Who is required to register a cash register (cash register) with the tax authority?
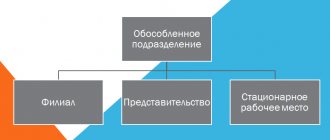
Tax Code of the Russian Federation in Art. 11 calls a separate unit located in a territory different from the location of the parent organization, with independent workplaces equipped for at least a month. The opening of a separate division requires its mandatory registration with the territorial tax authority at its location. To do this, fill out a message in form SO-09-3-1.
A cash register in such a department does not always need to be registered. So, according to clause 2. Art. 2 of the Law “On the Use of Cash Register Equipment...” dated May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ, it is possible to make cash payments and use plastic cards without using a cash register, provided that the buyer is issued a document to confirm the payment:
- payers of the single imputed income tax (UIIT), who are not engaged in retail trade and do not provide public catering services;
- organizations and individual entrepreneurs on OSNO or simplified tax system that provide services (except for catering services);
- when selling tickets on public transport.
However, this opportunity exists only until 07/01/2019. Next, this category of taxpayers will have to worry about purchasing and registering cash register machines.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
Also exempt from the obligation to use cash register systems are organizations and entrepreneurs that provide certain types of services and are engaged in established types of activities, for example:
- sale of securities;
- selling ice cream in kiosks;
- shoe repair, etc.
At the same time, engaging in such activities is not an unconditional basis for refusing control technology. Location features are also taken into account.
Property Relocation: Accounting
When moving inventory, fixed assets and money between the head office and other departments, the method of accounting depends on whether the OP has a dedicated balance sheet.
Important! All divisions maintain accounting records in accordance with the accounting policies of the “head”.
There is no separate balance
In this case, when moving, for example, equipment (OS), an internal transfer should be carried out in analytics.
Example No. 3: transfers to division “A-1” a lathe with an initial cost of 150,000 and depreciation accrued at the time of transfer in the amount of 54,000:
- D 01 "A-1" K 01 "A" - 150000, movement carried out.
- D 02 “A” D 02 “A-1” – 54000, depreciation on the transferred machine was transferred.
The same should be done with other inventory items. When a division does not have a separate balance sheet, cash is handled by the central accounting department, and settlements with suppliers and contractors are carried out through it. In this case, normal postings are performed.
Example No. 4: Organization “B” transfers to division “B-2” materials intended for the repair of the premises in which the OP is located, costing 20,000 rubles. To transport them, “B” hires a transport company (TC), its services cost 3,000 rubles:
- D 10.8 materials in the warehouse in “B-2” K 10.8 materials in the warehouse “B” - 20,000, materials were transferred to OP “B-2”.
- D 23 (23, 25, 20, 44) K 76 – 3000, reflects the costs of transporting materials for repairs.
- D 76 K 51 – 3000, paid for TK services.
There is a separate balance
In this case, account 79 “Intra-business settlements” is used to move property and funds.
When transferring fixed assets in the accounting of the head office, it is necessary to make the following entries (we use the data from example No. 3):
- D 79-1 “A-1” K 01 “A” - 150000, the transfer of equipment is reflected.
- D 02 “A” D 79-1 “A-1” – 54000, depreciation on the machine was transferred.
Postings when transferring inventory items and paying the costs of their delivery (we use the data from example No. 4): D 79-1 “B-2” K 10-8 – 20000, materials for repairs were transferred. Further postings depend on whether the department has a current account.
No invoice (services ordered and paid for by central accounting):
- D 23 (...) K 76 – 3000, transportation costs.
- D 76 K 51 – 3000, payment to the transport company.
There is no invoice (the order for services is made by the OP, and payment is made by the parent organization):
- D 79-2 K 76 - the unit transferred the debt to the TC to the “head”. In accounting for the separation itself, the postings will be as follows: D 23 (...) K 76 - 3000, transportation costs, D 76 K 79-2 - the TC debt was transferred to the head office.
