Who are considered tax agents for VAT in 2020
The Tax Code defines several cases when a company is considered a tax agent:
- if it purchases goods, works or services on the territory of the Russian Federation from a foreign company that is not registered for tax purposes in Russia (clauses 1, 2 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if the company leases property from the authorities, and also if the company buys or receives from the authorities property that constitutes the state treasury (paragraph 1, paragraph 3, article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if, on behalf of the state, the company sells property by court decision, as well as confiscated, ownerless or purchased property (clause 15, clause 2, article 146, clause 4, article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if the company acts as an intermediary - commission agent or attorney, participates in settlements and sells goods, work, services or property rights to a foreign company not registered in Russia (clause 5 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if the company owns the ship on the 46th calendar day after the transfer of ownership rights to it, if before this date the ship is not registered in the Russian International Register of Ships (clause 6 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if the company buys raw animal skins, scrap and waste of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, secondary aluminum and its alloys, as well as waste paper (clause 8 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if it provides railway rolling stock or containers on the territory of the Russian Federation on the basis of an intermediary agreement (with the exception of the international transportation of goods and transportation of exported (re-exported) goods, if the point of departure and destination are located on the territory of the Russian Federation) (clause 5.1 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Even if a company is not a VAT payer, it is not exempt from the duties of a tax agent. For example, “simplified people” or payers of UTII who perform the listed operations are recognized as tax agents.
Setting up the program
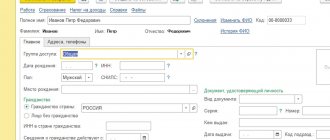
Let's open the "Directories" section/subsection "Purchases and Sales"/"Contracts". In the counterparty agreement card with the type of agreement “With a supplier”, we will make the settings in the “VAT” part:
- Set the flag “The organization acts as a tax agent for the payment of VAT”;
- Let’s choose the type of agency agreement “Sale of goods” (clause 8 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Fig.17 Program settings
https://youtu.be/uqVucxlpp-E
What should a VAT tax agent do?
In simple terms, the VAT tax agent must pay the tax instead of an organization or individual entrepreneur who cannot do this. In this case, the tax agent’s action plan is as follows:
- calculate the amount of VAT;
- withhold tax from the taxpayer’s income, which the tax agent himself pays;
- transfer taxes to the budget.
Tax agents - VAT payers who withheld VAT and transferred it to the budget, can accept the tax as a deduction (clause 3 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Tax agents who do not pay VAT cannot do this. The exception is if the company sells confiscated goods or acts as an intermediary, including providing railway rolling stock. In such situations, even the payers of this tax are not allowed to deduct the VAT paid.
How to pay VAT when purchasing goods from a foreign company
Read more…
Right to deduction
Tax agents applying the general tax system can deduct the amount of VAT actually transferred to the budget (clause 3 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, tax deductions are not provided to tax agents who:
- exempt from VAT under Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- sell confiscated property and valuables listed in paragraph 4 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- sell as intermediaries (with participation in settlements) goods (work, services, property rights) of foreign organizations that are not tax registered in Russia (clause 5 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This procedure follows from the provisions of paragraph 2 of paragraph 3 of Article 171, paragraphs 14 and 15 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
An organization that is a tax agent has the right to a tax deduction if it:
- purchases goods (work, services) from foreign organizations that are not tax registered in Russia (clause 1 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, the organization itself must be registered with the tax inspectorate (clause 2 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and the place of sale of goods (work, services) must be the territory of Russia (clause 1 of Article 161, Articles 147, 148 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ). The deduction can be used even if the cost of purchased goods (work, services) does not reduce taxable profit (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 24, 2010 No. 03-07-08/77);
- leases state or municipal property directly from state authorities and local self-government (paragraph 1, paragraph 3, article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- buys (receives) state or municipal property that is not assigned to state (municipal) organizations (paragraph 2, paragraph 3, article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This follows from the provisions of paragraph 3 of Article 171, paragraph 2 of paragraph 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
When transferring an advance (partial payment), such tax agents can take advantage of the tax deduction only after the goods (work, services) are accepted for accounting. The fact is that the rules for applying tax deductions for advances (partial payment) apply only to the tax amounts presented by the seller (performer) and indicated in his invoice. Since tax agents prepare invoices themselves, these conditions are not met. Consequently, until the goods (work, services) received as an advance payment (partial payment) are not accepted for accounting, they cannot accept the VAT amount for deduction. This follows from paragraph 12 of Article 171, paragraph 9 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 12, 2009 No. ШС-22-3/634 and is confirmed by decision of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated September 12, 2013 No. 10992/13.
