the amount (see postings above).
Sublease, unless prohibited by the contract, is documented by postings: Dt 62 Kt 91 and Dt 91 Kt 68.
Documenting
The purchase and sale of land plots are formalized by an agreement in 3 copies. Two of them - to the participants of the transaction, one - to Rosreestr for registration. A land lease agreement for a period of more than a year is also registered in Rosreestr (Article 609-2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The legislation does not provide for special unified forms that take into account the diversity of land plots and their types. When registering a landowner, it is recommended to use the following documents:
- Act OS-1 “On the acceptance and transfer of fixed assets (except for buildings and structures).” The document contains a number of indicators that should be ignored (crossed out) when filling out: manufacturer, depreciation rates, useful use, residual value, etc. At the same time, there are no special columns containing the characteristics of the land plot. They can be reflected in the field (section) “Other characteristics”.
- Act 401-APK “On the registration of land”. It is intended for organizations and enterprises in the agricultural sector and contains information about the land plot, its book value, type, quality of land, etc.
- Inventory card OS-6 “Accounting for fixed assets”.
You can include a clause in the agreement under which it will simultaneously serve as an act of acceptance and transfer, or you can develop your own local accounting form. It is advisable to consolidate the use of certain document forms for accounting of property in the accounting policy of the organization.
Registration is carried out on the date specified in the act or in an agreement equivalent to it.
On a note! Land and buildings on it are not considered a single property object in accounting.
Minakova Yulia
OKOF. Help with OKOF. Our institution is a state budgetary institution, we have received ownership of the land, what are the entries for accounting. Thank you. Hello, Nadezhda Ivanovna! In response to your question dated 04/03/2020, we accept the following: According to paragraph.
Okof code 2020 for land plot
Even if a period is set, depreciation on land plots does not need to be calculated in accounting. If there are various objects located on the site, then depreciation in respect of them is calculated in accordance with the generally established procedure.
Let us recall that in tax accounting, the useful life of fixed assets is established by the Classification of fixed assets included in depreciation groups (Government Decree No. 1 of January 1, 2002) (clause 1 of Article 258 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, the depreciation group in the Classification is not established for the land plot. But this is not surprising. After all, the question, “Which depreciation group does the land plot belong to” is, in principle, incorrect. For land, the depreciation group is not determined because land and other natural resources (water, subsoil, other natural resources) are not depreciated in tax accounting (clause 2 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Land accounting at cadastral value
The value according to the state cadastre reflects the nominal price of the plot. It depends on the category of land and its location.
Land received for perpetual use is accounted for at its cadastral value. Its change is documented with an accounting certificate (f. 0504833). They can occur for the following reasons:
- Conducting a state assessment (no more than once every 3 years);
- Changes in the quantity and quality of land between the previous and subsequent cadastre assessments;
- Successful refutation of the results of establishing the cadastral value in court or a special commission.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Bailiffs’ Act on the impossibility of collection
Changes in the value according to the cadastre do not affect accounting. They affect tax accounting when calculating land tax.
Is it possible to overvalue land?
Land Code of the Russian Federation dated October 25, 2001 N 136-FZ Article 66. Land valuation.1. The market value of a land plot is established in accordance with the federal law on valuation activities.2.
To establish the cadastral value of land plots, a state cadastral valuation of land is carried out, except for the cases specified in paragraph 3 of this article.3. In cases where the market value of a land plot is determined, the cadastral value of this land plot is established equal to its market value. According to Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 8, 2011 N 03-03-06/1/412, LETTER of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 09/08/2011 No. 03-03-06/1/544, revaluation is reflected only in accounting and does not affect taxes, except property, which directly depends on accounting. Those.
Accounting for land when selling/purchasing
When purchasing land, its initial cost is the amount of purchase costs. These include:
- Funds transferred to the seller under the agreement;
- Registration fees and charges;
- Payment to the competent authorities for cadastral documents and land surveying;
- Payment for registration data;
- Payment for the work of intermediaries (if any);
- Other purchase and registration costs.
| Operation | Account correspondence | A document base | |
| Debit | Credit | ||
| Paid plot of land | 60 | 51 | Bank statement |
| Purchase costs reflected | 08 | 60, 76 | Contract of sale |
| Acceptance of an object for accounting as fixed assets | 01 | 08 | Transfer and Acceptance Certificate |
After registration, the enterprise is required to pay land tax. Purchase costs reduce the taxable base under the Unified Agricultural Tax. Expenses are not accepted immediately, but over a certain period (indicated in the accounting policy). It must be at least 7 years.
To sell land, you need an agreement and an act in form OS-4. The cost on the balance sheet is included in other expenses, and the proceeds are included in income.
Dt 62 Kt 91-1 2,150 thousand rubles - the plot has been sold;
Dt 91-2 Kt 01 1,870 thousand rubles — the value of the land is written off according to the balance sheet;
Dt 99 Kt 91,280 thousand rub. — reflects the financial result of the transaction.
