Definition of Accounting
Any accounting is a systematic collection, recording and interpretation of information of a certain kind. When we talk about accounting, we mean a system that allows you to operate with data on all business transactions and obligations expressed in financial terms.
IMPORTANT REQUIREMENT! Documentary recording of this information must be permanent, continuous (from the moment of registration until the liquidation of the company), complete, in accordance with the established regulations.
Accounting takes into account the following business factors:
- property assets of a commercial organization;
- entrepreneur's agreements;
- transactions carried out in the business process.
https://youtu.be/dL2cKfYvhGo
What is a permanent tax liability?
The emergence of permanent differences leads to the appearance of permanent tax liabilities (PNO) or assets (PNA). When the difference increases the amount of the income tax payment, a PNA is formed, when the payment decreases, a PNA is formed.
PST is the amount of tax that increases the income tax. It appears if income is recognized exclusively in tax accounting, or expense is recognized only in accounting. In this case, the profit in accounting is less than in tax accounting. And you will have to pay more to the budget than is required according to accounting data.
The amount of PTI is determined as the product of the constant difference of the reporting period and the income tax rate. Recognize the IRR in the same period in which the permanent differences arise.
PNO = PR * 20%
Reasons for the need for accounting
The first and most logical reason for carrying out accounting according to a generally accepted procedure is legal requirements. The desire and capabilities of an entrepreneur do not matter when it comes to the legislative framework established by the state.
If accounting is not kept
An organization has no right not to keep accounting records. If business transactions were not recorded properly, and accounting records were never compiled and submitted to the regulatory government authorities, such an entrepreneur is subject to liability:
- for gross neglect of the rules for providing accounting documentation and maintaining appropriate records, as well as the timing and procedure for saving all accounting documents, officials will face a fine of 2-3 thousand rubles. (Article 15.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses);
- If the tax authorities were not provided with the information required by law about economic activity in due time, citizens will pay a fine of 100-300 rubles. (for each identified case), and officials risk 300-500 rubles. for each delay or failure to provide data (Article 15.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses).
general information
Accounting is based on logic and mathematics.
This business requires the ability to build cause-and-effect relationships and have a broad outlook. To understand accounting, you need to understand the reporting process. To do this, it is worth studying accounting for beginners from postings to balance sheets. In general, this is enough to work in the chosen direction. To increase labor efficiency and reduce the number of errors, from the point of view of supervisors, additional techniques can be trained, but they are not critically necessary, and knowledge is acquired during work.
Accounting objectives
The remaining factors that determine the use of accounting are related to the needs of the entrepreneur himself. Forming a complete picture of data on the property status and activities of an organization in its dynamics is necessary not only for stating facts, but also for making forecasts. So, accounting is designed to solve the following pressing tasks of the owner and manager of a business:
- current and constant provision of structured, objective and accurate economic information to management;
- finding out the reserves of the organization’s property assets to realize the financial stability of the company;
- implementation of the control function (on the part of the state and other external contractors);
- minimizing negative outcomes of economic activity.
What exactly is done in the accounting process
The process of any accounting is aimed at identifying significant factors, measuring essential indicators and presenting the results obtained. For accounting it will be:
- determination of the financial structure of the enterprise - its property assets, its capital, income, costs, dynamics of its fixed assets, financial liabilities;
- measuring the cash equivalent of the present assets in an appropriate manner applicable for reflection in the financial statements;
- provision of the received data in the form required by law, as well as in ways deemed convenient for users.
Domain name costs
A domain name is a symbol designation intended for addressing sites on the Internet in order to provide access to information posted on the Internet. This definition is given in paragraph 15 of Art. 2 of the Federal Law of July 27, 2006 No. 149-FZ.
As one might assume, without paying for a domain name, it is impossible for a website to operate to make a profit for an organization; therefore, one can assume that before paying for a domain name, the site cannot be put into operation.
A domain name is not an intangible asset. This is stated in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 26, 2002 No. 16-00-14/107.
