Accounting statements are perhaps the most important thing that an enterprise can have, because it is a reflection of all the complete and reliable information about the finances and economics of the organization. Therefore, it is so important to comply with the requirements for financial reporting.
Of course, in order to comply with something, you need to understand something about it or at least understand what we are talking about. In this article we will try to understand what the concept of “accounting statements” includes and what requirements apply to it.
Regulatory regulation
The basic requirements for accounting statements that you need to know and comply with are contained in the Federal Law “On Accounting” No. 402 of December 6, 2011, which came into force on January 1, 2013.
In addition, it is necessary to comply with the requirements of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 34 dated June 29, 1998, as amended on December 24, 2010, and the Regulations on accounting “Accounting statements of an organization,” approved by order of the Ministry of Finance Russian Federation No. 43 dated 07/06/1999.
Back to contents
Reporting of a newly created company
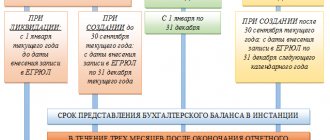
If the company was created after September 30, then the first annual report must be drawn up for the period from the moment of its state registration to December 31 of the following year. If the company was created before September 30, then annual reports must be prepared for the period from the date of state registration to December 31 of the same calendar year (Clause 2, Article 15 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ).
The forms that are approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n are used.
What is included in financial statements?
The financial statements include:
- balance sheet;
- Profits and Losses Report;
- statement of changes in equity;
- cash flow statement.
Basically, when we talk about financial statements, we mean the balance sheet.
At the request of the management of the enterprise, extensive reports on the movement of funds, profits and losses, explanatory notes, and so on can be attached to the balance sheet.
Back to contents
Why are financial statements necessary?
Accounting reports use:
- firstly, enterprise managers - to see a complete and clear picture of the profitability of production, business transactions carried out, the movement of funds, and so on;
- secondly, internal auditors and persons interested in the activities of the enterprise, for example, shareholders - in order to assess the economic and financial position of the enterprise, determine whether it makes sense to invest in it or support cooperation, etc.;
- thirdly, external auditors who do not have a direct interest in the activities of the enterprise, as well as representatives of tax services - at least once a year, the management of any enterprise, as well as individual entrepreneurs, submit a balance sheet and profit and loss statement to the tax service.
Typically, a complete package of financial statements is prepared once a year for submission to the tax service, but it is recommended not to neglect interim reporting - monthly and quarterly. The more often reports are compiled and data is double-checked, the easier it is to avoid errors and identify unreliable data.
Back to contents
The third section—Basic rules for the preparation and presentation of financial statements—sets out the basic requirements for the preparation of financial statements, defines their composition, the rules for evaluating items of financial statements, the procedure for their presentation, the basic rules for the preparation of consolidated financial statements and the procedure for storing accounting documents.
[p.31] PBU 4/99 Accounting statements of an organization determine the general requirements for the preparation of financial statements in the Russian Federation: reliability, completeness of data, neutrality of information, inclusion in the reporting of data on the activities of all divisions of the organization, consistency in the choice of methods for generating reporting indicators from one period to to another, providing data for at least two periods of activity - the reporting period and the one preceding the reporting period. [p.612] Accounting statements (provided to the auditor) include the balance sheet, profit and loss statement, appendices thereto, and explanatory note. The requirements for the preparation of financial statements are established by the Law of the Russian Federation dated November 21, 1996 (as amended on July 23, 1998) On Accounting and the Regulations on Accounting and Financial Reporting in the Russian Federation (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 29, 1998. as amended on March 24, 2000, No. 34n). The composition, content, forms and methodological basis for the formation of financial statements are established by the Accounting Regulations Accounting statements of organizations (PBU 4/99), approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 43n dated 07/06/1999 [p.68]
Requirements for the preparation of financial statements [p.721]
What are the requirements for the preparation of financial statements [p.439]
Thus, the requirements for the preparation of financial statements generally correspond to the requirements for the formation of current accounting. [p.394]
Having examined the concepts of elements characterizing the financial position of an enterprise, we will compare their reflection in the balance sheet as a reporting form in the Russian Federation and in IFRS. IFRS 1 lists the general requirements for preparing a balance sheet. While disclosing the content of assets, liabilities and capital, IFRS does not prescribe a strict form, list of items, order of location and titles of these items and identifies only those items that must be disclosed at a minimum. This [p.243]
