What it is?
Reference. A job description is a local regulatory act of an organization that regulates the powers and responsibilities of an employee.
The document is being developed in accordance with labor and federal legislation at the initiative of management.
The provisions of the instructions distribute the workload between the organization’s employees, taking into account their qualifications.
Other tasks that the instructions solve:
- development of criteria for assessing work activity;
- listing of labor actions expected from the employee;
- assessment of qualifications and development of guidelines for its improvement;
- assessment of suitability for a vacant position;
- ranking of positions with individual payment and discipline systems;
- maintaining disciplinary balance by setting deadlines for completing tasks;
- determination of functional connections with other departments or structures;
- establishing the rights and obligations of the employee.
The development of a job description is not mandatory, but it allows you to solve a number of management and executive tasks. For example, it can serve as evidence of a lawful refusal to hire due to insufficient qualifications. The law is mentioned indirectly in Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation No. 9 of 02/09/2004, which states that the provisions of the instructions are based on qualification characteristics.
Difference from functional management
The functions and responsibilities of an employee formally differ in several ways.
- Functional manuals highlight the general characteristics inherent in a profession or position and define the goals of work activity.
- Job titles allow them to be specified and classified, as well as to reflect the ways to achieve results.
How do functional guidelines differ from responsibilities?
- Essence. Functions mean the goal and result, responsibilities mean the means to achieve them.
- Hierarchy. Functional manuals are primary in relation to officials; on their basis, the employee’s responsibilities are established.
- Decor. Functional instructions may not be issued by a separate agreement, but may be part of an employment contract, while job descriptions act as an independent document.
For example, in accordance with the professional accounting standard approved by order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation No. 103n dated February 21, 2019, an accountant performs the functions of maintaining financial records, which form the responsibilities for accepting primary documents, monetary measurement of accounting objects and their final generalization. The listed positions are reflected in the employment contract and job description.
We solve legal problems of any complexity. #Stay home and leave your question to our lawyer in the chat. It's safer this way.
Ask a Question
Job Description
Why is it necessary to describe the position?
Success in selecting a candidate for a vacant position depends to a large extent on a thorough job description.
It gives you an inside look at the job process at the professional and personal characteristics that will be required of an employee to successfully perform the job, and will help you recognize the right candidate during an interview. Additionally, the job description lays the foundation for a clear understanding between employer and candidate about the responsibilities that come with the position. It will serve as the basis for setting goals, assessing the performance and development of your employee in the process of his work with you. The job description will also have a strong influence on the content of your Application for recruitment by our agency.
In the prompt publication of a vacancy, we use compressed information about the requirements, responsibilities and conditions taken from your Application, which also affects the efficiency of the search.
Thus, drawing up a Job Description is the basis for successful selection. If you know exactly who you plan to find before placing an order, then the entire selection process becomes more accurate and faster.
How to start
A job description is a list of the responsibilities, duties, working conditions, required personal qualities and reports for a given position.
The following details are required for the Job Description:
Personal qualities (related to the required position), for example:
· Communication skills, leadership, organizational skills, management skills, initiative, motivation, etc.
Work Environment (specific to your company):
· Working conditions
· Operating mode
General information about the position (related to structure and tasks):
· Job title and possible identifications
· Brief job description
· Description of tasks and responsibilities
· Description of subordination (which department, who is the direct superior, etc.)
· Working hours for this position
· Work control (reports, expected results, etc.)
Complex positions
For some positions, it is easier to indicate the area of responsibility by describing a list of tasks. But for the most complex positions, it will be even more effective to first outline goals and responsibilities, and only then tasks. An approach that considers the goal first, then must lead to the achievement of the result through individual responsibilities. For example:
Target:
Maximum awareness of potential customers about the company's products
Tasks:
• Tracking the trend of sales methods
• Defining a communication strategy
• Planning of advertising projects with calculation of costs and expected results
• Setting tasks for the creative department and monitoring their implementation
• Drawing up reports on advertising campaigns
• Coordination of producers and distributors of advertising material
• Coordination of collecting information about the company’s products (technical department, production department)
• Collection and analysis of the results of ongoing promotions
• Preparation of management reports with recommendations and development plans
You can expand some tasks to key indicators. From task-based information, the candidate will be able to infer what is expected of him.
