Powers of a branch and separate division of an organization
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Article 48 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that legal entities can be organized to engage in entrepreneurial activities.
They are created not only for profit, but also for other non-commercial purposes. Article 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that to carry out their tasks, separate parts of the company that are not separate legal entities can be created. They must be located at a different address than the organization and are created for a period of at least 30 days. Permanent jobs should be created there. This provision is fixed in Article 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (TC RF), which explains the basic concepts that are used in the formulations in the normative act.
This definition applies regardless of whether the activities are reflected in the statutory documents of the organization itself.
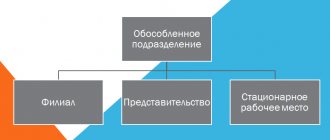
Article 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that separate parts can be branches or representative offices. In their pure form, the latter perform only the functions of representing the interests of the company in a given region and work with requests; they do not conduct commercial activities. A branch is organized for the purpose of making a profit; it is engaged in the same activities as the legal entity itself or in some separate areas. In particular, it can perform the functions of representation.
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation in Article 55 provides for the need for state registration for such separate parts. Currently, it is believed that the list of names of separate parts is open and is not limited to these two options.
Article 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation considers a separate part as being located at a different address and equipped with stationary workplaces. In this case, additional registration in this article is not required. However, the creation of a unit must be reported to the Federal Tax Service within 30 days.
If a license is required for an activity, it is not required to be obtained separately. For work, it is enough that the parent organization has the document.
Conditions under which a branch acquires the right to independently conclude contracts
Since the branch performs the functions of a company, in whole or in part, it can also participate in transactions with various counterparties. However, he can do this as a representative of the company:
- In order to have such powers, the manager must have a power of attorney to carry out transactions in certain areas of activity.
- Since activities are regulated by the company’s charter or other internal documents, they should allow agreements to be signed by the boss.
Subject to the specified conditions, the agreements concluded by him have legal force.
The individual parts have the following features:
- they do not participate in various kinds of legal relations regarding changes in organizational structure and the like, since they are not subjects;
- even having its own property, such a division will not dispose of it (the owner is the company, and it can only do with it what is allowed to it);
- the division is managed by an employee who has been appointed as the head of the enterprise for this purpose;
- activities take place according to the rules established by management (a detailed description of the powers of the division’s management can be found in the power of attorney; any actions other than this list are illegal);
- performs all the functions of its founder or part of them, if this is determined by internal regulations, but does not have the capabilities of a legal entity (change of ownership of property, reorganization or liquidation).
Separate parts are often organized for the following purposes:
- expanding its activities;
- creation of new shopping centers and service points;
- opportunities to operate closer to your clients;
- in cases where transport costs can be optimized in this way.
There may also be other reasons for expanding activities.
Agreements between branches of the same company
When carrying out economic relations between parts of one organization, it is necessary to take into account that they are not subjects of civil law relations. They cannot enter into agreements on their own behalf or be responsible for fulfilling the provisions of the signed document.
Even if the manager signs the agreement, he is actually signing a document from the parent organization, and it is the parent organization that assumes the responsibilities according to the signed document.
Thus, if we assume that a document is proposed for signing, where the parties designate divisions of the same company, then in fact both of them would be signed on behalf of the same organization.
The situation, therefore, boils down to the fact that two divisions of one company want to organize economic interaction between themselves (moving inventory, transferring documents or exchanging information, for example). To do this, it is enough for the management of internal orders to organize the implementation of the relevant work, that is, to organize internal document flow.
General structure of the organization
Separate divisions themselves do not have legal status, so they:
- are not subjects of legal relations;
- do not have civil legal capacity;
- are part of the whole company.
Often, ignorance of the above provisions creates confusion, for example, you can often find the wording “OP with the rights of a legal entity,” while the OP itself is part of a legal entity, and the law prohibits the entry of one legal entity. faces to another.
The emergence of a separate division may take place after the fact, without being reflected in the company’s constituent documentation. To do this, it is necessary that the workplace outside the company’s location be stationary and last more than a month.
Agreements with counterparties
When registering, it is necessary to take into account the fact that the rights and responsibilities of this unit are determined by:
- the charter of the enterprise, which states what tasks are assigned to this structure;
- internal orders and instructions of the enterprise.
