All documents of an organization can be divided into two groups: tax documents (documents necessary for calculating taxes and insurance premiums) and accounting documents (including personnel), they make up the entire document flow of the organization. Storage and timely destruction of documents is a pressing task for many managers and accountants. Most often, special attention is paid to legal requirements regarding the procedure and periods for storing documentation.
We will address these questions in the article.
Why keep accounting documents?
Any accountant knows that every document drawn up in a company or received from counterparties has its own value and must be preserved. Based on the information contained in the primary documents, accounting is carried out and financial statements are prepared. Verification of accounting and accounting data by all regulatory authorities is carried out using primary documents.
All primary accounting records and reports must be stored for legally defined periods.
The storage periods for accounting documents are regulated by the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ and the approved list of storage periods.
To learn about what groups documents arising in the activities of an organization are divided into and what their storage periods may be, read the article “Basic storage periods for documents in an organization (archive).”
Retention periods for documents for government agencies
Previously, the requirements of state archival affairs for the storage of documents were contained in the List of standard management documents generated in the activities of organizations with an indication of their storage period, approved by the Federal Archive Service of Russia on October 6, 2000. In accordance with the order of the Federal Archives of August 26, 2010 No. 63, the specified List lost its power. Currently there is a List of standard management archival documents generated in the process of activities of state bodies, local governments and organizations, indicating storage periods.
In general, documents according to storage period are divided into the following groups:
- documents with a limited storage period (1 year, 3 years, 5 years, etc.),
- permanent storage documents;
- storage until no longer needed;
- storage until replacement with new documents.
Thus, analytical documents (tables, reports) for annual financial statements must be stored for 5 years. Transfer, separation, liquidation balance sheets, appendices, explanatory notes to them, certificates of registration must be stored permanently. Workers' writs of execution - until the need has passed.
What is more important - the list or law No. 402-FZ
Comparing the storage periods for accounting documents specified in the list and Law No. 402-FZ, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- the list establishes different storage periods depending on the type and significance of documents classified as accounting;
- Law No. 402-FZ provides for a 5-year storage period for accounting documents, but does not specify the terms by type of documentation;
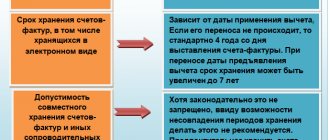
- in paragraph 1 of Art. 29 of Law No. 402-FZ states that the basis for determining the storage periods for documentation is a list.
Thus, when deciding the fate of an invoice, balance sheet or accounting certificate, it is necessary to proceed primarily from the deadlines indicated in the list. However, their storage period cannot be less than 5 years.
The storage period for accounting documents specified in Art. 29 of Law No. 402-FZ, also concerns the accounting policies and standards of the company, including documents existing in electronic form. The latter also cannot be destroyed within a 5-year period. The storage period begins with the year following the year of their last use (Clause 2, Article 29 of Law No. 402-FZ).
Deadlines for key IP documents: current standards
There are a huge number of documents named in the List of Order No. 236. The most popular individual entrepreneurs may be:
- Tax returns and calculations.
The current shelf life in accordance with the new rules of the Federal Archive is 5 years. At the same time, individual entrepreneur declarations up to and including 2002 are stored for 75 years (clause 310 of the List).
A separate period is established for Calculations for insurance premiums - 75 years for reports before 2003, 50 years for Calculations for periods from 2003 and later (clause 308 of the List). In this case, cards for recording payments and insurance contributions must be stored for 6 years (in the absence of personal accounts and salary statements - also 75/50 years).
A five-year period is used for 2-NDFL certificates, and in the absence of personal accounts or salary slips, they are stored for 75/50 years (clause 312 of the List).
Documentation on information exchange with the Federal Tax Service is stored for 6 years if it concerns debt restructuring, and 5 years in other cases.
- Book of accounting of income and expenses in “simplified” format (KUDiR).
The storage period for individual entrepreneur documents on the simplified tax system, namely KUDiR, according to the new rules is 5 years (clause 318 of the List).
- Invoices (drawn up by both VAT payers and non-payers in cases provided for by law).
Their shelf life is 5 years (clause 317 of the List).
- Personnel documents (if the individual entrepreneur has employees):
- employment contracts, job descriptions, personal files – 75/50 years;
- information about work activity – 75/50 years;
- orders for disciplinary sanctions - 3 years; about vacations, business trips – 5 years; on admission, dismissal, transfer, combination - 75/50 years;
- vacation schedules – 3 years;
- applications for the issuance of certificates and work documents from the employer - 1 year;
- Occupational safety and health (OH) briefing logs - 45 years, occupational safety knowledge testing logs - 5 years;
- lists of persons working in “harmful” production – 75/50 years;
- consent to the processing of personal data – 3 years.