- D 76 K 51 – paid for TC services
No invoice (OP independently ordered and paid for the services):
- For division “B-2”: D 23 (...) K 76 - 3000, transportation costs are reflected, D 76 K 51 - payment to TC is transferred.
- The OP can first receive funds for expenses, then in postings “B-2” there will be posting D 51 K 79-2 - funds have been received from the central accounting department for settlements. In this case, wiring D 79-2 K 51 will be reflected in the “head” control unit.
In most cases, the wiring looks like a mirror image, as you've probably noticed. Costs incurred are transferred to the central office by posting D 79-2 K 20, 25, 23, 44. Reverse posting, respectively, is from the head accounting department.
You can read more about taxation in a separate division here.
How is KKM registered?
In accordance with Art. 4.2 of Law No. 54-FZ, an application for registration of a cash register organization can be submitted to any tax authority or through the cash register office. However, attempting to register a cash register in the tax department at the place of registration of the head office does not make sense, since the application will be refused. In accordance with clause 21 of the Administrative Regulations, approved. By order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 29, 2012 No. 94n, cash register equipment of a separate division is registered at its location.
The package of documents required for this includes:
- application for registration of cash register in the form approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated May 29, 2017 N ММВ-7-20/ [email protected]
- KKM passport;
- agreement on technical maintenance of the cash register with the service center.
All documents, except the application, will be returned to the applicant along with the equipment registration card. The tax authority is given 5 working days from the date of acceptance of the documents to enter the necessary information into the register of cash register equipment.
We draw your attention to the fact that it is impossible to register a cash register without first submitting a notification about the opening of a separate division in the form SO-09-3-1. The fact is that now, during registration, the inspector does not have the opportunity to enter the address manually, since it is issued automatically by the program based on the entered information about the addresses registered for the enterprise.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Read us on Yandex.Zen Read us on Telegram
Should - don't: don't guess with a daisy
If you are in doubt whether you need to open the OP or not, most likely the answer is yes, it is necessary. Please note that neither the Tax Code nor the Civil Code contain any restrictions on the number of employees of a separate division, as well as the absence of an order for its creation in internal documents.
There are difficult situations when it is really difficult to understand whether an OP occurs or not:
- We hire an employee in another city to provide services or perform work on the territory of clients (customers). Let's say a company provides cleaning services in another city and hires cleaners. In this case, there is no separate division, because there are no stationary jobs. A similar approach is applied to the situation when a worker (electrician, finisher) goes to the customer’s site. Depending on the position and type of occupation, the employee is drawn up with both a regular employment contract and an agreement on home-based or remote work.
- Construction work is underway. Here you need to consider each specific situation individually.
- Road works are being carried out. In this case, the Federal Tax Service believes that there is no need to create an OP. The work is being carried out “in the field”; there is no talk of any permanent location.
- Storage space is rented or purchased. This is one of the frequent subjects of controversy. There are permanent employees at the warehouse: storekeeper, watchman, loaders, which means that you will definitely need to register an OP.
- Premises in the same building. The company rents an office in a business center and decides to open a cafe on another floor. On the one hand, both premises are located in the same building and, naturally, belong to the same tax office, so it is logical to assume that there is no need to open an OP. The judges confirm this point of view, since they consider one of the signs of territorial isolation to be assigned to a tax inspectorate different from the parent enterprise. On the other hand, tax authorities do not always agree with arbitration practice. Their position is that even if in fact the legal address of the organization and the cafe differ slightly, for example, in the number of the premises, then formally such a difference is already a reason for registering the separate entity. The conclusion is drawn from the definition of OP in Article 11 of the Tax Code, the concepts established by Article 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and the determination of the location of a legal entity (according to paragraph 2 of Article 54 of the Civil Code, this is the place of state registration). You will either have to contact the Federal Tax Service for clarification, or act at your own peril and risk.