When concluding transactions with counterparties, responsibilities are acquired not by a separate division, but by the parent company.
With clients
If the director signs the agreement, he must indicate in it the party for whom he negotiated. Here you can do two things:
- Indicate that the party is the part of the company that he is obliged to manage.
- Write that he signs the papers on behalf of the entire enterprise.
He has the right to do this, provided that there is a executed power of attorney in which he is given the authority to enter into transactions.
Therefore, the conclusion of transactions with clients will occur in the usual way. In this case, the signatory will appear in the documents only formally. The signing will be made between the executive bodies of two business entities.
With suppliers and service organizations
The conclusion of a transaction in this case occurs in the same way as signing with counterparties. Here agreements are concluded with suppliers by the parent organization.
The difference is that the contract must specify the address for the provision of services or performance of work by service companies. It is clear that the agreement can only be concluded in relation to premises or objects that are on the balance sheet or transferred for use for the needs of the branch. It is illegal to enter into transactions with other offices.
Paying taxes
The head of the OP, as a responsible person, is responsible for the financial and economic operations of the unit entrusted to him. Provided that these operations were carried out on the basis of documents signed by the manager and had a corresponding order, and the actions themselves did not go beyond the competence of the manager.
The head of the OP is responsible for concealing, understating the income of the unit or concealing any objects of taxation. Also, the head of the department will be responsible if the tax service is not promptly provided with accounting reports, calculations and other documents necessary for paying taxes. If the listed violations occur, the manager is fined in the amount of 2-5 minimum wages, and in case of repeated violation - 5-10 minimum wages.
Also, the head of the OP in special cases may be brought to criminal liability, for example, in case of deliberate concealment of income or distortion of data in documents submitted to the tax authorities. In this case, the manager faces up to 4 years of imprisonment, followed by restrictions on holding certain positions.
A sample order for the creation of a separate division is signed by the head of the enterprise.
A table of transport tax rates by region in 2020 is presented here.
From here you will learn about the rules for entering information into the EFRS.
Can a separate division enter into an agreement?
According to Art. 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and taking into account the provisions of paragraph 2 of Art. 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, separate structural divisions of an organization include any geographically remote departments with permanently equipped places for work. At the same time, in accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, these entities are not legal entities - therefore, they do not have their own civil personality and legal capacity. Separate divisions operate in accordance with the regulations approved by the parent organization. The head of a remote representative office or branch acts on the basis of a power of attorney, which determines the scope of his powers (clause 129 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation “On the application by courts of certain provisions of Section I of Part One of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation” dated June 23, 2015 No. 25). Such powers may include signing agreements with counterparties.
Therefore, the conclusion can be drawn as follows: independently, that is, on its own behalf, a separate division does not have the right to enter into contracts, but its management can do this on behalf of the legal entity. person (parent company) on the basis of a power of attorney. At the same time, it is worth paying attention to the position of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, which prescribes recognizing as committed on behalf of a legal entity. persons of the transaction, if the right to do so is established in the power of attorney, even if the agreement itself does not indicate that the agreement was concluded on behalf of the parent organization (paragraph 2, paragraph 129 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation No. 25).
Don't know your rights? Subscribe to the People's Adviser newsletter. Free, minute to read, once a week.
Rights and obligations of the Employer
2.1.
The employee manages the activities of a separate structural unit of the Employer in the manner determined by _______________________________________________________ (charter, regulations on the unit, etc.) 2.2. In internal organizational relations, the Employee, as the head of a separate structural unit of the Employer, acts within the powers granted to him by the regulations on the unit, job description (other local regulatory legal acts of the Employer), in external civil and economic relations related to the implementation of the activities of the unit, on behalf of the Employer on based on the power of attorney issued to him.
2.3. The Employee has the right to represent the interests of the Employer in relations with employees of a separate structural unit within the framework of the powers determined in accordance with the labor legislation of the Russian Federation, the constituent documents and local regulations of the Employer, in particular: ____________.
2.4. The employee has the right to:
- providing him with work stipulated by this employment contract;
- ensuring safety and working conditions that comply with state regulatory requirements for labor protection;
- timely and full payment of wages in accordance with their qualifications, complexity of work, quantity and quality of work performed;
- …
The employee has other rights provided for by the labor legislation of the Russian Federation and this employment contract.
