What is a personal matter
An employee’s personal file is a package of documents and information about the employee regarding the positions he holds and work at the enterprise. This set of documents is prepared for each employee of the organization.
According to the Federal Law of April 27, 2004 No. 79-FZ and the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of May 30, 2005 No. 609, maintaining personal files is mandatory for civil servants, for other categories - at the request of the employer.
In practice, every enterprise keeps records of personal files, which helps to systematize the work of the personnel department and the organization. The storage period for the personal files of dismissed employees is 50 years.
Compound
A file, or a set of documents enclosed in a separate cover, is maintained for each employee of the enterprise. What documents need to be collected for employees, in what form to systematize them and how to store employees’ personal files in the organization is determined by the employer. Typically this includes:
- questionnaire;
- application for employment (for employees of commercial enterprises this is an optional document, but for civil servants it is mandatory to write it in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 26 of Federal Law No. 79-FZ of July 27, 2004);
- copies of passports, diplomas, military IDs, etc.
For civil servants, the list of contents of the case is regulated by clause 16 of the Regulations, approved by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation No. 609 of May 30, 2005.
All documents that are filed in files are recorded according to the internal inventory.
Sample inventory
The legislative framework
- Federal Law dated April 27, 2004 No. 79-FZ
- Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of May 30, 2005 No. 609
- subp. “c” clause 6, part 1, art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
- Art. 192 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- clause 7, part 1, art. 243 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Art. 13.11 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation;
- 14 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation;
- Art. 137 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation;
- 140 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation;
- Order of the Ministry of Culture dated August 25, 2010 No. 558;
- “List of standard management archival documents generated in the process of activities of government agencies, local governments and organizations, indicating storage periods” (Order of the Ministry of Culture dated August 25, 2010 No. 558).
How long are they stored?
Specific storage periods for documents generated during the functioning of business entities are described in detail in the List of standard management archival documents (Appendix to Order of the Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation dated August 25, 2010 No. 558).
So, in accordance with paragraphs. 656 clause 8.1 of subsection 8 of section II of the regulatory document mentioned above, the storage periods for employees’ personal files can be divided into two groups:
- Personal files that are stored on a permanent basis.
This includes personal files of company managers, members of executive, control and governing bodies of organizations, persons who are representatives of the government of the Russian Federation, including constituent entities, employees who have received government titles, awards, bonuses, etc.
- Personal files that are kept for at least 75 years.
This deadline is established for the personal files of all other personnel not included in the first group. This also includes state civil and municipal employees.
Reference. In the case of conducting personal affairs of employees by commercial organizations, they are also subject to the obligations for storing documents about employees established by the above-mentioned Order.
Additionally, it should be noted that documents that are not included in the folder with the employee’s personal file must be stored in accordance with the deadlines provided for by Order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation No. 558 for the corresponding categories of documents.
How an employee’s personal file is formed
The personal file of a dismissed employee is formed according to the dossier principle and is stored in the personnel department of the organization until the end of the calendar year. Within 3 years after dismissal, documents undergo archival and technical processing and are transferred to the archive.
After archiving, there are some aspects that need to be completed:
- The case needs to be stitched or bound.
- Remove all paper clips and staples, stitch 4 protocols into a hard cover.
- Personal documents are placed in an envelope filed in the file and numbered as a sheet. Each investment is numbered in turn (military ID, work record book, diploma, identity card, etc.).
- At the end of the case, it is necessary to file a blank sheet and draw up a document certifying the case, which is not included in the total number of sheets of the folder.
Documents inside the folder should be arranged chronologically - from the first documents to the last. Thus, the earliest document comes first, for example, consent to data processing, and the last is the order to dismiss the employee.
This is also important to know:
Certificates upon dismissal of an employee in 2020: what certificates does the employee receive?
According to Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated May 30, 2005 No. 609, the enterprise implements a mandatory procedure for collecting data on employees. These include the following documents:
- Application form, resume, characteristics and personnel records sheet.
- Copies of passport, educational documents (diplomas, certificates), TIN, insurance certificate, documents on marital status.
- Information from certification.
- Labor contract.
- Employer orders (on appointment, transfer to another position or place of work, vacations and business trips).
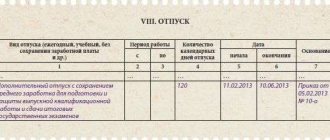
Personal file of a dismissed employee, sample internal inventory
Sample of a personal file certification sheet
Personal cards and personal files: systematization, prompt storage and transfer to the archive
To achieve efficient and effective work of the personnel department, and subsequent processing and storage, the following nomenclature of cases is used:
- A register for systematizing the titles of personal files opened by the personnel department, indicating the period of their storage.
- Mandatory reference book for the classification of the complete register of opened cases of white-collar workers.
- The main record keeping register, which, after the expiration of the standard storage periods for personal files, is handed over with volumes of files to the departmental archive, and continues to serve as an accounting document for storage.
- Basis for compiling information retrieval files and reference books.
There are 2 types of nomenclature:
- The standard nomenclature is the approved composition of the personal files of a particular enterprise, as well as the indexing of files in this industry.
- Approximate nomenclature is a recommended version of the nomenclature and establishes the approximate composition and indexes of cases.
For these two types of nomenclature, there are several stages of formation:
- Studying the documentary base of the institution: statutory documents of the organization, planning and reporting documentation, job descriptions of employees, applied classifiers, departmental registers of documents of the nomenclature of previous years, documentation indicating the main activities of the enterprise.
- Includes a database of documents confirming the authority of the enterprise.
- Management of unfinished personal files transferred for further management from related structural units upon transfer of an employee.
- The systematization of documents for official use is compiled into a separate nomenclature.
For the next year, the list of cases is formed in advance, in the second half of the current annual period.
The formation of a nomenclature of affairs begins with the qualification of departments of the organization: for example, planning department - 01, accounting - 02, office - 03, etc.
Column 1 of the document reflects the indexation, which is the indexed unit and the current number in order of the structural department.
Column 2 reflects the sequence of case names:
- Organizational documentation base.
- Documentation reflecting planned indicators.
- Documentation of the reporting period.
- Documents about the main activities of the institution.
- Information base for auditing the implementation of the target direction of the institution.
Column 3 reflects the number of pages of the personnel file; information in this part of the document is entered at the close of the reporting year and is no more than 250 pages in size.
The storage period is reflected in column 4.
Column 5 is used to enter various types of notes.
The following aspects apply to the formation of a case:
- It is necessary to group documents within the same calendar year.
- Grouping of information from documents of permanent and temporary use is carried out separately.
- The volume contains either the original copy or a certified copy.