Situation: is it possible to accept the amount of VAT as a deduction if the organization - tax agent for VAT did not withhold the amount of tax from a foreign supplier and transferred it to the budget at its own expense?
Yes, you can.
Based on the literal interpretation of paragraph 3 of clause 3 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a tax agent can take advantage of the deduction only if the amount of VAT was withheld by him from income paid to the counterparty (taxpayer). However, in letters dated June 5, 2013 No. 03-03-06/2/20797 and dated February 28, 2008 No. 03-07-08/47 (brought to the attention of the tax inspectorates by letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 17, 2008 No. 03-1-03/908) The Russian Ministry of Finance allows the possibility of applying a deduction, even if the VAT was transferred to the budget at the expense of the tax agent. Therefore, if a Russian organization had to withhold tax from the income of a foreign supplier, but transferred it to the budget from its own funds, it does not lose the right to a tax deduction. The legality of this approach was confirmed by the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation in Resolution No. 16907/09 dated May 18, 2010.
To apply the deduction, the tax agent must independently draw up an invoice and register it in the purchase book in the tax period in which the VAT amount was transferred to the budget.
Situation: is it necessary to restore VAT when writing off an under-depreciated fixed asset, if the organization declared the deduction for the purchase of such an object as a tax agent?
No no need.
It is necessary to restore input VAT accepted for deduction only in those cases that are expressly specified in paragraph 3 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The write-off of under-depreciated fixed assets is not mentioned in this paragraph.
If previously an organization legally reimbursed input VAT on a fixed asset, then writing off this object before its full depreciation does not cancel its right to deduction. The main thing is that before the property was written off, the organization used it to perform operations subject to VAT.
This follows from paragraph 2 of Article 171 and paragraph 3 of paragraph 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Similar conclusions are contained in letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated June 17, 2020 No. GD-4-3/10451 and dated May 21, 2020 No. GD-4-3/8627. In both documents, the tax service relies on the position of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation, set out in decision No. 10652/06 dated October 23, 2006, and on letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 7, 2013 No. 03-01-13/01/47571.
In addition, based on the literal content of paragraph 3 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the obligation to restore VAT is generally provided only for taxpayers. And taxpayers and tax agents are different categories of participants in tax relations (Article 9 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When do you need to pay agency VAT?
The tax agent must transfer the VAT withheld from the taxpayer's income to the budget at his location. The entire tax amount must be divided by three and each third transferred to the budget. This must be done no later than the 25th day of each of the three months following the quarter in which VAT was withheld (clause 1.3 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
That is, when:
- payment was transferred to a foreign company for the purchased goods;
- money was transferred to a government agency under an agreement for the rental of premises;
- the intermediary received payment for goods, works, or services sold by a foreign person.
Another rule has been established for the transfer of VAT when purchasing works and services from a foreign organization that is not registered for tax purposes in Russia. In this case, VAT must be paid to the budget simultaneously with the transfer of money to the foreigner (clause 4 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Therefore, you will have to send two payments to the bank at once: one to pay for the work or services of a foreigner, the other to transfer taxes to the budget.
How to pay VAT when selling foreign goods by an intermediary
Read more…
Tax agent calculates VAT: transactions and accounting details
VAT is charged by the tax agent based on the contract amount at a rate of 10% or 18%. If the final price in the contract includes VAT, then the amount of tax payable is determined by multiplying the contract amount by 18/118 or 10/110. When making payments in foreign currency, income is calculated in rubles at the exchange rate at the time of transfer of money. If there is no VAT in the amount of the agreement, its amount is found by multiplying the total cost of goods and services by 10% or 18%.
