Balance sheet of an enterprise - form 1 or 0710001?
Form 1 balance sheet was officially called until 2011, while the reporting forms approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 22, 2003 No. 67n were in effect.
In the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n, which approved the accounting forms that are currently relevant, the concept of “form 1” is not used. Now the forms are coded according to OKUD - the All-Russian Classifier of Management Documentation (OK 011-93), approved by Decree of the State Standard of Russia dated December 30, 1993 No. 299. And according to it the balance sheet code is 0710001.
However, most of us continue to call the balance sheet in the old way - out of tradition or for the sake of convenience. After all, any accountant understands what the one who requires form number 1 from him wants to receive.
For information about the forms in which the balance sheet form exists, see the article “Balance Sheet (assets and liabilities, sections, types).”
Read about the features of filling out a simplified balance sheet form here.
ATTENTION! From 06/01/2019, the balance sheet form is valid as amended by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated 04/19/2019 No. 61n. It is also necessary to keep in mind that due to the introduction of a non-working day regime from March 30 to April 30 and from May 6 to 8, 2020, the deadline for submitting financial statements has been extended until the first working day after quarantine. For most organizations, the deadline for reporting is 05/12/2020. Read more about this here.
The key changes to it (and other reporting) are:
- now reporting can only be prepared in thousand rubles, millions can no longer be used as a unit of measurement;
- OKVED in the header has been replaced by OKVED 2;
- The balance sheet must contain information about the audit organization (auditor).
The auditor mark should only be given to those companies that are subject to mandatory audit. Tax authorities will use it both to impose a fine on the organization itself if it ignored the obligation to undergo an audit, and in order to know from which auditor they can request information on the organization in accordance with Art. 93 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If you have access to ConsultantPlus, check whether you have filled out your balance sheet correctly. If you don't have access, get a free trial of online legal access.
More significant changes have occurred in Form 2. Read more about them here.
Reporting rules
Accounting data is used to assess the liquidity and efficiency of an organization. This is especially important when choosing business partners for joint activities. It is also necessary for management to make important strategic decisions on the management of the company and for prompt decision-making.
There are several forms of financial statements. Some of the most important rules in accounting financial statements are:
- Compliance with legal reporting standards.
- Filling out the financial reporting form established by law.
There are different types of financial statements. In particular, it is divided into the following forms: general and private, external and internal, consolidated, annual and intra-annual. Annual reporting can be called the most important.
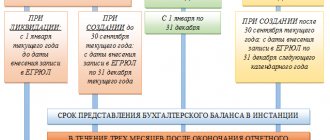
It is important to comply with the deadlines for submitting reports and the requirements for filling out reporting forms, which are specified in the legislation. After completing all reporting, it is submitted to the tax service and Goskomstat within the period established by law - three months from the beginning of the calendar year (I quarter).
Strict reporting forms were approved and put into operation by order on accounting reporting forms of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 66 dated 06/02/2010 (with subsequent revisions dated 10/05/2011, 08/17/2012 and 12/04/2012).
Balance Sheet Structure
The balance sheet (F-1) consists of assets and liabilities, including sections, in each of which there are lines containing data on certain types of property or liabilities.
The asset includes 2 sections:
I. Non-current assets
It contains information about fixed assets, intangible assets, R&D, long-term financial investments, i.e., about property that cannot be sold quickly.
II. Current assets
These are the so-called short-term (easily realizable) assets: inventories, accounts receivable with a maturity of up to 1 year, short-term financial investments, cash.
The passive has 3 sections:
III. Capital and reserves
It reflects information about the organization’s capital (authorized, reserve, additional) and retained earnings (uncovered loss).
IV. long term duties
These are obligations with a maturity of more than 12 months (borrowed, assessed, deferred).
V. Current liabilities
This section provides information on liabilities with a maturity of less than a year, including borrowed funds, accounts payable, estimated and other liabilities.
For more information about some of the nuances that require consideration when filling out individual balance lines, read this material.
Financial reporting forms
There are 4 forms of financial (accounting) reporting :
- Balance sheet (it groups the assets and liabilities of the organization).
- Financial results report (the report presents data on the organization's income).