2.5. The employee is obliged:
- conscientiously fulfill his labor duties assigned to him by this employment contract, comply with established labor standards;
- comply with the internal labor regulations in force at the Employer, labor protection and labor safety requirements, and other local regulations of the Employer directly related to the Employee’s work activities, with which the Employee was familiarized with signature;
- observe labor discipline;
- treat with care the property of the Employer, including the property of third parties located at the Employer, if the Employer is responsible for the safety of this property, and other employees;
- immediately inform the Employer or immediate supervisor about the occurrence of a situation that poses a threat to the life and health of people, the safety of the Employer’s property, including the property of third parties owned by the Employer, if the Employer is responsible for the safety of this property, and the property of other employees;
- during the validity period of this employment contract and after its termination for _____ years, not to disclose secrets protected by law (state, commercial, official and other secrets) that became known to the Employee in connection with the performance of his job duties;
- …
The employee is obliged to fulfill other duties provided for by the labor legislation of the Russian Federation and this employment contract.
3.1. The employer has the right:
- demand from the Employee the conscientious performance of duties under this employment contract;
- adopt local acts directly related to the Employee’s work activities, including internal labor regulations, labor protection and occupational safety requirements;
- bring the Employee to disciplinary and financial liability in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
- encourage the Employee for conscientious, effective work;
- unilaterally change the content of the Employee’s powers as the head of a separate structural unit without changing the labor function;
- …
The employer has other rights provided for by the labor legislation of the Russian Federation and this employment contract.
3.2. The employer is obliged:
- provide the Employee with work stipulated by this employment contract;
- ensure the safety and working conditions of the Employee that comply with state regulatory labor protection requirements;
- provide the Employee with equipment, tools, technical documentation and other means necessary to perform his job duties;
- pay the full amount of wages due to the employee on time;
- …
The employer fulfills other obligations provided for by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreements, agreements, local regulations and this employment contract.
Contents of the agreement with the branch, sample
When concluding a contract through a representative office, special attention should be paid to the following points:
- Precise identification of the party on whose behalf the contract is concluded. Since the separate division itself has no rights in this matter, first comes the introductory part, for example: “Vilar LLC, hereinafter referred to as the Buyer, represented by the director of branch No. 1 of Vilar LLC, acting on the basis of a power of attorney...”. Then the exact details of the mentioned power of attorney are indicated.
- Indication of the address and details in the final part of the contract. Since the agreement is concluded on behalf of the parent organization, the address and details of the legal entity. persons must be included in the contract without fail. At the same time, it is not forbidden (and in some cases it is even advisable) to additionally indicate the address and details of the branch whose head signs the agreement.
- In terms of content, contracts concluded in the parent organization and in the branch are fundamentally no different from each other. However, it would be useful to additionally specify the addresses of shipment, unloading, delivery, etc., if the transaction is carried out at the location of the branch, as well as the procedure for resolving disputes through the court, if contractual jurisdiction is assumed.
Thus, despite the fact that the branch cannot enter into agreements on its own behalf, execution of the transaction at the location of the separate division is quite likely. You can download a standard sample agreement with a branch of a legal entity using the example of a supply agreement on our website.
Answers to questions about work books
An open webinar was held at the School of Accountants, at which expert Evgenia Konyukhova explained in detail how to correctly fill out a work book. Read a selection of the most interesting questions from webinar listeners.
How to fill out work books correctly
Question 1. After recording the appointment, the personnel officer signed and stamped the next line. What to do?
Answered by Evgenia Konyukhova, presenter of the webinar “Employment books: standards of maintenance, corrections, records upon dismissal”:
“The stamp is not affixed after the appointment is recorded, only after the dismissal is recorded. To make corrections, follow the Rules approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 16, 2003 No. 225, and the Instructions approved by Decree of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated October 10, 2003 No. 69. Algorithm of actions:
Important: after the words “The entry number... is invalid” in column 3, you must rewrite the correct version of the employment entry. The date of employment in this situation also fits into column 3.”
Download answers to questions from webinar listeners about work books.
Question 2. Is it necessary to indicate the address of a separate unit in the work book?
