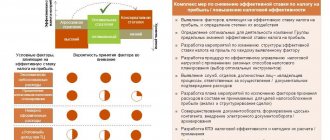
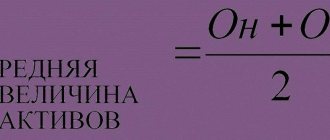Of course, accountants usually do not have any difficulties with calculating VAT - they do not even use any special formulas, because for them it is a normal routine work, organized to the point of automation. However, the question of how to correctly make calculations often worries other company employees, such as sales managers, marketers, and even those in management positions. It is logical that managers should be well versed in financial documents and understand where this or that figure comes from, otherwise they can easily get into trouble during important negotiations.
Let's discuss what VAT is, where it is reflected and how to calculate it in different ways depending on the situation. For clarity, let's look at a few examples.
What is VAT?
The abbreviation stands for as follows: VAT is a value added tax ; it is indirect, and with its help the state budget receives part of the cost of goods (works, services) created in the production process (performance of works, provision of services).
Knowing the formulas, it will not be difficult to subtract VAT from the amount
As a rule, people who are far from economics are interested in: who added value and how? The answer lies on the surface - every participant in the production cycle. That is, when purchasing a product, the buyer pays tax to the seller, but deductions to the budget occur even earlier than the final sale, since each link in the chain pays tax on that part of the cost of the product that was added by it.
In Russia, value added tax was introduced in 1992, and today in our country, according to Article 164 of the Tax Code, there are three rates:
- 18% – considered basic and used by default in most cases;
- 10% – used in the sale of some printed publications, children's goods, certain categories of medical equipment, as well as a number of food products (bread, milk, sugar, some meat products, etc.);
- 0% – applies to exported products and some specific things, such as licenses, duties and letter stamps.
Important: all the nuances relating to the calculation and payment of value added tax are covered in detail in Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. To keep your finger on the pulse and keep up to date with current information about debt obligations to the budget, it is best to access your personal account on the tax service website. Of course, this will take some time, and data on debts is sometimes required immediately - then you can use services that offer a search for tax debt by TIN.
Bid
According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, there are currently three options for the value added tax rate for different categories of goods.
The general VAT rate is 18 percent. It is paid by taxpayers whose products do not fall into the preferential category according to current legislation.
A rate of 10 percent is paid upon sale of:
- essential food products, such as meat, fish, dairy, cereal groups;
- non-food products for children, such as school supplies, shoes, knitwear, toys;
- some types of medicines, both domestic and imported;
- pedigree livestock products.
A zero tax rate is applied when selling:
- products in the customs union;
- services related to the international transportation of goods by various modes of transport such as air, rail, road, sea;
- work performed by organizations for the transportation and pumping of petroleum products;
- space activities;
- extraction of precious metals or their production from scrap.
The amount of value added tax changes periodically and there is a tendency to reduce its size. Initially, when this tax was introduced, its size was 28 percent. Product groups are also undergoing changes.
https://youtu.be/lUtsVSOP5Ts
How to calculate VAT?
Most business entities operating on the general taxation system are payers of value added tax. To avoid problems with fiscal authorities, it is very important to clearly understand how it is calculated. If you do not understand the calculation mechanism, then it is quite easy to find yourself in a situation where a completed transaction for the sale of any product will not bring profit due to the fact that the employee responsible for pricing simply forgot about the markup. It is necessary to have a good understanding of how to correctly make calculations in order to set adequate prices for the goods sold.
Important: as a rule, in practice, when calculating tax, two situations may arise:
- There is an amount that does not take into account the tax surcharge. How to calculate VAT on the amount?
- There is an amount including tax. How can I find out its value directly, that is, VAT included? And the amount without surcharge?
Thus, it is very important to decide: what do you have initially and what do you want to get as a result of the calculations? Let's look at how to calculate tax in different cases.
This is interesting: Business in the production of photo tiles
See also: How to calculate vacation pay?
Calculation of VAT on the amount
Here, as a rule, no one has any problems, because even a junior school student can calculate 18 or 10 percent of the amount.
The calculation is carried out using the formula : VAT = Amount without VAT * Tax rate / 100. Since we are considering the option when the rate is 18 percent, the formula can be simplified: VAT = Amount without VAT * 18 / 100 = Amount without VAT * 0.18 .
VAT calculation including
Calculating VAT also means determining the amount of tax already included in the existing figure. For example, they say this: the price of a product is 1000 rubles, including VAT. In order to calculate value added tax in this case, you need to use the formula.