- Report on changes in capital (the report provides information on the movement of authorized, reserve and additional capital).
- Cash Flow Statement (the report displays information about cash flows).
The most used in the practice of financial analysis are the first two forms: Balance Sheet and Statement of Financial Results
Filling out Form 1 of the balance sheet in 2020 for 2019 (sample)
All balance sheet indicators are given as of one of the dates:
- reporting date (in mandatory cases, this is December 31 of the reporting year);
- December 31 of the previous year;
- December 31 of the year preceding the previous one.
Balance lines are coded. The code is taken from Appendix 4 to Order No. 66n. Taking into account these codes, a sample balance sheet form 1 will look like this:
| Explanations | Indicator name | Code | On ____ 20__ | As of 12/31/20__ | As of 12/31/20__ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| ASSETS | |||||
| I. NON-CURRENT ASSETS | |||||
| Intangible assets | 1110 | ||||
| Research and development results | 1120 | ||||
| Intangible search assets | 1130 | ||||
| Material prospecting assets | 1140 | ||||
| Fixed assets | 1150 | ||||
| Profitable investments in material assets | 1160 | ||||
| Financial investments | 1170 | ||||
| Deferred tax assets | 1180 | ||||
| Other noncurrent assets | 1190 | ||||
| Total for Section I | 1100 | ||||
| II. CURRENT ASSETS | |||||
| Reserves | 1210 | ||||
| Value added tax on purchased assets | 1220 | ||||
| Accounts receivable | 1230 | ||||
| Financial investments (excluding cash equivalents) | 1240 | ||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | 1250 | ||||
| Other current assets | 1260 | ||||
| Total for Section II | 1200 | ||||
| BALANCE | 1600 | ||||
| PASSIVE | |||||
| III. CAPITAL AND RESERVES | |||||
| Authorized capital (share capital, authorized capital, contributions of partners) | 1310 | ||||
| Own shares purchased from shareholders | 1320 | () | () | () | |
| Revaluation of non-current assets | 1340 | ||||
| Additional capital (without revaluation) | 1350 | ||||
| Reserve capital | 1360 | ||||
| Retained earnings (uncovered loss) | 1370 | ||||
| Total for Section III | 1300 | ||||
| IV. LONG TERM DUTIES | |||||
| Borrowed funds | 1410 | ||||
| Deferred tax liabilities | 1420 | ||||
| Estimated liabilities | 1430 | ||||
| Other obligations | 1450 | ||||
| Total for Section IV | 1400 | ||||
| V. SHORT-TERM LIABILITIES | |||||
| Borrowed funds | 1510 | ||||
| Accounts payable | 1520 | ||||
| revenue of the future periods | 1530 | ||||
| Estimated liabilities | 1540 | ||||
| Other obligations | 1550 | ||||
| Total for Section V | 1500 | ||||
| BALANCE | 1700 |
For a sample of filling out a full-form balance sheet, created on specific figures, see the article “Procedure for drawing up a balance sheet (example)” .
Accounting reporting forms
Form No. 1 “Balance Sheet”.
A balance sheet is a way of grouping and reflecting the state of property, equity and liabilities in monetary terms as of a specific date for a specific organization.
In appearance, the balance sheet is a two-sided table: an asset (the organization’s property) and a liability (equity capital + the organization’s liabilities).
The balance sheet asset consists of two sections: Non-current assets (I) and Current assets (II).
The balance sheet liability consists of three sections: Own capital and reserves (III), Long-term liabilities (IV) and Short-term liabilities (V).
Form No. 2 “Report on financial results”.
From an accounting point of view, the final financial result of an enterprise is the difference between income and expenses. In other words, this is the result of the enterprise’s economic activity for the reporting period.
The income statement reflects information about the organization's income and expenses, as well as its financial results for the reporting period and the same period of the previous year.
Form No. 3 “Report on changes in capital”.
A report on changes in capital is a report that discloses information on the movement of authorized capital, reserve capital, additional capital, as well as information on changes in the amount of retained earnings (uncovered loss) of the organization and the share of own shares purchased from shareholders. In addition, adjustments due to changes in accounting policies and corrections of errors are indicated in this form.
