Transactions that are reflected in accounting on account 71
Account 71 in the accounting department is intended to reflect the company’s settlements with its accountables, i.e., with persons who received money on account from the company to pay for any of its needs.
Such expenses may include:
- procurement of goods and materials;
- payment for work or services;
- expenses associated with business trips.
Only persons working for the company under an employment contract or within the framework of the GPA can be accountable. The issuance of money on account can be carried out on an ongoing basis or on a one-time basis.
The list of employees who receive money regularly is approved in the order of the manager. It also indicates the period for which the employee is given the company's money. To receive money one-time, the employee must write an application indicating the amount and period for which it is required.
The employee who received the money, in accordance with clause 6.3 of the instructions of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation “On the procedure for conducting cash transactions” dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U, must report on expenses no later than 3 days:
- after the end of the period for which the money was issued;
- completion of a business trip;
- the end of the period of incapacity;
- coming out of vacation.
Accountable persons report by filling out an advance report. How to reflect in accounting the expenses of an accountable person and exchange rate differences on an advance report in foreign currency? The answer to this question can be found in a ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus experts. If you don't already have access to the system, get a free trial online.
Operations on account 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” are carried out in accordance with the requirements of the Chart of Accounts, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 30, 2000 No. 94n.
Accrual and write-off of debt
Cash may be issued to employees for the following purposes:
- to pay for transport services;
- to pay for communication services;
- to pay for utilities;
- to pay the costs of renting property;
- for the acquisition of material supplies for business needs;
- for the acquisition of fixed assets, intangible assets, etc.
As we have already said, funds are issued for reporting in three ways, which are reflected in accounting as follows:
State institution (Instruction No. 162n)
Budgetary institution (Instruction No. 174n)
Autonomous institution (Instruction No. 183n)
Issuing funds in cash through the institution's cash desk
Transferring funds to an institution's debit card
Receiving funds from a card or paying using a card
This is interesting: Claim against a legal entity
Transferring funds to an employee’s bank card
When receiving funds, the accountable person incurs a debt, which remains with him until the submission of an advance report and (or) return of the unused amount. If the deadlines for submitting an advance report and returning funds established by the regulations on settlements with accountable persons are not met, then grounds arise for collecting such receivables.
According to Art. 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, funds not returned on time, for which the accountable person has not accounted, may be withheld from his salary.
The decision to deduct from the employee’s salary should be made no later than one month from the date of expiration of the period established for the return of the advance, and provided that the employee does not dispute the grounds and amount of the deduction.
In the accounting records of institutions, operations for the accrual and retention of debt will be reflected as follows:
State institution (Instruction No. 162n)
Budgetary institution (Instruction No. 174n)
Autonomous institution (Instruction No. 183n)
Withholding the debt of an accountable person from wages
Reducing the debt of an accountable person through deductions from wages
Example 1 . An employee of a budgetary cultural institution received 3,000 rubles on the institution’s debit card as a report. to purchase stationery using funds received from income-generating activities. The funds were completely withdrawn from the card. Based on the advance report, stationery was purchased for 2,500 rubles. The remaining 500 rubles. the employee did not return it either to the cash register or to the card. According to his application, these funds were withheld from wages.
These transactions will be reflected in the accounting of a budgetary institution in accordance with Instruction No. 174n as follows:
Funds were transferred to the institution's debit card
Received funds from the card for reporting
Stationery goods were accepted for accounting on the basis of an advance report
The debt of the accountable person is withheld from his salary
The debt of an accountable person is written off after it has been deducted from wages
If the accountable person disagrees, deduction can only be made by court decision. If the court finds the debt collection unfounded, then the institution must write it off as unrecoverable.
Other conditions in accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation under which receivables cannot be collected are:
- expiration of the limitation period (Articles 196, 197 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- death of a citizen-debtor (Article 418 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- impossibility of fulfilling an obligation (when this is caused by a circumstance for which neither party is responsible) (Article 416 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- adoption of an act of a state body declaring the debt unrealistic for collection (Article 417 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Uncollectible receivables from the moment they are recognized as such in the manner established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, an act of the chief administrator of budget revenues, are written off from the balance sheet of the institution and accepted for off-balance sheet accounting in account 04 “Debt of insolvent debtors” (clause 339 of Instruction No. 157n (in ed. Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 6, 2015 N 124n)).
Uncollectible receivables are written off from the balance sheet based on inventory results, written justification and an order (instruction) from the head of the institution.
Accounting for this debt is carried out during the period of possible resumption, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, of the debt collection procedure, including in the event of a change in the property status of the debtors, or until the insolvent debtors receive funds to repay the debt within the specified period, until the execution (termination) of the debt otherwise does not contradict the law way.
When the procedure for collecting the debt of debtors is resumed or funds are received to repay the debt of insolvent debtors on the date of resumption of collection or on the date of crediting the accounts (personal accounts) of the institutions with the specified receipts, such debt is written off from off-balance sheet accounting with simultaneous reflection on the corresponding balance sheet accounts of settlements on receipts.
Debt is written off from off-balance sheet accounting is carried out on the basis of a decision of the institution’s commission on the receipt and disposal of assets if there are documents confirming the termination of the obligation by the death (liquidation) of the debtor, as well as upon expiration of the period for the possible resumption of the debt collection procedure in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
No other clarifications on this issue have been provided at this time.
Let's consider how the above explanations can be used in practice.
Based on the results of the inventory, this debt was recognized as unrecoverable.
We propose to reflect these facts of economic life in the accounting of an autonomous institution as follows:
Account 71 active or passive
To understand whether account 71 is active or passive, you need to understand what the postings reflected on it show.
Accounting account 71 is a synthetic account, the analytics of which are carried out for each accountable amount. It can have a credit and debit balance both for analytical accounts and for the account as a whole. Therefore, account 71 in accounting is classified as active-passive accounts.
At the same time, this is essentially an active account. After all, what is shown here are settlements with employees for amounts received to pay for the company’s needs, and not at all settlements for “hidden lending” to the organization by its employees in the form of payment for production and business expenses.
When preparing financial statements, the balance of settlements with accountable persons on account 71 is shown in detail. The debit balance of account 71 is shown as part of short-term receivables on line 1230, and the credit balance is shown as part of short-term accounts payable, which is shown on line 1520.
Small enterprises that have the right to keep records in a simplified manner in accordance with clause 4 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ, reflect credit balances in line 1230 “Financial and other assets”, and credit balances in line 1520 “ Accounts payable".
How debt is written off
The mechanism for writing off each debt is very specific. All existing cases may differ radically from each other. To write off the balances of accountable amounts, you should do the following manipulations:
- Set the start date for the limitation period. If a person was obliged to return the money and report on July 7, 2020, then July 8 is considered such a date.
- Then count three years from this date. In this case it is July 8, 2020.
- After which the amount of money is considered uncollectible and is written off in accounting against the reserve for doubtful debts.
Please note that a write-off is not a cancellation. For five years, the debt should be reflected in the balance on account 007.
Reflecting receivables and payables, even for an experienced accountant, sometimes poses a problem. All money in the organization’s circulation must be recorded when preparing accounting records. Therefore, you need to monitor periodically changing reporting rules.
You can learn about settlements with accountable persons from the video:
https://youtu.be/3HkNkofSHaA
Attention! Due to recent changes in legislation, the legal information in this article may be out of date!
Our lawyer can advise you free of charge - write your question in the form below:
Free consultation with a lawyer Request a call back Still have questions? Call the number and our lawyer will answer all your questions for FREE
What does the debit of account 71 show?
The debit of account 71 shows the issuance of funds for reporting to employees of the organization in correspondence with accounts reflecting the accounting of funds:
- Dt 71 Kt 50 - the employee was given money for household needs from the company’s cash desk;
- Dt 71 Kt 51 (52) - money was transferred to the employee from the company’s current or foreign currency account for travel expenses,
Where:
accounts 50, 51, 52 - accounts on which funds are kept. The operation shows the advance of expenses made by the employee in the interests of the company. Such transactions are reflected in the left table on the front side of the expense report. The debit balance of 71 accounts consists of funds remaining in the hands of the accountants.
Nuances of issuing funds against an advance report from the cash register (posting Dt 71 Kt 50)
The main regulatory legal act regulating the process of issuing funds to accountants is the instruction of the Bank of Russia “On the procedure for conducting cash transactions...” dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U.
According to paragraph 5 of these instructions, it is allowed to pay funds only to your employees (both full-time and those drawn up under GPC agreements).
Payment algorithm:
- Receive a written application from the employee (from August 19, 2017, another document sufficient for payment is the manager’s order, Bank of Russia instruction No. 4416-U dated June 19, 2017), written in free form, indicating the following information:
- purpose of receiving funds;
- amounts;
- the period for which the money is issued;
- executive visas;
- dates.
- Check the balance of the accountant. Until 08/19/2017, clause 6.3 of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation Directive No. 3210-U prohibited the issuance of funds on account to an employee who had not reported on the previously received amount. As of August 19, 2017, this ban has been lifted, but the check will still not be superfluous, since it will exclude unjustified payments if there is a balance registered with the accountable person.
- Issue a cash receipt order.
- Issue money by making an entry in the accounting records: Dt 71 Kt 50.
The legislation does not provide for a specific period for which money can be issued. But if the debt is not repaid for a long period of time, tax authorities will most likely reclassify such a payment as a loan or consider it the employee’s income and charge additional personal income tax. At the same time, such decisions will be made by tax authorities taking into account the principle of reasonableness of calculations.
The law also does not provide for a maximum amount for reporting. At the same time, the rule of the 100 thousand limit does not apply to the issuance of cash to employees on account (clause 6 of the instruction of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated October 7, 2013 No. 3073-U).
IMPORTANT! If an employee pays in cash with counterparties on behalf of the organization, then under one agreement you can pay no more than 100,000 rubles.
If the employee has not spent the funds issued for the report, he must return them after the accounting department accepts the JSC. In this case, wiring Dt 50 Kt 71 is done.
The legislation provides for the possibility of transferring funds against an advance report to an employee’s salary card (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated August 25, 2014 No. 03-11-11/42288).
In the purpose of payment when filling out the payment form, you should indicate that the funds transferred are accountable.
In this case, it is possible to attach documents to the JSC confirming the fact of payment by bank card.
The wiring in this case will be as follows: Dt 71 Kt 51 (52).
By transferring from his bank card, the employee can also return unused accountable amounts, indicating in the payment its appropriate purpose. The wiring here will be as follows: Dt 51 (52) Kt 71.
The issuance of funds to an employee can be carried out in several ways.
The simplest and most common way is to issue money from the cash register. In this case, the cashier, at the time of issue, formalizes the operation with an expense cash order.
Until mid-2020, when issuing money, the employee must fill out an application for the issuance of the amount. This had to be done by any employee of the organization, including the director. Applications were allowed not to be filled out when reimbursing excess reporting and issuing daily allowances for business trips.
Since 2020, changes have been made to this procedure. The company can continue to use statements, or issue an order from the manager, which will indicate the full name. accountants, amounts and deadlines for reporting on funds received.
Attention! If there is no application or order, or if they are drawn up incorrectly, fines of up to 50 thousand rubles may be imposed on the company and responsible persons.
The application for the director should differ from the forms of ordinary employees - in it he does not ask for a report, but gives an order to perform this action.
The latest amendments to the procedure for cash transactions allow the issuance of a new amount if the employee has not yet reported the old one. Previously, such a step was prohibited.
In addition to cash, reports can also be issued by transferring from a current account to an employee’s card. For this step, he fills out an application and includes in it the bank details for making the payment.