- The employee works in coworking mode. A popular way to work outside the home. Freelancers usually resort to it. The point is to engage in some kind of activity in a room where fellow “free artists” gather, perhaps in the process exchanging opinions, achievements and experiences, or simply working in a calm environment. Let’s imagine that a space is rented for an employee under a coworking agreement, is this equivalent to renting an office, is it necessary to organize an OP? In reality, this option involves a short-term rental, usually for a few hours a day, and the employer has no control over such a workplace. This means that it cannot be recognized as stationary and the creation of a separate unit is not required.
Note! Homeworkers and remote workers clearly do not have workplaces controlled by the employer.
Example No. 1: the construction site where the workers are sent is equipped with cabins owned by the organization, the workers are given tools by the employer, and he also controls the progress of the work - there is an OP.
Example No. 2: workers come to the construction site every day from home, safety at the site is monitored not by the employer (subcontractor), but by the general contractor, who also controls the progress of construction. Based on the definition of jobs (Article 209 of the Labor Code), there are none in this case, since construction is not under the control of the employer.
It should be noted that in most cases, tax authorities, regardless of the circumstances, believe that a construction site requires the creation of a separate division.
What if it’s just a room where goods or materials are delivered, unloaded, and picked up, if necessary, by visiting drivers and forwarders? Despite the fact that employees are not constantly in the warehouse, it is considered that there are jobs, and the time spent on them does not matter.
By the way! A similar approach is valid in a situation where an organization has rented or purchased an office, but the employee uses it occasionally.
After the company has decided to create an OP, it is necessary to prepare documents regulating its activities and register it with the Federal Tax Service.
Is it possible to avoid registering at the address of a separate subdivision?
Some entrepreneurs trade using one device in several places or simply do not want to re-register it later and are looking for ways to bypass specifying the address during registration. Let's look at some of these “methods”.
Registration of cash registers for outbound trade
There is an opinion that this is possible if you enter the phrase “outbound trade” in the address line of the application. However, this is not true. The popularity of this opinion is due to the incorrect interpretation of the letter of the Department of Tax Administration in Moscow “On the use of cash register machines...” dated 04/17/2002 No. 29-12/17513, which explains the procedure for using cash register machines exclusively for outbound sales (that is, the letter is simply not applicable for other types of sales).
There is a rather narrow definition of the very concept of outbound trade, which can be found in GOST R 51303-2013, approved by order of Rosstandart dated August 28, 2013 No. 582-st. According to this document, distribution trade is understood as small-scale retail trade outside a stationary retail chain, subject to the use of equipped transport and special mobile equipment to be used exclusively in the vehicle.
This significantly narrows the range of possibilities in which such registration will be justified and legal. In particular, if an entrepreneur uses such a device in the office, there is a violation of the law. After all, the method is acceptable only if trade is carried out directly using vehicles.
However, it must be recognized that the law does not really limit the number of checks that can be issued in one place, and such a solution may well be suitable for those who trade on an ongoing basis using transport (even if he does not move during sales). At the same time, the cash register itself must be able to operate on battery power, that is, be mobile.
Registering a cash register as a backup
The second option is to register the cash register as a backup. Indeed, in accordance with the explanations given in the letter of the Federal Tax Service for Moscow dated February 11, 2005 No. 22-12/9705, it is possible to register a spare cash register marked “reserve” in the address line. However, it is not indicated that it is necessary to register the main cash register before registering the reserve one.
However, there is one caveat: in accordance with clause 21 of the Administrative Regulations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated June 29, 2012 No. 94n, KKM is subject to use in the service territory of the tax division that registered it. This means that if the cash register is used outside this territory, the organization risks being punished in the form of a fine under Part 4 of Art. 14.5 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. Thus, this should not be considered a way to avoid registration at the unit address.
Procedure for registration of cash registers
Sections:
- Background
- New procedure for using cash register equipment
- Modern requirements
- Requirements for fiscal documents
- Registration procedure
- Procedure for using CCP
- Procedure for re-registration and deregistration of cash registers
- Who is exempt from using CCT?