All data in the Statement of Changes in Capital must be presented for three years - the reporting year, the one preceding the reporting period and the one preceding the previous reporting period.
Form No. 4 “Cash Flow Statement”.
The report is compiled based on data from cash accounts and contains information about the organization's cash flows.
The rules for drawing up a cash flow statement are established by PBU 23/2011 “Cash Flow Statement”.
In accordance with clause 6 of PBU 23/2011, cash flows should be understood as the movement of cash (payments to the organization and receipts of cash to the organization) and cash equivalents, as well as their balances at the beginning and end of the reporting period. Information about fund balances is identified according to accounting data and confirmed during the inventory.
Summary, consolidated and segmental reporting
Consolidated accounting (financial) statements are a system of indicators reflecting the financial position as of the reporting date and financial results for the reporting period of a group of related organizations.
Consolidated financial statements are a special type of financial statements compiled by combining data from the financial statements of several organizations within the same owner or for statistical observation, for example, consolidated financial statements of federal executive authorities (ministries) or consolidated financial statements for an organization that has branches and other structural divisions allocated to a separate balance sheet.
A distinctive feature of consolidated financial statements is their preparation by simple line-by-line summation of the relevant reporting indicators of enterprises subordinate to the ministry or reports of structural divisions (branches) of the organization.
In accordance with Federal Law No. 208-FZ dated July 27, 2010 “On Consolidated Financial Statements,” consolidated financial statements mean systematized information reflecting the financial position, financial performance and changes in the financial position of an organization that, together with other organizations and (or) foreign organizations in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (hereinafter referred to as IFRS) are defined as a group.
This law applies:
— to credit organizations;
— to insurance organizations (with the exception of medical insurance organizations operating exclusively in the field of compulsory medical insurance);
— for non-state pension funds;
— management companies of investment funds, mutual funds and non-state pension funds;
— to clearing organizations;
— to federal state unitary enterprises, the list of which is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation;
— for joint-stock companies whose shares are in federal ownership and the list of which is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation;
- to other organizations whose securities are admitted to organized trading by including them in the quotation list.
Consolidated reporting is prepared on the activities of a group of interconnected legally independent organizations that jointly control certain activities, operations, and property. Consolidated reporting is prepared by the head (parent) organization (company) on the activities of a group of organizations (companies) as a single economic entity, but without a legal entity.
Segmental reporting is reporting generated for individual business segments of an organization. The regulatory justification for the content and preparation of segmental reporting is PBU 12/2010 “Information by Segments”, based on the provisions of IFRS 14 “Segment Reporting”.
Organizations issuing publicly offered securities must disclose information on segments in the notes to the financial statements in accordance with the Regulations. Other organizations, if they decide to disclose information by segments in their financial statements, also apply PBU 12/2010. Information that does not comply with the requirements of the Regulations cannot be referred to as segment information in the financial statements.
The provision does not apply when generating reports compiled for state statistical observation, reporting information submitted to a credit institution in accordance with its requirements, and compiling reporting information for other special purposes, unless the rules for compiling such reporting and information provide for it.
When disclosing information by segments, the organization applies general requirements for the presentation of information in the financial statements of organizations established by regulatory legal acts on accounting.
Disclosure of information by segments should provide interested users of the organization's financial statements with information that allows them to assess the industry specifics of the organization's activities, its economic structure, and the distribution of financial indicators in individual areas of activity.
Results
The balance sheet is drawn up on a specific form approved for this purpose by the Ministry of Finance of Russia, and in compliance with certain rules for entering information into it. As of June 1, 2019, the balance sheet form has a new edition. Forms and examples of filling out the balance can be found on the Federal Tax Service website and on our website.
Sources:
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 N 66n
- OK 011-93. All-Russian Classifier of Management Documentation
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
For what periods is data entered into F-1 of the balance sheet?
All balance sheets must be compiled by one of the following dates:
- The reporting date corresponding to December 31 of the year for which the report is being prepared (for example, 2015).
- December 31 of the year preceding the reporting year (for example, 2014).
- December 31 of the year that came before the previous one (for example, 2013).
Thus, the balance sheet is prepared for the reporting year preceding and the year before the previous one.