Who should develop a document in an enterprise?
The distribution of workload and job responsibilities among subordinates lies with the manager. He has the authority to delegate management functions to employees of the organization or controlled structures. Job descriptions are developed both individually and as part of a working group, which includes:
- HR employee developing methodological recommendations;
- head of the department , defining the scope of responsibilities;
- in-house lawyer , who approves legal aspects and determines the compliance of the instructions with the law;
- director issuing an order approving the instructions.
Important! If the head of the organization is not involved in the development of labor documents, then the powers are transferred to another employee on the basis of an order to impose additional obligations. It lists the functions, responsibilities and details of authorized employees.
How to properly apply for DI in 2020?
The form of the document is not regulated by law, but when developing a job description, it is recommended to adhere to the directory of jobs and professions (ETKS) or the classifier of positions of managers, specialists and employees (EKS). The structure of the form is developed in accordance with the requirements of GOST.
GOST requirements
The current GOST R 7.0.97.2016 reflects recommendations for the preparation of production and organizational regulatory documents. Among them:
- General requirements;
- conditions for registration of details and diagrams of their location;
- sample forms.
Local acts are filled out in common readable fonts No. 12-14 with a paragraph indent of 1.25 cm. Basic requirements according to GOST:
- the logo of the organization is placed in the upper central or left field of the document under the details;
- details are located on the right, top or middle at the top of the sheet, which lists the name of the organization, registration address, TIN, OGRN, date of approval, position and name of the employee authorized to approve the instructions;
- in the created copies, marks are placed that decipher the location of the original;
- signatures and seals are placed separately and do not merge;
- for certification by several persons, blocks with their details are distributed under each other in accordance with the official hierarchy.
Attention. Electronic documents are certified with a digital signature, which does not cover the text of the document. On paper, the instructions are presented on an A4 sheet.
When information is placed on several pages, they are numbered. Layout diagrams of details and sample forms are given in the Appendix to GOST.
Structure and sections: how to compose a document?
When creating job descriptions, you can use standard samples collected in the GARANT database https://base.garant.ru/6135453/. For employees of departments performing functions to combat illicit trafficking in narcotic and psychotropic substances, instructions are filled out in accordance with the requirements of Order No. 235 of the State Drug Control Service of November 25, 2003.
According to the generally accepted form, under the word “I approve” in the header at the top, the details of the organization are listed, below in the middle the name of the document and position, the date of approval and the account number are indicated. The structure involves sections numbered with Roman numerals:
- General requirements indicating the position, the name of the unit or department, the procedure for appointment and release from obligations, the procedure for replacing a temporary employee, and qualification requirements.
- Functions that reflect the goals and objectives of the employee in accordance with the position.
- Job responsibilities that list the employee’s actions to perform assigned functions.
- Rights in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as those arising from work activities, for example, making proposals, familiarizing themselves with management decisions, providing assistance and obtaining information.
- Responsibility reflecting the fulfillment of obligations in accordance with instructions, financial responsibility, and the inadmissibility of violations.
The last section may be a section regulating the terms of interaction between the employee and other departments. Below are the details of the regulatory act on the basis of which the instructions were developed (reference classifier, Labor Code of the Russian Federation, accounting standard).
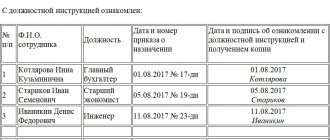
The document is agreed upon with the head of the department to which the employee is registered, as evidenced by his signature. At the very bottom, the employee puts a mark on familiarization. Also, a mark of familiarization can be placed in a journal or familiarization sheet as an attachment.
Important! The details indicate the date of approval, not the date of execution of the instructions.
Contents of the “Position Description” section
The meaning of job descriptions Read further: Link to the document in accordance with which the job description was developed
3 Contents of the “Position Description” section
3.1. Responsibilities
This section indicates the employee’s job responsibilities, taking into account the tasks and functions of a specific structural unit of the organization, with a detailed description of the main directions of his official activities. In addition, the section may indicate the employee’s responsibilities assigned to him in accordance with the established practice in this structural unit of distributing other responsibilities performed by the unit by decision of the head of the organization.
