Selection of the most important documents upon request Retention period of the employment contract
(regulatory legal acts, forms, articles, expert consultations and much more).
Regulatory acts. Duration of retention of the employment contract
Order of the Ministry of Culture of Russia dated 08/25/2010 N 558 (as amended on 02/16/2016) “On approval of the “List of standard management archival documents generated in the process of activities of state bodies, local governments and organizations, indicating storage periods” (Registered with the Ministry of Justice of Russia 09/08/2010 N 18380) 657
Articles, comments, answers to questions. Duration of retention of the employment contract
A guide to labor disputes. Controversial situations regarding dismissal due to the expiration of the employment contract Facts of the case: The employer sent written notice of the expiration of the employment contract to the employee’s place of residence. The employee did not receive the notice and was returned to the employer due to the expiration of the storage period. The recipient’s failure to receive correspondence occurred due to reasons beyond the control of the employer and the postal organization.
A Guide to Corporate Litigation. Issues of judicial practice: Expulsion of a participant from a limited liability company Subsequently, Solodovnikova V.N. On 02/07/2013, she sent a written request to the second participant of the company, Kumar Rakesh, and the manager to convene an extraordinary general meeting of participants with the following agenda: to amend the charter of LLC “011” regarding the sole executive body of the company; on approval of the new edition of the company's charter; on the release from the duties of the sole executive body of the company, the manager of IP Kovrigina A.V. due to the expiration of the term of office; on the decision to elect Yu.A. Rynkovsky as director; on making a decision to transfer to the director all financial and accounting documents, business contracts, the entire list specified in clause 12.8 of the company’s charter; on instructing the chairman of the meeting to sign an employment contract with the director of the company; on the appointment of an audit of the financial activities of LLC “011” for the period from 2011 to 2012. The specified requirement was sent to the address of the company, as well as the managing company, and was returned by the communications authorities due to the expiration of the storage period.
The document is available: in the commercial version of ConsultantPlus
Duration of retention of an employment contract
Hello! Recently, a representative of the employer contacted me and, explaining that he wanted to sort out the archive, inquired about the retention period of the employment contract. and in general personal files and documents of employees.
Let's try to figure this out now!
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Section III, dedicated to the employment contract, does not say a word about the rules and terms of storage of employee documents. However, paragraph 3 of Art. 3. Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 125-FZ of October 22, 2004. “On archiving in the Russian Federation,” says that personnel documents are archival documents that reflect the labor relationship of the employee with the employer, which means their storage is regulated by this Federal Law.
At the same time, personal data of employees is private property. upon employment, transferred to the employer (Article 9 of the Federal Law “On Archival Affairs in the Russian Federation”). The employer has the right to create archives to store the necessary information, including on personnel - personal files of employees, which most often include: personal cards of employees, orders for a given employee (copies of orders), cards for issuing personal and collective protective equipment, employment contracts, copies of documents provided by the employee upon employment.
Paragraph b) clause 4 of Art. 22. Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 125-FZ of October 22, 2004. says that documents on personnel are stored for 75 years. But this period applies only to those documents that, based on the results of the examination, the value of the documents were included in the Archival Fund of the Russian Federation (Clause 7, Article 6. Federal Law “On Archival Affairs in the Russian Federation”).
Previously, there was a List of standard management documents generated in the activities of organizations, indicating storage periods, approved by the Federal Archive on October 6, 2000. In accordance with this list, non-governmental organizations were required to store documents for up to 10 years. But this list lost its validity due to the publication of Order of the Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation No. 558 dated August 25, 2010.
By Order of the Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation No. 558 of August 25, 2010. a new List of standard management archival documents generated in the process of activities of state bodies, local governments and organizations was approved, indicating storage periods (List of standard documents).
Section 8 of the new List of Standard Documents contains a list of personnel documents, indicating storage periods to be stored in the organization.
In accordance with paragraphs 656 and 657 of the List of Standard Documents, personal files of employees and employment contracts that are not included in personal files must be stored for 75 years in the organization, or until the organization is liquidated.
Thus, the retention period of the employment contract is 75 years. But do not forget that this period can be changed by departmental regulations.
Good luck to you! If there is a desire to discuss this topic, I will be glad to receive comments!
Author: Baranovsky Sergey
Upon dismissal of an employee
In case of dismissal, personal files, contracts and other documents must be kept in the archives. For this purpose, folders are created where files are filed. If the organization's staff changes quickly, then a new folder is created every year. If, on the contrary, there are few employees, then one folder may contain documents for several years. Papers are separated by year using a blank sheet of paper. The date of filing can be indicated either in the year the person entered the position or in the year of dismissal.