- All documentary elements included in the case must meet government requirements and standards.
- The personal file of an employee must be no more than 250 pages in length and no more than 4 centimeters thick.
- The distribution of copies is made in chronological order.
We suggest you read: How to fire an unbalanced person and a boor
The constituent documents of a personal file can be divided into 3 formal groups:
- Documents when applying for a job: application form, resume for the position; application for a job; a copy of education documentation; letters indicating work reviews; data on passing the commission in a medical institution; labor contract; employment order, appointment to a position, materials on appointment on a competitive basis.
- The personal file can be supplemented with: copies of orders on bonuses and incentives, transfers and transfers, etc.; copies of materials reflecting the fact of a change in questionnaire metrics; copies of a diploma received during work, training and advanced training; various kinds of statements and notes; certification certificates.
- Documentary elements reflecting dismissal or termination of an employment contract.
All photocopies must be certified by an employee of the HR department.
Creating a case involves several operations:
- Arrangement of processed information based on the nomenclature used.
- Distributing documentation within a personal folder in the appropriate order.
- Drawing up a title page for the front of the folder.
There is an independent office work folder for each employee, indicating the name of the enterprise or departmental structural unit.
Below is an index and the exact title specified in the nomenclature of cases. Specify the start date of maintaining and the period for saving the folder.
Stage 1
Occurs during the hiring process after signing the employment contract and hiring order. At this stage, documents are distributed in the appropriate order:
- Internal documentation register.
- A copy of education documents.
- Employment contract (agreement).
- Extract (copy) of the issued order for admission to the position.
Stage 2
Includes the distribution of incoming documentation throughout the entire work activity.
All incoming documents are subject to verification and copy certification by an employee of the HR department.
All documentation must be supported in chronological order.
After termination of employment, a personal file filled out in accordance with these stages serves as the primary source for restoring the employee’s lost work book.
A personal file must be created separately for each employee. It is best to stitch or bind the completed case.
An employee’s personal file is a package of documents and information about the employee regarding the positions he holds and work at the enterprise. This set of documents is prepared for each employee of the organization.
According to the Federal Law of April 27, 2004 No. 79-FZ and the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of May 30, 2005 No. 609, maintaining personal files is mandatory for civil servants, for other categories - at the request of the employer.
In practice, every enterprise keeps records of personal files, which helps to systematize the work of the personnel department and the organization.
To avoid such unpleasant situations, it is better to store personal files in a specially designated room, or in safes and metal cabinets, to which third parties cannot gain access.
- Questionnaire for personal information
- Internal inventory of personal files
- Title page/cover of personal file
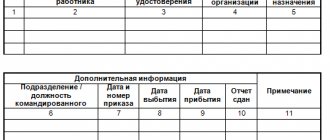
A sample of filling out an internal inventory for a personal file and a surveyor’s sheet.
It is necessary to take into account personal files opened for employees. Its standard form has not been approved, which means you can take a sample from the Internet or purchase it in a store. The content of each column can be changed depending on the organization.
The log contains: case numbers, their start date, surname and initials of employees and other information. When a personal file is closed, a note is made in the journal: they put a date and enter the reason why the case was closed.
Additional information is usually entered in the “Other” or “Notes” column.
- Rudina Natalya
An employee’s personal card is an accounting document in which basic information about the employee’s work activities is entered. It is required to be maintained by all employers (see clause 12 of the Rules for maintaining and storing work books, producing work book forms and providing them to employers, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225).
The form of the personal card (No. T-2) was approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 5, 2004 No. 1. Despite the fact that for the 6th year (since 2013) unified forms of primary accounting documents are not mandatory for use, the need to maintain personal cards no one canceled the workers.
It is rare that organizations in Russia invent their own forms; the vast majority use the familiar Form No. T-2, which does not raise any questions among inspectors, with minor improvements to suit their specific needs.
A personal file is a collection of documents about an employee’s work activities. An employer is not obliged to keep personal files for its employees; they are required to keep them only for civil servants (Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated 01.06.
1998 No. 640 “On the procedure for maintaining personal files of persons holding public positions in the Russian Federation in the order of appointment and public positions in the federal public service”). True, the responsibility to manage personal affairs can also be assigned to a government agency by industry regulations.
In private business, the decision on whether or not to manage personal affairs of employees is made by the head of the organization. Only a higher organization can order him to do this - of course, if there is one.
A personal file is much more informative than a personal card. It contains not only general information about a person’s work in an organization, but specific documents in the form of originals and copies issued by your organization to document labor relations and provided by the employee (education documents, personal data, etc.).
Please note: the fact that the organization maintains the personal files of employees does not relieve it of the need to maintain personal cards. The personal card in this case will always be kept separately from the employee’s personal file, i.e. in the nomenclature of cases these will be different cases!
Their storage period is determined according to Art. 22.1 of the Federal Law of October 22, 2004 No. 125-FZ “On Archival Affairs in the Russian Federation” (hereinafter referred to as the Law on Archival Affairs). Let us remind you: now the storage period for documents on personnel is 50 years, if the documents were closed by office work starting from 01/01/2003.
In general, personal files and personal cards are stored according to the same rules, but there are nevertheless nuances and differences. Let's look at them.
What documents are included in a personal file?
The composition of personal files, as well as the procedure for formation, for private entrepreneurship is not fixed at the legislative level, but it must be properly prescribed in the local act of the company.
Documents that usually belong to a personal file can be divided into several groups:
- Primary documentation for hiring. This includes those documents that employees provide upon employment, and those that are filled out and entered directly during registration. It can be:
- summary;
- documents on education and qualifications;
- copies of identification documents (passport, SNILS, identification code, if any);
- recommendations or reviews from previous employers (if necessary);
- a document or a copy thereof regarding military registration (if available);
- certificate of no criminal record (needed when applying for certain positions);
- medical examination data;
- completed application form (if provided);
- employment application;
- a copy of the admission order;
- concluded employment contract, etc.
- Papers that appeared in the process of working in this position. They may reflect the employee's professional achievements or his social dynamics. These may include:
- various qualification certificates;
- driver license;
- marriage or divorce certificate, if these events occurred during employment;
- birth certificates of children (same justification);
- job description;
- additional agreements concluded (if this was done);
- a copy of the agreement on financial responsibility (if the position provides for it);
- certification certificates;
- data from regular medical examinations;
- documents establishing medical restrictions or disability (if this happened during work);
- copies of orders about internal changes in position (transfer, promotion, demotion, etc.);
- data on disciplinary sanctions and work incentives;
- leave requests;
- reports, explanatory notes, memos, etc.