VAT = Amount including VAT * Tax rate / (100 + Tax rate). Knowing that the tax rate is 18 percent, it is easy to write the formula differently: VAT = Amount including VAT * 18 / 118.
If you need to calculate the amount without tax, you can go in two ways:
- Amount excluding VAT = Amount including VAT – VAT;
- Amount excluding VAT = Amount including VAT / 1.18.
Of course, any of the formulas will lead to the same result; you just need to focus on how it is more convenient for you to make calculations.
Calculation of the amount including VAT
Why is it usually required and what formula to use? Let's imagine that there is a price excluding VAT, resulting from an increase in the cost of the product by the desired profit. Before selling, it is necessary to calculate the amount including VAT, which will be the final price for the buyer.
This can be done in several ways, for example, using one of two formulas:
- Amount with VAT = Amount without VAT + VAT;
- Amount with VAT = Amount without VAT * 1.18.
How to calculate the tax included in the price: calculation based on a rate of 20 percent
Another calculation formula is used if it is necessary to allocate tax from an amount that already includes VAT. Such a need may arise when receiving an advance payment (advance payment) or when specifying in the contract the cost of the goods, including tax. Then the shipping documents and the invoice (advance invoice) indicate the amount of tax calculated at the estimated rate.
How to calculate VAT at a rate of 20 percent in this case is shown in the figure:
These two calculation methods are also modifications of the same formula. The results of the calculations, if they are made without errors, should coincide in both cases.
Let us show with an example how to calculate VAT at a rate of 20% of the amount including tax.
Example 2
The agreement between Foggy Bereg LLC and Rybolov LLC states that the supply of products is carried out on the basis of a 30% prepayment. Products of Foggy Bereg LLC are taxed at a rate of 20%. Rybolov LLC transferred an advance payment of 325,100 rubles to the supplier. When issuing an invoice for the advance payment, the accountant of Foggy Bereg LLC calculated VAT:
VAT = 325,100 × 20 / 120 = 54,183.33 rubles.
To check, the calculations were made in the second way:
VAT = 325,100 / 1.2 × 0.2 = 54,183.33 rubles.
The calculation results coincided. This amount was indicated on the invoice.
When filling out an advance invoice, accountants often make mistakes, which subsequently lead to a tax gap and additional VAT charges during audit. How to correctly fill out an advance invoice is described step by step in the ready-made solution ConsultantPlus. Subscribe in 2 steps and get trial access completely free.
Examples of VAT calculation and allocation
Guided by the above formulas, let's look at examples of how to correctly allocate value added tax if it is already included in the price, and charge it when the price is indicated without a surcharge.
See also: Order a Sberbank debit card - online application
Example No. 1
Dream House LLC is engaged in trade in building materials. An order has been received for a batch of red bricks in the amount of 1200 pieces. The price of one brick is 9 rubles excluding VAT. Tax rate – 18%.
It is necessary to calculate VAT and calculate the total amount with 18% tax; To do this, we will use the formulas presented earlier:
- Cost of a batch of bricks excluding VAT = 9 * 1200 = 10800 rubles;
- VAT on the amount = 10800 * 0.18 = 1944 rubles;
- Cost of a batch of bricks including VAT = 10800 + 1944 = 12744 rubles.
Tip: usually a faster calculation method is one that is performed in one step, so you can not calculate VAT separately, but immediately multiply the amount excluding VAT by 1.18. Then the cost of the batch including VAT = 10800 * 1.18 = 12744 rubles.
Example No. 2
Landysh LLC sells garden products. The buyer wants to purchase one greenhouse, its price list is 35,400 rubles including VAT. Let's calculate the amount of tax (at a rate of 18%) and the price of the greenhouse without a surcharge, referring to the formulas indicated above:
- VAT = 35400 * 18 / 118 = 5400 rubles;
- The price of the greenhouse without VAT = 35,400 – 5,400 = 30,000 rubles.
This is interesting: How you can make money for free on Odnoklassniki: all possible ways
You can carry out the calculation in another way - simply divide the existing figure by 1.18, and then subtract the resulting number from the original one to find out the tax amount. Then:
- Price without VAT = 35,400 / 1.18 = 30,000 rubles;
- VAT = 35400 – 30000 = 5400 rubles.
To check the correctness of the calculation , we will charge tax on the price received: 30,000 * 1.18 = 35,400.
Fast VAT calculation
In order not to use the above formulas for calculating VAT, accountants often use so-called coefficients. Here's an example of how quickly taxes are calculated:
- for example, calculating VAT on the amount
34600 *1.18 = 40828 rub.
- reverse operation for the second example (subtracting VAT from the total cost of goods or services):
16300 * 0.152542 = 2486.44 rubles.