How you store agreements doesn't matter much.
The main thing is to keep order in the archive and observe the retention period of employee employment contracts, so that the head of the organization does not face administrative or even criminal penalties for violating the rules.
Most often they are of the following types:
- Profile. This refers to all types of contracts and documents that directly relate to the scope of the enterprise’s activities and are stored for no more than 5 years.
- Household. They are similar to the previous type of contract and are also stored for no more than 5 years.
- Labor. Often, this type of agreement is also stored for no more than 5 years, but in some cases the period can be increased, for example, in a situation where there is no personal account, the period can reach 75 years.
We suggest you read: Should sick leave be paid after dismissal?
Determine the storage period by document type:
- Core contracts, as well as documents that are directly related to the activities of the organization. They are stored in archives for no longer than 5 years.
- Business contracts. The shelf life is the same as in the first case.
- Employment contracts. The shelf life of employment contracts for employees created before 2003 is 75 years. Documents dated after 2003 are stored for up to 50 years. In the event of liquidation or bankruptcy of an enterprise, employee files are transferred to the municipal archive in processed form.
Contact the professionals
If you would like to establish the exact storage period for employee employment contracts at your company, our representative can help you with this. The archivist will quickly put things in order in the document flow and deal with all the papers (including those whose shelf life is controversial or unknown due to the loss of the relevant organization regulations).
Labor relations, as well as the procedure for their registration, are regulated by the Labor Code. Article 85 of this document contains
collection of the employee’s personal data. This is information about a specific employee that is necessary for the employer in connection with the formation of an employment relationship with him.
The organization's processing of personal data of employees involves the receipt, storage, combination, transfer or any other use of personal data. According to Part 2 of Article 87 of the Labor Code, the procedure for storing and using personal data of employees is established by the employer, if it is not regulated by law.
The organization has the right to decide on its own whether it is necessary to open personal files for employees. They can be created for all employees of the company or for certain categories (for example, for management). It is necessary to draw up personal files in accordance with the current rules of record keeping.
According to clause 3.5.3 of the Basic Rules for the Operation of Archives of Organizations (approved by the decision of the Board of Rosarkhiv dated 02/06/2002) “personal files. are formed during the entire period of work of this person in the organization.”
A personal file is opened after the issuance of an order on appointment to a position. All documents in the personal file are filed in chronological order as they are received. They are stored in the company safe and issued for personal use only to a certain category of employees who have access to personnel information. Changes to personal files are made by personnel department employees. If the organization does not have such a position - accountant.
The list of documents that are attached to the personal file can be found in paragraph 5 of Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated 01.06.98 No. 640 “On the procedure for maintaining personal files of persons holding public positions in the Russian Federation in the order of appointment and public positions.” Despite the fact that this document regulates the management of personal files of civil servants, this list can also be used by other companies. As a rule, a personal file includes:
— copies of education documents (including all qualification certificates), identity cards;
— certificates and other documents confirming changes in the employee’s personal data (copies of marriage certificate, Taxpayer Identification Number, insurance certificate, children’s birth certificate);
The internal inventory lists all the documents that are filed in the personal file. The removal of documents from a personal file and the replacement of originals with copies are reflected in the internal inventory in the “Note” column. During the employee’s work in the company, every document in the personal file is taken into account in the internal inventory. Also, HR department employees keep a record of additional information about the employee and place it at the beginning of the case along with a personal personnel record sheet. When closing a personal file, the employee’s statement of resignation at his own request or other documents that serve as the basis for dismissal, and a copy of the order are filed with it. The internal inventory is signed by the compiler, indicating the position, the transcript of the signature and the date of compilation.
https://youtu.be/dKJTsXfvALc
Saving data
All files of dismissed employees must be stored for the period that is regulated for a particular document. Dismissal orders, employment contracts, vacation applications, etc. are stored separately. Papers must be filed in chronological order. If there is no archive in the company’s office, they should be placed in a special fireproof cabinet. It must be remembered that storing employment contracts and personal files of working and dismissed employees in one place is not allowed.
As for the periods of storage of personal files of employees after dismissal, these rules were approved by the Board of Rosarkhiv. They do not apply to documents related to former employees and must be disposed of within 10 years or less.