- Documents confirming the employment relationship with this employer. Before the case is dismissed, it must be properly completed. The latest documents in the personal file folder may be:
- resignation letter;
- a copy of the dismissal order;
- documents on dismissal due to external transfer;
- employee's death certificate.
Personal files of employees: correct registration, storage periods, destruction
Personal files of employees - the correct execution of this documentation is important, since it allows not only to maintain order in personnel documentation, but also to avoid fines for violations that personnel officers sometimes commit. Is it necessary to create personal files for employees? How to properly complete them, arrange them and how long to store them? What documents should not be included in an employee’s personal file? You will find answers to these and other questions in our article. You will also be able to download the forms and samples necessary for maintaining personal affairs.
https://youtu.be/1Zbn-q-0OpE
Is it necessary to keep personal files of employees?
Composition of an employee's personal file in 2019-2020
Formation of an employee’s personal file: sample 2019-2020
Storing personal files of employees in the HR department
Results
Is it necessary to keep personal files of employees?
Maintaining personal files of employees is not mandatory for all employers. Thus, it is mandatory to open personal files for civil servants. This is the requirement of the Law “On State Civil Service in the Russian Federation” dated July 27, 2004 No. 79-FZ. They contain personal data and other information related to entry into the civil service, its passage and dismissal from it, as well as information necessary to ensure the activities of the relevant government agency.
As for commercial organizations (namely, we will talk about them further), they do not have a corresponding obligation. They can conduct personal affairs of staff on their own initiative. In practice, companies do just that. This allows you to systematize and streamline personnel document flow, and also helps you quickly find the necessary information about an employee at the right time. We will tell you below what requirements need to be met so that you don’t have to pay for all these amenities.
Composition of an employee's personal file in 2019-2020
We probably all imagine a personal file in the form of a folder or file containing a certain set of documents about the employee and his work and their copies. As a rule, this is true. What should be in an employee's personal file? The employer determines its composition based on his own ideas and needs. Since managing personal affairs is a right, not an obligation, the procedure for their registration is established in each specific company. It is advisable to consolidate it in a local regulatory act.
Typically the list of documents in an employee’s personal file is as follows:
- application form to be filled out when applying for a job;
The employee application form for your personal file can be downloaded here.
- employment contract;
- job description;
- copies of employee orders.
IMPORTANT! Personal cards in the T-2 form do not need to be included in personal files. They are stored separately.
Now attention! Very often, copies of documents provided by the employee during employment are filed in the personal file: passport, SNILS document, TIN certificate, diplomas, etc. All these documents contain the person’s personal data. Therefore, it is impossible to store them just like that (so that they exist).
At a minimum, you must obtain consent from the employee to process personal data indicating the specific purpose for which it will be used. At least Rostrud allows you to do this. But it’s better to stop collecting copies of personal documents altogether.
We received the documents, recorded all the information necessary to formalize the employment relationship and returned everything to the employee. This will eliminate the risk of claims during inspections.
And of course, you should not keep copies of documents for dismissed employees. The Law “On Personal Data” dated July 27, 2006 No. 152-FZ allows the storage of personal data no longer than required by the purposes of their processing. And with the dismissal of an employee, the corresponding goal is lost.
IMPORTANT! For violations in working with personal data, Art. 13.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses provides for quite significant fines. Roskomnadzor conducts checks of compliance with personal data legislation.
See also: “Photo pass may result in personal information fine.”
And by the way, keep in mind that personal files themselves also belong to personal data. Therefore, when working with them, you must act strictly within the framework of the law.
Find out more about the rules for working with personal data from the materials in our section of the same name.
Formation of an employee’s personal file: sample 2019-2020
When organizational issues and legal issues regarding personal matters have been resolved, all that remains is to compile and formalize them. Typically the order is as follows:
- A separate folder (or file) is created for each employee.
- Documents in the personal file are filed in chronological order as they are received, starting with admission documents (application, employment contract, admission order) and ending with a copy of the dismissal order.
- Each sheet of the case is numbered.
- No more than 250 sheets are filed in one volume (clause 4.20 of the rules for organizing the storage, acquisition, recording and use of documents of the Archive Fund of the Russian Federation, approved by order of the Ministry of Culture dated March 31, 2015 No. 526), if more documents have accumulated, a new volume is opened.
- Each incoming document is recorded in the internal inventory of the case.
A sample list of documents in a personal file and recommendations for its preparation can be found here.
The cases themselves are numbered and registered in the employee personal affairs journal (the form of the journal can be developed independently).
See also: “Nomenclature of HR Department Affairs.”
Who do they file personal files against?
This question can be answered unequivocally only in relation to civil servants: for all, as required by law.
Since maintaining personal files is not necessary for private entrepreneurs, they themselves can decide which employees to keep this documentation for, and which ones can do without such detailed personnel records. Some managers who practice this system prefer to keep personal records for all personnel in order to systematize data for each employee. But some, in order to save time, organize the management of personal files only for certain categories of employees.
This is also important to know:
Can a pregnant woman be fired from work: reasons for dismissal according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Personal files are usually opened for employees of what positions:
- management;
- deputy managers at various levels;
- key specialists;
- employees bearing financial responsibility;
- personnel reserve, etc.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! It is advisable to open a personal file for such employees, regardless of the form and time of his employment - he works part-time or at his main job, under a fixed-term employment contract or on a permanent basis.
Less often, positions are provided with personal records for which educational, qualification or other special requirements are not provided, for example, cleaner, watchman, janitor, etc.
What is a personal matter?
The personal file for any employee is presented in the form of a folder where the entire package of documents and information about the employee is collected. All positions held by the employee while working at the enterprise are indicated there. This set of documents is prepared individually for each employee. Taking into account Federal Law No. 79-FZ and Presidential Decree No. 609, all personal files for civil servants and other categories of workers can be processed at the request of the employer. As experience shows, every enterprise keeps records of personal files, as this helps to systematize the work of the personnel department and organizations.
Procedure for conducting personal affairs
A personal file (PD) is a set of documents relating to one employee and containing information about his labor (official) activities and length of service.
In budgetary organizations, as a rule, records are maintained for all employees. However, it is possible to conduct them selectively, for example, only for management personnel, financially responsible persons, etc. By maintaining we mean:
- timely entry of records of all changes: personal and biographical information, job position, etc.;
- inclusion of incoming materials and their withdrawal;
- issuance of case materials, certification of copies;
- maintaining an internal inventory;
- periodic checking of the state of affairs;
- closing and preparation for transfer to the archive, etc.
- The procedure for maintaining and the list of documents attached to the LD is approved by local regulations.