Andrey_Popov / .com
Registration or re-registration of cash registers with the tax authorities is free of charge, in accordance with the procedure established in Art. 4.2 of Law No. 54-FZ. In addition, to the extent that does not contradict the provisions of Law No. 54-FZ, the Regulations on the registration and use of cash register equipment used by organizations and individual entrepreneurs (will cease to apply on July 1, 2020), the Administrative Regulations for the provision of state registration services by the Federal Tax Service cash register equipment used by organizations and individual entrepreneurs in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Administrative Regulations) and Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated April 9, 2008 No. MM-3-2/ [email protected] “On approval of registration application forms cash register equipment, cash register equipment accounting books and cash register equipment registration cards.”
To start working under the new rules, taxpayers need to purchase a cash register that meets the requirements for online cash registers, or upgrade an existing one. It is necessary to purchase a new cash register only for those users who use equipment that is incompatible with the new software and on which it is impossible to install a fiscal drive (FN). Information about the possibility of modernizing a CCP can be obtained directly from its manufacturer, or from an authorized CCP technical service center (CTC).
If a cash register can be modernized, then it must first be deregistered with the tax office.
Before contacting the tax office to register a cash register, the user of cash register equipment must first solve some technical problems. In order to start working with an online cash register, taxpayers need to enter into an agreement for processing fiscal data with a fiscal data operator (FDO) and ensure that the cash terminal is connected to the Internet. Let us note that OFD does not have the right to refuse to conclude such an agreement with the user (clause 6 of article 4.6 of Law No. 54-FZ). The new procedure for using cash register equipment does not require, when registering a cash register, the mandatory submission of an agreement on technical support for the cash register equipment subject to registration with the technical service center.
Need an electronic signature? The GARANT certification center will help you select and purchase an electronic signature certificate for both a legal entity and an individual.
After concluding agreements with the Internet provider and OFD, you can proceed directly to registration procedures.
Previously, the procedure for registering a cash register required the physical presence of an entrepreneur at the tax office. Moreover, I had to visit the tax office more than once. Thus, when registering a cash register, it was first necessary to present it for inspection. Then, after filling out the necessary documents, you had to go to the tax office again to get a KKT registration card. Moreover, a year later it was necessary to bring the cash register to the inspection again in connection with the replacement of the EKLZ. Now all necessary registration actions can be carried out through the cash register account on the website nalog.ru, without the need to appear at the tax office in person. However, to do this, the user will need a strengthened qualified electronic signature. Access to the cash register account can be obtained through the personal accounts of organizations and individual entrepreneurs on the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia (nalog.ru).
Meanwhile, you can also register or deregister a cash register in the classical way - directly at the tax office, and at any, and not just at “your own”, as before (clause 1, clause 10 of article 4.2 of Law No. 54- Federal Law).
The procedure for registering cash register equipment is enshrined in Art. 4.2 of Law No. 54-FZ.
If the user decides to register an online cash register remotely, he will need to send an electronic application to the tax office via the cash register account to register the cash register.
The application for registration of cash register equipment, regardless of the form in which it is submitted to the tax authority (electronic or paper), must contain the following information:
- full name of the user organization or last name, first name, patronymic of the individual entrepreneur;
- User INN;
- address (for online payments – the address of the user’s website) and location of installation (use) of the cash register;
- name of the CCP model and its serial number;
- FN model name and serial number;
- number of the automatic device for calculations (in the case of using a cash register as part of an automatic device for calculations);
- information on the use of a registered cash register in a regime that does not provide for the mandatory transmission of fiscal documents to the tax authorities in electronic form (if such a regime is applied);
- information on the use of registered cash register equipment only when providing services (in the case of registration of an automated system for BSO);
- information on the use of a registered cash register only when making payments using electronic means of payment on the Internet (in the case of registering a cash register intended for use only when making such payments);
- information on the use of cash registers when carrying out the activities of a bank payment agent or payment agent, when accepting bets and paying out funds in the form of winnings when carrying out activities related to organizing and conducting gambling (in case of registration of a cash register intended for use in carrying out such activities) (clause. 2 Article 4.2 of Law No. 54-FZ).