By law, the storage period for contracts and other papers is 75 years. This list includes:
- personal cards of people fired in 2003 or earlier;
- travel affairs of employees working outside the country;
- information about income, property and liabilities of employees;
- rehabilitation data;
- original copies of personal documents of dismissed employees - work books, certificates of qualification, certificates, certificates, etc. They should be stored during this period until required;
- acts of acceptance and transfer of personal files during transfer (only for employees of government agencies);
- papers about the subject of personal data (notification and consent to the processing of personal information).
Other documents in the archive should not be preserved for so long. In particular, the personal cards of those dismissed after the beginning of 2003 are in it for no more than 50 years. The following are stored for five years:
- resumes and autobiographies of those fired;
- characteristics;
- official and memos;
- travel certificates;
- copies of orders and extracts from them;
- statements.
If a person was never hired, then all documentation about him is stored in the archive for one to three years. HR or accounting representatives must strictly adhere to these rules as required by law.
Employee personal card
The main document for registering the personnel of an enterprise is a personal card (unified form No. T-2). which is established for each employee hired for permanent and temporary work. The form was approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 5, 2004 No. 1.
A personal card is filled out for employees hired in accordance with the order (form No. T-1 or T-1a). as well as on the basis of documents presented by the employee in accordance with Article 65 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This:
— passport or other identification document;
— insurance certificate of state pension insurance;
— military registration documents (for those liable for military service);
- a document on education, qualifications or special knowledge, as well as additional information provided by the employee about himself.
In some cases, taking into account the specifics of the work, in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation, it may be necessary to present additional documents.
The section “Hiring, transfers to another job” should contain references to the dates and numbers of orders on the appointment, transfer or dismissal of employees. This information must be entered as accurately as possible, since it serves as the basis for confirming the employee’s work experience. At the end of each section of this record (in column 6) there must be an employee’s signature.
An employee’s continuous length of service is calculated on the basis of a work record book in accordance with the Rules for calculating the continuous work experience of workers and employees when assigning state social insurance benefits, approved by Resolution of the USSR Council of Ministers dated April 13, 1973 No. 252.
Work experience (general, continuous, giving the right to a bonus for length of service, other benefits established in the organization) is calculated on the basis of entries in the work book or other documents confirming the relevant length of service.
When information about an employee changes, data is entered into his personal card, which is certified by the signature of a personnel service employee.
The main documents on the basis of which section II “Information on military registration” is filled out are (see below for a sample of filling out the section):
- military ID (or temporary certificate issued in place of a military ID) - for citizens in reserve;
Document retention periods
When putting your organization’s personnel records in order, be very careful when destroying personnel documents. According to paragraph 1 of Article 17 of the Federal Law of October 22, 2004 No. 125-FZ “On Archival Affairs in the Russian Federation”, “organizations and citizens engaged in entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity are obliged to ensure the safety of archival documents, including documents on personnel, during their storage periods” established by law.
The storage periods for documents are determined in the List of standard management documents accompanying the activities of organizations indicating storage periods, approved by the Federal Archive on October 6, 2000 (hereinafter referred to as the List). The list is intended for use as the main regulatory document when determining storage periods and selecting standard management documents for storage and destruction, that is, common to all or most organizations (including non-governmental ones). The storage periods for personnel documents are presented in the table on p. 89.
Section 8.1 of the List provides storage periods for documents related to the hiring, transfer and dismissal of employees. Thus, employment contracts, orders for admission, transfer, dismissal, personal cards of form No. T-2, personal accounts of employees, personal files and registration forms for these documents have a shelf life of 75 years. Unclaimed work books, a book of records of work books and inserts for them are stored for 50 years. The storage periods for documents on personnel are established by the List of standard management documents accompanying the activities of organizations, indicating the storage periods. All specified documents must be submitted to the archives. The personal files of dismissed employees are transferred to archival storage for 75 years. The personal files of the company's managers are kept permanently.
Temporary storage periods are applied by all organizations without exception, and permanent ones are applied by those state and municipal institutions whose documents are received for storage in the relevant archives, as well as non-governmental organizations with which agreements have been concluded, that is, sources of archive acquisition.
Retention periods for personnel documents
Journal of employment contracts and additional agreements
The organization is obliged to store primary documents, including employment contracts and additional agreements with employees. If the company's document flow is large, it can be difficult to find the required agreement in the folders. The log book helps.
The log book is an optional document. It is filled out to make it easier to keep track of documentation. The serial number of the contract, the date of conclusion, and the full name of the employee are recorded in the book. Registration records the fact of document creation and is executed in accordance with GOST R51141–98. Cases when a journal is useful:
- legal proceedings upon dismissal of an employee;
- drawing up a certificate of employment for the employee for a new place of work;
- when searching for documents for internal use.