Composition of an employee's personal file in 2019-2020
Personal files (PD), in accordance with the requirements of Federal Law No. 79 of July 27, 2004, are required to be maintained by government agencies for all employees and officials. This obligation does not apply to other organizations (commercial and non-profit organizations). Therefore, all legal entities and individual entrepreneurs may not maintain them or conduct them at their own discretion.
Since generated personal files allow for the best systematization of an organization’s personnel data and give HR officers the opportunity to quickly find any necessary information, in practice they are maintained by almost all companies. It is more convenient to do this in accordance with existing recommendations.
Therefore, let's get to know them more carefully.
Concept of LD
The legislation states that the concept of “deed” means a special way of drawing up a document or a set of documents related to one issue or area of activity. In accordance with sub. 95 clause 3.2.2 GOST R 7.0.8-2013, these are documents placed in a separate cover (folder).
There are no special regulations for maintaining personal records (there are only for state and municipal employees), however, if a company decides to maintain personal affairs, it will have to approve the corresponding regulations and regulate this process at the enterprise level.
It is in this internal regulatory act that one can define:
- what papers will be kept in personal files (composition), and for what purpose;
- order of conduct;
- list of employees for whom LD will be issued;
- procedure for access to information;
- terms and storage conditions;
- features of archiving or destruction after dismissal.
In addition, the company must appoint an employee who will be responsible for this process.
The employer usually has at his disposal both the originals of employee documents (forms, registration cards) and their copies. Therefore, both of them fall into the LD.
It should be remembered that a copy of the passport in the employee’s personal file, as well as all similar copies, must be properly certified in the prescribed manner (for state employees, copies of passports are mandatory in the LD; for other categories of employees, this issue is resolved at the company level). All documents that are part of the personal file can be divided into:
- formed at the time a person gets a job;
- arising in the course of work in the company;
- documents on dismissal from a specific company.
The first group may include:
- resume compiled for the vacancy by the applicant;
- employee's personal file form (use a free form if desired);
- application for a job;
- reference from a previous place of work or recommendations (if any);
- copies of documents with the personal data of an individual (passports, INN, SNILS, military ID cards (for those who have served and those who are still subject to conscription into the army), diplomas);
- a certificate of the presence (absence) of a criminal record (when applying for a job, the implementation of which is not allowed for persons with a criminal record or who have been subject to criminal prosecution);
- certificate of completion of a medical examination (for employment in cases provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and a medical book;
- employment contract (employer's original);
- The order of acceptance to work.
The second group will contain personal documents for the employee’s children (necessary for paying benefits, assigning vacations and providing deductions for personal income tax), an agreement on financial responsibility, a copy of the job description, additional agreements to the employment contract (if concluded), orders for transfers, appointments , incentives or penalties.
- copies of applications and orders for granting leave;
- explanatory notes,
- office notes,
- various acts and notifications.
The third final group includes the employee’s statement and the organization’s order for dismissal.
There are several key points.
The first and main thing is to determine what documents will be in the personal file and for what purpose they are included there. A lot of personnel documents are generated. If you set out to formalize the entire life of a person during his work in an organization, then personal files can become multi-volume in terms of one employee. This complicates the work, and does nothing in general.
When dealing with personal matters, it is very important to remember that the processing of personal data must be limited to achieving specific, pre-defined and legitimate purposes. Processing of personal data that is incompatible with the purposes of collecting this information is not permitted (clause 2 of Article 5 of Federal Law No. 152 of July 27, 2006 (as amended on July 29, 2017) “On Personal Data”).
The list of documents in the employee’s personal file is a list of mandatory documentation related to work activities, which is stored in the personnel department.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with a sample statement of claim for invalidation of a will.
ConsultantPlus TRY FREE
Get access
In many organizations, HR officers manage employees' personal files; They don’t always know what documents are needed. And this is not surprising, because the law does not oblige you to have them in principle. This means that this is an initiative of the HR department. And, at first glance, its employees decide for themselves which papers to request.
But this opinion is wrong. The HR officer is required to know what documents can be stored in the employee’s personal file from 01/01/2019. More precisely, Rostrud provided clarifications in the report for the second quarter of 2020. But in practice, violations are still common, and in order for the organization to avoid a fine, check the contents of the stored documentation.
The personnel officer files each additional paper in a folder, observing chronological order, and compiles an inventory.
Documents in the employee’s personal file for verification by the labor inspectorate must without any problems be supplemented with consent to the processing of personal data. An internal inventory indicating a complete list of contents is also required.
In accordance with the explanations of Rostrud, any official papers not related to work activities are subject to the ban. It’s easier to remember this: we don’t even keep copies of what government agencies issue:
- passport pages;
- certificate of assignment of TIN;
- SNILS cards;
- marriage and birth certificates;
- military tickets.
Their presence in a personal file is a violation of a citizen’s constitutional right to privacy. Collecting such information without the individual's consent is prohibited.
In addition, their storage violates the norms of Federal Law No. 152-FZ of July 27, 2006. For this, an administrative fine is provided under Part 1 of Article 13.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. And, as judicial practice shows, even consent to the processing of personal data in this case is not an excuse.
When wondering what should be kept in the personal file of an employee 2020, one cannot help but mention medical books, although they are not stored in the personal file. If the job involves contact with children, food or medicine, the employer must request it. You can store it, but subject to consent to the processing of personal data from the employee.
The same goes for documents:
- about education;
- about advanced training;
- no criminal record;
- certification sheets;
- characteristics from previous places of work.
Work records should be kept separately from other personnel documentation. As a rule, a reliable safe is allocated for them, to which only the personnel officer has access.
How to lead correctly
When creating an employee’s personal file, you need to understand what should be included in it in 2019. However, it will not be possible to form it once and forever. Information must be updated promptly.
And this can only be done upon a written application from the employee. On his own initiative, the personnel officer has no right to make any adjustments.
The HR department can only issue a case to someone on the orders of the manager. Moreover, this also applies to the person to whom it is instituted. An interested person can familiarize themselves with the materials at any time, but they cannot be taken outside the office without the appropriate permission from management.
If a third party wishes to obtain the folder for review, it must submit a formal request. The transfer can be carried out after receiving the manager’s resolution and drawing up an act in two copies.
How long to store
We found out what documents are stored in the employee’s personal file. And obviously, their shelf life may vary. Therefore, a deadline has been set for the entire folder as a whole. Initially, they remain in the HR department for three years after leaving. Then you can transfer them to the archive for a legally prescribed period.
In accordance with Article 22.1 of the Federal Law of October 22, 2004 No. 125-FZ, personnel documents are stored for 50 or 75 years (depending on the date of establishment or graduation - before or after 2003).