But in this case, you need to remember that the coefficients do not reflect the true essence of VAT calculation. The slightest change in the rate will lead to the loss of the meaning of the applied coefficient. Therefore, you should calculate the VAT amount correctly and use simple formulas for calculations.
https://youtu.be/9Ft0JDNs4pk
In what document is the allowance indicated?
Usually, when selling a product, performing work or providing services, a package of documents is collected, which includes an invoice and a delivery note (or a certificate of completion, etc.). The documents that are drawn up upon sale indicate the following information:
- Cost without VAT;
- The amount of tax charged to the buyer;
- Total payable including VAT.
Important: companies using the general taxation system need to carefully monitor the documentation: if a product is purchased for the purpose of subsequent resale, and there is no invoice with allocated VAT, then it is impossible to obtain a tax deduction for this operation according to the law. Therefore, before concluding a transaction, it would be useful to assess the reliability of a potential partner - you can find information about a legal entity or individual entrepreneur by using the counterparty search by TIN.
How to simplify the calculation procedure
Legal individuals calculate the amount of value added tax using the 1 C “Accounting” software package. The software package allows you to systematize the accounting of tax data and simplifies the work of accountants.
Individual entrepreneurs who have a small number of transactions carried out during the month can calculate taxes using a calculator located on the Internet. With its help, you can easily determine the amount of tax that is included in the cost of the product. But in this case, a certain inconvenience arises with system accounting. After calculating the VAT amount, it must be recorded either on paper or on electronic media, i.e. double work is being done. In order to simplify accounting and automate as much as possible the procedure for calculating and accounting for tax, it can be calculated using xls files. In the file, mark up the table and write the formulas necessary to calculate VAT amounts when purchasing and selling goods. Thus, tax calculation and system accounting are carried out simultaneously. The capabilities of the xls file will allow you to automate VAT accounting as much as possible for individual entrepreneurs who are payers of this tax and it is not advisable for them to purchase the 1C software package.
Let's sum it up
Organizations located on OSNO work with VAT and are payers of this tax, unless otherwise provided by law for any reason. That is, tax must be included in the final cost of the product offered to the consumer. Calculating it is not difficult if you have minimal knowledge of mathematics. In fact, there is no point in memorizing formulas; it is enough to have logical thinking and a calculator. It is important not to get confused and understand the difference between the price without VAT and the price with the surcharge included. Companies that plan to receive a tax deduction at the end of the reporting period should take a responsible approach to collecting documents - all transactions must be accompanied by invoices.
See also: How to top up Megafon balance from a bank card?
Of course, sometimes situations arise when some points are overlooked, resulting in the formation of tax debts, which can be found out online if you monitor the Federal Tax Service service. Today, such information is easy to find out even for individuals - it is possible to discover a debt from bailiffs by last name in a couple of minutes; Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs most often use their TIN to track outstanding obligations.
VAT calculator online
The VAT calculator allows you to calculate and allocate VAT: calculate the amount with and without VAT. In the table below, enter the values of the amount on which you want to allocate VAT or charge it.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
In order to calculate VAT, you can use the online calculator presented above. But if you don’t have an online calculator for calculating VAT at hand, you can easily calculate it yourself using a simple formula.
Results
So, in the article we talked about how to calculate VAT 20 from an amount that does not include tax, and how to calculate the amount of tax at a 20% rate if the total amount is known along with the tax included in it. Despite the fact that now any accounting program includes automatic calculation of VAT, accountants need to be able to do all the calculations themselves; this will help check the issued documents and not miss any accounting errors.
***
You will also be interested in reading the materials that we wrote specifically for our Zen channel.
An example of calculating tax at a rate of 20% of the amount
We will show with an example how to calculate VAT 20% when the cost of shipped products without tax is known
Example 1:
On January 23, 2020, Stroyles PJSC ships plywood in the amount of 150 sheets to PromStroyMag LLC. The price of one sheet is 850 rubles. without VAT. Sales of this type of product from January 1, 2019 are subject to a VAT rate of 20%. The accountant of PJSC "Stroyles" needs to issue a set of documents for shipment (waybill and invoice) indicating the total cost of plywood and VAT.
First, the accountant calculated the cost of shipped plywood without VAT by multiplying the price of one sheet by the number of sheets shipped:
850 rub./sheet x 150 sheets = 127,500 rub.
At the next stage, the accountant calculated the VAT amount based on the allowed rate:
RUB 127,500 x 20% = 25,500 rub.
The final action will be to calculate the total cost of plywood sold, taking into account tax:
RUB 127,500 + 25,500 rub. = 153,000 rub.