If an employee is hired to work in a separate unit, then in the employment contract it is enough to indicate the name of the organization and the locality. The parent organization will be the employer in relation to the employees. Therefore, in the employment contract, employment order, work book, the parent organization must be indicated as the employer.
Is it necessary to indicate the address of a separate unit in the work book in accordance with the employment contract and, accordingly, make an entry when changing a separate unit in one organization? Evgenia Konyukhova believes that in this situation it is necessary to look at what is specified in the employment contract and the employment order. “We don’t write the address, but the name of the locality must be indicated if it is present in the name of the separate subdivision,” the expert notes.
Question 3. Part-time work has become the main job. How to put it in a work book?
The Labor Code does not regulate the transfer from a part-time job to the main place of work.
Situation. The employee is registered as an accountant in another company, and this place of work is his main place of work. It is necessary to formalize his transfer to another company as a director, and now this will be his main place of work, and leave his job as an accountant part-time. How to correctly fill out entries in a work book?
Will the changes happen automatically? Of course not.
Expert Evgenia Konyukhova said that there are different points of view on this issue, and according to one of them, such changes need to be formalized through additional agreements to the employment contract. But the expert categorically does not recommend adhering to this position:
“It is correct to first dismiss the employee from the position of accountant from his main place of work. The next day, hire him to his main place of work as a director. Make a record of hiring as a director. On the same day, you can draw up documents for employment as an accountant, but on a part-time basis (remember about the limitation on working hours established by Article 284 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
That is, first there must be a record of dismissal from the main place of work, where the employee works as an accountant, and only then is employment formalized for the main place of work as a director.”
You should remember the rule of clause 20 of Government Decree No. 225 of the Russian Federation: a record of part-time work is made only at the request of the employee and only at the main place of work. If an employee wants a record of part-time work as an accountant to be included in his employment record, then to his main place of work, where he will work as a director, he will need to bring a certificate or a copy of the order for employment as a part-time accountant.
Question 4. How to prepare an insert for a work book?
The insert is issued if the sections of the section are completely filled out. In this case, you need to enter new information. In practice, a more common situation occurs when the sheets containing information about the work are filled out. Do not enter data in another section - such actions by the personnel officer are regarded as unlawful.
A webinar listener wrote about the following problem:
Situation . When dismissing an employee, the employer made several entries about part-time work and an entry about dismissal in the section on awards, correcting the title of this section by striking out. How to correct this situation and is it necessary to do it? Maybe a new employer should just create an insert and make a note about the appointment already in the insert?
Evgenia Konyukhova recalled that a new employer never corrects the mistakes of other employers. The main rule for correcting records: the one who committed the violation corrects it.
The new employer simply sews in the insert, in the “Employment Information” section, writes the name of his organization in column 3, and puts down the next number in the “Employment Information” section of the work book. In this case, the numbers in the information about awards are not taken into account.
Question 5. Is it possible for foreigners to have two work books?
Difficulties often arise when hiring people from other countries. Workers rarely provide work books filled out in accordance with the rules in force in the Russian Federation. In the case of citizens of other states, there are two algorithms of action:
The first option is suitable if a foreign citizen has a work book on Russian or Soviet letterhead. In the second case, you can have two work books as an exception. This right is granted to Crimeans and residents of Sevastopol (letter of the Ministry of Labor dated November 24, 2014 No. 14-2/B-862).
The employer opens a Russian-style book. You can make a copy of a Ukrainian document, but the employer does not take the original; he only keeps a new work book of the established form.
Situation. We employ a Ukrainian with a residence permit in the Russian Federation. His work record is Ukrainian. Previous Russian employers made entries in this work book, and in the Ukrainian part. Can we do the same? If you open a new Russian work book, should you indicate something about previous work?
Evgeniya Konyukhova commented on this situation as follows: “See if this is really a Ukrainian-style work book. If this is a bilingual work book from 1975 (Soviet form), then you can continue to make entries. If the work book is truly of the Ukrainian type, then it is necessary to create a new work book that is recognized as valid on the territory of Russia.
You can calculate information about places of work in Ukraine in the insurance record from this work book, but the entries of Russian employers in such a work book are not taken into account in the work record.
Certificates from these places of work will be needed to include them in the length of service. When drawing up a Russian-style document, the employer does not fill out a foreign copy of the book; the employee only works using one book.”