What is an audit and its types
An audit of financial statements is the implementation of strictly defined methods of checking the data contained in the accounting reports in order to establish the degree of reliability.
The audit of financial statements is carried out in accordance with current regulations in several stages.
They can be roughly represented as follows:
- collection of information;
- carrying out the study of all submitted data without exception;
- making a decision, which should contain the auditor’s opinion on how much the presented data can be trusted.
- The opinion of an independent specialist is issued in the form of a conclusion. It reflects how much you can trust the reporting data.
Attention: drawing up an audit report is the final stage of the audit.
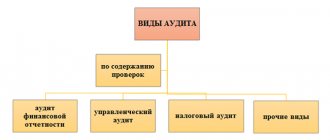
It must be remembered that the auditor is given the right to present an audit report in the form of a refusal to confirm the reliability of the information contained in the report. Depending on who is the initiator of the verification of the data contained in the report, the following types of audit are distinguished:
- The audit is mandatory due to the law. A mandatory audit is possible based on a decision made by a judge. Only accredited specialists are allowed to conduct such an audit. When implementing it, specialists must be guided by accepted auditing standards.
- Initiative audit - It is carried out on the basis of a decision of the founders of the organization or by order of the company’s management. With this type of audit, the scope of work and objects of study are determined based on the customer’s decision. The main purpose of such an audit is to assist the company in restoring its accounting records and providing advice to the customer.
Types of financial statements
Now let's look at what types of financial statements exist. Depending on the completeness of information and timing, documents can be divided into the following types:
1. Internal documents (intended for use only within an organization or enterprise). 2. External documents (intended to be provided to inspection authorities, as well as potential investors, clients or interested investors). 3. Annual reports (contain information about the financial condition and economic activities of the organization for the calendar year). 4. Interim reports (contain information about any period during the calendar year - for a month, a quarter, a week). 5. Private reporting (contains information about the work of a separate section or department of an enterprise or organization). 6. General reporting (contains data on the work of the organization as a whole).
It should be noted that an audit of financial statements may be aimed at studying individual documents (for example, for a particular industry or for a specific period of time). An annual audit of an organization’s financial statements involves checking all documents of the enterprise.
For what purpose is it carried out?
In accordance with current regulations, the main purpose of an audit is to establish an independent specialist opinion on the data presented in the reporting.
The importance of auditing is reflected in the meaning currently attached to the information. It is one of the main resources for the work of an economic entity. Its correct perception allows you to adequately make decisions based on it and enter into relationships with other companies.
It is very important for the company’s partners to know that the information presented in the reports is reliable.
Therefore, the following objectives for conducting an accounting audit can be determined:
- Determination with what accuracy and correctness of registration the information was reflected in the accounting financial statements generated for the past reporting year.
- Identification of facts of deviation from current accounting rules, refusal of accepted accounting methods, non-compliance with legal norms in order to timely intervene and correct inaccuracies.
- Ensuring a high level of reliability of the information reflected in the reporting.
Important: conducting an audit is also beneficial for the business entity itself. After all, a positive audit report from an independent expert organization is additional confirmation of the company’s reliability.
Notification of upcoming inspection
As we have already found out, the essence of an audit of financial statements is to determine whether the maintenance of documents complies with the law. Before conducting an audit, the organization must receive notification of the upcoming audit, unless the audit is unscheduled. The notice specifies exactly what to prepare for and how long the accounting audit will take.
An unscheduled inspection of an enterprise may be carried out in the event of an investigation into any serious offense.
During an audit of financial statements, the auditor typically examines:
1. Contents and composition of forms of accounting documentation. 2. Correspondence of various indicators from different reports. 3. Interrelation of indicators of financial statements. 4. Correctness and correctness of evaluation of reporting items. 5. Correctness and accuracy of the formation of consolidated reporting.
For whom is an audit required?
Legislation defines cases in which an audit of financial statements must be carried out.
They define the criteria upon which the organization must involve an independent expert. At the same time, the period during which a mandatory audit must be carried out is determined by regulations.
In accordance with the standards, an audit must be carried out:
- The form of organization of the enterprise is a joint-stock company.
- A company is engaged in a specific type of economic activity. According to the law, a mandatory audit is required if a company is engaged in insurance, lending, clearing, it is a lending history bureau, professional participants in the securities market, non-state pension funds, trade organizers, or is engaged in professional investments.
- A condition for the circulation of an organization’s securities is that if its securities are traded on world markets, it is obliged to conduct a mandatory audit.
- The criterion for the volume of revenue received during the year is that a mandatory audit of the company must be carried out if its revenue for the year exceeds 400 million rubles.