This section of the job description is developed on the basis of the “job responsibilities” section of the qualification characteristics for employee positions.
If necessary, the job responsibilities contained in the qualification characteristics for a particular employee position can be distributed among several performers. In the process of improving the organization of work, introducing technical means, taking measures to increase the volume of work performed, and reducing the number of personnel, it is possible to expand the range of responsibilities of employees in comparison with those established by the corresponding qualification characteristics. In these cases, the employee may be entrusted with the performance of job duties stipulated by the qualification characteristics for other positions, related in the content of work, equal in complexity, the implementation of which does not require another specialty, qualifications, or a change in job title.
Requirements for an employee’s qualifications can also be set out in a separate section of the job description with the same name. It is also advisable to include in this section a provision on the performance of one-time official assignments.
3.2.Rights
This section provides a list of employee rights defined by law and internal documents of the organization.
The design of the “Rights” section in its most general form can be as follows:
The employee has the right:
1. Get acquainted with the draft decisions of the head of the organization (structural unit) relating to the activities of the structural unit in which he performs his duties, or the area of work he performs.
2. Attend meetings and meetings of the organization (structural unit) on issues related to the activities of the organization (structural unit).
3. Participate in the discussion of issues regarding his duties.
4. Submit for consideration the head of the organization (structural unit) proposals to improve the activities of the organization (structural unit) and improve the working methods of the team; comments on the activities of the structural unit; options for eliminating existing shortcomings in the activities of the organization (structural unit).
5. Interact with employees of all (separate) structural divisions.
6. Request personally or on behalf of the head of the organization (structural unit) from other structural units information and documents necessary to fulfill his official duties.
7. Involve specialists from all (individual) structural divisions in solving the tasks assigned to the structural division (if this is provided for by the regulations on structural divisions, if not, then with the permission of the head of the organization).
8. Sign and endorse documents within your competence.
9. Require the head of the organization (structural unit) to provide assistance in the performance of official duties assigned to him and in the exercise of the rights provided for in this job description.
This article may establish the employee’s right to career growth, participation in professional associations and other public organizations not prohibited by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Job descriptions of heads of structural divisions can be supplemented with the following items:
1. Act on behalf of a structural unit and represent its interests in relations with other structural units of the organization within its competence.
2. Submit proposals on the appointment, relocation and dismissal of employees of a structural unit for consideration by the head of the organization; proposals to encourage them or to impose penalties on them.
3. Inform the heads of other structural divisions about shortcomings identified in the departments entrusted to them.
Certain rights can be specified taking into account the specifics of the employee’s job responsibilities.
For example:
The chief accountant of an organization has the right to:
1.
2.
…
3. Check in the structural divisions of the organization compliance with the established procedure for acceptance, posting, storage and expenditure of funds and inventory items.
However, we should not forget that specifying rights often leads to errors. Thus, the right of the chief accountant, set out in paragraph 3 of the above example, is rather his responsibility.
The provisions on interaction with structural divisions of the organization can be summarized in a separate section “Relationships”.
The structure of such a section, for example, could be as follows:
During the work process, the head of the documentation support department interacts with:
1. With all heads of structural divisions of the organization - on issues of record keeping, organizing control and verification of execution, improving the style and methods of working with documents, preparing and presenting materials necessary to management.
2. With the legal department - on legal issues related to the preparation of documents.
3. With the HR department - on issues of selection, admission, dismissal, advanced training and placement of department personnel, documentation support.
4. With the logistics department - on the provision of office equipment, document forms and stationery.
5. …
As a rule, the procedure for interaction between employees of structural units is determined by the Regulations on departments and services, and duplication in job descriptions is not necessary - a reference is enough. In the event that we are talking about the job description of an independent specialist (not part of the staff of any department), it is advisable to set out in detail his relationship with departments and individual specialists.
3.3.Responsibility
Here they indicate the extent of the employee’s responsibility for failure to comply with their job duties, as well as legal requirements. In this section of the job description, you can either limit yourself to general references to branches of legislation, or specify in what cases a penalty may be imposed on an employee (failure to perform or improper performance of specific job responsibilities specified in the job description; allowing specific violations of the law and internal procedures of the organization). .