When the auditor issues an opinion based on the full scope of audit procedures, he must prepare a report to the principal auditor that sets out the auditing standards followed by the auditor and on which the auditor's opinion is based. If the accounting (financial) statements do not comply with generally accepted requirements for the preparation of accounting (financial) statements or legal requirements, these inconsistencies must be reflected in the auditor's report. In addition, it may be necessary to express the auditor's opinion on any additional information included in the consolidated statements. [p.104]
Topic 6. Accounting (financial) reporting. Goals and objectives of preparing financial statements. Requirements for financial statements. Composition of financial statements. [p.415]
The classification of financial reporting indicators is presented in PBU 4/99 [7]. It is well known that this classification is given in the specified PBU without reference to accounting account numbers. In this sense, it is possible to draw up financial statements that would satisfy the interests of users, with the same result, on the basis of accounting data obtained using both the 1991 Chart of Accounts and the new Chart of Accounts. For example, the absence of account 06 Long-term financial investments in the new Chart of Accounts does not eliminate the requirement to classify financial investments into short-term and long-term for the purposes of preparing financial statements. [p.545]
A feature of the preparation of financial statements is the abandonment of its standard forms. Russian organizations are given the right to independently develop forms of financial statements based on the samples proposed by the Ministry of Finance of Russia, subject to such general requirements for reporting information as completeness, materiality, neutrality, set out in PBU 4/99 Accounting statements of an organization. It is also necessary to be guided by the Federal Law on Accounting, the Regulations on Accounting and Financial Reporting in the Russian Federation, the Chart of Accounts for accounting of financial and economic activities of organizations and other provisions, recommendations and guidelines regulating the issues of reporting. In this case, the codification of samples must be observed in individual forms. [p.39]
The principles for preparing financial statements, proclaimed in the Concept of Accounting in a Market Economy of Russia (hereinafter referred to as the Concept) [6], are very similar to the principles of IFRS. It is no coincidence that the Concept was initially aimed at compliance with IFRS with the Accounting Reform Program in the Russian Federation. In the domestic Concept, similar to IFRS, two groups of reporting principles are distinguished: the main assumptions in organizing accounting and the requirements for information generated in accounting. [p.228]
In addition to the Concept, the formulation of a number of principles for preparing financial statements contains a number of Russian legislative and regulatory acts. The most detailed statement of principles is contained in the Accounting Regulations Accounting Policy of Organizations (PBU 1/98). By analogy with the Concept, it identifies two groups of principles, the main assumptions and requirements for information generated in accounting. At the same time, the main assumptions formulated in PBU 1/98 completely coincide with the assumptions of the Concept. The requirements related to the second group of principles are disclosed in PBU 1/98 less fully than in [p.230]
It is necessary to take into account the differences between an audit and an audit (no longer in the procedural sense, but in terms of economic control), which is an integral part of the management control system, designed to establish the legality, reliability, feasibility and economic efficiency of completed business transactions. The main objectives of the audit are to monitor compliance with state discipline, the use of public funds, the safety of material and monetary resources, the correctness of accounting, as well as suppression of violations of legal requirements for accounting and preparation of financial statements. [p.240]
In order for the financial statements to meet the requirements for them, when drawing up the financial statements, the following conditions must be ensured: full reflection of all business activities for the reporting period [p.347]
In a socialist state, each individual enterprise is an integral part of the country's national economy. Therefore, balance sheets and reports of enterprises serve as the basis for drawing up consolidated reports for the national economy as a whole. In connection with the improvement of the economic mechanism and increased attention to management and planning issues, the importance of reporting is steadily increasing. Under these conditions, increased demands are placed on the organization of financial statements. Promotion. the quality and reduction of reporting timelines largely depend on the organization of accounting at enterprises and the qualifications of the accounting staff, as well as on the mutual coordination of the work of accounting with operational departments. . . [p.205]
Example. If, when preparing financial statements, a significant claim against an organization is recognized as a conditional fact, then among the factors taken into account when assessing this conditional fact, the organization must take into account the stage at which the consideration of this claim is at the date of signing the financial statements expert opinions on this claim and the existing practice of considering similar claims. [p.107]