If the application is not completed, the tax authority, upon inspection, will decide that income (salary) was transferred and will charge additional personal income tax on the amount. Also, the payment order must indicate that it is the issuance of the report.
If the issue is made to a card, then the employee can attach a receipt from the terminal, ATM, bank statement and similar forms as a supporting document. If the employee is on a business trip and an additional daily allowance is transferred to him, then there is no need to fill out another application. But you will need to report all amounts at the same time.
Attention! If the employee has not spent the accountable amount in full, then after completing the advance report, he must return the unused balance back to the cashier
What does account credit 71 show?
Credit 71 of the account shows expenses made by the accountant for the needs of the organization. At the same time, the debit side of the transaction indicates the accounts on which the costs of purchasing goods and materials, services, etc. are kept. They show for what purposes the money received under the report was spent:
- Dt 10, 11, 41 Kt 71 - inventory items paid by the accountable were capitalized;
- Dt 19 Kt 71 - VAT issued by suppliers is accepted for accounting;
- Dt 76 Kt 71 - paid for the services of a third party;
- Dt 20, 26, 44 Kt 71 - reflects the payment of costs associated directly with the needs of the main production, general economic needs or with the sale of goods;
- Dt 50 (51) Kt 71 - the accountant returned unused money to the cash desk or to the company’s current account,
Where:
Subscribe to our newsletter
Read us on Yandex.Zen Read us on Telegram
- accounts 10, 11, 41 - accounts for recording material assets;
- account 19 - “VAT on acquired values”;
- accounts 20, 26, 44 - accounts for recording costs for main production, economic needs or sales of goods;
- account 76 - “Settlements with other debtors and creditors.”
These entries to account 71 are made after the accountable person submits the advance report and are reflected in the right table on the front side of the advance report.
The credit balance of the account shows the presence of overspending on the accountant.
Situation two: a credit balance has formed on account 71 “Settlements with accountable persons”
It happens that there is not enough money in the company's cash register to issue it on account. In this case, an employee (most often a manager) purchases goods or pays for services for the organization from personal funds. After which he prepares an advance report and submits it to the enterprise. The accountant, in turn, makes an entry to the credit of account 71, thereby reflecting the company's debt to the employee. The debt will remain until there is cash in the cash register and the cashier will reimburse the funds spent. Sometimes the credit balance on account 71 is not written off for several months or even years.
There is nothing in this situation that is against the law. In fact, a purchase from personal funds is a special case of overspending the accountable amount, and it is provided for in the advance report form**. There is a special field for the details of the consumables issued when reimbursing an employee for overspent money. The logic is this: since it is permissible to partially pay for the goods from personal funds, then it is not forbidden to pay in full with your own money.
This is interesting: Accounting for inventories in a budgetary institution 2020
True, difficulties may arise when accounting for goods and services purchased with employee money. It is possible that tax authorities will argue that this product (or service) does not belong to the company. Therefore, it is impossible to include its cost in expenses and deduct VAT.
In practice, many chief accountants try to avoid a credit balance on account 71. To do this, they act in one of two ways.
The first method is to draw up an interest-free loan agreement, under which the employee allegedly lends the company a certain amount of money. The accounting department brings them to the cash desk and then issues them to the same employee for reporting. He spends the funds, submits an advance report, and mutual settlements with him as an accountant go to zero. In this case, the company remains in debt, but not to the accountable person, but to the lender.
The second method is to repurchase from the employee goods (or services) that he purchased with his own money. And in this case, the organization owes a debt, but not to the accountable person, but to the supplier.
Both methods have their drawbacks. In the first case, inspectors may consider that the company received taxable income in the form of unpaid interest on the loan. In the second case, they may find fault with the employee-seller and charge him personal income tax on the proceeds.
We believe that it is more reasonable to reflect these transactions as they are, that is, in account 71. But it would not hurt to play it safe and issue an order at the beginning of the year allowing purchases from employees’ own funds. And supporting documents should be drawn up not for an individual, but for an enterprise.
Postings and accounting of unreturned imprest amounts
Amounts not returned on time by the accountable person are shown on credit account 71 in correspondence with account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables”:
Dt 94 Kt 71 - writing off amounts not returned by the accountable as shortages.
Thereafter, depending on the circumstances, such amounts may be reflected as follows:
- deductions from the employee’s salary - Dt 70 Dt 94;
- other settlements with employees - Dt 73 Dt 94.
The unspent amount of the account can be withheld from the employee’s salary only within one month after the date by which the advance must be returned (Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The deduction is made on the basis of a written order from the manager with the consent of the employee.
In all other cases, this amount is included in other expenses with the employee.
Note! According to Art. 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the amount of deduction cannot exceed 20% of the wages paid to the employee.
Debt of accountable persons
Return to Accountable Persons
The debt of accountable persons is subject to monthly revaluation in connection with changes in the exchange rate of the ruble against foreign currencies in the generally established manner. The procedure for writing off exchange rate differences is determined by the accounting policy adopted by the enterprise regarding exchange rate differences.
The debt of accountable persons to the enterprise and the enterprise to accountable persons must be shown in detail in the accounting registers.
Repayment of the debt of an accountable person to the enterprise is shown using the corresponding entry in the credit of account 71 with the amount within the established standards being debited to the corresponding expense account.
Accounts receivable include the debt of accountable persons, suppliers upon expiration of the payment period, tax authorities upon overpayment of taxes and other obligatory payments made in the form of an advance. It also includes debtors for claims and disputed debts.
The debit balance shows the debt of accountable persons to the enterprise. Money for reporting is issued from the cash register.
When it is established that the debts of accountable persons have been written off without submitting relevant supporting documents confirming the expenses incurred, accountable amounts that were unreasonably written off from employees without deduction from wages, on the basis of Articles 2 and 7 of the Law of the Russian Federation on personal income tax, are subject to inclusion in the total taxable income. the income of these employees of the calendar year in which the amounts were received by them.
The debit balance of account 71 means the debt of accountable persons for advances received.