Upon receiving a copy of the contract in hand, the employee puts his signature, which confirms that he has the document.
The organization is obliged to maintain and, upon request, provide regulatory authorities with a log of registration of employment contracts, if it is specified in the accounting policy as the primary supporting document.
Maintaining a logbook is the responsibility of the HR specialist. When filling out the book, he puts his signature as the responsible person.
The logbook for registering employment contracts can be prepared in a simple notebook or you can purchase an account book at an office supply store. There is also the possibility of electronic recording with subsequent printing.
The composition of the accounting document - the names, number and content of columns is developed by a human resources specialist and agreed with the head of the organization.
Despite the absence of legal requirements for the register of employment contracts, there are general rules for filling out accounting books.
The title page indicates the dates of validity of the journal and the name of the employer.
We invite you to read: Extension of the lease agreement for a land plot
When compiling a printed magazine, first fill out the title page. Indicate on it:
- name of company;
- journal start date (leave blank for end date);
- Full name of the head of the organization and the person in charge.
The hiring of an employee is fixed by an employment contract; if it is necessary to make changes to it, the parties draw up an additional agreement.
If we take into account that the number of personnel in an organization can be quite large, then the issue of streamlining documentation management is more than relevant. A journal for registering employment contracts was created specifically for this purpose.
What it is
The register of employment contracts is a document intended to record all contracts and additional agreements drawn up in an organization with employees, confirming the exact date of conclusion, addition and possible termination.
This journal does not belong to the category of mandatory documents that must be maintained in the process of personnel records management.
The advantages of an electronic journal are the convenience of finding the necessary information, reducing the time spent filling it out, simplifying the issuance of certificates and statements that can simply be printed.
Is it necessary
Some personnel workers doubt the need to keep a journal for registration, since there is no liability for its absence. In this case, you should find out in detail what exactly the purpose of this document is.
Thanks to this, information about any document will not be lost, which is quite likely with large volumes of document flow.
The convenience of using the registration journal is that it stores information about many documents stored in the archive, and if there is a need to obtain data from an already archived contract or agreement, then you will not need to sort through a bunch of pieces of paper.
The practical advisability of keeping a journal in strengthening the employer’s position in the event of labor disputes.
At the same time, the legislation does not oblige the creation of such a journal, unlike, for example, a journal for recording work records. Therefore, the form of management, as well as the fact itself, is entirely at the discretion of the head of the organization.
But if we consider the advantages of management in practice, we can highlight the following points:
- an accusation from an employee of improper registration of employment can be refuted by an entry in the journal about the signing of the contract;
- using the contract, you can “remember” the date of conclusion of the contract if for some reason the employer has lost his copy, but he needs to send a notification about the expiration of the term of the fixed-term contract;
- a note in the journal can confirm that the employee was notified on time;
- if it is necessary to prove the existence of an additional agreement, then this can also be done through a journal;
- using the information recorded in the journal, it is convenient to draw up statistical reports, sometimes required in personnel activities;
- Due to the absence of the need to sort through stacks of documentation, employee time is saved and the work process is optimized.
The procedure for maintaining a registration log falls within the competence of the HR employee, or it can be carried out by the HR manager. As a rule, the journal is kept by the person who carries out personnel work.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EQ0qIzi7kI4
With the assistance of the information displayed in the log, a personnel officer can quickly issue a certificate of hiring or dismissal of an employee; in addition, thanks to strict recording, it is easy to trace the employee’s movement over the entire period of his activity in the organization.
This helps to prove the existence of an employment relationship with a specific employee. In controversial circumstances, the journal makes a strong argument that all employee rights are respected in accordance with the requirements of the law.
The part-time employment contract is discussed on this page.
The requirements for the registration log are standard and comply with the rules of office work. The log looks something like this:
- thick hard cover, which is necessary due to long-term storage of the document;
- the presence on the title page of the full name of the organization, the name of the journal, its start date and, necessarily, its end date;
- sequential numbering of all pages, including blank ones;
- the presence in the journal of information about the person responsible, indicating the full name, position, period of responsibility and the basis for the authorized keeping of the journal.
As for journal keeping itself, there are no clear standards; the organization itself can develop a document registration form and determine what data needs to be recorded.
Hiring a new subordinate in accordance with general rules implies drawing up a working agreement. If there is a need to amend the specified document, then an additional agreement takes place.
However, with a large number of employees, it is difficult to keep records, especially given the many activities that may occur. Because of this, in order to organize all documents and information about employees, the organization must maintain a logbook. It helps to avoid many mistakes and also allows you not to violate the deadlines established by law.