At the same time, the user, no later than one business day after submitting the application, must write in the FN using the cash register:
- CCP registration number received from the tax authority;
- full name of the user organization or last name, first name, patronymic of the individual user;
- information about CCP, including FN.
After receiving the electronic application, specialists from the Federal Tax Service of Russia will, within one working day, check the serial numbers of the fiscal drive and cash register indicated in the application for their presence in the registers and send the user a registration number of the cash register, which will remain unchanged throughout the life of the cash register. Please note that a cash register, information about which is not in the register of cash registers, as well as a cash register that has a FN established and not registered in the register of fiscal drives, are not subject to registration.
FORMS AND FORMS Application for registration of cash register equipment
Other documents
The user, using the cash register itself or the computer-cash system that includes the cash register, must write this number, as well as other information specified by law, into the fiscal drive and generate a registration report, which will be sent by the cash register to the tax authority. The report can also be submitted on paper. All this must be done by the owner of the online cash register no later than one business day from the moment he receives the registration number of the cash register. And the date of submission of the report in electronic form is considered to be the date of its placement in the cash register account or its transfer to the fiscal data operator. As a result, information about a specific cash register and its user will be reflected in the cash register register of the Federal Tax Service of Russia (clause 3, clause 13 of Article 4.2 of Law No. 54-FZ).
Tax inspectors will enter the information provided by the user in the application for registering a cash register in the accounting journal and the cash register registration card (clause 3, article 4.2 of Law No. 54-FZ).
At the end of registration actions with the cash register, the tax authority will send an electronic cash register registration card to the user. This document is generated in the form of a document signed with an electronic signature and sent by the tax authority to the user within five working days from the date of completion of registration through the cash register account or through the OFD (clause 11 of article 4.2 of Law No. 54-FZ).
A user who has received a cash register registration card in the form of an electronic document has the right to receive a corresponding card on paper from the tax authority (paragraph 2, clause 12, article 4.2 of Law No. 54-FZ).
Thus, now all registration actions can be performed remotely - without visiting the tax office directly.
Related documents:
- Federal Law of May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ “On the use of cash register equipment when making cash payments and (or) payments using electronic means of payment”
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 29, 2012 No. 94n “On approval of the Administrative Regulations for the provision by the Federal Tax Service of the state service for registering cash register equipment used by organizations and individual entrepreneurs in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation”
- Order of the Federal Tax Service of April 9, 2008 No. MM-3-2/ [email protected] “On approval of application forms for registration of cash register equipment, cash register equipment registration books and cash register equipment registration cards”
What is the fine if the cash register is not registered?
From 02/01/2017, in the event of detection of violations related to the use of an unregistered cash register or non-compliance with the procedure for its use, the norms of Part 4 of Art. 14.5 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The provisions of this article provide for liability in the form of a fine in the amount of:
- 1500–3000 rub. - for officials;
- 5000–10,000 rub. - for legal entities.
As an alternative to a fine, the rule allows tax officials to limit themselves to warning the violator. However, such a measure is usually applied only when violations are first detected and only if this is the only violation detected. It seems that these measures should encourage entrepreneurs to register cash registers in a timely manner.
***
So, registration of a cash register of a separate subdivision takes place in the territorial body at the place of registration of the subdivision itself, but you should not evade it, since administrative liability is provided for violating the registration rules.
General provisions on a representative office that is a structural unit
Civil legislation of Russia establishes the right of every organization of the Russian Federation to have and create separate divisions (Article 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
No structural unit can be physically and legally located at the address of the main organization. In any case, the address must be different from the parent company. Such a structure must have jobs whose validity period exceeds 30 days (Article 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). A structural unit of a company is a branch, representative office or other separate division (Article 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and Article 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation