Basic requirements for the issuance of workwear
Requirements for providing workers with PPE
An employee engaged in labor activity must be provided with all necessary means to protect himself from dangerous and harmful factors. First, you need to understand what factors of the labor process we are talking about:
- harmful factors are factors, when exposed to substances harmful to health (industrial dust, excess gas content in the air and the presence of hazardous substances that a person inhales, electromagnetic radiation, physical overload, etc.);
- dangerous factors are factors in the presence of which a worker may be injured (open moving parts of machine equipment that cannot be protected with a casing due to the conditions of the technical process).
If an employer has any doubts about what kind of workwear and PPE to issue to an employee, then you can always refer to the certification card; this document contains all the details, so that errors are excluded.
But in addition to SOUT, there are requirements at the legislative level:
- The labor legislation states that the employer is obliged to provide the employee with special PPE and RPE clothing in accordance with the standards.
- The standards establish what special clothing is required for a certain category of workers and types of production.
- The requirements of documents developed at the state level can be recorded in local regulations for the enterprise and organization.
Under any circumstances, the requirements of regulations adopted at the legislative level must not be violated.
Under what conditions are personal protective equipment issued to employees?
For employees who work in harmful or dangerous conditions, at special temperatures or in polluted conditions, PPE is issued by the employer free of charge (Article 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 4 of the Appendix).
PPE, as well as flushing and neutralizing substances, are provided to employees:
- in accordance with standard standards for issuing PPE and the corresponding type of substances;
- based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions.
The company, taking into account the position of the trade union, has the right to establish its own standards for the free provision of PPE, which presuppose a higher quality of equipment for workers with PPE than is provided for by standard standards. These internal corporate standards must be recorded in the company’s local legal acts (clause 6 of the Appendix).
The company, also taking into account the position of the trade union, can provide the issuance of personal protective equipment alternative to those provided for by the standard standards, provided that these personal protective equipment provide equivalent protection of workers from exposure to hazardous and harmful factors.
Workers can only be issued PPE that has a certificate or declaration of conformity certifying that the PPE meets the safety criteria. If the protective equipment belongs to the dermatological category, then its use is possible only if there is a conclusion from the sanitary and epidemiological services or a certificate confirming the state registration of PPE of the appropriate type (clause 8 of the Appendix).
The employer does not have the right to purchase or rent PPE that does not have a valid certificate or declaration of conformity.
The protective equipment issued to the employee must be returned to the company upon dismissal or transfer to another position in which the use of personal protective equipment is not necessary. In addition, if the issued PPE expires, it must be returned to the employer for write-off.
On the procedure for providing PPE
How is special clothing, safety footwear, PPE and RPE properly provided at enterprises? The support strategy is developed in a regulatory act, and the requirements of the Labor Safety Rules must be taken into account.
Recommended provisioning algorithm:
- A standard is being developed to describe the sequence of receipt and issuance of PPE. This document must be familiarized with farm managers, storekeepers, occupational safety specialists, as well as economists in supply departments. This document must set out a clear sequence of providing workers with special clothing and other protective equipment.
- It is necessary to fill out an application for the purchase of PPE and workwear for a year. Applications are collected from all departments of the enterprise, and then summarized into a document, on the basis of which the required amount of funds for the purchase is calculated. This will make financial planning easier.
- Next comes the purchase of special clothing and PPE directly for workers. When purchasing, you should take into account that all purchased products must comply with government requirements and standards.
- After purchase, it is necessary that the purchased product undergoes incoming inspection so that it truly meets quality requirements. Plus, a representative of the supply department must request a certificate for workwear, which must indicate GOST in accordance with the SOUT map.
- Direct issuance of workwear and PPE is carried out in the departments where employees work. In this case, the issuance is carried out against a signature on the personal clothing issuance card.
Contents and sample
The implementation of the Regulations in the company must be approved by order of the manager. There is no prescribed form for the Regulations.
This document may consist of several points:
Normative references
This paragraph indicates the main legislative acts on the basis of which the Regulations are developed.
Terms and Definitions
If this clause is present, it can contain explanations of all terms that will be used further in the document.
General provisions
Here is the basic information
information regarding the issuance of protective clothing, for example:
- reasons for this;
- the employer’s obligation to familiarize new employees with the approved standards for issuing it;
- existence of liability in relation to the manager if he does not comply with established requirements;
- the employee’s obligation to use the funds issued to him correctly and carefully.
The procedure for drawing up standards for issuing workwear
This paragraph may indicate exactly how its required number for personnel is determined, as well as which types of it are interchangeable. The timing of its intended use (a specific period or until wear) may also be indicated.
Rules for submitting applications for workwear
These applications can be issued either annually or unscheduled, in case of changes in the staffing table or the hiring of new employees.
Procedure for issuance, delivery and accounting
The following information is noted here:
- on the basis of what documents can an employee receive special clothing;
- which service of the enterprise he needs to contact;
- how clothing can be marked when issued;
- for how long it is issued;
- features of the issuance of clothing for certain categories of persons (for example, temporary employees, trainees or students).
The period when a particular type of clothing is issued (for example, winter and summer) can also be determined. If it is damaged due to the fault of the employee, management may force him to compensate the cost of the damage in the manner prescribed by Art. 39 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Disposal of workwear
Most often it is established that this occurs after its service life has expired or if it has been severely damaged. This procedure is formalized by a special act.
Reception and storage
The main part of the clothing is most often stored in the enterprise warehouse (or in other special premises), where they are issued to the employee. For the latter, specially equipped rooms can also be provided. All features of the arrangement of these premises at a particular enterprise can be displayed in this paragraph.
Care measures
These activities may vary and include:
- clothing labeling;
- rules for washing or cleaning it;
- the need for sanitization, etc.
Specific activities may depend on the characteristics of a particular field of activity.
A sample Regulation on the issuance of workwear at an enterprise can be downloaded here.
On standard standards for issuing PPE
Contents of standard standards for issuing PPE
For convenience, standard standards for issuing PPE have been developed. This document is used by experts when conducting a special assessment of working conditions. They consist of the following columns:
- names of positions and professions;
- list of personal protective equipment;
- standards for issuance (once every 12 months or every 24 months, before wear, once a quarter, etc.);
- information depending on climate zones and how much is supposed to be issued.
A number of items have notes with information about what is required additionally for certain purposes.
As a clear example, we can consider the following: a turner works on the machine equipment entrusted to him, that is, he is required to wear a cotton suit, boots or sandals, a headdress, and a protective screen. A turner cannot perform work wearing cotton knitted gloves, since he works with constantly moving open mechanisms, and gloves can get into the danger zone and the employee can get injured, but when cleaning chips, a worker cannot do without gloves, he will get hurt.
Then the note states that to clean the workplace it is necessary to provide the employee with gloves. Further, the same turner performs work on removing snow from roofs; therefore, he must be provided with warm special clothing, a safety harness, a helmet and other equipment.
That is, it turns out that the issuance of special clothing, PPE and RPE should be issued specifically to perform immediate tasks, as well as differentiated, based on what additional duties are assigned to the employee. This may be prescribed in the standards, determined on the basis of certification of workplaces by expert organizations, but they must be observed.
Responsibilities of the employer to provide collective and individual protective equipment to employees
In accordance with Art.
221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to provide workers of his organization with special clothing and personal protective equipment (PPE) if they have to work in difficult or health-threatening conditions. Allowing employees to enter the workplace without the necessary protection or with faulty PPE is strictly prohibited. Let's look at how legislation regulates the provision of workers with protective equipment. In Art. 209 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides an interpretation of the concept of “personal protective equipment”. These are special clothing and equipment used to protect against pollution, as well as to prevent or reduce the impact of harmful and dangerous production factors on the worker’s body. Such means include special clothing, safety shoes, etc., as well as flushing and neutralizing agents. The employer is obliged to ensure that employees are informed about the protection they are entitled to at the stage of concluding an employment contract. At the same time, the employee becomes familiar with the rules for the provision and use of PPE, as well as with the standard standards for issuing them corresponding to his profession and position.
Responsibility for providing personal protective equipment at the enterprise lies entirely with the employer. When purchasing workwear, the employer must check the availability of certificates and declarations of conformity confirming its safety. The issuance and use of funds that do not have the appropriate documents is not permitted. In addition to the above, the employer is responsible for the care and timely repair of personal protective equipment. These procedures include:
- cleaning;
- degassing;
- deactivation;
- disinfection;
- dust removal;
- neutralization;
- repair.
The employer does not have to provide the care themselves. He has the right to enter into an agreement for the provision of such services with a specialized organization. The employer is also responsible for the quality storage of unused work clothing and equipment; a separate room is allocated for this purpose at the enterprise.
The employer may, taking into account the opinion of the trade union, replace the personal protective equipment specified in state regulations with similar ones that provide equivalent protection from undesirable production factors. Depending on the financial and economic situation and the recommendations of the trade union, our own standard for providing personal protective equipment for workers may be established, improved in comparison with standard protection standards. Or softer standards may be introduced regulating the provision of personal protective equipment; the established procedure according to GOST standards for workwear cannot be reduced, nor can the conditions for their use be tightened.
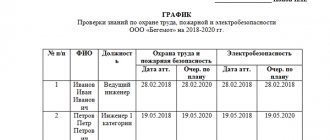
Management must monitor the provision of personal protective equipment to employees at each workplace, as well as analyze their effectiveness (control in this case is carried out by comparing the actual items issued with the norms for issuance), check compliance with the rules for providing personal protective equipment (the presence of a personal accounting card filled out in the prescribed manner). The assessment of the provision of workers with personal protective equipment is documented using a separate protocol.
How is workwear issued?
Organization of distribution of workwear
It is known that the same professions are found in different production sectors, but the standards for issuing are the same for all. It is important for an employer to correctly assess which PPE should be chosen for a particular employee.
When issuing workwear, certain rules should be followed, but if the employer additionally provides the employee with PPE, then he does not violate the requirements, but, on the contrary, increases the degree of protection. However, based on some criteria, it is necessary to understand in more detail whether legal requirements are being violated, otherwise the inspection authorities may also show interest in this circumstance.
If for some reason special clothing was purchased from a foreign manufacturer, then it should be checked for compliance with the requirements of Russian standards. In this case, certificates, declarations and other documents must be drawn up, the information in which must comply with the requirements of Rospotrebnadzor.
The timely issuance of PPE must be ensured by the employer in full compliance with the requirements of the regulatory framework. It is also necessary to organize points for the repair and washing of workwear and personal protective equipment at the enterprise.
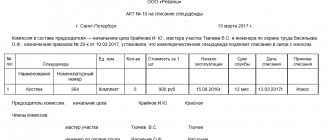
To record the issue of special clothing to an employee, it is necessary to organize the work as follows:
- create a special clothing issuance card for each employee;
- keep records of the issuance of personal protective equipment against signature;
- control the timely replacement of special clothing and personal protective equipment;
- when issuing, be guided by the special assessment card for working conditions;
- replace PPE that has expired ahead of schedule;
- There must be certificates of conformity for workwear, footwear, PPE and RPE.
Supply of PPE to workers: employer’s responsibility and control over the fulfillment of its obligations
If the employer cannot provide the employee with the necessary PPE, then the employee has the right not to begin performing his work functions, while the company will be obliged to pay him a salary for downtime (clause 11 of the Appendix). Therefore, if an employer fails to comply with the legal requirements to provide employees with personal protective equipment, he primarily experiences direct economic losses.
In addition, if employees are not provided with PPE, the employer may receive a fine from the labor inspectorate based on Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. If the failure to issue protective equipment led to an incident at work, the employer may be held criminally liable in accordance with Art. 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Control over the employer’s fulfillment of obligations to equip employees with PPE can be exercised by:
- labor inspectorate - in accordance with Art. 353 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- trade unions - in accordance with Art. 370 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Tips for a safety engineer
Control over the use and issuance of special clothing and personal protective equipment is assigned, as a rule, to an occupational safety engineer or another person appointed by order of the manager.
But in order not to get into trouble before the inspection authorities, the responsible employee is recommended to:
- Prepare a list of all working employees, and update it every month, this will make it easier to navigate who was issued what.
- Opposite the last name of each employee, you should indicate what exactly he is entitled to, that is, list all workwear and shoes, as well as PPE and RPE.
- Opposite each name of PPE it is necessary to indicate which GOST requirements apply to them.
- At least once a month, communicate with the supply manager to know the problem of missing personal protective equipment, how they are washed and repaired, and by what rules they are issued.
- When checking personal cards for issuing personal protective equipment, you should pay attention to the presence of employee signatures, as well as the issuance deadlines and compliance with the requirements of the certificates.
- It is also necessary to monitor the washing and repair of workwear.
- Monitor how workers use protective clothing when performing work.
Providing workers with personal protective equipment
Memo for the employee
I.
Each employee has the right to be provided with personal and collective protective equipment in accordance with labor protection requirements at the expense of the employer (Article 219 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Personal and collective protective equipment for workers (PPE) are technical means used to prevent or reduce the impact of harmful and (or) hazardous production factors on workers, as well as to protect against pollution.
Thus, workers must be provided with personal protective equipment at work:
- with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions,
- performed under special temperature conditions,
- associated with pollution.
There are individual PPE and general use PPE. Individual PPE is issued to employees, while general-use PPE is assigned to workplaces. PPE must be marked.
The employer is obliged, in accordance with established standards, to provide at his own expense:
- timely issuance of special clothing, special shoes and other personal protective equipment, flushing and (or) neutralizing agents that have passed mandatory certification or declaration of conformity;
- their storage, washing, drying, repair and replacement (Article 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
After issuing PPE, the employer is obliged to ensure that measures are taken to:
- testing and checking the serviceability of PPE used by employees,
- storage of personal protective equipment in a specially equipped room,
- care of personal protective equipment, which includes washing, cleaning, disinfection, degassing, decontamination, dust removal, neutralization.
Mandatory requirements for the acquisition, issuance, use, storage and care of special clothing, footwear and other personal protective equipment are established by the Intersectoral Rules for Providing Workers with Special Clothing, Special Footwear and Other Personal Protective Equipment (approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated 06/01/2009 No. 290n).
The provision of PPE to employees is carried out in accordance with the standard standards for the free issuance of special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment that have been duly certified or declared conformity, and based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions.
The employer may establish standards for the free distribution of special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment to employees, which, compared to standard standards, improve the protection of employees from harmful and (or) dangerous factors present in the workplace, as well as special temperature conditions or pollution.
The employer is obliged to inform employees about the personal protective equipment they are entitled to.
Workers are not allowed to perform work without PPE issued to them in the prescribed manner, as well as with faulty, unrepaired or contaminated PPE.
II.
The employee is obliged to correctly use personal and collective protective equipment.
The employer organizes control over the correct use of personal and collective protective equipment by employees.
When issuing PPE, the use of which requires practical skills from workers (respirators, gas masks, self-rescuers, safety belts, mosquito nets, helmets, etc.), the employer is obliged to ensure that workers are instructed on the rules for using the said PPE, the simplest ways to check their functionality and serviceability, and also organizes training on their use.
III.
Accounting and control over the issuance of PPE to employees at the specified time is organized by the employer.
The issuance and handing over of PPE to an employee is recorded by an entry in the personal record card for the issuance of PPE.
PPE issued to an employee must correspond to his gender, height, size, as well as the nature and conditions of the work he performs.
At the end of the working day, employees are prohibited from taking personal protective equipment outside the employer’s territory or the territory where work is carried out by the employer - an individual entrepreneur.
In some cases, when, due to working conditions, the specified procedure cannot be followed (for example, in logging, geological work, etc.), PPE may remain with employees during non-working hours.
Employees must notify the employer (or his representative) of the failure (malfunction) of PPE.
If PPE is lost or damaged in the designated storage areas for reasons beyond the control of employees, the employer will issue them with other serviceable PPE.
The employer is obliged to ensure the replacement or repair of personal protective equipment that has become unusable before the end of the wearing period for reasons beyond the control of the employee.
PPE returned by employees after the wear period has expired, but suitable for further use, is used for its intended purpose after taking measures to care for it (washing, cleaning, disinfection, degassing, decontamination, dust removal, neutralization and repair).
The suitability of the specified PPE for further use, the need for and the composition of measures to care for it, as well as the percentage of wear of the PPE are established by an official authorized by the employer or the labor protection commission of the organization (if any) and are recorded in the personal record card for the issuance of PPE.
IV.
The employer ensures that employees must use PPE.
Workers are not allowed to perform work without PPE issued to them in the prescribed manner, as well as with faulty, unrepaired or contaminated PPE.
For refusal to use PPE, an employee may be subject to disciplinary action in accordance with Art. 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation as for failure to perform or improper performance through his fault of the labor duties assigned to him.
During underground work, failure by an employee to use personal protective equipment issued to him in the prescribed manner is grounds for removal from underground work (Article 330.4 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
V.
Responsibility for the timely and full issuance of PPE that has been duly certified or declared conformity to employees in accordance with standard standards, for organizing control over the correct use of it by employees, as well as for the storage and care of PPE rests with the employer (his representative).
If the employee is not provided with personal and collective protective equipment in accordance with established standards, the employer does not have the right to require the employee to perform work duties and is obliged to pay for the downtime that arises for this reason in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Part 6 of Article 220 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
An employee has the right to refuse to perform work, since performing it if PPE is not provided in the prescribed manner may pose a danger to the life and health of the employee.
Types of PPE
In accordance with GOST 12.4.011-89, introduced back in the USSR, PPE is divided into classes depending on their purpose:
- special protective clothing (overalls, jackets, trousers);
- foot protection (boots, shoes), including from vibration and electric current;
- hand protection products (mittens, gloves, oversleeves), including dermatological products (pastes, ointments, creams);
- head protection equipment (hard hats, helmets);
- face protection equipment (face shields);
- eye protection (goggles);
- hearing protection (headphones, earplugs);
- respiratory protection equipment (gas masks, respirators);
- fall protection equipment (safety belts, cables);
- dermatological protective products (skin cleansers);
- complex protective equipment (devices that provide protection for the respiratory system, vision, hearing, as well as the face and head).
Legislative framework regarding workwear
The state has provided quite a lot of nuances related to the wearing of special clothing by workers in potentially harmful and dangerous professions. These norms are enshrined in various regulations, including:
- for most professions from all industries - Order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation No. 997n dated December 9, 2014;
- for professions where “signaling” workwear is required - Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated April 20, 2006 No. 297;
- for professions where warm workwear is required - Decree of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated December 31, 1997 No. 70.
Intersectoral rules for supplying personnel with free protective clothing, footwear and other personal protective equipment, which also regulate its storage, care, replacement procedure, etc., were approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation of June 1, 2009 No. 290n.
Additionally, provisions regarding workwear are given in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- Art. 212 obliges the employer to purchase at its own expense and issue to staff the required protective clothing free of charge;
- Art. 221 defines issuance standards.
About 70 specific documents approve industry-specific features of the use of necessary workwear: for workers in agriculture, water and forestry, coal and chemical industries, pharmaceuticals, metallurgy, road work, etc.
NOTE! The standards determine not only the type and quantity of protective clothing issued, but also the features of its operation.
What is workwear
At many enterprises, employees are required by internal regulations to wear uniforms, the purpose of which is to maintain corporate culture and unify the appearance of employees. Special clothing should be distinguished from uniforms.
Workwear refers to personal protective equipment (PPE). It is not designed for distinction or identification, but primarily to ensure safety during work activities. Special clothing (“overalls”) is designed to prevent damage to the health of workers, if the characteristics of their profession can provoke this.
The main differences between workwear and branded clothing:
- wearing branded clothing is not mandatory, and special clothing is provided unconditionally;
- uniform regulations are introduced by internal regulations, the procedure for issuing and wearing special clothing is provided for by state legislation;
- The employer can entrust the purchase of branded clothing to the employees, while purchasing and issuing special clothing to the staff is his direct responsibility;
- the main function of branded clothing is demonstration, and that of special clothing is protective;
- branded clothing is essentially a uniform, and special clothing is personal protective equipment.