- Criterion. Which is determined by the size of the balance sheet currency reflected in Form 1 of the reporting. In the balance sheet this figure as of December 31, if it is more than 60 million rubles, the organization must involve independent auditors in the audit.
- Another criterion for conducting a mandatory audit is the publicity of financial statements, that is, the obligation of a business entity to publish them. Current regulations stipulate that an audit must be carried out before financial report data is published in an official source.
Attention: these cases of auditing reporting are mandatory in the audit legislation.
Federal regulations may define additional criteria, upon the occurrence of which it is necessary to conduct a mandatory audit of financial statements for the year.
When is an LLC audit required?
There are two types of LLC audit: proactive and mandatory. In the first case, any participant or manager of the enterprise can contact the audit company for services; all costs are also covered by the initiator. The decision is made at the meeting.
Is an audit required? – mandatory if the company meets the following requirements:
- if the turnover for the reporting period exceeds 400 million rubles;
- assets at the end of the reporting period exceed 60 million rubles;
- shares and securities are traded on stock exchanges;
- if summary reporting for the past year is provided;
- A mandatory audit of an LLC is carried out if the enterprise belongs to credit and banking institutions, pension funds, and insurance companies.
You can always find out whether an audit is mandatory for your company from the specialists of our company.
(495) 917-27-78 (495) 621-59-77 Moscow, Kitay-Gorod metro station, st. Solyanka, 9, building 1
International auditing standards
When carrying out audits, the contractor must comply not only with Russian laws in this area, but also with international standards. The latter are called MSA.
International Standards are a list of standards adopted by the International Federation of Accountants. They have effect all over the world. Russian auditing standards must be developed in compliance with international provisions.
The need to apply ISA is caused, first of all, by preparing financial statements under IFRS. Currently, more than 50 adapted ISA standards are used in Russia.
What documents need to be prepared for an audit?
The list of documentation that inspection specialists will study is very extensive. Mandatory minimums include:
- statutory documents of the company, including the memorandum of association (if any);
- extract on entry into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities;
- certificate of registration with the tax service;
- licenses and certificates;
- information about bank accounts;
- tax and accounting reporting for the analyzed period;
- agreements with counterparties;
- acts, invoices, funds accounting cards;
- staffing schedule and documents of the HR department;
- calculations for the distribution of indirect costs;
- tax registers;
- audit report for the previous period (if available).
Who conducts the audit
Inspections, both mandatory and at the initiative of the company, can be performed by both private auditors and audit companies. But the law specifies several situations when an audit can only be carried out by an audit organization.
In particular, this happens if the client is:
- Insurance Company;
- Credit company;
- Non-state pension fund.
- A company whose securities are traded on stock exchanges.
- Government company or corporation.
- A company where the state has a stake of more than 25% in the authorized capital.
Important: in addition, only those private auditors and companies who are members of the SRO of auditors have the right to carry out inspections.
By law, the auditor is required to refuse an audit if one of the following events is discovered:
- The owners of the customer's company are the owner of the audit firm, its management or one of the employees;
- Employees, any of the management, the owner of the audit company are employees of the client’s organization, and occupy a position there that involves accounting.
- Employees, some of the management, the owner of the audit company have a relative in the client organization, and he occupies a position there that involves accounting.
- The customer company is one of the founders of the audit firm;
- The contracting company is a subsidiary of the company that will perform the inspection;
- The customer company and the contractor have the same founders;
- Any of the contractor’s employees have been involved in accounting for the customer company in the previous 3 years;
- The audit is ordered by the insurance organization, which is the liability insurer of the auditor company.
FAQ
In the second case, it will take more days to check all the statements.
The duration of an audit of an LLC enterprise may increase for the following reasons:
- if there are inventories and inventories of goods, in this case auditors must be personally present during the inventory;
- for non-standard activities - this applies to microfinance organizations, pawnshops and non-state pension funds;
- in the presence of complex transactions: loans, leasing, and so on;
- if the enterprise falls under additional control in accordance with Federal Law No. 307, Part 3, Article 5.
A mandatory audit of an LLC is not only the work of specialists in the office of the audited organization; 30% of the time is spent on drawing up reports, analyzes and paperwork.
When contacting the audit office, we guarantee a high-quality result and a conclusion that reflects the real state of affairs, which will allow us to avoid not only penalties, but also to correct all shortcomings in the accounting department. Our specialists are always happy to provide qualified assistance already at the stage of a telephone conversation and answer questions about the timing and prices of an audit of an LLC enterprise.
Call us now!