Of course, this is not an exhaustive list of documentation that can be used in business: an entrepreneur needs to carefully study the new standard from Rosarkhiv and determine which documents named there he uses in practice.
Let's understand deadlines using an example
Landscape Design LLC, formed several years ago, has steadily gained a foothold in its market segment. The accounting part of the work was carried out by a team of 4 people. Each specialist was assigned specific accounting areas, and the chief accountant was in charge of reporting and interaction with controllers.
Over the past period of accounting work, countless folders with documentation have accumulated in closets and utility rooms. It's time to deal with them.
Most of the primary data were acts of work performed - on their basis, the company’s revenue was regularly determined, reflected in its financial statements.
Read about the preparation of certificates of completed work in this article .
Significant volumes of paper deposits consisted of invoices for purchased materials, payment slips, salary slips and related calculations.
A separate shelf was completely filled with accounting records, declarations, reports to the pension fund and social security, as well as statistical forms.
Each accountant compiled a list of cases with accounting documentation for his area, and the chief accountant systematized all the information in a single table, one of the columns of which was dedicated to the standard storage periods for documents taken from the list.
Table “Retention periods for accounting documents in an organization”
| Document from Landscape Design LLC | Shelf life according to the list |
| Certificates of work performed under contracts for core activities | Within 5 years after the end of the term for which the contract was concluded |
| Treaties and additional agreements thereto | Within 5 years after expiration (unless otherwise specified in specific items of the list) |
| Powers of attorney for receiving money and goods and materials | At least 5 years after the expiration of the power of attorney or its revocation |
| Statements for the issuance of salaries, benefits, financial assistance and other payments | At least 6 years (from 02/18/2020, previously the period was 5 years) In the absence of personal accounts: 50 years - if the documents were completed after 01/01/2003; 75 years old - if documents were completed before 01/01/2003 |
| Register of information on the income of individuals | At least 5 years (from 02/18/2020, previously the period was 75 years) |
| Employment contracts and personal cards of employees | No less than: 50 years - if the documents were completed after 01/01/2003; 75 years old - if documents were completed before 01/01/2003 |
| Time sheets, working time logs | At least 5 years (at least 75 years under dangerous, difficult and harmful working conditions) |
| Information about the income of individuals | At least 5 years In the absence of personal accounts: 50 years - if the documents were completed after 01/01/2003; 75 years old - if documents were completed before 01/01/2003 |
| Annual accounting (financial) statements | Constantly* |
| Accounting policies, chart of accounts, forms of primary accounting documents | At least 5 years |
| General ledger, turnover sheets, account cards, etc. | At least 5 years |
| Fixed asset accounting cards | At least 5 years after disposal of the object |
| Declarations (calculations) for all types of taxes | At least 5 years |
| Calculations for insurance premiums (annual and quarterly) | 50 / 75 years |
| Information submitted to the Pension Fund for individual (personalized) accounting | At least 5 years, in electronic form - 75 years |
| Reporting to statistics: – annual and more frequently, one-time; – semi-annual and quarterly; – monthly – ten-day, weekly | - Constantly*. – 5 years or permanently* in the absence of annual ones. – 3 years or constantly* in the absence of annual, semi-annual, quarterly. - 1 year |
| Correspondence about penalties and fines imposed on the company | At least 5 years |
Do not ignore the * sign in the table. It means that the document must be kept for the entire time the company operates.
All documentation indicated in the table directly or indirectly relates to accounting, therefore, the chief accountant of Landscape Design LLC increased the periods exceeding the 5-year storage period provided for by Law No. 402-FZ to the limits indicated in the list.
Considering that the company has not yet celebrated its 5th anniversary since the start of work, none of the documents presented in the table can be destroyed. To clear out the paper-cluttered premises, the accounting department allocated a special office, where they placed documents awaiting expiration.
See also “The Ministry of Finance reminded how long primary materials need to be stored.”
For more information about the storage periods for tax documentation, documents on insurance premiums, including accident insurance premiums, see the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus.
Retention periods for personnel documents
Federal Law No. 127-FZ dated June 18, 2017 “On Amendments...” introduced a new Article 22.1 on the retention periods for personnel documents into the Law “On Archival Affairs in the Russian Federation” dated October 22, 2004 No. 125-FZ. Now documents reflecting labor relations in organizations between employees and employers must be stored for 75 or 50 years , namely 50 years is the storage period for documents created after January 1, 2003, 75 years is the storage period for documents created before January 1, 2003.