However, it is not recommended to file documents for short-term storage (less than five years) in a general folder.
The HR department must take into account all available documents in the journal. You can keep it in any form, the main thing is that the numbering on the cover of the folder and in the corresponding column of the journal match.
Currently, organizations give preference to maintaining personal files of employees, although the law does not make similar requirements for all employers. This is done in order to streamline the work with personal data and ensure the safety of the information received.
If your organization has decided to manage personal files of employees, you must immediately resolve the issue of organizing their storage.
A personal file (PD) is a set of documents relating to one employee and containing information about his labor (official) activities and length of service.
In budgetary organizations, as a rule, records are maintained for all employees. However, it is possible to conduct them selectively, for example, only for management personnel, financially responsible persons, etc. By maintaining we mean:
- timely entry of records of all changes: personal and biographical information, job position, etc.;
- inclusion of incoming materials and their withdrawal;
- issuance of case materials, certification of copies;
- maintaining an internal inventory;
- periodic checking of the state of affairs;
- closing and preparation for transfer to the archive, etc.
Responsibility for personal affairs
The list of employees who have access to personal files is regulated by order of the head of the organization. The employee also has the right to familiarize himself with any information regarding his person, which is kept by the personnel officer.
Access of third parties to personal information is prohibited and is classified as a violation of the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
Ask a Question
According to the current legislation of the Russian Federation, those responsible for violating the inviolability of personal data can be held accountable:
- disciplinary (subparagraph “c”, paragraph 6, part 1, article 81 and article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- material (clause 7, part 1, article 243 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- administrative (Articles 13.11 and 13.14 of the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation);
- criminal (Articles 137 and 140 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
According to Part 2 of Art. 13.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, working with personal data without written consent entails a fine of 3,000–5,000 rubles. (for citizens) up to 15,000–75,000 rub. (for legal entities).
Responsibility
A list of employees who can deal with personal matters must be compiled by the organization’s leaders and the corresponding order is issued to them. Each employee has every right to get acquainted with the information that concerns him from the personnel officer.
Third parties cannot have any relation to such information, because this will already be considered a violation of the legislation of the Russian Federation. The laws provide for liability under Art. 81 and art. 192 Labor Code of the Russian Federation, art. 243 Labor Code of the Russian Federation, art. 13.11 and 13.14 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, Art. 137 and 140 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
The procedure for creating an employee’s personal file after dismissal
The personal file is closed on the day the person is fired. After this, the authorized specialist must complete it in full:
- check the presence of all documents;
- check the chronology of papers in the folder;
- check the numbering of sheets (all sheets are numbered in Arabic numerals with gross numbering in the upper right corner of the sheet with a simple pencil or numberer).
Then you need to make a final entry on the internal inventory. It indicates the number of sheets included in the LD, as well as the number of sheets of the inventory itself (its sheets should be numbered separately). After which the compiler must sign both the inventory and the final entry. After which you can draw up a so-called certification sheet, which will contain a description of your personal file. Next, all the papers are stitched together: at the beginning of the folder there is an inventory, and at the end there is a certification sheet. On the title page you need to write the closing date in accordance with the dismissal order, as well as the retention period of the entire folder.
Please note that if the dismissed person did not take any original documents, for example, a military ID or medical record, they must be kept until required in his LD. To do this, they should be placed in envelopes (each document separately) and filed in a folder. Such envelopes are numbered, sealed and certified by the signature of an authorized person.
Who has access to personal files
All cases contain personal data (PD), and compliance with the requirements for their protection is the direct responsibility of employers (Chapter 14 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Federal Law No. 152 of June 27, 2006). The list of persons with access to personal data is approved by order of the head. At the same time, persons who have access to PD are obliged not to disclose to third parties or distribute this data without the consent of the PD subject, unless otherwise provided by federal law.
This is also important to know:
Dismissal of a part-time worker: how to fire an external or internal part-time worker
The head of the organization, by order, appoints those responsible for maintaining and storing personal records (usually the head of the personnel department and his subordinates), and also approves the list of persons who have access to them (this information can also be fixed in the Instructions for maintaining personal files). This list usually includes:
- the head of the organization and his staff deputies;
- head and employees of the HR department;
- head and employees of the legal service;
- accounting employees who calculate wages and make tax and other deductions;
- heads of structural units (in relation to subordinate employees);
- other responsible employees approved by order.
Representatives of third-party organizations can access LD only with the permission of the head of the organization upon an official written request.
Sample order for admission
How to properly store personal files in a budget organization
Currently, organizations give preference to maintaining personal files of employees, although the law does not make similar requirements for all employers. This is done in order to streamline the work with personal data and ensure the safety of the information received.
If your organization has decided to manage personal files of employees, you must immediately resolve the issue of organizing their storage.
Procedure for conducting personal affairs
A personal file (PD) is a set of documents relating to one employee and containing information about his labor (official) activities and length of service.
In budgetary organizations, as a rule, records are maintained for all employees. However, it is possible to conduct them selectively, for example, only for management personnel, financially responsible persons, etc. By maintaining we mean:
- timely entry of records of all changes: personal and biographical information, job position, etc.;
- inclusion of incoming materials and their withdrawal;
- issuance of case materials, certification of copies;
- maintaining an internal inventory;
- periodic checking of the state of affairs;
- closing and preparation for transfer to the archive, etc.
The procedure for maintaining and the list of documents attached to the LD is approved by local regulations.
Who has access to personal files
All cases contain personal data (PD), and compliance with the requirements for their protection is the direct responsibility of employers (Chapter 14 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Federal Law No. 152 of June 27, 2006). The list of persons with access to personal data is approved by order of the head. At the same time, persons who have access to PD are obliged not to disclose to third parties or distribute this data without the consent of the PD subject, unless otherwise provided by federal law.
The head of the organization, by order, appoints those responsible for maintaining and storing personal records (usually the head of the personnel department and his subordinates), and also approves the list of persons who have access to them (this information can also be fixed in the Instructions for maintaining personal files). This list usually includes:
- the head of the organization and his staff deputies;
- head and employees of the HR department;
- head and employees of the legal service;
- accounting employees who calculate wages and make tax and other deductions;
- heads of structural units (in relation to subordinate employees);
- other responsible employees approved by order.
Representatives of third-party organizations can access LD only with the permission of the head of the organization upon an official written request.
Storing personal files of employees in the HR department
The HR department should keep records of only working employees. They are placed in a specially designated place, excluding access to them by third parties, as well as the possibility of their theft or loss. These must be specially equipped locked safes (metal cabinets) or rooms.
