Labor legislation defines an employment contract as an agreement between an employer and an employee, according to which the employer must provide the employee with appropriate work, provide the necessary working conditions, pay wages in full, and the employee undertakes to perform a labor function and comply with internal labor regulations. Therefore, any omission in the employment contract, intentional or accidental, can lead to trouble for both the employer and the employee.
What mistakes do entrepreneurs most often make?
Error 1. The employer does not enter into an employment contract with the employee at all.
This is perhaps the most common mistake entrepreneurs make. Wanting to save on tax expenses, they hire a new employee under a civil contract. Such an agreement allows you to evade various obligations that an employment contract implies: payment of sick leave, downtime, provision of paid leave, payment of compensation upon dismissal, regular payment of wages, etc.
Civil contracts should be concluded with individuals only if it is necessary to perform one-time temporary work or provide some occasional services. The substitution of an employment contract with a civil law one can be detected during the process of checking the organization by employees of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation and tax authorities. The ban on substitution is established by Chapter 2 of Art. 15 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: “The conclusion of civil contracts that actually regulate labor relations between an employee and an employer is not allowed.”
Since last year, the consequences for replacing employment contracts with civil ones have become more severe. In accordance with Part 3 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, from January 1, 2020, the conclusion of a civil contract, which actually regulates labor relations between an employee and an employer, threatens a fine for officials in the amount of 10,000 to 20,000 rubles, and for an organization - from 50,000 to 100,000 rub.
An error was made in the contract when specifying an authorized person
Having provided legal support for real estate transactions for 15 years and regularly participated in courts to challenge transactions, we can confidently answer: nothing is guaranteed. On the contrary, a transaction certified by a notary contains more pitfalls.
The fact is that notaries do not perform a complete legal check of the apartment from the moment the house is built, as clients of lawyers, lawyers and realtors receive. The notary is limited to information from the real estate register at the time of the transaction being certified, and, at best, transfers of rights. We have not heard any questions from the notaries regarding what was there before with the apartment, who used it, where and why they left.
The agreement and other important documents must be signed by an authorized person - the director of the company or an employee who has a power of attorney to conclude the agreement. But it happens that, due to an error, one person is indicated in the preamble, and another person signs the agreement.
An error in the preamble of the contract when specifying the signatory will affect both the company and the signatory. The court will find out why one person was indicated in the contract, but the signature belongs to another. If it turns out that the signature was put by an employee without authority, and the company itself did not approve the transaction and did not accept execution on it, then the rights and obligations under this transaction arise not from the company, but from the signatory (Clause 1 of Article 183 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Resolution of the Ninth AAS dated March 20, 2017 in case No. A40-55855/16).
If the name of the director appears at the beginning of the contract, but the document was signed by an employee with a power of attorney, this is not considered an error in the text of the contract. This circumstance does not entail the invalidity of the document. The agreement is considered concluded with the subject of civil relations (resolution of the Thirteenth AAC dated October 3, 2007 in case No. A56-666/2007).
A notary's mistake can lead to refusal of registration, time and financial costs. We all want to believe that the document is certified by a qualified person, but no one is immune from inaccuracies. If the notary made a mistake, you will have to correct it. To do this, you will have to write a statement and give it to the culprit.
If, after notarization, the client discovers an error that he made independently when drawing up the contract, it is considered that the inaccuracy was his fault; in this case, it is impossible to demand a free correction from the notary.
We discuss in this article whether it is necessary to contact a notary to certify the car’s registration certificate.
If an error is made through the fault of a notary, he must correct it free of charge. However, there are also situations when notaries indicate that “the client, checking the accuracy of the paper, did not notice this inaccuracy.” The question can be called philosophical: on the one hand, the notary made a mistake, on the other hand, the recipient accepted the document, i.e. I was actually satisfied with the work done. By and large, the outcome of the case depends on the honesty and integrity of the notary.
In any case, the user, depending on the availability of free time, has several options - contact the same notary, find another one, or go to court.
Errors in
car purchase agreement
may affect the completion of the transaction and have legal consequences. The main thing is to detect inaccuracies in a timely manner. If it is important and threatens the agreement itself, we advise you to draw up an additional agreement by mutual agreement.
In it, indicate a link to the main document, describe all inaccuracies, provide correct information and submit this paper along with the main purchase and sale agreement. If an error was made during the certification of the contract by a notary, contact him; a specialist will be able to correct the inaccuracies for free or for a fee.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and press Ctrl Enter.