As a rule, a domain name is paid once a year.
Accounting
As can be seen from the definition above, without a domain name, an Internet site cannot function. Therefore, the costs of the initial registration of a domain name on the basis of clause 9 of PBU 14/2007 can be included in the initial cost of the website as an intangible asset.
In the future, the costs of paying for a domain name in accounting can be considered either as an advance for a year with a monthly offset of such an advance, or as deferred expenses. At the same time, it is necessary to recall that currently deferred expenses are subject to write-off in the manner established for writing off the value of assets of this type (clause 65 of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n ).
In other words, the costs of a domain name are taken into account as a lump sum as part of expenses for ordinary activities. How exactly to take into account subsequent costs for paying for a domain name should be determined independently by the organization and fixed in its accounting policies for accounting purposes.
The costs of the initial payment for a domain name should be reflected in the accounting:
Debit 08-5, subaccount “Site” Credit 60 (76)
— the costs of registering a domain name are reflected.
Expenses for paying for a domain name in the periods subsequent to the site’s registration as an intangible asset should be reflected:
1. How to make an advance:
Debit 76, subaccount “Advance for domain name” Credit 51
— paid domain name;
Debit 20 (26, 44) Credit 76, subaccount “Expenses for a domain name”
— part of the costs for a domain name is included in the organization’s costs;
Debit 76, subaccount “Expenses for a domain name” Credit 76, subaccount “Advance for a domain name”
- the advance has been credited.
2. How are the running costs:
Debit 20 (26, 44) Credit 76, subaccount “Expenses for a domain name”
— costs for a domain name are included in the organization’s costs;
Debit 76, subaccount “Expenses for a domain name” Credit 51
— paid for domain name.
Tax accounting
The costs of the initial registration of a domain name for income tax purposes are included in the initial cost of the site if it is an intangible asset.
The costs of domain name re-registration are recognized as current expenses of the organization. Re-registration is carried out, as a rule, annually and provides the organization with the opportunity to retain a specific name for its website on the Internet. Re-registration of a domain name does not lead to a change in the quality characteristics of the website and therefore does not affect its initial cost. Therefore, on the basis of subparagraph. 49 clause 1 art. 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, re-registration costs are included in other costs associated with production and sales.
Organizations that determine income and expenses using the accrual method reduce their taxable income monthly during the validity period of the domain name registration specified in the agreement. If such a period is not specified, expenses are taken into account at a time.
A similar position is reflected in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated January 17, 2007 No. 20-12/004121.
As we can see, in order to bring accounting and tax accounting closer together, the costs of domain name re-registration should be distributed not only in tax accounting, but also in accounting.
Accounting principles
This type of accounting is not conducted arbitrarily, but in strict accordance with the basic provisions adopted and approved at the legislative level.
- The principle of autonomy - only information related to the own property of this particular organization is taken into account, separated from related data (for example, property of co-owners, employees, etc.).
- The principle of double entry - the balance is compiled according to double accounts (debtors and creditors), which must coincide numerically (how much is lost on one account must be earned on the other).
- The operating organization principle provides for the mandatory fulfillment by the organization of its obligations in the foreseeable future.
- The principle of objectivity - all activities of the organization must be objectively reflected in the relevant documentation and registered at all stages of accounting.
- The principle of prudence prohibits overstatement of assets and understatement of liabilities, and vice versa.
- The principle of periodicity - the balance sheet is compiled in strictly defined accounting periods (they can be a month, a quarter, a half-year and, without fail, an accounting year), which allows you to compare financial results for any time period of interest.
- The principle of confidentiality - some accounting data intended for internal use, which does not fall into the category of reporting to government agencies, may constitute a trade secret.
- The principle of monetary measurement - the unit of measurement in accounting is the current currency of the country, that is, in the case of the Russian Federation, it will be the ruble.
- The principle of continuity - accounting provisions take into account the achievements of domestic economic science and national characteristics.