After making payment under an agreement with a foreign company or government authorities, the tax agent must issue an invoice to himself within 5 days. In the details fields of the counterparty, all his data is indicated, except for the TIN. At the same time, VAT entries are made for the tax agent for the foreigner:
- When providing services by a foreign organization, Dt 25, 26, 44 and Kt 60.
- When reflecting accrued but not paid VAT in the option with a foreign counterparty Dt 19 - Kt 68.
- When paying tax, the amount is written off from Dt 68 and Kt 51.
- When reflecting the VAT tax deduction Dt 68 and Kt 19.
VAT calculated and paid as a tax agent is always accounted for in separate sub-accounts. When drawing up a payment order for KBK VAT, the tax agent indicates the combination of numbers 182 1 0300 110. The transfer of funds must be made before the 20th day of the month that follows the current quarter (when purchasing goods) and simultaneously with the payment of an advance to a foreign company for services. By the 20th day after the end of the quarterly period, you must submit a VAT Return with the second section completed.
How to fill out a VAT return as a tax agent
Tax agents do not fill out the entire declaration, but only section 2 “The amount of tax to be paid to the budget, according to the tax agent.”
This section is filled out separately for each foreign partner, lessor (government body), in relation to whom the company acts as a tax agent. A separate section must be completed for each seller according to the agreement for the sale (transfer) of state property, which constitutes the state treasury.
How to pay VAT when purchasing and leasing state property
Read more…
Tax agents - ship owners - fill out section 2 separately for each ship that is not registered in the Russian International Register of Ships within 45 calendar days after acquisition.
An exception to this procedure is provided for companies that sell property by court decision, as well as confiscated or ownerless property. Such companies fill out this section on one page.
How to pay VAT if a company sells property by court decision
Read more…
You also need to fill out Section 2 on one page if the company paid income to only one lessor (government agency), but under several contracts.
Other sections are included in the declaration if there is a need to reflect relevant data in them.
An example of filling out a tax agent declaration
Read more…
What kind of reporting is required?
An organization calculating VAT as a tax agent is required to submit a declaration at the end of the tax billing period (quarter). It is drawn up in the form approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] The amount of agent value added tax payable to the budget is reflected in section 2.
If during the quarter the organization had other transactions subject to VAT, then it additionally includes section 2 in its declaration. In this case, the report can only be submitted electronically.
If the company has not had any transactions other than agent transactions for value added tax, then the report can be submitted both in electronic form and on paper. It must include:
- title page;
- Section 1 (put dashes in it);
- section 2 - it is necessary to reflect the amount of VAT calculated for payment on agency transactions;
- section 9 - contains information about all issued invoices, including agency invoices.
We wrote in detail about filling out the declaration in the article “How to fill out a VAT return as a tax agent.”
How to submit a VAT return to a tax agent
Tax agents must submit a VAT return to the Federal Tax Service with which they are registered. Some of them can choose for themselves whether to submit the declaration to them on paper or electronically. These are tax agents who simultaneously:
- are not intermediaries acting in the interests of another person;
- are not VAT payers or are such, but are exempt from the obligation to pay tax (clause 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- are not the largest taxpayers;
- have an average number of employees for the previous calendar year of no more than 100 people (clause 3 of Article 80). Newly created organizations should focus on the number of employees, which should not be more than 100 people.
Other tax agents must submit returns exclusively electronically. A declaration submitted on paper is not considered accepted (clause 1, clause 3, article 76, clause 5, article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Rights and obligations of a tax agent
Rights and obligations are specified in Article 24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The rights are identical to the rights of the taxpayer, therefore they are ensured and protected in accordance with Article 22 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Responsibilities include:
- correctly and timely calculate, withhold and transfer fiscal payments from income paid to the taxpayer;
- if it is impossible to make a deduction, notify the regulatory authorities;
- keep records of paid income and calculated taxes as part of the performance of tax agency duties, and also preserve for four years the documents and registers necessary to verify the correctness of calculations;
- provide relevant reports to regulatory authorities.
For failure to fulfill duties, the tax agent bears administrative liability in accordance with Article 123 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as well as criminal liability in accordance with Article 199.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Renting property of municipal or state structures
When using federal or municipal property, the tenant is obliged to pay the landlord income, minus the calculated VAT, which should be transferred to the treasury account.