At the storage location, files are arranged in a vertical position by serial numbers, in alphabetical order, by structural divisions, etc. A list of LDs located in it is placed in the storage facility.
All cases are subject to accounting and are recorded in a separate journal. The form of the journal has not been approved, so it can be developed independently, in terms of functionality for a specific organization.
Every day at the end of the working day, HR employees check the availability of cases in the storage room. Then the cabinets (safes) or rooms are closed and sealed. If the absence of LD is detected by the responsible employee, measures are taken to return it or search for it.
Retention period for personal files of dismissed employees
The question often arises, how long are employee personal files kept? LD are long-term storage documents (cases opened after 2003 are stored for 50 years; earlier - 75 years (Article 22.1 of the Federal Law of October 22, 2004 No. 125)), therefore, in the event of an employee’s dismissal, they are subject to careful verification and closure. To do this, all documents in the case are verified, the inventory is closed, a certification sheet is inserted at the end of the case, and then the case is stitched with 4 punctures.
How long is an employee’s personal file kept after dismissal? Archiving of personal files of dismissed employees occurs three years after its closure (for municipal and civil servants this period is 10 years). The records of dismissed employees must be kept separately from the records of existing employees. If the organization has a room for storing archival files, then they are temporarily moved there. If there is no specially equipped room, then they are located either on a separate shelf in the storage room or in another safe.
Responsibility for dissemination of personal data
When working with PD, you must remember that this is simultaneously working with PD, which, in turn, relates to confidential information and has restrictions on its collection, processing, storage and distribution.
For violation of the provisions of the legislation on the protection of personal data, disciplinary, material, civil, administrative and criminal liability is provided (Article 90 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Federal Law No. 152 of July 27, 2006).
Source: https://gosuchetnik.ru/kadry/kak-pravilno-khranit-lichnye-dela-v-byudzhetnoy-organizatsii
Storing personal files of employees in the HR department
The HR department should keep records of only working employees. They are placed in a specially designated place, excluding access to them by third parties, as well as the possibility of their theft or loss. These must be specially equipped locked safes (metal cabinets) or rooms.
At the storage location, files are arranged in a vertical position by serial numbers, in alphabetical order, by structural divisions, etc. A list of LDs located in it is placed in the storage facility.
All cases are subject to accounting and are recorded in a separate journal. The form of the journal has not been approved, so it can be developed independently, in terms of functionality for a specific organization.
Every day at the end of the working day, HR employees check the availability of cases in the storage room. Then the cabinets (safes) or rooms are closed and sealed. If the absence of LD is detected by the responsible employee, measures are taken to return it or search for it.
How much and how to store
In the organization, personal files are stored in specially equipped places. These can be metal cabinets (safes) or premises that prevent access to them by third parties, as well as theft or loss of information. Cases are subject to accounting and are recorded in a separate journal. You can arrange them in storage by serial numbers, alphabetically, etc.
Personal files of dismissed persons are subject to being archived after three years after their closure, and for municipal employees - after 10 years of storage at the last place of service.
It is necessary to take into account that if a personal file was opened after 2003, then its storage period will be 50 years, if earlier - the storage period is 75 years (Article 22.1 of the Federal Law of October 22, 2004 No. 125). If materials with different storage periods are attached to it, the entire file is stored for the maximum period.
Archiving personal files of fired employees is a process that every organization faces. At some point, the transfer of cases of employees dismissed during a specified period is required. To ensure complete safety of these documents, it is recommended to convert them into electronic form.
Retention period for personal files of dismissed employees
The question often arises, how long are the personal files of dismissed employees kept? LD are long-term storage documents (cases opened after 2003 are stored for 50 years; earlier - 75 years (Article 22.1 of the Federal Law of October 22, 2004 No. 125)), therefore, in the event of an employee’s dismissal, they are subject to careful verification and closure. To do this, all documents in the case are verified, the inventory is closed, a certification sheet is inserted at the end of the case, and then the case is stitched with 4 punctures. How long to keep personal files of dismissed employees?
Archiving of personal files of dismissed employees occurs three years after its closure (for municipal and civil servants this period is 10 years). The records of dismissed employees must be kept separately from the records of existing employees. If the organization has a room for storing archival files, then they are temporarily moved there. If there is no specially equipped room, then they are located either on a separate shelf in the storage room or in another safe.
Storage and accounting
Cases are stored both in safes and in special locked cabinets. The only requirement is that third parties’ access to the contents of these repositories is prohibited. Documents in safes are arranged by number, in small organizations - in alphabetical order or by structural division.
Answering the question of how long the personal files of dismissed employees are kept, we note that this is determined by law: in commercial organizations, papers containing personal data are stored for 75 years (see the List approved by Order of the Federal Archive No. 236 of December 20, 2019), then they are destroyed.
For civil servants the procedure is different. While a person is working, papers with his personal data are kept in the personnel department; after dismissal, they will be moved to a separate closet (for those dismissed) and will be kept there for another 10 years. In accordance with Art. 22.1 Federal Law “On Archival Affairs in the Russian Federation” No. 125-FZ dated October 22, 2004, the employee’s personal file after dismissal is stored:
- 75 years - completed office work before 01/01/2013;
- 50 years - completed office work after 01/01/2013.
After the expiration of the storage period, the papers are destroyed in the manner prescribed by the organization.
If at any time a person gets a job in government agencies again, information about him will be collected and sent to the new employer upon his written request.
Archiving and resolving the issue of where employees’ personal files should be stored are entrusted to employees of the HR department, specially authorized to do this by order of the head of the organization (even in HR, not everyone prepares files for archiving).
Rules for using archival information
There are rules regarding the use of archival information established by current legislation and office practice:
- Organizations and individuals undertake to retain data about former employees during the above periods.
- Citizens and representatives of enterprises have the right to submit requests to obtain information from the archives.
- Copies and certificates of documents regarding social and pension issues, benefits and compensation are issued free of charge.
- Archival data can be transmitted in the form of electronic documents.
Document storage
At the level of regulations, the required composition of documents in a personal file is not indicated.
This is also important to know:
Deduction for unworked vacation days upon dismissal: detailed instructions
A strictly approved list is regulated only for employees of public services.
Each enterprise can use this list in its work, and depending on the direction of the enterprise’s activity, determine the need to include a particular document in its personal file.
List of required copies of documents:
- passport (page with photo, registration, marital status);
- diploma, certificate of advanced training;
- SNILS, INN;
- military ID;
- employment history.
Also involved in the matter:
- certificates of passing a medical examination and no criminal record;
- a specialist’s personal application for employment;
- autobiography, employment contract;
- documentation of past certification;
- photographs of workers.