For example:
The chief accountant is responsible for:
1. …
2. …
3. Untimely inspections and documentary audits in the structural units of the enterprise.
4. Violation of deadlines for submitting quarterly and annual accounting reports and balance sheets to the relevant authorities.
As a rule, such detailed regulation of an employee’s responsibility in a job description is due to the most common violations of specific provisions of the law and negligent attitude towards individual duties. However, the main regulatory documents that, for example, the chief accountant of an organization should know and be guided by are the Law of the Russian Federation “On Accounting”, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and other documents that provide for liability for specific offenses and failure to fulfill their duties by the chief accountant . It is very difficult to list in a job description all possible offenses characteristic of a given area of work in the financial and economic activities of an organization.
It seems that the development by lawyers of the organization of special tables, sets of extracts from the main regulatory legal acts on issues of employee liability and familiarization with them against a signature is more reasonable and effective. The job description can reflect groups of offenses and the method of determining the extent of responsibility for their commission.
It is also advisable to include clauses on responsibility for incorrect attitude towards subordinates in the job descriptions of heads of structural divisions, and clauses on insubordination in the job descriptions of department employees.
The meaning of job descriptions Read further: Link to the document in accordance with which the job description was developed
Information about the work “Regulation of personnel activities: analysis of job descriptions (using the example of the Novosibirsk City Hall)”
Section: Management Number of characters with spaces: 43073 Number of tables: 0 Number of images: 0
Similar works
Regulation of personnel activities: analysis of job descriptions using the example of the Organizational and Control Department of the Administration of the Central District of Novosibirsk
34315
2
0
... division. The assessment of the specific contribution of an employee is determined by the head of the unit, and the latter by the director of the enterprise [1]. Chapter 2. Analysis of job descriptions using the example of the organizational and control department of the administration of the central district of Novosibirsk. The main task of the administration is to resolve issues of local importance, implement decisions of the City Council, ...
Public relations as a strategic direction of activity of territorial public self-government bodies on the example of TOS Petrovsky microdistrict of Barnaul
156342
5
4
... involving the population in solving issues of local importance (using PR technologies using the example of TOS of the Petrovsky microdistrict) 3.1 Description of the analytical framework and research methods First, let us briefly describe the general context of the study. Territorial public self-government of the population of the Petrovsky microdistrict is carried out within the structural unit of the residential ...
Certification of municipal employees (using the example of the Administration of the Central District of Novosibirsk)
61950
14
0
... cases of quantitative coefficient) of compliance (non-compliance) of civil service positions with municipal service positions, taking into account the amount of knowledge, work experience and other indicators required for their replacement. Chapter 2. Certification in the administration of the Central district of Novosibirsk 2.1. Peculiarities of certification of employees of the administration of the Central District of the city...
Participation of the Russian prosecutor's office in law-making activities
223205
0
0
... in accordance with the goals and objectives of the study, the main problematic issues related to the participation of prosecutors in law-making work are considered. The work provides a brief historical outline of the development of the function of participation of the Russian prosecutor's office in law-making activities, examines the procedure for its implementation by the prosecutor's office (and bodies performing similar functions with the prosecutor's office) in ...
Alteration
According to the explanations in the letter of Rostrud No. 4412-6 dated October 31, 2007, the manager has the right to independently determine the procedure for making changes to the instructions. If the adjustments are related to changes in the employment contract, then it is necessary to notify the employee about this in writing against signature. It is recommended to present the document in a new edition. The provisions of the instructions may be adjusted on the basis of an order for amendments.
We solve legal problems of any complexity. #Stay home and leave your question to our lawyer in the chat. It's safer this way.
Ask a Question
Responsibilities of an employee of an organization according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
In Art. 12 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides the general rights and obligations of an employee. The latter include:
- conscientious fulfillment of obligations in accordance with the employment contract;
- compliance with labor discipline;
- compliance with occupational health and safety requirements;
- careful handling of the employer's property;
- notifying management about situations that threaten life or health.
Important! The employer has the right to indicate other rights in the employment contract and job description arising from the specifics of work activity and assigned functions.
Provisions that infringe on the interests of the employee and are contrary to the law are declared invalid.
Responsibility borne by the employee to the employer for failure to fulfill duties
The employee is obliged to comply with the provisions of the employment contract. If they are not followed, the employee will be held accountable.