The balance of account 71 reflects the amount of debt of accountable persons to the enterprise or the amount of unreimbursed overexpenditure.
The balance of this account reflects the amount of debt of accountable persons to the enterprise or the amount of unreimbursed overexpenditure.
In the first case, they mean the debt of accountable persons for advances issued to them for business trips and operating expenses within the deadlines established for the submission of reports, as well as suppliers and contractors for payment for goods.
What can the balance sheet show for account 71
The balance sheet for account 71 allows you to see the process of forming balances on the synthetic account in the context of its analytics.
The analytical attribute (subconto) on which the statement is constructed is the accountable persons.
The balance sheet is formed over a certain period of time and allows you to control:
- incoming and final debt of accountable persons to the organization;
- incoming and final debt of the company to employees;
- amounts received for reporting;
- amounts reported by accountables.
It consists of 7 columns:
- the first indicates the score and its analytical sign;
- in the 2nd and 3rd - the balance at the beginning of the period;
- in the 4th and 5th - debit and credit turnover of account 71;
- in the 6th and 7th - the balance at the end of the period.
A separate final result is displayed for each column of the table.
Account 71 in accounting: characteristics and postings with examples
Account 71 of accounting is an active-passive account “Settlements with accountable persons”, used to record issued accountable amounts and return unspent amounts.
At enterprises, employees may be allocated funds to account for business expenses, the purchase of materials or travel expenses.
Let's look at how to keep records of settlements with accountable persons and examples of accounting entries for account 71.
Account 71 in accounting
Account 71 is active-passive, so the account balance can be either debit or credit.
- Dt account 71 reflects the amount of money received by the employee;
- CT account 71 reflects the expenditure of funds.
Analytical accounting for the account “Settlements with accountable persons” is carried out for each accountable person separately.
The procedure for issuing reports
It is allowed to issue money against an advance report only to employees of the enterprise. Accountable amounts are issued in cash from the cash register or transferred non-cash to a bank card.
The main rule when issuing money is that the employee must account for the previously accountable amount received. At enterprises, as a rule, an order is assigned to persons who have the right to receive funds on account, since an agreement on financial liability is concluded with them:
When paying money to an accountable person, the following rules must be followed:
- Check the balance of the accountable person (according to the accounting register data). Reason: clause 6.3 of the instructions of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3210, which states that it is prohibited to issue funds for reporting to an employee who has not reported on a previously received amount.
- Receive a written statement from the employee in any form, reflecting the main details: purpose of receipt, required amount, deadline for submitting the report, date. The application must be endorsed by the head of the company or an authorized person.
A 3-day period has been established when the employee must account for the accountable amounts received, return the funds to the cash desk and submit a report. If the employee does not report on time, then the amount received by him should be withheld from the employee’s income and personal income tax should be charged (Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Wherein:
Important: deductions from an employee can only be made upon written application and no more than 20% of wages (Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If a debt (especially a large amount) of an accountable person has been registered for a long time, then the tax inspector, during an audit, can re-qualify such a payment as a loan or consider it income (paragraph 3 of Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and charge additional personal income tax.
The maximum amount for reporting is not provided for by law, but it is worth considering that if an employee settles accounts with contractors on behalf of the enterprise, then under one agreement you can pay no more than 100,000 rubles.
Advance report
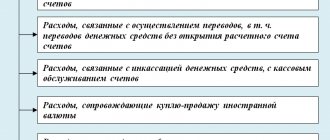
The employee reflects all cash expenses in the advance report. An employee can spend accountable amounts on the purchase of goods, materials, fixed assets, intangible assets, and payment for the business needs of the company.
The diagram shows the types of expenses for account 71 and the primary documents that should be attached to the expense report:
Get 267 video lessons on 1C for free:
If an employee has an overspend on accountable amounts, that is, the employee has spent his personal funds, then the company has the right to reimburse it subject to established procedures.
Examples of typical transactions for account 71
| No. | household operations | Debit | Credit | Foundation documents |
| 1 | Payment of cash to the account | 71 | 50 | Cashier's report, expense order |
| 2 | Transferred to the travel allowance report on a bank card | 71 | 51 | Bank statement, payment order |
| 3 | Funds were transferred to the corporate card account | 71 | 55 | Statement from special accounts |
| 5 | Accepted expenses for the advance report for the purchase of fixed assets | 08 | 71 | Certificate of acceptance of works and services |
| 6 | Materials purchased by the accountable person were capitalized | 10 | 71 | Invoices, transportation documents, acceptance certificate |
| 7 | The amount of expenses for production and economic needs is reflected | 20/26/44 | 71 | Advance report, job assignment, business trip report |
| 9 | Goods for resale purchased by an accountable person were capitalized | 41 | 71 | Advance report and invoices |
| 11 | Return of unspent funds to the cash desk | 50 | 71 | Cashier's report, receipt order |
| 12 | Debt accrued for amounts not returned on time by the accountable person | 73 | 71 | Advance report |
Let's look at practical examples with postings to account 71 for the issuance, expenditure and return of accountable funds.
Example 1. Reimbursement of overexpenses according to the advance report - postings
Employee of Romashka LLC Ivanov I.I. funds were allocated to the report in non-cash form in the amount of 2,500 rubles. (to a bank card) to purchase stationery. In fact, Ivanov I.I. spent 2,840 rubles.
An advance report was drawn up for actual expenses and supporting documents (sales receipt) were attached to the report. The overexpenditure of funds on the advance report amounted to 340 rubles. The funds were credited to Ivanov I.I.
to a bank card.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h5OOL0dUlDk
Romashka LLC has generated entries for account 71:
| Dt | CT | Description | Amount, rub. | A document base |
| 71 | 51 | To the bank card of Ivanov I.I. funds transferred for household needs | 2 500 | Payment order |
| 10 | 71 | The stationery purchased by I.I. Ivanov has arrived. by check without VAT | 2 840 | Advance report, sales receipt |
| 71 | 51 | To the bank card of Ivanov I.I. overspending amount credited | 340 | Payment order |
Example 2. Return of imprest amounts on an advance report - postings
Romashka LLC and Vasilek LLC concluded an agreement for the provision of transport services in the amount of 7,200 rubles, incl. VAT. To pay for services under the contract, employee of Romashka LLC Ivanov A.B. received a report for the amount of 7,500 rubles. After making settlements with Vasilek LLC, Ivanov A.B. I submitted the advance report and returned the remaining funds to the cashier.