The procedure for preparing written information from the auditor involves the development of a preliminary version of it, reflecting the requirements for making corrections to accounting data and preparing a list of clarifications to previously compiled financial statements. The company's management may prepare a written response containing its point of view on the auditor's comments. The client's opinion is taken into account by the auditor when preparing the final version of the written information. [p.68]
Requirements for the provision of audit-related work and services (development and adoption in 1998). The content of services related to the audit is revealed (establishment, restoration and maintenance of accounting records, preparation of financial statements, improvement of the current accounting system, conducting economic analysis, consulting on a wide range of financial and legal issues, etc.). The requirements for the quality of the auditor's provision of these services are described, as well as the limitations associated with verifying the reliability of the reporting of the enterprise to which such services are provided. [p.229]
Regulations on accounting Accounting statements of an organization PBU 4/96 regulates the composition, content of requirements and methodology for preparing financial statements of enterprises. It establishes the rules for evaluating items in financial statements and the content of explanations thereto. The provision of PBU 4/96 also reflects issues of audit, publicity and frequency of financial statements. [p.260]
In order for financial statements to meet the requirements for them, when drawing up accounting reports, the following conditions must be ensured: complete reflection for the reporting period of all business transactions and inventory results of all production resources, finished products and calculations; complete coincidence of synthetic and analytical accounting data, as well as indicators of reports and balance sheets with synthetic and analytical accounting data; recording business transactions in accounting only on the basis of properly executed source documents or equivalent technical media; correct assessment of balance sheet items. [p.538]
The primary documents of an enterprise include bank documents (payment orders), cash documents (receipt and expense orders), accounts, invoices, invoices, powers of attorney, advance reports with attached documents, acts of completion of work, accounting certificates, payroll statements and etc. Requirements for the preparation, form, volume and content of primary documents are established by the Law of the Russian Federation No. 129-FZ of November 21, 1996 (as amended on July 23, 1998) On Accounting, Regulations on Accounting and Financial Reporting in RF (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 34n dated July 29, 1998, as amended on March 24, 2000), albums of unified forms of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation, and other regulations. [p.67]
The contents of the book should not replace or repeat official instructional materials. The purpose of this chapter is to show the most important points when preparing financial statements and consider filling out reporting forms (example 9.1). Official requirements for quarterly and annual reporting are formulated in letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. [p.351]
Documentation of property, liabilities and other facts of economic activity, maintenance of accounting registers and financial statements is carried out in Russian. Primary accounting documents compiled in other languages must have a line-by-line translation into Russian. The requirement for accounting is separate accounting of current costs for production of products, performance of work and provision of services and costs associated with capital and financial investments. Due to the ongoing transition to international accounting standards, current accounting requirements are evolving and being refined. [p.21]
The requirement of consistency reinforces in the practice of preparing financial statements the need for consistency in the content and forms of the balance sheet, profit and loss statement and explanations thereof from one reporting year to another. [p.103]
The content and procedure for drawing up the published forms of the balance sheet and profit and loss statement have been clarified, as well as the requirements for drawing up the reporting form “Information on the quality of loans, loan and similar debt”. [p.57]
Russia's upcoming accession to the World Trade Organization (WTO) will require business companies to disclose not only the internal market for foreign securities and foreign investors, but also information about their status and the preparation of financial statements in accordance with the requirements of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). It is important to avoid possible mistakes when carrying out transactions with securities, organizing accounting, tax and internal accounting. [p.4]
The created regulatory documents radically changed the approach to the methodology for calculating financial results for their reflection in financial statements and calculating revenue from sales of goods, products (works, services). In particular, for the preparation of financial statements, revenue from the sale of goods, products, performance of work, provision of services is established only upon their shipment and upon presentation of settlement documents to the buyer (customer). If the contract stipulates the moment of transfer of the right of ownership, use and disposal of the shipped products to the customer after the moment of receipt of funds in payment for the shipped products to the bank or to the enterprise's cash desk directly, as well as the offset of mutual claims for settlements, then the proceeds from the sale of such products (goods) are included in the “Profit and Loss Statement” on the date of receipt of funds (offset). A similar procedure applies to work performed and services provided. [p.315]