- Accrual principle – financial transactions are recorded not at the moment of transfer of funds, but at the stage of their occurrence. They are taken into account in the time period when the given business transaction was carried out. Available in two forms:
- fixation of revenue (income part of the balance sheet) - profit is reflected at the time of receipt, not payment (in the Russian Federation this is the moment of paid shipment, in other countries this moment may be associated with delivery or delivery of payment);
- correspondence of profits and expenses - in the same reporting period, income must balance the expenses that made it possible to obtain these incomes, separate accounting of income and expenses relating to different accounting periods.
How to record the creation or purchase of a website in your accounting?
Almost every modern company is faced with the need to create a website. It is worth noting that sites have different purposes, and its appearance depends on what result you want to get. As a rule, the type of site depends on your type of activity and needs.
Advice. To create a website, contact a professional who will conduct a market analysis for your type of activity and draw up a clear business plan, which will indicate when you will begin to receive the intended benefits. This kind of work takes from one to three months. If the website creator says that a website can be made in a week, most likely it will be of poor quality and will not bring you the desired result.
Documenting
To confirm that the site belongs to your organization or individual entrepreneur, you must have a certain set of documents. The composition of the documents depends on whether you create the site yourself or with the help of a third party.
Important: all documents for the site are issued in the name of your organization or individual entrepreneur, otherwise the costs of creating the resource cannot be included in expenses.
If you create a website yourself, then you must have an agreement with the person who does it. For example, your employee creates a website. An agreement can be concluded of a civil law nature, in which there must be no condition on the preservation of exclusive rights for the employee who created the site. The exclusive rights to the site must belong to you and these conditions should be written down in the contract.
If the site is created by a third-party organization or individual entrepreneur, then an agreement is also concluded. As in the case of the creation of a website by your employee, the contract must contain a provision that the exclusive rights belong to you and not to the contractor.
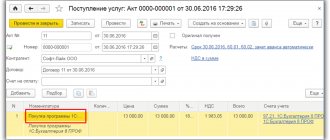
In addition to the contract, there must be documents that confirm the fact that work has been completed to create the site and transfer it to you. The completion of work, either by your employee or by the contractor, is confirmed by the work completion certificate (site acceptance certificate). The act should describe the composition of the site (domain name, hosting, etc.). The document is signed bilaterally.
In addition to the above documents, you may need documents confirming payment of the costs of creating (purchasing) the site. Such documents are important for recognizing expenses in tax calculations under the simplified tax system and income tax using the cash method of accounting.
Advice. Try to pay for website costs from your current account, this will make it easier to confirm expenses both for the tax office and in case of questions from other inspection agencies.
How to include website costs in expenses?
The costs of creating or purchasing a website can be taken into account in the form of: - an intangible asset, if all criteria are met; — other expenses if you apply the general taxation regime (OSNO). Or as the cost of acquiring exclusive rights to computer programs and databases, if you use the simplified taxation system (STS).
simplified tax system
Let's figure out when a website needs to be recognized as an intangible asset (intangible asset) in order to take into account the costs of it in calculating the simplified tax system. Let us remind you that expenses on the simplified tax system are taken into account in calculating tax under the object “income minus expenses”.
The criteria for recognizing a website as an intangible asset are as follows: – an organization or individual entrepreneur owns exclusive rights to the website; – the site was created (acquired) for use in the production of products (performance of work, provision of services) or for the management needs of an organization or individual entrepreneur; – the period of use of the site exceeds 12 months (the period is usually specified in the contract); – use of the site can generate income for an organization or individual entrepreneur; – the organization or individual entrepreneur has properly executed documents confirming the existence of the site and exclusive rights to it; – the cost of the site is more than 100 thousand rubles. Please note that input VAT from the supplier (if the site is developed by a third party on OSNO) is better included in the price.
If the site does not meet the specified criteria, then it cannot be recognized as an intangible asset.
Intangible assets must be taken into account in expenses if the following conditions are met: – acceptance of an intangible asset for accounting. You can be registered by issuing a card in the form of NMA-1.; – payment (partial payment) of an intangible asset. In case of partial payment, expenses are recognized in the amount of the amounts paid.
Expenses should be recognized starting from the reporting (tax) period in which the most recent of the above events occurred.
If the conditions are met in the 1st quarter, the entire amount spent is divided into 4 parts and written off as expenses quarterly, on the last day of each period (March 31, June 30, September 30, December 31).
If the conditions are met during the 3rd quarter, then the cost of intangible assets is divided into 2 parts and, as in the first example, is written off quarterly, on the last day of each period (September 30, December 31).
If the conditions are met during the 4th quarter, then the entire amount is included at a time in expenses on December 31, because there are no more quarters in the current year, and there is nothing to divide the amount into.
Possible situation: an intangible asset was paid for in one quarter (let’s say, in May), but it was received according to the acceptance certificate later, as a result, it was accepted for accounting using the intangible asset-1 card in July. Expenses for the purchase of intangible assets are divided into two parts and taken into account in calculating tax under the simplified tax system on September 30 and December 31.
So, when calculating tax according to the simplified tax system, the value of intangible assets is written off quarterly in equal parts, starting from the period when the right to take into account the expense arose, i.e. You now have all the supporting documents to account for this expense.
If the site does not fit the conditions of the intangible property rights (for example, if the cost does not exceed 100 thousand rubles), then the expenses under the simplified tax system with the object “income minus expenses” are taken into account as the costs of acquiring exclusive rights to computer programs and databases. You can recognize such expenses only after the work on creating the website is fully completed and paid for. Based on the latest date and the smallest amount, costs must be taken into account when calculating the simplified tax system.
BASIC
Just as with the simplified tax system, website costs in calculating income tax can be taken into account in expenses either as depreciable intangible assets or as another expense.
The criteria for recognizing a website as a depreciable intangible asset when calculating income tax are as follows: – an organization or individual entrepreneur owns exclusive rights to the website; – the site was created (acquired) for use in the production of products (performance of work, provision of services) or for the management needs of an organization or individual entrepreneur; – the period of use of the site exceeds 12 months (the period is usually specified in the contract). If it is not specified, then the useful life of a depreciable intangible asset recognized as depreciable property can be set at your discretion, but not more than 2 years; – use of the site can generate income for an organization or individual entrepreneur; – the organization or individual entrepreneur has properly executed documents confirming the existence of the site and exclusive rights to it; – the cost of the site is more than 100 thousand rubles. Please note that input VAT from the supplier (if the site is developed by a third party on OSNO) does not need to be included in the initial cost. Input tax can be deducted provided that the site is used in activities that relate to OSNO, the supplier has presented you with VAT, all costs have been taken into account (for example, an intangible asset-1 card has been issued), and also if there is an invoice.
The cost of depreciable intangible assets is generally written off as expenses through depreciation. It is accrued from the 1st day of the month following the month in which the depreciable property was put into operation. Commissioning for intangible assets coincides with the date of acceptance for accounting, but a separate order can be issued in any form. This is an internal document and is important for taking into account the costs of your website when calculating your income tax. Moreover, if you use the cash method of accounting for income and expenses, then depreciation is calculated when the intangible asset is put into operation and fully paid for.
It is worth noting that there are exceptions for accounting for depreciable intangible assets in the calculation of income tax. For example, periodic website payments (RPAs) are not subject to amortization, but are gradually written off as part of other expenses.
The moment at which depreciation is recognized in tax calculations depends on the method used to account for income and expenses.
If you use the accrual method, then depreciation is included in expenses based on the date of accrual. If you use the cash method, then you need to write off accrued depreciation as expenses after full payment of intangible assets.
Non-depreciable intangible assets costing less than 100 thousand rubles. excluding VAT, you have the right to include it among other expenses associated with production and (or) sales, and are taken into account in calculating tax depending on the method used for accounting for income and expenses.
If the site does not meet the definition of intangible assets by any other criteria, then the purchase costs are also taken into account as part of other costs associated with production and (or) sales.
With the accrual method, other expenses are taken into account based on the date of their accrual (repayment of mutual claims with the supplier), the actual payment does not matter. If, for example, you paid for the site in full on March 1, and the supplier performed the work according to the act on April 30, then this expense must be recognized starting from the date of the act. In this case, the cost of the site must be divided in equal parts by the useful life under the contract and recognized as an expense on the last day of each reporting period and at the time of expiration of the contract (use period). If the term of use is not specified in the contract, then the cost of the site must be divided into five years and recognized as an expense on the last day of each reporting period and at the time of expiration of the contract (use period).
If the cash method is used, then in addition to the accrual condition, the expense must be paid. Based on the latest date and the smallest amount, the expense is taken into account in calculating the tax.
If the site is not an intangible asset and was created on its own, the costs can be taken into account when calculating the tax in the form of labor costs (if employees are involved in creating the site) and material costs (if any materials were purchased to create the site).
Elements of accounting
Accounting consists of the use of a set of special economic techniques to reflect the actual availability and dynamics of an organization's property and financial assets. These include:
- documentation;
- assessment;
- list of accounting accounts (strictly regulated by law);
- double entry (credit-debit);
- inventory;
- calculation;
- balancing;
- maintaining records on paper and/or electronic media that have the force of legal evidence of the organization’s economic activities.
How to learn accounting yourself from scratch?
If you don’t have the slightest idea about what an accountant does, then you will have to make a lot of effort to not just memorize, but understand how accounting works. Without these ideas put into practice, it will be difficult to apply the acquired knowledge to entrepreneurial activity.
Students today are supported by various forums and courses, and there are options for online seminars.
The answer to the question of how to learn accounting yourself from scratch will be the following steps:
- purchasing serious literature - books for beginners are only the first stage, then you will need serious publications on in-depth accounting and financial reporting;
- completion of special courses - if there is an opportunity to attend official classes that guarantee a certificate or certificate, it should not be neglected;
- application of knowledge to personal business - as a rule, those who need it to improve their own business come to study accounting; try organizing the same double entry system instead of single entry, control cash transactions;
- employment in your specialty is the best practice option; if you have the corresponding desire, start your career under the guidance of a more experienced mentor.
What official sources should you read?
Be sure to read:
Federal Law No. 402-FZ “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011.
Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Pay attention to the chapters on value added, profit and personal income taxes.
Chart of accounts of accounting for enterprises.
Accounting Regulations - the latest edition of PBU dated March 29, 2020 describes the general requirements for accounting, rules for documenting transactions, evaluating reporting items, and taking inventory of property.
Federal Law No. 212-FZ “On insurance contributions to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund, and Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.”
All this is written in a specific language that is difficult to understand. But a general understanding of these documents will help you better navigate the topic and see contradictions in popular articles.
If you work for the simplified tax system, you need Article 26.2 of the Tax Code. To understand all the intricacies, the Code alone is not enough, look at Svetlana Smyshlyaeva’s book “Rules and nuances of applying the simplified taxation system.”
Accounting
All registered organizations and individual entrepreneurs have this obligation.
As a rule, this concept additionally includes tax accounting and reporting. Overall, this is a rather complicated matter. After all, to work as an accountant, you must have knowledge of tax reporting, accounting skills and monitor changes in the current legislation in this area. How should you work? To improve efficiency, it is necessary to ensure the functioning of an orderly system for collecting, registering and summarizing data on property, liabilities and their movement through continuous documentary recording of absolutely all business transactions of the organization. At the same time, it is imperative to monitor what new things appear in accounting from the point of view of legal requirements.
It is fundamentally stipulated that the director monitors everything. But since accounting is a complex matter, a specialist is hired for this - an accountant or a company to support reporting; in fact, responsibilities are transferred to the outside under the terms of outsourcing.