Land for a quarry or landfill
In certain cases, the company can still charge depreciation on the land and thus reduce taxable profit. According to the law, land depreciation is charged if it is established that the consumer properties of the site have changed over time. Here are the most common options for this situation:
- The land is used as a quarry for mining. If a site is acquired for the purpose of mining, its cost must be depreciated in the general manner. The quarries belong to the 7th OS group with a useful life of 15 to 20 years.
- The site is used to accommodate a waste dump. If land is acquired for use as a municipal waste dump, the site has a limited useful life and is therefore subject to depreciation as required.
In each of the listed cases, the useful life of the site is established by internal regulations (accounting policies). The amount of monthly deductions is determined based on the period of use. The accounting records the monthly posting Dt 02 Kt 01.
Tax accounting
Land tax
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreatorsru
Organizations and entrepreneurs who own and use land plots indefinitely are payers of land tax (Article 388-1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The tax base is determined by the cadastral value of the site and is a fixed value. Tax rates are determined at the regional level depending on the category of land.
Land purchase and sale transactions are not subject to VAT (RF Tax Code Art. 146-2, paragraph 6). This applies to both entire plots and shares in them. At the same time, according to Art. 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 3, paragraph. 2, municipal property is subject to VAT when it is sold. The Ministry of Finance (Letter No. 03-07-11/03 dated 13-01-10) explained that municipal and state-owned land plots, despite the above, are excluded from VAT taxation. At the same time, buildings on it are subject to VAT.
Lease of land in state ownership, municipal ownership, as well as land of constituent entities of the Russian Federation is not subject to VAT (Article 149 2 paragraphs of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, sublease of such lands is subject to VAT (Letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-07-11/436 dated 10/18/12). Under private property lease agreements, VAT is applied (Letter No. GD-3-3/2391 of the Federal Tax Service dated 06/18/15).
Income tax
You can take into account the costs of purchasing land only at the time of its sale, reducing income by the amount of the purchase of land and the costs of its sale (Articles 268, 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). According to Art. 264-1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses for the purchase of land in state or municipal ownership, on which buildings, structures, structures are located, or which are acquired for capital construction purposes, can be recognized as income tax expenses.
Land accounting in a budgetary institution
Institutions carry out land accounting in accordance with Instructions No. 157n and No. 174n. Lands in perpetual circulation are reflected by state employees on the analytics to the account. 0 103 00 000 “Non-produced assets” according to the title document (clause 71 of Instruction No. 157n).
Before registration, the land is taken into account on the balance sheet of the account. 01 “Property in use.”
Regardless of the source of acquisition, plots should be taken into account as settlements with the founders: account. 210.06.
The nuances of transactions with plots in the budget are regulated by Art. 36, 37, 38 Land Code of the Russian Federation. This includes:
- The sale of land owned by the state or municipality to the owners of structures and buildings erected on the land is carried out at prices approved by the relevant authorities;
- The price of land cannot exceed its value according to the cadastre;
- Lands that have been registered with the cadastral service can be bought and sold;
- The purchase of state land or lease rights is carried out through auctions (tenders).
The purchase of land in the accounting of state employees is reflected in accordance with Art. 330 “Increase in the value of non-produced assets” KOSGU on the account. 0 106 13 000.
Dt 106 13,333 Kt 302 33,730 2,850 thousand rub. — the cost of the plot is reflected.
Dt 302 33 830 Kt 201 11 610 - the debt for the land has been repaid.
Dt 103 11 330 Kt 106 13 330 - land accepted for registration.
Accounting services for organizations and entrepreneurs
Renting is an excellent way to obtain the use of a building or part of it, as well as various equipment and land plots. The cost of real estate is estimated at quite decent amounts, and in order to purchase it, significant sums are needed. If there is not enough money, or perhaps the purchase is not necessary, since the company needs the premises for a short time, then the only way out is to rent.
After the property is transferred for use to the tenant, the rights to it still remain with the lessor and it also continues to be listed on his balance sheet.
Briefly
- The purchase, sale and lease of land plots for a period of more than a year are registered in Rosreestr.
- It is permissible to register land plots using the forms of primary documents developed by the organization.
- When selling part of a plot, it is necessary to divide it, and not write off and register new objects.
- The purchase and sale of land is not subject to VAT.
- Rental of private land is subject to VAT.
- Sublease of any land is subject to VAT.
- Income tax expenses can include the costs of a plot only when it is sold.
- Otherwise, expenses for land plots of a state or municipal nature are included in income tax calculations if there are buildings on them or their construction is expected.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Making an extension to the house, what documents are needed
Revaluation method
The valuation method for determining the market value of the work (including materials) to create a copy of the revalued property can be any, but the comparative unit method is most often used. This assessment method is based on the use of data from various reference books of aggregated construction cost indicators. For real estate properties built before 1991, you can use the UPVS (aggregated indicators of replacement cost) directories, for newer properties - the UPSS (aggregated indicators of construction cost) directories and other materials produced by . Learn more about the different methods of real estate valuation...