A significant part of the analytical work at the enterprise is carried out on a planned basis. The analytical work of the accounting, planning and financial services of an enterprise is regulated by state regulatory documents (official guidelines for the analysis of financial statements of enterprises are determined by the Federal Law of November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ On Accounting, the Regulations on Accounting and Reporting in the Russian Federation (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance RF dated December 26, 1994 No. 170) Regulations on accounting Financial statements of an organization PBU 4/96 (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 8, 1996 No. 10) regular orders of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation on the procedure for preparing financial statements of enterprises by resolution of the State Committee Russian Federation on Statistics dated September 16, 1997 No. 63 On approval of unified forms of federal state statistical observation and other documents), requirements of higher authorities, as well as internal document flow regulations. [p.61]
One of the main trends in the world economy is the increasing role of foreign economic relations, international relations and integration processes. The emergence of transnational corporations places stringent demands on the uniformity and transparency of the principles for generating income and expenses, investment conditions, and financial reporting algorithms used in different countries. The problem of inconsistency between accounting models of different countries hinders the development of the world economy and is of a global nature. In this regard, the study, analysis and generalization of international accounting standards is of particular importance. [p.174]
Federal ministries and other federal executive bodies of the Russian Federation, carrying out, in accordance with the established procedure, the preparation and presentation of financial statements for unitary enterprises, as well as for joint-stock companies (partnerships), part of the shares of which are assigned to federal ownership (regardless of the size of the share), also it is necessary to determine the requirements for the structure and content of accounting reporting forms for their subordinate enterprises and organizations in order to develop and adopt uniform forms that take into account the industry specifics of their activities. [p.338]
The requirement of comparability is also expressed in the use of accounting reporting forms. In accordance with PBU 4/99 [7], an organization must, when drawing up a balance sheet, profit and loss statement and explanations thereto, adhere to its accepted content and form consistently from one reporting period to another. [p.65]
Both IFRS and Russian accounting regulations state that financial statements must give a fair view of the financial position, financial results and changes in financial position. However, according to IFRS, statements prepared in accordance with IFRS will be considered reliable. According to Russian regulations, reporting prepared on the basis of the rules established by the accounting regulations of the Russian Federation is considered reliable. Thus, the reliability of reporting is made dependent on the reliability of the requirements established (both by IFRS and Russian regulations) for the procedure for preparing financial statements. At the same time, it should be noted that both IFRS and Russian regulations provide for the possibility of deviation from the established rules if the latter do not allow, due to any exceptional reasons, to reflect the real financial position of the enterprise. [p.71]
The accounting registers of an enterprise include the General Ledger, Cash Book, Sales Book, Purchase Book, order journals, account statements, chess statements, etc. Accounting registers are designed to systematize and accumulate information contained in primary documents accepted for accounting, and to reflect it on the accounting accounts. The requirements for the compilation and maintenance of accounting registers are established by the Law of the Russian Federation No. 129-FZ of November 21, 1996 (as amended on July 23, 1998) On Accounting, Regulations on Accounting and Financial Reporting in the Russian Federation (order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 34n dated July 29, 1998, as amended on March 24, 2000), by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation [p.67]
Types of financial statements
Before talking about what requirements exist for the preparation of financial statements, it is necessary to understand that reporting can be divided into two large groups:
- internal reporting;
- external reporting.
The second group represents information about the profit and loss of the enterprise, its property and economic status and is subject to public access - for example, it is published on the enterprise’s website, where anyone can familiarize themselves with it.
Internal reporting, as you might guess from the name, is intended exclusively for the management of the enterprise or its departments and is a trade secret. Disclosure of such information is a violation of labor discipline and is strictly punishable.