With all this, the presented book requires correct design and observance of rules and order.
An employment contract is one of the most important documents in an enterprise, regulating the relationship between an employee and an employer. Is it necessary to keep a log of employment contracts and what is it? What is the shelf life of the employment contract register, and how to keep records and store them.
https://youtu.be/7MH380F2T6M
From this article you will learn:
- why do we need a journal for registering employment contracts and is it required by law;
- how to keep records and store a log of employment contracts;
- what is the storage period for the employment contract registration log in 2017;
- what to do if the registration log is kept incorrectly.
Why save personnel documents, and what determines their retention period?
Storing personnel documents is the responsibility of all companies and individual entrepreneurs. This is determined by Art. 17 of the Law of October 22, 2004 No. 125-FZ on archival affairs in the Russian Federation. Everyone is equal before this requirement of the law: both businessmen and government agencies.
Personnel documentation occupies a significant place in the total volume of papers processed at the enterprise. If a company has several hundred or thousand employees, the number of personnel documents can reach several thousand. But micro-companies that employ 2-3 people cannot do without these kinds of documents. And all of them are subject to storage for legally established periods.
The main feature associated with the storage period of personnel documents is the length of the period during which they cannot be destroyed. For example, information related to the personnel of a company is subject to long-term storage (75 years or for the entire period of the company’s existence). Such personnel documents include employment contracts and additional agreements thereto, personal cards of employees and other documents created by the company related to the labor relationship between the employee and the employer.
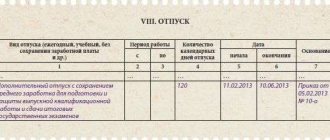
The shelf life of cases generated in the personnel service is influenced by many factors. For example, due to the different degrees of importance of the vacation schedule and staffing schedule, the storage periods for these documents differ by 5 times (1 year and 5 years, respectively).
We will consider in more detail the features of the retention periods for personnel documentation in the following sections.
Numbering
One original agreement must be handed over to the employee after registration. Therefore, the personnel officer must follow the procedure. If the number is specified, it is entered in a special journal. Many people still use paper versions of such books, so special requirements are placed on them.
The magazine is stitched, pages are numbered, etc. In addition to the contract number, it may contain additional information. For example, information about a subordinate, his position, length of work, details of orders from superiors, etc. And only after this the employee receives his document, and the second copy is stored at the enterprise. At the same time, the employee puts his signature in the registration book. Many enterprises have the practice of signing a copy of the TD, which remains with the employer.
Storage periods for personnel documents using an example
When she was hired, N.P. Savina, an accountant at Premiere LLC, was informed that in addition to her direct responsibilities related to accounting and reporting, she would have to keep personnel records. According to the management, the personnel document flow in the company is insignificant and little time will be required for this area of work, since the company has a staff of 18 people.
Having agreed to such additional responsibilities, Savina N.P. began her duties. Since there was a lot of accounting work, direct accounting responsibilities took up all of her working time. The preparation of personnel documents was not required so often - new employees did not appear, the rest were successfully working in their places, no one was going on business trips yet, and internal transfers from one workplace to another were not practiced in the company. Therefore, almost no one looked into the cabinet with personnel documentation.
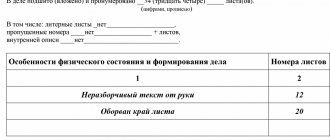
Nevertheless, accountant Savina N.P. did not forget about her personnel responsibilities, therefore, after submitting the next report, she began to study the personnel documents available at that time. The results of examining the contents of the “personnel” cabinet turned out to be disappointing - documents were arranged chaotically in folders, employees’ personal files were not fully completed, some of the documentation had become unusable due to long storage or contained difficult-to-read text. Some cases included documents with different storage periods (1 year, 3 years, 5 years and 75 years), including some of them that had lost their quality as information carriers.
Savina N.P. began work on sorting out personnel documentation by systematizing all available personnel documents. Before getting rid of damaged or unreadable documents, she decided to check the standard storage periods provided for in the List approved by Order No. 558. The results of her work will be discussed in the next section.
Shelf life table
The cabinet with personnel documentation consisted of several compartments. Accountant Savina N.P. began sorting through papers from the first compartment. The results of her work are presented in the table.
From the contents of the last column of the table it follows that part of the personnel documentation needs to be restored, since its storage period has not yet expired. And other papers simply take up space because their standard storage period has expired. We will talk about the consequences of analyzing personnel documentation in the next section.