Nuances of accounting for storage periods of accounting documentation
In the practical activities of Landscape Design LLC, there were cases of selling fixed assets at a loss. For the purposes of accounting and tax accounting for fixed assets, the same documents are used. The difference lies only in the recognition of expenses associated with their disposal. This fact must also be taken into account when determining the storage period for documents.
For example, 2 years ago the company purchased a VAZ-21102 car (OKOF code 15 3410010). Based on the fact that, according to the classification of the fixed asset, it belongs to the 3rd depreciation group, the useful life (USI) was set at 5 years. Due to constant breakdowns, it was decided to sell the car at any price offered. The proceeds from the sale turned out to be less than the residual value of the property, and the loss from the sale according to tax accounting standards for 3 years (the remaining SPI) will be evenly taken into account when calculating income tax.
IMPORTANT! The nuances of tax accounting for losses from the sale of fixed assets are reflected in clause 3 of Art. 268 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Read about the specifics of grouping expenses for tax accounting purposes in this material .
Thus, all documents related to the formation of the initial and residual value, the term of the joint venture investment, contracts and acts of sale, as well as certificates and calculations for accounting for losses from the sale of fixed assets must be preserved for at least 4 years after the end of inclusion of the specified loss in the tax base . This is due to the fact that during an audit, tax authorities have the right to examine documents for the 3 years preceding the audit. Thus, documents on the specified fixed asset will have to be stored for at least 9 years.
The case considered is not the only one where the storage period for documents is extended. In the next section we will present other situations.
What documents need to be kept
- If an entrepreneur works with VAT on a common system, then the storage of accounting documents, tax accounting data, any documentation on income received and expenses necessary for calculating taxes, as well as documents confirming tax payments already made must be stored for at least 4 years .
- Accounting statements and primary accounting documents must be stored for at least 5 years.
- An individual entrepreneur must keep all primary accounting and registration documents for individual entrepreneurs, the book of income and expenses (KUDiR) for at least 4 years.
- Documents confirming the payment of insurance contributions to the Pension Fund (PFR), Social Insurance Fund (FSS) and the Compulsory Health Insurance Fund (MHIF) must be kept for 6 years.
- Personal files and cards of employees, including those temporarily hired, employment contracts with employees, documents on dismissal and hiring must be kept for 75 years.
- The labor inspectorate may require any documents on the basis of which you pay wages, bonuses, vacation pay, benefits, and count length of service.
Other cases of increasing the shelf life of primary products
If Landscape Design LLC operated with a loss, and then took it into account when calculating income tax, the documents would have to be kept for the entire period of transferring the loss plus 4 years after it was completely written off. In this case, it is impossible to get rid of either the primary document confirming the loss received, or other certificates and calculations on the basis of which this loss was transferred.
For example, accounting and tax documents for losses incurred in 2020 and taken into account over the next 10 years will have to be stored until the end of 2033.
Read more about the nuances of accounting for losses in the article “How and for what period can losses be carried forward?” .
The storage period for accounting documents will also have to be increased in the following case. Landscape Design LLC provided services to a customer who did not promptly pay for the work performed and did not respond to letters and complaints. The company was not excluded from the state register, but did not repay its debt. Landscape Design LLC was able to take into account bad receivables only in 2020, and all documents of the organization related to this situation will have to be stored until the end of 2023.
Retention period for tax documents
The Tax Code has established a maximum 4 (four-year) period for storing accounting and tax accounting documents that are necessary for the calculation and payment of taxes and contributions (Article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This period also applies to documents confirming the receipt of income, expenses, as well as payment (withholding). ) taxes. A corresponding requirement has been established for tax agents who are obliged to ensure the safety of documents necessary for the calculation, withholding and transfer of taxes for four years. In addition to paying VAT and income tax for foreign legal entities, tax agents, in particular, are employers who calculate and pay personal income tax. When carrying forward losses for profit tax purposes, taxpayers are required to keep documents confirming the amount of the received loss for the entire period when it reduces the tax base of the current tax period by the amounts of previously received losses - no more than 10 (ten) years.
Results
Invoices, certificates of work performed, salary payment statements, reports - taxpayers are required to keep these and many other accounting documents for the periods established by a special list. These terms cannot be reduced, but in some cases they have to be increased (when carrying forward losses, writing off bad receivables, selling fixed assets at a loss).
Sources:
- Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ
- Order of Rosarkhiv dated December 20, 2019 No. 236
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.