Therefore, of course, the requirements for the preparation of internal and external financial statements will differ somewhat, although only slightly. For example, the principle of transparency and reliability will be observed in both cases, but some of the information that constitutes a trade secret will not be included in external reporting.
In addition, some enterprises are not required to provide public reporting at all. According to the law, this requirement applies only to credit and insurance organizations, investment funds, open joint-stock companies and funds that are created at the expense of private, public and government sources.
Back to contents
Utility requirement
Information presented in the reporting is considered useful if, in accordance with paragraphs. 6.1, 6.5.1 Concepts of accounting in the market economy of Russia, approved by the Methodological Council on Accounting under the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, the Presidential Council of the IPB RF on December 29, 1997:
- appropriate;
- reliable;
- comparable;
- timely.
Information is relevant (clause 6.2 of the Concept) if its presence or absence has or is capable of influencing the decisions (including management) of users of the statements, helping them evaluate past, present or future events, confirming or changing previously made estimates.
Information is reliable (clauses 6.3, 6.3.1 of the Concept) if it does not contain significant errors. The materiality of accounting errors is discussed in PBU 22/2010 “Correcting Errors in Accounting and Reporting” (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 28, 2010 No. 63n) and, in particular, its paragraph 3. To be reliable, information must objectively reflect the facts of economic activity to which it relates.
Information is comparable (clause 6.4 of the Concept) if it provides users of reporting with the opportunity to compare performance indicators for different periods of time in order to determine trends in the financial position of the organization and the financial results of its activities.
Information is timely (clause 6.5.1 of the Concept) if it satisfies the needs of users related to decision-making.
To learn how to analyze the financial stability of a legal entity based on balance sheet data, read the article “Analyzing the financial stability of an organization.”
General requirements for financial statements
First of all, it must be taken into account that each financial reporting document must be drawn up in Russian (if some document has already been drawn up in another language, it must have a literal interlinear translation), using forms approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and forms, and all amounts must be indicated in rubles.
In addition, the financial statements must be:
- reliable;
- neutral;
- holistic;
- consistent;
- significant;
- comparable;
- timely;
- prudent;
- consistent;
- rational;
- with a predominance of content over form.
Back to contents
Reliability requirement
This principle means that financial statements must give the most reliable and complete impression of the business operations of the enterprise, its economic and financial position. That is, all transactions must be recorded indicating the primary accounting documents, in chronological order.
https://youtu.be/fW8xcVv6sFE
If the enterprise decides that the report on business operations does not give a complete picture, at the request of the management, additional information can also be provided - other reports and documents.
Back to contents
Neutrality requirement
Neutrality of accounting reports means that they should only give an idea of the activities of the enterprise, and not encourage those for whom the report is intended to make any decision. The report should contain only facts and figures, but not advertising, commercial proposals, rationalization ideas, etc.
Back to contents
Integrity requirement
The principle of integrity presupposes the inclusion in reporting of the maximum amount of information about the enterprise and its divisions.
Of course, if the enterprise is large and has, for example, several branches in other cities, the financial statements should include information about all branches and their activities.
Back to contents
Consistency requirement
Consistency means that the enterprise is obliged to follow the once adopted accounting policies and activities. Any change must be approved in advance. If an enterprise, for example, suffered from a natural disaster, the reporting should include forecasts of how its balance sheet and activities will change.
Back to contents
Principle and requirement of materiality
Essential information is considered to be the information without which the assessment of the enterprise will not be complete and objective. At the same time, the decision about which indicator is significant remains with the management of the enterprise.
Back to contents
Comparability requirement
Financial reporting indicators should be easily comparable with the same indicators for any reporting period. This means that data for each indicator must be submitted for the previous period and the reporting period, and they must be brought to a single, comparable form - if an adjustment has been made, this is indicated in the explanatory note to the report.
Back to contents
Timeliness requirement
Timeliness means that all business transactions performed must be immediately recorded in accounting documents. If this cannot be done immediately, the information should be entered as soon as possible.