Accounting for land in construction
A construction company can buy a plot of land or lease it. The most attractive option is to register a lease with subsequent purchase. There are a number of reasons for this:
- There is no need to conduct auctions (Article 30 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
- Advantage when purchasing state and municipal lands;
- Reducing financial costs and saving time on selling land if a construction permit is refused.
Dt 91-2 Kt 01 - site retired;
Dt 62 Kt 91-1 - revenue is taken into account as other income.
Dt 76 subaccount “Settlements with investors” Kt 08 - the site is handed over to the investor upon completion of construction work.
In some cases (Article 49 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation), plots may be seized from the owner for the needs of the state or municipalities. The terms are described in the agreement. The compensation amount includes the market value of the land, buildings on it and compensation for losses from the procedure (lost profits).
The land is written off from the register on the day the rights to it are terminated. The cost of the site on the balance sheet is included in other expenses, and compensation is included in income.
When writing off a plot before the transfer of ownership of it is registered, an account is used to record the disposal. 45 subaccount “Transferred real estate”.
We buy and sell land plots
Income from the sale of a land plot is accepted for accounting at the time of transfer of ownership to the buyer. In our case, this is the date of making the corresponding entry in the Unified State Register (clause 30 of PBU 6/01, clauses 10.1, 16 of PBU 9/99). The book value of the land is written off from account 01 “Fixed assets” to the debit of account 91, subaccount 91-2 “Other expenses” (clause 11 of PBU 10/99). Thus, expenses for the acquisition of land plots are accepted in accounting only when selling plots (clause 11
Putting a plot of land on balance
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=upload
The acquired plot of land, like other assets, must be registered. First, the cost of the plot is determined. This information is contained in the purchase and sale agreement or other documents accompanying the transaction. If the necessary data is not available, an expert assessment of the land is carried out. The plot must be distributed by type of land in hectares.
Next, a special commission is created with specialists in land issues. She draws up an act for the registration of land (form No. 111-APK). All data about the site is entered into it: area, type, location, soil fertility, balance sheet value, reasons for purchase, etc.
Dt 01-6 Kt 91 - the purchased plot of land was put on the balance sheet.
If an organization received a plot of land from the state not for ownership, but for indefinite disposal, then it is taken into account off the balance sheet. This applies to the land and under buildings transferred to budgetary organizations for operational management.
Peculiarities
The land plot meets all the criteria of accounting legislation, the presence of which indicates that the asset can be recognized as a fixed asset:
- the company acquires land to use it in its core business or for subsequent rental;
- the period of its use exceeds a calendar year;
- the acquired land plot will not be resold in the future;
- the company, investing in a new site, plans to make a profit from its use.
Therefore, it is included among the company's fixed assets. If the land is intended for further sale, then it is not included in non-current assets, but is reflected in the goods account.
The cost of the object in question consists of all the costs that the company incurred to acquire it. This includes:
- the amount under the purchase and sale agreement or other agreement;
- amounts paid to intermediaries, for example, a real estate agency, if he was involved in the transaction;
- the amount of state duty that was paid upon registration of the site;
- the amount of interest paid on the loan, if the company decided to purchase a new property using borrowed funds (here it should be noted that interest on the loan increases the cost of the land only until it is classified as fixed assets);
- other amounts paid during the acquisition of the site.
Neither in accounting nor in tax accounting can land be depreciated, because it does not lose its beneficial properties. This means that it will not be possible to include the costs of its purchase in the cost of the company’s products. Only if it is sold, the acquisition costs reduce the profit received.
An important point that must be taken into account when operating a new asset is that the ways of its use are determined only by the State Real Estate Cadastre. That is, a company cannot simply buy land and independently decide what buildings to build on it. If it needs new production premises, then it should buy plots only for industrial purposes.
Acquired and improved land (accounting policies)
Land improvement includes reclamation work, uprooting stumps, drainage, irrigation, soil clearing, etc.
When improving land, accounting can be done in two ways. The selected option is fixed in the accounting policy of the organization.
Dt 01 Kt 08 - costs for land improvement are taken into account.
Method number 2. The cost of radical improvements is added to the original price of the site.
Let's look at accounting for land improvements in the budget using an example.
Dt 1,106 03,330 Kt 1,302 21,730 2,550 thousand rub. — the costs of acquiring land are reflected;
Dt 1 106 03 330 Kt 1 302 21 730 380 thousand rub. — drainage costs are taken into account;
Dt 1 103 01 330 Kt 1 106 03 430 2 930 thousand rub. - the site has been registered.
Capital investments for land improvement are reflected in accounting accounts on the basis of acts of work performed.