If necessary, the list is subject to adjustment.
Without the personal consent of the employee, it is prohibited to include information about the worker’s personal life, his religious and political views.
Accounting and registration: entering other data
The accounting procedure is regulated by legislative standards in the labor sphere. Accordingly, they are stored and registered in the personnel department in a certain order. For convenience, a magazine is used, the form of which is determined by job descriptions. At the time of registration, the following information must be entered in the journal:
- Registration number;
- First name, last name and patronymic of the employee;
- Date of registration;
- A note on deregistration of the enterprise.
The moment of registration of the organization is the date of recording in the registration book. In the field of office work, in the direction of storing and registering files, it is possible to make changes to folders with personal files. Such changes should be recorded at the time of marriage, change of place of residence, advanced training or transfer to a workplace in another department of the organization.
To make changes, the employee himself contacts the personnel department of the enterprise, after which the head of the archive is called upon to record all changes. The general procedure for entering data is determined by compliance with the following algorithm:
- Providing a statement from staff requesting changes to the documentation, as well as submitting supporting documentation. Data can be changed only if there are significant circumstances;
- Issuing an order on the need to introduce innovations into accounting documentation;
- Registration of an order in the journal for recording orders that apply to personnel;
- Direct recording of information.
Thus, the preparation and registration of documentation, the procedure for storing and destroying personal files of enterprises are regulated by state legislation.
Sample log book
Sample test card
Electronic personal file
Nowadays, many Russian companies have implemented or have begun to implement HR automation. It can hardly be called following fashion, rather a necessity. Employees' personal files are increasingly maintained and stored in computer databases. Paper documents are used, but mostly as reinsurance.
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Call: 8 800 511-39-66
Ask a Question
This is also important to know:
Compensation upon dismissal: types of payments upon dismissal
Maintaining and storing personal files in electronic form is, above all, convenient. A HR employee does not need to bite the dust, shifting things around in order to find what he needs. Therefore, one of the absolute advantages of electronic files is the ability to find everything quickly, without wasting time and effort.
It is worth noting that not all documentation can be kept in electronic form; work books, for example, cannot.
If the document must contain the personal signature of the employee, it must also be in paper form.
Additional questions
Correctly setting the retention period for documents is very important
In this case, the files of dismissed employees must be kept for 75 years. At the same time, the personal files of managers must be kept permanently. In order to archive personal files electronically, it is necessary to digitize all the documents that make up these files. To do this, a scan is performed. Moreover, pre-processing is carried out, a number of settings are assigned so that documents to be archived are sent directly to storage folders. This will help significantly reduce operating time.
The storage period for employee personal files will be reduced by almost four times
If any changes are subsequently made, they must be noted on the certification sheet, referring to the relevant act.
The internal inventory is included at the beginning of the case, and the certification sheet completes it. Then the folder is filed and sealed. The closing date and shelf life are indicated on the title page.
If for some reason the employer still has the personal documents of the dismissed employee (identity cards, work book, military ID), they must be placed in a separate envelope, filed with the file and the attachments numbered.
How to deal with the affairs of dismissed employees
When a person quits, his file is closed, removed from the file and filed. In this case, a certification sheet must be drawn up. It includes data on how many sheets are stitched and numbered. This sheet also indicates whether there are damaged documents in the case, or whether new ones have been attached.
The certification sheet is pasted onto the cover of the case from the inside. The HR employee puts his signature on this sheet.
An employee’s personal file is kept in the archive for 75 years; for managers, this period is usually longer. But at the same time, if on the last working day an employee asks for copies of the necessary documents, this can be done; in this case, the file will not have to be stored, and the archive will be unloaded.
How to create an archive of personal files of dismissed employees?
Related publications
The period for retaining documentation regarding former personnel depends on the nature of the information.
How long are the personal files of dismissed employees kept? According to the current Federal Law No. 125-FZ dated October 22, 2004, personnel records are left in the archives for 75 years. Documents for personnel dismissed after January 1, 2003 remain in the archives for 50 years. Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated June 1, 1998 No. 640 regulates the procedure for collecting information about personnel. The documentation required by the employer includes:
- Questionnaire, resume, characteristics and personal sheet for personnel records.
- Copies of passport, educational documents (diplomas, certificates), TIN, insurance certificate, documents on marital status.
- Information from certification.
- Labor contract.
- Employer orders (on appointment, transfer to another position or place of work, vacations and business trips).
The personal file of a dismissed employee, formed according to the dossier principle, remains in the organization’s personnel service until the end of the calendar year. Within 3 years from the date of dismissal, documents undergo archival and technical processing and are transferred to the company archive.
Storage of personal files of dismissed employees in the archive is carried out in the presence of an annual inventory. An authorized personnel specialist compiles a list of employees dismissed in a particular year. The year of termination of the employment relationship is indicated on the cover of the case.
This period is calculated from the end of the calendar year when the citizen was dismissed. According to the established practice of archiving, the storage period for the personal files of dismissed employees begins to count from January 1.
Order of the Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation dated August 25, 2010 N 558 establishes specific periods during which documents must be kept in the archive. According to the law, the storage periods for the personal files of dismissed employees are:
- 75 years - for personal cards of persons who left office before the beginning of 2003.
- 50 years – for personal cards of citizens who terminated their employment relationship later than January 1, 2003.
- 75 years - for travel cases of those workers who were sent abroad.
- 75 years – for data on income, property and liabilities of civil servants.
- 5 years – for characteristics and resumes of specialists.
- 75 years – for data on rehabilitation issues.
- 3 years – for documents about persons not hired.
- 75 years – for original copies of personal documents (certificates, employment certificates, diplomas, certificates, certificates).
- 5 years – for papers that are not included in personal files (applications, certificates, reports, memos).
- 75 years – for acts of acceptance and transfer of personal files of civil servants during transfer.
- 75 years – for documents about the subject of personal data (notifications, consents to information processing).
Civil servants, legal entities and individuals are responsible for ensuring the safety of information about former personnel during regulated periods. Citizens and company representatives can submit requests and appeals for access to the archive of personal files of dismissed workers.
HR specialists provide free copies and certificates of documents related to social and pension issues, benefits and compensation. The data can be used as evidence. After use, the seized documents must be returned to the owner or possessor.
Archival information can be transmitted in the form of electronic documents. In some cases, specialists from libraries, museums, scientific organizations, and government agencies publish reference and information publications.
Cases can be stored both in safes and in special locked cabinets. The only requirement is that these cabinets and safes must prevent access to their contents by third parties. Documents in safes are arranged by number, and in small organizations in alphabetical order or by structural division.