Back to contents
Requirement of diligence
This requirement means a ban on the creation of hidden reserves, taking into account only those incomes that are actually received by the enterprise. At the same time, when taking into account expenses, it is possible to plan a higher figure than what may ultimately be obtained, and to form a reserve to cover, for example, the cost of defective products. The formation of reserves must be reflected in the accounting policies of the enterprise.
Back to contents
Consistency requirement
Consistency simply means that the data in the primary accounting documents and the data that is transferred to the reports must match. The data from analytical and synthetic accounting must also match.
Back to contents
Requirement of rationality
The requirement of rationality means that the accounting of an enterprise must be carried out taking into account its characteristics, size, nature of production, and so on. If, for example, all the necessary information can be reflected in one report for an object, there is no need to fill out additional registers.
Back to contents
Requiring content to take precedence over form
The priority of content over form means that business transactions should be reflected in accounting primarily according to economic indicators, and only then according to legal ones. For example, the accounting for a purchased building that requires major repairs before being put into operation will be listed as construction in progress, despite the fact that the building may already be properly registered and paid for.
Back to contents
Composition of reporting
An expert is ready to tell you about the composition of financial statements:
https://youtu.be/YDX55KlqhR8
It includes the following information:
- A balance sheet is a kind of comparison of an organization's assets and liabilities. All property, debts, the presence and valuation of intangible assets are reflected here in monetary terms. The asset and liability items must be equal in amount, otherwise the statements are considered incorrectly prepared. It is necessary to check the completeness of all data entered into the balance sheet, as well as their correctness.
- Financial results of the enterprise . Shows how much the enterprise pays off, its level of profitability and liquidity. Moreover, the data of the reporting period are indicated in comparison with the previous ones. This makes it possible to analyze indicators over several years.
- Appendices to the Balance Sheet are filled out only in cases where there is a need to reflect data that does not fall under one of the articles of previous reports. They are also filled out to reflect changes in accounting policies (Explanatory Note), to provide detailed and visual information about their business activities for investors and founders (more often this is done by large organizations with a large production volume). An audit report on the fact of such an audit is also filled out.
The first two reports are required to be completed, the rest are subject to information that is not included in the first two reports.
What special tax regimes are in effect in the Russian Federation?
Summer business: interesting ideas.How to calculate profit before tax?
Requirements for preparation of financial statements
As mentioned above, financial statements must be kept in Russian, in Russian currency and on standard forms.
In addition, each component of the overall report must contain:
- Name;
- reporting date or indication of the period for which it is compiled;
- name of the enterprise and its details;
- format of presented numerical indicators of financial statements.
The financial statements are signed by the head of the enterprise and the person who compiled it (as a rule, this is the chief accountant of the enterprise). Any errors or corrections found must be confirmed by the date and signature of the person who corrected them.
Was the information interesting or useful?
Yes45
No9
Share online
Design rules
All reporting documents must be drawn up in Russian. The ruble is set as the payment currency. It is mandatory to fill out the prescribed forms.
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation has established details that must be present in reports:
- The name of the report, as an integral part of the reporting,
- Reporting date,
- The name of the legal entity whose activities served as the basis for the preparation of these reports. The name must be complete, abbreviations are not allowed,
- Identification number received by a legal entity when registering with the tax authority,
- Code of the type of activity of the organization (according to OKVED) in accordance with the requirements of the State Committee on Statistics,
- Organizational and legal form and ownership code according to the Classifier of forms of ownership,
- Unit of measurement,
- Location address (only on Balance),
- Dates of approval, dispatch,
Reporting corrections and errors are not omitted. Any correction must be certified by the signature of the responsible person and the head of the organization. It is also necessary to indicate the date the corrections were made.
Regardless of the size and volume of production and enterprise, there is no difficulty in studying its economic condition. Of course, if the organization maintains accounting records correctly - in compliance with all the above requirements and conditions.
Only in this case will potential investors have the opportunity to consider reliable data and results of the enterprise’s economic activities. And the tax authorities will not need to impose penalties on the organization. Correct accounting in an enterprise is the key to a successful and long life of the enterprise, regardless of the type of activity.