To solve your problem, get a free LEGAL consultation RIGHT NOW:
7 St. Petersburg
Error 3. The place of work is not indicated.
The place of work is a condition that must be included in the employment contract. Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation specifies: if an employee is hired to work in a branch, representative office or other separate structural unit of an organization located in another area, the place of work is indicated, indicating the separate structural unit and its location.
If the employment contract does not contain specific information about the place of work, the employee may not return to work on the first day. At the same time, the employer will not be able to take disciplinary action against him, since even in court a person can explain his absenteeism by the absence of important information in the contract.
In addition to everything listed above, the employment contract must indicate the taxpayer identification number if the employer is not an individual entrepreneur.
Error in the contract: what to do?
Important
Civil law contains clear regulations regarding the interpretation of the terms of any agreement. These are the norms that courts adhere to when discovering technical errors in a contract.
Attention
The general meaning of the concluded agreement and the direction of the will of the parties are also taken into account. That is why typical typos, omissions of letters, words, signs, inconsistencies and other technical errors usually do not matter.
Such inaccuracies, as a rule, are contained in all copies of the agreement, since they are made at the stage of computer typing of the text of the agreement.
Error 4. Working hours and number of vacations are not indicated.
Working hours and vacation are the employee’s rights to rest. If this issue is not discussed in advance, then in essence a person is not obliged to be at the workplace from 9:00 to 18:00. The elements of the working time regime include: the length of the working week, the duration of daily work (shift), the start and end time of work, the time of breaks in work, the number of shifts per day, shift schedules, alternation of working and non-working days.
If a person is entitled to 31 days of leave (disabled), then this must be stated in the contract.
Regarding the clause related to working hours, small employers often get off with general phrases, for example, “works according to the established schedule,” etc. But during the inspection process, GIT inspectors pay attention to this clause and ask to correct the contract if it contains inaccurate wording.
In the internal labor regulations
According to current practice, the internal labor regulations must necessarily reflect the timing of payment of wages (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, specific dates should be specified.
“The official salary is paid to the Employee every half month for the time actually worked based on the time sheet: for the first half of the month - on the 16th day, for the second half - on the 1st day of the next month.”
As for the amount of wages for the first part of the month (the so-called advance), the rules need to stipulate that it is paid according to the time actually worked (Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated May 23, 1957 No. 566; Letter of Rostrud dated 09/08/2006 No. 1557- 6) in accordance with the report card. Setting the first part of the salary at a specific amount, for example 40%, is illegal.
In the terms of remuneration, it will be illegal to establish that the employee is obliged to receive wages from a certain bank, for example, as part of a salary project (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Please note that to change the bank, the employee must inform in writing about the change in the details for the transfer of wages no later than five working days before the day of payment of wages.
“The Employer indexes the wages of employees, as a rule, by 3% annually in the second quarter of the current year based on the financial capabilities of the Employer and the approved budget.”
Write down all the guarantees and compensations provided to employees by law (allowances, additional payments, compensation), and also secure other payments established by the employer (for example, the possibility of bonuses).
Error 5. Lack of information about the place and timing of payment of wages.
According to the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, wages are paid every half month on the day established by the internal labor regulations, collective agreement or employment contract.
It is worth adding that all the previous points can also be described in the collective agreement. However, small businesses often do not do this.
Contents of the employment contract in accordance with Art. 57 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The employment contract specifies:
- Full name of the employee and name of the employer (full name of the employer - an individual);
- information about documents proving the identity of the employee and the employer - an individual;
- TIN (for employers, with the exception of employers - individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs);
- information about the employer’s representative who signed the employment contract and the basis on which he is vested with the appropriate powers;
- place and date of conclusion of the employment contract.
Mandatory terms of the employment contract:
- place of work, including address and name of a separate structural unit;
- labor function (work according to the position in accordance with the staffing table, profession, specialty indicating qualifications; specific type of work assigned to the employee);
- the date of commencement of work, and in the case where a fixed-term employment contract is concluded, also its validity period and the circumstances (reasons) that served as the basis for concluding a fixed-term employment contract;
- terms of remuneration (including the size of the tariff rate or salary (official salary) of the employee, additional payments, allowances and incentive payments);
- working hours and rest hours (if for a given employee it differs from the general rules in force for a given employer);
- guarantees and compensation for work under harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions;
- conditions that determine, in necessary cases, the nature of the work (mobile, traveling, on the road, other nature of work);
- working conditions in the workplace;
- condition on compulsory social insurance of the employee;
- other conditions in cases provided for by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms.