The accountant of Romashka LLC generated the following entries:
| Dt | CT | Description | Amount, rub. | A document base |
| 26/44 | 60 | reflected in costs (RUB 7,200 - RUB 1,098) | 6 102 | Certificate of completion |
| 19 | 60 | The amount of VAT on the cost of transport services has been allocated | 1 098 | Certificate of completion |
| 68/2 VAT | 19 | The amount of VAT on the cost of transport services is accepted for deduction | 1 098 | Certificate of completion of work, invoice |
| 71 | 50/1 | From the cash register of Romashka LLC Ivanov A.B. received funds for reporting | 7 500 | Expense cash order, statement of the accountable person |
| 60 | 71 | The accounting reflects the payment for services made by Ivanov A.B. on behalf of Romashka LLC | 7 200 | Advance report, certificate of completion of work |
| 50/1 | 71 | The balance of unspent funds was returned to the cash desk of Romashka LLC (7,500 rubles - 7,200 rubles) by A.B. Ivanov. | 300 | Expense cash order, advance report, act of completed work |
Example 3. Accounting entries for travel expenses
Employee Vasilkov I.I. sent on a business trip for 3 days, he was given an accounting amount of 20,000 rubles. The daily allowance is 2,000 rubles.
Upon return, he submits an advance report with supporting documents attached:
- Railway tickets in the amount of 8,000 rubles, including VAT of 1,220 rubles, are highlighted in a separate line.
- Hotel invoice on strict reporting form for RUB 5,000, incl. VAT 763 rub. VAT is also highlighted as a separate line.
Reflection of travel expenses on account 71 in postings:
| Dt | CT | operations | Amount, rub. | A document base |
| 71 | 50 | Funds were issued to I.I. Vasilkov. from the cash register | 20 000 | Account cash warrant |
| 20 | 71 | Ticket expenses are written off without VAT | 6 780 | Advance report, train ticket |
| 19 | 71 | VAT allocated on ticket costs | 1 220 | Railway ticket |
| 68.VAT | 19 | VAT is deductible | 1 220 | Entry in the purchase book |
| 20/44 | 71 | Accommodation (hotel) expenses are written off without VAT | 4 237 | Strict reporting form, hotel cash receipt |
| 19 | 71 | VAT allocated on hotel expenses | 763 | |
| 68.VAT | 19 | VAT is deductible | 763 | Entry in the purchase book |
| 20/44 | 71 | Daily allowance written off | 6 000 | Advance report |
| 50 | 71 | The employee returned unspent funds to the cash register | 1 000 | Receipt cash order |
Source: https://BuhSpravka46.ru/buhgalterskiy-plan-schetov/schet-71-v-buhgalterskom-uchete-harakteristika-i-provodki-s-primerami.html
An example of filling out a balance sheet
As of 04/01/2020, the accountable Simonov S. has an overexpenditure of one amount received under the report in the amount of 1000 rubles. and debt on the second in the amount of 5,000 rubles. The deadline for the report has not yet arrived. The amounts are reflected in the opening balances.
In the second quarter, S. Simonov received 1,000 rubles from the cash register. (debit turnover) and compiled an advance report for the second amount in the amount of 4,500 rubles. (credit turnover).
After this, another accountable Vasiliev A. received an amount for household needs - 2800 rubles. (debit turnover).
Now the ending balance in the statement will look like:
Simonov S. - final debit balance: 500 rub.
Vasiliev A. - final debit balance: 2800 rub.
The company records settlements with accountants using subaccount 71.01 “Settlements with accountants in rubles.”
Note! An employee can receive a new sum of money against the report before the previous one is fully settled.
Account 71 in accounting
Account 71 in accounting is a separate accounting account designed to reflect the amounts issued to the company's employees. Let's understand the features of its application, designate the wiring and the rules for their preparation.
ConsultantPlus TRY FREE
Get access
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 94n approved that account 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” is intended to reflect transactions for the issuance and return of accountable amounts.
https://youtu.be/bOktS8UkPYQ
What is a subreport? This is a certain amount of money from the organization that is transferred to the employee for specific purposes. Moreover, the purpose of expenses and the reporting period are strictly limited.
After the allotted time has passed, the subordinate must provide a report on the expenses incurred.
In simple words, money is given in advance, but with the condition that the employee provides a report - this is the essence of reporting.
For example, the company secretary was given 100 rubles from the cash register to buy an envelope and send a letter. When the reporting employee sends the letter, he will be given a receipt or check at the post office. It is these payment documents that the secretary will attach to the report, which will confirm the fact that the funds were spent on purpose.
For what purposes can a report be issued:
- Advance on travel expenses. This is relevant when an employee is sent on a business trip. Travel allowances include payment for accommodation and travel, daily allowances and other expenses en route.
- Expenses for the business needs of the company. Money can be issued for any purpose, from buying a light bulb for a utility room to building materials for major repairs.
- Settlements with counterparties. For example, the issuance of money is subject to payment for the services of third-party organizations. The operation is used less and less often, since non-cash payments are much more convenient.
- Other goals fixed by the decision of the company management. The director has the right to order the issuance of a report for any purpose. For example, for the purchase of equipment, exclusive rights, software products, etc.
Loans and advances to employees cannot be reflected in account 71. For this purpose, a separate account is provided in accounting - 73. Some companies, wanting to simplify accounting and evade taxes, issue short-term loans to employees through 71 accounts. This is a violation.