An important circumstance that fundamentally determines the tenant’s obligation to pay VAT is the conclusion of a lease agreement directly with the federal or municipal government authority (property management committee). It is possible to conclude a triple agreement, where, in addition to the tenant, there is a government agency and the economic entity whose balance sheet contains the fixed assets leased out.
In cases of leasing real estate or equipment from a person who disposes of state property on the basis of economic ownership (management), the tenant is not a tax agent and is not required to calculate and pay VAT.
You should know: when leasing federal/municipal property, the tax agent can be either a legal entity or an individual.
VAT when leasing state property should be calculated from the amount of the contract fee, including tax, at a rate of 18%/118%.
In accordance with the general requirements of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, within 5 days from the date of payment of rent, the tenant draws up an invoice. In the fields intended to indicate the seller, the data of the authority specified in the contract is entered.
When using federal or municipal assets (or acquiring them), the tenant/buyer is required to submit a VAT return to the tax office, filling out section 2. The deadline for its preparation is the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter.
How Russian tax agents will pay VAT on electronic services
But if there have been no global changes with tax agents (the procedure is similar to the acquisition of other services), then we can safely say that the main innovation that has emerged since the beginning of this year is a special procedure for paying VAT when selling electronic services to individuals. In this case, the foreign organization is obliged to register with the Russian tax authorities and independently calculate and pay VAT to the budget of the Russian Federation. Let's look at this in more detail.
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 174.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when foreign organizations provide services to individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs in electronic form, the place of sale of which is recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation, the tax base is determined as the cost of services, taking into account the amount of tax, calculated on the basis of the actual prices of their sales. This means that the tax amount is determined by calculation. Let's give an example.
https://youtu.be/gLKr305zAEg
Preparation of invoices
In accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, upon the sale of goods (work, services), transfer of property rights, as well as upon receipt of payment amounts, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights, appropriate invoices are issued - invoices no later than five calendar days, counting from the day of shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services), from the date of transfer of property rights or from the date of receipt of payment amounts, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights right
As noted in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 12, 2009 No. ШС-22-3/ [email protected] , tax agents, as well as VAT taxpayers, are required to issue invoices. However, the procedure for issuing such invoices will differ from the generally accepted one. Table No. 1 discusses the features of issuing invoices by tax agents when purchasing goods (work, services) from foreign organizations that are not registered in the Russian Federation, as well as when leasing state or municipal property.
Table 1.
| Invoice Line | Category of the payer filling out this line | |
| Tax agents leasing state (municipal) property | Tax agents purchasing goods (work, services) from foreign organizations that are not tax registered in Russia | |
| Line 2 (seller) | Provide the full or abbreviated name of the seller (specified in the agreement with the tax agent) for whom the tax agent fulfills the obligation to pay tax | |
| Line 2a (address) | The location of the seller (specified in the agreement with the tax agent) for whom the tax agent fulfills the obligation to pay tax is given. | |
| Line 2b (TIN/KPP of the seller) | The identification number and reason code for registering the seller (specified in the agreement with the tax agent) are provided. | A dash is placed |
| Line 3 (shipper and address) | A dash is placed (for purchased works or services) | |
| Line 4 (consignee and his address) | A dash is placed (for purchased works or services) | |
| Line 5 (to payment and settlement document No. _from__) | The number and date of the payment and settlement document indicating payment for purchased services and (or) property is indicated. | Indicate the number and date of the payment and settlement document indicating the transfer of the tax amount to the budget (when purchasing works, services) Indicate the number and date of the payment and settlement document indicating payment for purchased goods (when purchasing goods) |
Additionally, it is necessary to pay attention that dashes are also placed on line 5 of the invoice when using a non-cash form of payment.
With regard to filling out individual columns of invoices, it is worth considering that in column 7 “Tax rate” you should indicate the tax rate determined by paragraph 4 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (10/110 or 18/118).
In 1C: Accounting 8, an invoice is entered based on a payment document or by processing Registration of tax agent invoices. In this case, the payment document means the document that registers the payment to the supplier.
The document Invoice issued (see Fig. 1) generates a posting
Debit 76.NA Credit 68.32.
Rice. 1