E-mail: This e-mail address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it
Phone fax,
Moscow, st. Solyanka, 9, building 1.
Audit evidence is information received by the auditor during the audit from the client and third parties or the result of its analysis, allowing one to draw conclusions and express his own opinion on the subject of the audit. Audit evidence includes: -Primary documents and accounting records -Written explanations from authorized employees of the audited entity -Information received from third parties.
The auditor obtains audit evidence by performing the following procedures: Inspection - examination of records, documents or tangible assets. Surveillance – such as monitoring inventory
Inquiry – seeking information from knowledgeable persons within or outside the entity being audited.
Confirmation is a response to a request for information contained in accounting records.
Recalculation – checking the accuracy of arithmetic calculations.
Analytical procedures – analysis and assessment of information received by the auditor, study of financial and economic indicators.
Audit sampling is a method of conducting an audit in which the auditor checks the accounting documentation of an economic entity not in a continuous manner, but selectively, while following the requirements of the relevant rule (standard) of auditing activities. The purpose of a random inspection is to significantly reduce the inspection time while ensuring its proper effectiveness (quality).
The concept of “ audit quality ” can be defined as the degree of necessary and sufficient level of trust in the opinion of the auditor on the part of users regarding the reliability of information in the financial (accounting) statements of the audited entity.
control is divided into internal and external.
Internal quality control of the audit organization is divided into preliminary, current, subsequent and is ensured by three factors:
· proper guidance over the course of the audit from the head of the audit organization;
· supervision by auditors of the actions of assistants during the audit;
· checking the results of the work done. Preliminary internal audit quality control is carried out by the head of the organization at the planning stage.
External quality control of the work of audit organizations and individual auditors is carried out by self-regulatory organizations of auditors in relation to their members.
The inspection can be scheduled or unscheduled.
Cost
The law does not establish the cost of audit services. Each company sets a price tag depending on experience and scope of work.
As a rule, the price depends on several factors:
- Which audit needs to be performed;
- What work should the auditor do;
- How broad is the activity of the customer company;
- How well does the customer’s accounting work, and is there internal document flow?
If the contractor is given a wide range of tasks that need to be solved during the verification process, this will entail an increase in the cost of the service.
| Type of audit | Average execution time | Approximate price |
| Mandatory audit | Up to 14 days | From 60 thousand rubles |
| Initiative audit | Up to 7 days | From 30 thousand rubles |
| Audit in production | Up to 14 days | From 70 thousand rubles |
| Audit in trade | Up to 14 days | From 60 thousand rubles |
| Audit in public catering | Up to 14 days | From 60 thousand rubles |
| Audit in the service sector | Up to 14 days | From 60 thousand rubles |
| Audit in construction | Up to 14 days | From 90 thousand rubles |
| Foreign trade audit | Up to 14 days | From 70 thousand rubles |
An audit organization is...
Auditing activities in the Russian Federation can be carried out by legal entities and individuals, that is, auditors working as individual entrepreneurs. An audit organization is a commercial firm that carries out auditing activities after obtaining the appropriate license. The main purpose of its operation is to make a profit, achieve the assigned audit objectives and provide specialized services (for example, maintaining, restoring accounting records, consulting).
It is important to know! A catalog of franchises has opened on our website! Go to catalog...
There are certain requirements for organizing the activities of an audit company:
- there cannot be less than 5 auditors on staff;
- at least half of the auditor staff must have Russian citizenship and reside in the country (and if the head of the company is a foreign citizen, then no less than 75%).
You can create a company of this profile in almost any organizational and legal form (business partnership, production cooperative, unitary enterprise, LLC, JSC). But due to the peculiarities of work in the economic segment, an audit organization is most often created as a limited liability company. If a young entrepreneur cannot successfully develop his business on his own, is faced with a crisis, or wants to implement an innovative project, business angels, not auditors, can help him. It is important to remember that transactions that go beyond the legal capacity of the company will be considered invalid.
In practice, audit organizations are divided into different types depending on the nature of their activities, functions performed and the volume of services provided: universal and specialized, large, medium and small. Auditors and audit firms may form unions to coordinate their actions and protect professional interests. To carry out work, they must obtain the appropriate license and certificate to carry out auditing activities. Auditing organizations, their managers, individual auditors, audited persons and persons subject to audit bear civil, administrative and criminal liability.
Stages of inspection
The verification procedure can be divided into several stages.
Step 1 - preparation for inspection
At this stage, the audit firm and the client should get to know each other. During such an acquaintance, the auditor needs to obtain as much information as possible, which will allow him to clearly decide whether to carry out an audit or refuse it.