Rules for issuing money report
The organization is obliged to independently develop and approve the procedure for settlements with accountable persons. For example, by identifying uniform provisions in the annex to the accounting policies. The company calculates limits and standards on an individual basis.
Key requirements for conducting settlements with accountable persons:
- Money can only be given to an employee of the company. That is, accountable persons (account 71 is used only in this case) must be determined by a separate order of the manager.
- Funds can be transferred in cash from the cash register or by bank transfer. Which method will be used in settlements with accountable persons should be specified in the accounting policy.
- The maximum amount to be issued for reporting can be fixed by a separate order of management.
- It is recommended to approve the limits on travel expenses in the subsistence report separately.
- The deadline for submitting a report on accountable money is also fixed in the regulations or in the accounting policy.
- All settlements with accountable persons (account 71) must be documented. To do this, checks, invoices, tickets, receipts and other documentation are attached to the report.
Money is issued based on a written application from the employee or by order of management. The recipient is required to sign the cash receipt order if funds are issued in cash from the cash register.
When making purchases or while on a business trip, the reporting employee must keep all receipts and checks in order to account for the advance received. Upon returning from a trip or upon completion of the purchase, the subordinate draws up an advance report.
Supporting documents are attached to the report. The deadline for drawing up a report on accountable money is 3 days.
Characteristics of account 71
71 accounting accounts are considered active-passive accounts. This means that account balances can have both a debit and a credit balance at the end of the reporting period. This means that at the end of the month the debt may be registered with the employee. For example, a subordinate has just received an advance and has not yet had time to report.
The debt may also be attributed to the company. For example, if an employee spent his own funds to provide for business needs or on a business trip. Overexpenditure is reflected in accounting after the employee has provided an advance report and documented his expenses.
Debit and credit of account 71: what to reflect
| What we reflect on the debit of account 71 | What do we indicate in the credit of accounting account 71 |
| 71 debit account is the amount that was provided to the company employee in advance for specific expenses. That is, this is the money that the employee received for reporting. For example, the cashier issues cash from the cash register. The balance of account 50 “Cash” decreases - the turnover to the credit account is reflected. 50. And at the same time the debit turnover on the account is reflected. 71 - the employee received accountable funds. Before the subordinate provides an advance report, he will be credited with an advance - a debit balance on the account. 71.Or a debit balance is formed if the employee reported less than the amount received in advance. The remainder should be returned to the organization's cash desk. | In the credit of the account we reflect the expenses of the accountable person, supported by documents. That is, the employee submitted an expense report, and the manager checked and approved it. Then the accountant accepts the transactions for accounting and accrues expenses according to the report. The expenditure of funds is reflected in the credit of accounting account 71. At the same time, the debit balance of the account decreases. The result of the operation may be the balance of the loan if the reporting employee spent his money on company expenses. The company must repay this debt. That is, pay the amount of the credit balance to the accountable person. |
Accounting entries for account 71
Let's look at how to correctly make transactions for 71 accounts. Here are typical transactions and correspondence of accounts. Let us indicate which documents to draw up during the operation.
| Operation | Debit | Credit | Foundation documents |
| Money issued in cash report | 71 | 50 | A cashier's report and an expense order were drawn up |
| Funds are credited to the bank card account | 71 | 51 | Bank statement, payment order for transfer |
| Funds are credited to the report on the organization’s corporate card | 71 | 55 | Bank statement from special company accounts |
| The purchase of fixed assets is reflected in the advance report | 08 | 71 | Certificate of acceptance of works and services |
| Materials and raw materials purchased by the accountable person were capitalized | 10 | 71 | Invoices, sales receipts, transportation documents, acceptance certificate |
| The amount of expenses according to the advance report for production and economic needs is reflected | 20, 26, 44 | 71 | Advance report, invoices |
| Return to the cash desk of funds unspent by the accountable person | 50 | 71 | Cashier's report, receipt order |
| Debt accrued for amounts not returned on time by the accountable person | 73 | 71 | Advance report |
Now let's look at examples of posting entries for various situations.
Example No. 1. Overspending - debt in favor of an accountable employee
Vesna LLC issued in June to secretary P.P. Karandashikov. 3000 rubles for the purchase of pencils. The funds were issued from the cash register. The employee made a purchase in the amount of 3,150 rubles. An advance report was drawn up on the costs incurred, a fiscal receipt and a delivery note were attached to the documents.
Postings:
| Operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| The report was issued from the cash register | 71 | 50 | 3000 |
| The advance report has been approved, the expenses for the purchase of pencils have been taken into account | 10 | 71 | 3150 |
| The overspending was transferred to the secretary's bank card | 71 | 51 | 150 |
Example No. 2. The balance is the debt of the accountable person
To purchase a laptop for Vesna LLC specialist K.K. Barankin. 35,000 rubles were transferred to the card. A computer hardware store provided Barankin with a 10% discount on the cost of the laptop (3,500 rubles). The total purchase amounted to 31,500 rubles. Barankin provided an advance report and returned the balance to the cashier.
Postings:
| Operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| The sub-report is listed on the Barankin map | 71 | 51 | 35 000 |
| The advance report has been approved, the expenses for the purchase of a laptop have been taken into account | 08 | 71 | 31 150 |
| The balance was returned to the cash desk of Vesna LLC | 50 | 71 | 3500 |
Example No. 3. Reporting travel expenses
Accountant of Vesna LLC Dorozhkin I.P. sent on a business trip for 3 days to submit reports. Dorozhkina was provided with an advance payment for travel expenses in the amount of 20,000 rubles.
https://youtu.be/1GGHmrqlYrY
The actual expenses of the accountant amounted to 19,000 rubles, including:
- Travel 4000 × 2 = 8000 rubles, including VAT 1220 rubles.
- Accommodation 2500 × 2 days = 5000 rubles, including VAT 763 rubles.
- Daily allowance 2000 × 3 days = 6000 rubles.