It comes in the following types:
- disciplinary;
- administrative;
- criminal;
- material.
First of all, the employer is obliged to assess the severity of the employee’s disciplinary offense. If the employee’s actions did not lead to undesirable consequences, it is necessary to limit oneself to only a verbal remark.
Video
https://youtu.be/kzU-Hmkw6ro
The concept of financial liability is given in Article 238 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It rests with the employee who has entered into an agreement with the employer. The person must compensate for damage caused during the performance of duties. However, if the employer himself is to blame for the situation, it will not be possible to recover funds from the employee. Lost profits are not recognized as losses.
Please note: In accordance with Article 243 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employee bears full financial responsibility. This means that the person is obliged to compensate the entire amount of losses caused. However, in a number of situations, liability is limited to the size of the citizen’s salary.
A person may be held administratively liable if the provisions of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation are violated. Typically, it involves persons working illegally on the territory of the Russian Federation. However, the Labor Code provides a list of persons who cannot be fired.
The list includes:
- parents of one or more children under 3 years of age;
- single parents raising a child under 14 years of age;
- a person raising a minor citizen who has lost his parents;
- women carrying a child or on maternity leave;
- parents with a disabled minor child;
- other citizens who are protected by law.
Video
https://youtu.be/1VeIk-Ot9_A
Improper performance of duties
For failure to fulfill or improper performance of official obligations, a reprimand, reprimand or order of dismissal is issued. As evidence of misconduct, the employer requests an explanatory note, which is provided by the employee within 2 days. In case of refusal, a report is drawn up, and then disciplinary sanctions are applied.
An employee is not punished for refusing work that poses a threat to his life and health (Article 220 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), for participating in legal strikes (Articles 413-414 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), or for failure to fulfill duties not provided for by the employment contract or instructions.
The job description is approved at the initiative of the employer if it is necessary to regulate the functions and responsibilities of employees. The document is drawn up by the manager or an authorized person and comes into force on the basis of the order. For failure to fulfill or improper fulfillment of assigned obligations, a disciplinary sanction may be applied to the violator.
Responsibility for violations
There are legally formulated types of liability for failure to fulfill one’s labor function (Article 192 of the Labor Code). The employer has the right to independently determine the degree and measure of punishment, including discussing the issue of violation without documenting it.
Types of penalties:
- warning;
- rebuke;
- termination of an employment contract based on the employee’s fault.
- submission of a document on official non-compliance;
- demotion in position.
Penalty is applied to situations where no valid reasons have been identified for the violation. Moreover, the violation includes job responsibilities both under the employment contract and according to the job description.
If an employee was absent from work during working hours without a valid reason, the fact must be confirmed by an appropriate act drawn up with the involvement of witnesses. The concept of “workplace” does not mean a specific room, workshop, etc., but a point where the employee must be at the time appointed by the manager (business trip, work visit, flight, etc.).
If an employee refuses to fulfill his obligations under TD or DI, the employer has the right to take disciplinary action. If an employee avoids work due to changes in the TD or DI, the solution is to terminate the employment agreement by agreement of the parties. A violation is considered if an employee violates labor protection and fire safety rules.
Failure to comply with the requirement to undergo a regular or unscheduled examination by a medical commission is the basis for penalties and liability, if specified in the contract. Refusal to go to work without undergoing health and safety training is a violation.
An employee’s refusal to sign an agreement on collective financial responsibility is tantamount to a violation of labor discipline. Responsibility is provided for by clauses on failure to fulfill one’s official duties if the DKMO is integrally connected with direct labor functions.
If during the official proceedings it is established that, as a result of failure to fulfill his labor function, the employee resulted in events causing damage to the company, material damage may be recovered. In such situations, employers do not need a court decision; the right to receive compensation for losses as a result of the employee’s actions is specified in Art. 238. Labor Code of the Russian Federation. For example, in the event of a violation of the labor function by an accountant, which resulted in significant material damage beyond the scope of the accrued salary, the balance of the debt to the enterprise is recovered through the court.
The law also applies if property is lost, damaged, or worn out. When recovery requires financial contributions or compensation for damage, the amount is also deducted from the employee.