Also during this stage, the auditor must assess the upcoming scope of work and determine whether he has the required number of specialists for this work. He must make a preliminary calculation of future costs, as well as calculate the time he will need to spend on the inspection.
During the meeting, you must obtain the following information:
- How the client interacts with the industry and region;
- What is the state of his finances now?
- Does it have specifics in the organization and production technology;
- How qualified personnel work in the accounting department;
- Is accounting automated?
- Are there any outstanding obligations, pending litigation, etc.
Attention: if after meeting the auditor agrees to conduct an audit, he issues a letter of commitment. It specifies the rights and obligations of each party, as well as the cost of these services. If the client agrees to the proposed conditions, then an inspection agreement is signed.
Step 2 - Test Plan
This step typically takes up the most time in the overall audit cost. Here it is necessary to draw up a plan according to which the inspection will take place, divide it into separate sections and assign a responsible person to each.
The drawn up plan is not considered final. If during the inspection any new circumstances are discovered, the plan may be revised.
At this stage, the auditor should also conduct an analysis of the enterprise's control system. If he determines that it is strict and its data can be relied upon, then the test can be carried out in less detail.
Step 3 - verification
Next, specialists must complete a list of procedures aimed at obtaining and analyzing evidence:
- Oral survey;
- Inspection;
- Confirmation;
- Recalculation;
- Inspection of provided documents;
- Inspection;
- Measures to evaluate the found indicators.
Attention: all this is aimed at identifying facts of activity that were not taken into account at all when preparing reports, or were taken into account incorrectly.
Step 4 - Conclusion
After collecting all the evidence, the auditor reviews and makes a decision on the reliability of the submitted statements. The opinion can be positive or modified. Under certain conditions, an opinion may be refused.
Purpose of the audit
The objectives of the audit are determined by the Federal Auditing Rules and the International Standard on Auditing. An audit of such a profile is carried out to form an objective professional opinion on the reliability of the financial (accounting) statements of the audited entities and the compliance of the procedure for its maintenance with the law. They take into account such criteria as the actual existence of assets and liabilities reflected in the balance sheet, the occurrence of business transactions during the reporting period, the legality of ownership of assets, the completeness of liabilities, the accuracy of data, the correctness of presentation and the degree of disclosure of information in the statements of the audited entity.
But such an opinion should not be taken as an indicator of confidence in the continuity of the company's activities or as a complete guarantee of high business efficiency in the future. In addition, the inspector does not evaluate whether the interests of the owners are respected and the success of individual operations; for this, a separate service accompanying the audit must be ordered. The main purpose of the audit is to clarify the correctness of the financial statements, the reliability of the data in them, and assess the accuracy of the reflection of assets, liabilities and financial results of the company for the reporting period. According to the concluded agreement, the basic goal can be supplemented by others (for example, identifying ways to optimally use financial resources, optimizing spending, income and expenses, analyzing the correctness of calculation and withholding of taxes, etc.).
Rating of auditing companies in 2019
The RAEX rating agency (“RAEX-Analytics”) annually compiles a rating of auditing companies in Russia. Information for it is collected until March of each year, after which it is analyzed and a rating is compiled based on the results of the past year.
The rating compiled based on the results of 2020 is currently in effect. It looks like this:
| Number in the rating | Name of audit firm | Location | Year. income, million rubles | Number of employees, people |
| 1 | KPMG | Moscow | 9196,00 | N/A |
| 2 | Ernst & Young | Moscow | 6104,00 | N/A |
| 3 | “PricewaterhouseCoopers Audit” | Moscow | 5157,00 | 1 691 |
| 4 | Deloitte & Touche CIS | Moscow | 4963,00 | 1390 |
| 5 | "BDO Unicon" | Moscow | 1394,00 | 694 |
Tags: Audit
When is an LLC audit required?
There are two types of LLC audit: proactive and mandatory. In the first case, any participant or manager of the enterprise can contact the audit company for services; all costs are also covered by the initiator. The decision is made at the meeting.
Is an audit required? – mandatory if the company meets the following requirements:
- if the turnover for the reporting period exceeds 400 million rubles;
- assets at the end of the reporting period exceed 60 million rubles;
- shares and securities are traded on stock exchanges;
- if summary reporting for the past year is provided;
- A mandatory audit of an LLC is carried out if the enterprise belongs to credit and banking institutions, pension funds, and insurance companies.
You can always find out whether an audit is mandatory for your company from the specialists of our company.
(495) 917-27-78 (495) 621-59-77 Moscow, Kitay-Gorod metro station, st. Solyanka, 9, building 1