Postings:
| operations | Dt | CT | Amount, rub. |
| An advance for travel expenses was issued to Dorozhkina from the cash register | 71 | 50 | 20 000 |
| The costs of paying for a travel ticket without VAT have been written off | 20 | 71 | 6780 |
| VAT allocated on ticket costs | 19 | 71 | 1220 |
| VAT is deductible | 68.VAT | 19 | 1220 |
| Expenses for accommodation in a hotel room are written off without VAT | 20, 44 | 71 | 4237 |
| VAT allocated on living expenses | 19 | 71 | 763 |
| VAT is deductible | 68.VAT | 19 | 763 |
| Daily allowances are written off according to the advance report | 20, 44 | 71 | 6000 |
| The accountant returned the unspent balance to the cash desk of Vesna LLC | 50 | 71 | 1000 |
Source: https://ppt.ru/art/buh-uchet/schet-71
***
Account 71 reflects settlements between the organization and its accountable persons. The debit of the account shows the amounts issued to pay for the needs of the company, and the credit of the account shows paid goods, works, and services. To clearly monitor the movement of amounts in an account, a balance sheet is used.
Even more materials on the topic can be found in the “Accounting” section.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
Accounts payable and its reflection
If the debit balance is the arrears of the staff, then the credit balance is the debt of the enterprise itself. If we evaluate accounts payable from an accounting perspective, then this is a financial assessment of the organization’s debt to other persons. Accounting is maintained on account 60 “Settlements with suppliers”.
This type of debt must be reflected in active-passive settlement accounts. Debt obligations are entered into passive accounting accounts. When recording accounts payable, the following rules should be followed:
- Offsetting should not be allowed between items of assets and liabilities.
- In the balance sheet, this type of debt is always presented as short-term and is reflected in section IV.
- If the debt is in a foreign currency, then when drawing up the balance sheet, it must be converted into Russian rubles at the rate that was established on the reporting date.
- If the organization has received at least part of the payment, then the debt is recorded in the balance sheet in the valuation minus the amount of VAT that has already been paid or is just about to be paid.
- If the debt has arisen from loans and credits, then it is reflected taking into account the accrued interest by the end of the reporting period.
Movements of funds should be reflected in accounting
Account 71 in accounting: what is it used for, correspondence, subaccounts, main entries
While conducting its business activities, a business entity can interact with partners and other persons through its employees. At the same time, while representing the interests of their employer, they can incur expenses for which the company management allocates money to them as an account. To account for settlements with accountable persons, a business entity must use account 71 in accounting.
Account 71 in accounting: what is it used for
At the enterprise, by order of the manager, a list of accountable persons is introduced to whom money can be issued for established purposes. Since it is mandatory that after the activities for which employees were allocated money are carried out, a report is required to be submitted to the accounting department with documents confirming the expenditure attached, these persons are accountable.
The current rules for settlements with accountants are regulated by the procedure for conducting cash transactions. In addition to company employees, citizens engaged under contract agreements can also act as accountable persons.
The chart of accounts provides that account 71 must be used to account for settlements with accountable persons.
It reflects information about the occurrence of the employee’s debt to the organization for the amounts issued to him, as well as its repayment by submitting expenses according to the advance report.
The company’s debt to the accountable person is also reflected here if he spent his own funds for production purposes. By order of the manager, it is reimbursed in the approved amount upon acceptance of the advance report.
Important! Loans issued to employees cannot be taken into account in this account. For this purpose, a separate account 73 is used. Many business entities try to disguise loans provided to employees for short periods under the issuance of accountable amounts. However, this is a violation of the law.
Accountable amounts must be issued only for the purposes established in the order and the employee must report for them within a certain time frame or return the money. During inspections, the Federal Tax Service may identify these cases and assess additional taxes and fines.
To record settlements with accountable persons, you need to use journal order No. 7, which reflects during the month all expenses made by the accountable person, amounts issued for reporting, etc.
Account characteristics
Synthetic accounting of settlements with persons to whom accountable amounts have been issued is organized on account 71. To answer whether this account is active or passive, you need to remember that its balance can be located either as a debit or as a credit. Thus, account 71 is an active-passive account with a double balance.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ng4Ifp0Mgog
The balance at the beginning of the period in the debit of the account reflects the debt of the company's accountable persons for the money issued to them for established purposes. The account credit balance records the company's debt to the employee for expenses incurred at his own expense in the interests of the organization.
The debit of account 71 reflects the issuance of money for the purposes established by the enterprise or reimbursement to the employee of expenses approved by management that were previously made at his expense.
The credit of the account reflects the approved expenses of the accountable person, which are accepted by management, as well as the return of unspent funds to the cash desk or withholding them from the salary of the accountable person, if they are presented with an application for this method of repaying the debt.
To determine the ending balance, you must use the following algorithm:
- If the opening balance on account 71 is in debit, then you need to add the debit turnover on the account to it and subtract the amounts for the selected period on the loan. If you get a positive value, then the balance at the end will be a debit. Otherwise, it is reflected in the credit of the account.
- If the opening balance on account 71 is located in the credit of the account, then the turnover on the credit of the account should be added to it and subtract the total amount of movement on the debit of the account for the period under review. If the total value is greater than zero, it must be reflected as a credit to the account. A negative amount must be reflected in the debit of the account.
Subaccounts
The construction of analytical accounting for the account is carried out in the context of each issued sub-report.
Also, account 71 may have the following subaccounts:
- Settlements with accountable persons in rubles.
- Settlements with accountable persons in foreign currency.
In accordance with the accounting policy of the organization, sub-accounts are opened for each accountable person separately for account 71.
Correspondence
Account 71 can participate in transactions with many accounts.
According to the debit of account 71, he can correspond to the credit of accounts:
- Account 50 - when issuing imprest amounts from the cash register;
- Account 51 - when transferring accountable amounts from a current account to a card;
- Account 52 - when issuing accountable amounts in foreign currency (for example, when traveling abroad);
- Account 55 - when issuing a report from special accounts;
- Account 76 - when issuing money, reporting according to the bank register;
- Account 79 - when issuing the account at the expense of the branch, separate division;
- Account 91 - when writing off exchange rate differences if the funds were issued in foreign currency.
By crediting the account, it can enter into transactions with the debit of the following accounts:
- Account 07 - when registering equipment for further installation purchased through accountable amounts;
- Account 08 - when reflecting costs (business trips, other costs) associated with the acquisition of non-current assets;
- Account 10 - when purchasing materials using imprest amounts;
- Account 11 - when purchasing animals for fattening using accountable amounts;
- Account 15 - when purchasing materials, if the accounting policy stipulates accounting using account 15;
- Account 20 - when writing off accountable amounts for the main production;
- Account 23 - when writing off accountable amounts for auxiliary production;
- Account 25 - when writing off accountable amounts for general production expenses;
- Account 26 - when writing off accountable amounts for administrative expenses;
- Account 28 - when writing off accountable amounts to correct a previously committed defect;
- Account 29 - when writing off accountable amounts for the costs of service and subsidiary farms;
- Account 41 - when reflecting the acquisition of goods through reporting;
- Account 44 - when writing off accountable amounts for the costs of selling products;
- Account 45 - when writing off accountable amounts for the purchase of goods that have not yet arrived at the organization;
- Account 50 - when returning unused imprest amounts to the cash desk;
- Account 51 – when returning unused imprest amounts to the current account;
- Account 52 – when returning unused imprest amounts to a foreign currency account;
- Account 55 – when returning unused imprest amounts to a special bank account;
- Account 70 - when deducting unreturned accountable amounts from wages (one-time deduction);
- Account 73 – when deducting unreturned accountable amounts from wages (multiple deduction);
- Account 76 - when closing a debt to a supplier for previously written off work or services;
- Account 79 - when transferring debt between branches and parent organizations;
- Account 91 - when reflecting a shortage of purchased materials within the limits of natural loss, when reflecting exchange rate differences when issuing a report in foreign currency;
- Account 94 - when reflecting a shortage, if the expenditure of the accountable amount is not confirmed by documents and it is not returned to the cash desk;
- Account 97 - when reflecting accountable costs that will be written off in future periods;
- Account 99 - when writing off accountable funds for liquidation of emergency situations and natural disasters.
The procedure for issuing money for reporting
The issuance of funds to an employee can be carried out in several ways.
https://youtu.be/UeIfIj6jzF0
The simplest and most common way is to issue money from the cash register. In this case, the cashier, at the time of issue, formalizes the operation with an expense cash order.
Until mid-2020, when issuing money, the employee must fill out an application for the issuance of the amount. This had to be done by any employee of the organization, including the director. Applications were allowed not to be filled out when reimbursing excess reporting and issuing daily allowances for business trips.
Since 2020, changes have been made to this procedure. The company can continue to use statements, or issue an order from the manager, which will indicate the full name. accountants, amounts and deadlines for reporting on funds received.
Attention! If there is no application or order, or if they are drawn up incorrectly, fines of up to 50 thousand rubles may be imposed on the company and responsible persons.
The application for the director should differ from the forms of ordinary employees - in it he does not ask for a report, but gives an order to perform this action.
The latest amendments to the procedure for cash transactions allow the issuance of a new amount if the employee has not yet reported the old one. Previously, such a step was prohibited.
In addition to cash, reports can also be issued by transferring from a current account to an employee’s card. For this step, he fills out an application and includes in it the bank details for making the payment.
If the application is not completed, the tax authority, upon inspection, will decide that income (salary) was transferred and will charge additional personal income tax on the amount. Also, the payment order must indicate that it is the issuance of the report.
If the issue is made to a card, then the employee can attach a receipt from the terminal, ATM, bank statement and similar forms as a supporting document. If the employee is on a business trip and an additional daily allowance is transferred to him, then there is no need to fill out another application. But you will need to report all amounts at the same time.
Attention! If the employee has not spent the accountable amount in full, then after completing the advance report, he must return the unused balance back to the cashier
The legislative framework contains instructions for what purposes accountable amounts can be issued, these include:
- Payment for business trips and similar trips;
- Payment for services or work;
- Purchase of materials and goods;
- Incurring entertainment expenses;
- Other similar expenses.
An organization can establish the areas on which accountable persons have the right to spend the amounts issued to them by issuing an Accountability Regulation.
Important! The law prohibits the issuance of accounting funds for the acquisition of fixed assets. Also, accountable amounts cannot be used to make one-time transactions with organizations and entrepreneurs, the amount of which exceeds 100 thousand rubles.
Typical accounting entries
Let's look at how, in typical situations, accounting entries are made for reporting for dummies.
Purchasing materials through reporting
| Debit | Credit | Name of the situation |
| 71 | 50/1 | Money issued, report from the cash register |
| 10 | 71 | Materials were purchased for accountable amounts |
| 19 | 71 | Accepted for VAT accounting on purchased materials |
| 20 | 10 | Purchased materials were released into production |
| 50/1 | 71 | The person handed over the unspent balance of the accountable amount to the cashier |
| 71 | 50/1 | The accountable person was issued an overexpenditure on the accountable amounts from the cash register |
Travel expenses
| Debit | Credit | Name of the situation |
| 71 | 50/1 | Money was issued according to the cash register for a business trip |
| 20 | 71 | Expenses for purchasing travel tickets have been written off |
| 19 | 71 | Accepted for VAT accounting on purchased tickets |
| 44 | 71 | Hotel expenses and daily allowances written off |
| 19 | 71 | Accepted for VAT accounting for hotel stays |
| 50/1 | 71 | The accountable person returned the remaining funds to the cash desk |
Help us promote the project, it's simple: Rate our article and repost! ( 2 5.00 out of 5)
Source: https://buhproffi.ru/buhuchet/schet-71.html