How long an employee’s personal file is kept after dismissal is determined by law: in commercial organizations, papers containing employees’ personal data are stored for 75 years (see paragraph 656 of the List approved by Order of the Ministry of Culture of Russia dated August 25, 2010 No. 558), then destroyed.
For the government, it’s a little different. While a person is working, his papers with personal data are in the personnel department; after dismissal, they will be moved to a separate cabinet (for fired people) and will be kept there for another 10 years.
If at any time a person gets a job in government agencies again, information about him will be collected and sent after him to the new employer upon his written request.
Archiving of personal files of dismissed employees is carried out by employees from the personnel department, specially authorized to do this by order of the head of the organization (even in personnel, not everyone can prepare files for archiving).
Hello! In this article we will talk about such a concept as an employee’s personal file.
Today you will learn:
- What is called a personal file and in what cases should it be kept;
- What documents should be contained in it;
- How much and how to store files.
Not all categories of employers are required to maintain personal files of their employees. But for the effectiveness of team management, it is advisable to form them. Today we will discuss how to do it correctly.
It is mandatory to maintain personal files for those employed in the state civil service. This is required by Russian legislation. Entrepreneurs can regulate this issue by local regulations.
This group includes:
- Management staff and their replacements;
- Chief specialists;
- Persons who are responsible for property and valuables;
- Employees with prospects for career advancement.
But still, it would be useful to create such dossiers for all employees, since they reflect information about employees that may be required at any time.
The composition of a personal file is not regulated at the level of regulations. It is strictly approved only for the state. employees. Any organization can use the approved list and decide which documentation to include in the files of its employees and which not.
- Photocopy of passport (most often the first page, marital status and place of registration);
- A photocopy of a diploma, advanced training document, etc.;
- Photocopy of SNILS;
- If the employee is liable for military service - a copy of the document confirming this;
- Photocopy of TIN;
- Documentation of passing a professional examination and medical examination (if this is provided for by the company’s activities);
- A certificate stating whether the citizen has a criminal record or lack thereof (if provided for by law);
- A job application written by the employee personally;
- Autobiography;
- A copy of the employment contract;
- A photocopy of the work record;
- Materials about certification (if carried out);
- Employee photographs that are periodically updated;
- Description of personal file.
This list may change and be supplemented, depending on what activities the company conducts and what personnel policy it implements.
In addition, all documents must be placed in the file in chronological order: the very first ones that were included when the person was hired, then those that appeared during his activity.
It is prohibited by law to include in the file information about the personal life of an employee, about his views on politics and religion, if he did not give written consent to this.
When a person quits, his file is closed, removed from the file and filed. In this case, a certification sheet must be drawn up. It includes data on how many sheets are stitched and numbered. This sheet also indicates whether there are damaged documents in the case, or whether new ones have been attached.
We invite you to read: Transmashholding transfer of an employee within the organization
The certification sheet is pasted onto the cover of the case from the inside. The HR employee puts his signature on this sheet.
An employee’s personal file is kept in the archive for 75 years; for managers, this period is usually longer. But at the same time, if on the last working day an employee asks for copies of the necessary documents, this can be done; in this case, the file will not have to be stored, and the archive will be unloaded.
- Rudina Natalya
Cases for transferring documents to the archive are formed by name in different folders. This needs to be done correctly. In one folder you can store data for vacations, and in the second there should be documents for dismissals.
But documents need to be folded and stapled to form an archive of dismissed employees in a sequential order. Must be stored for at least 75 years. During the archiving process, documents are divided taking into account standard storage periods.
The documents are then sealed and presented to the archivist. If you don't have a file cabinet, you can lock the folders in a fireproof cabinet. Documents of dismissed employees should be kept separately from those of active employees.
According to the instructions, only original documents can be submitted to the archives. Photocopies may be left as attachments to orders for admission, dismissal or relocation. Personal cards of workers should be stored according to the following rules:
- Cards for former employees are kept on paper.
- They are put into folders with further numbering and firmware.
- On the cover of any created folder there are numbers and the number of cases in it.
- The HR department can store cards of currently employed employees.
- The personnel officer hands over all personal cards of employees dismissed from the organization to the archive and stores them by date, and within the dates they distribute them alphabetically.
The law establishes the time for which documents must be preserved. The main rules were approved back in February 2002 by the Board of Rosarkhiv.
The rules for creating an archival fund do not apply to papers with a storage period of less than ten years. Personal files of dismissed citizens are stored as follows:
- Employment contracts, cards and personal files are saved for 75 years.
- Data on admission and relocation - 5 years.
- Questionnaires - at least 12 months.
- Extracts from reports - 75 years.
- The lists of employees are also 75 years old.
- Informative data on tariffs and salaries - 10 years.
- Acts of accounting of labor books - 36 months.
- Substitution applications are valid for 3 years.
- application for a job;
- a copy of an identity document;
- a copy of the insurance certificate of state pension insurance;
- copy of TIN;
- job description;
- copies of education documents;
- characteristics and letters of recommendation;
- employee personal statements;
- employment contract;
- copies of personnel orders relating to this employee;
- certification sheets;
- reviews of officials about the employee;
- health certificates;
- photos;
- document certifying the file (drawn up when submitting the personal file to the archive).
conclusions
When dismissing an employee, some rules must be followed:
- the case is closed on the day of termination of the employment relationship;
- the folder is handed over to the archive no later than 3 years after the date of its completion;
- The personnel officer is responsible for storing personal information.
Personnel documentation should be stored in a room inaccessible to unauthorized persons. To prevent loss of papers, it is advisable to place them in a safe (metal cabinet).
If a former employee needs to send a request to the company for documents, but the company has already gotten rid of them, then this indicates a violation of the law on archival matters and is punishable under Art. 13.20 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation in the amount of a fine of up to 500 rubles.
Sources:
- https://truddogovor.ru/kak-proisxodit-xranenie-lichnyx-del-sotrudnikov-obrazcy-dokumentov/
- https://assistentus.ru/sotrudniki/lichnoye-delo/
- https://gosuchetnik.ru/kadry/kak-pravilno-khranit-lichnye-dela-v-byudzhetnoy-organizatsii
- https://clubtk.ru/formirovanie-lichnogo-dela-rabotnika
- https://rossiz.ru/skolko-hranitsya-lichnoe-delo-sotrudnika-posle-uvolneniya/
- https://pravostoriya.ru/lichnye-dela-uvolennyh-sotrudnikov/
- https://obd2bluetooth.ru/lichnye-dela-uvolennyh-sotrudnikov/
Subscribe to the latest news