The absence of any information or conditions in an employment contract is not grounds for its termination or recognition as not concluded. In this case, it is enough to supplement the contract with the missing clauses. This can be done by drawing up a written application or additional agreement, in two copies, signed by the employee and the employer.
Alina Galiulina , project manager at SKB Kontur
Contractual mistakes of an entrepreneur
Elmira Bagautdinova
independent expert, tax consultant, member of the Chamber of Tax Consultants of Russia, certified teacher of the Institute of Taxation of Russia of Russia
Entrepreneurs formalize their relationships with counterparties through various business agreements. In order to correctly prepare the text of the contract and avoid mistakes, you must have certain knowledge.
Contractual activity of an entrepreneur
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 420 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a contract is an agreement between two or more persons to establish, change or terminate civil rights and obligations. The rights and obligations of the parties to a transaction arise only after the conclusion of an agreement. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides for entrepreneurs the same rules as legal entities for carrying out economic activities, except for cases expressly provided for by law. This is established by clause 3 of Article 23 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Agreements with both legal entities and individuals are concluded in simple written form.
In practice, there are cases when entrepreneurs do not pay due attention to the content of the contract being concluded, as a result of which the contract contains errors, including serious ones, leading to the invalidity of the contract, both in whole and in part.
The legislator comes to the aid of the entrepreneur, allowing the court to interpret an incorrectly drawn up agreement, based on the totality of all the factors that preceded the conclusion of the agreement.
In Art. 431 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes that “when interpreting the terms of a contract, the court takes into account the literal meaning of the words and expressions contained in it.” However, as they say, “trust in God, but don’t make a mistake yourself.” It is better to avoid a situation in which the concluded agreement contains controversial issues.
Failure to include in the contract mandatory (material) conditions provided for by law
Every entrepreneur should know that any agreement provides for:
- mandatory (essential) conditions provided for by law (Civil Code of the Russian Federation), as a rule, they are conditions on the subject of the agreement. Each type of agreement has its own subject.
— conditions that the parties set themselves (for example, fines and penalties).
You need to be able to distinguish one conditions from others. Essential are the conditions on the subject of the contract, the conditions that are named in the law or other legal acts as essential or necessary for contracts of this type, as well as all those conditions regarding which, at the request of one of the parties, an agreement must be reached. Otherwise, entrepreneurs will face serious problems.
The contract is considered concluded if agreements are reached between the parties on all essential terms. Vague and non-specific wording can lead, if not to disputes between the parties, then to claims from tax authorities regarding the recognition of tax expenses.
Sometimes essential conditions are not directly stated by law, but, based on the interpretation of the norms of current legislation, they are mandatory.
For example, based on the provisions of Art. 606 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, we can make an unambiguous conclusion that the essential terms of the lease agreement are the leased object, the lease term and the rent. Failure to include in the contract essential conditions provided for by law entails the invalidity of such a contract according to the rules provided for in the above Art. 168 Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Another important point. In practice, it is customary that the signature of an authorized person under an agreement must be supported by the seal of the organization (entrepreneur). Therefore, many consider an agreement that does not contain the seals of the parties (one of the parties) to be invalid (illegal). This is a misconception. A seal imprint in a contract is necessary only when it is provided for by law or by agreement of the parties (that is, the contract itself).
Currently, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation does not contain a requirement for the mandatory affixing of a seal in relation to all major civil contracts.
Inaccuracies in the contract and consequences
Incorrect contract date. This is one of the typical errors that is usually considered simply a technical error. Such an error may result in the contract being concluded earlier than the counterparty was registered. In this case, the tax authorities have the right to refuse to accept tax expenses under such an agreement.
An incorrect date may result in re-qualification of the contract.
Contract number. This detail is not a mandatory element of the contract. But its absence may lead to claims from tax authorities. For this reason, inspectors, for example, refuse to deduct VAT paid to suppliers or contractors. Such claims from tax authorities are unfounded, since the number and date of the agreement are not among the mandatory details of the invoice.
It is not necessary to indicate the contract number and date in the payment order. The absence of the number and date of the contract or their inconsistencies in the accompanying documents are not in themselves considered a violation. But in combination with other factors, it may be the basis for recognizing the tax authorities’ claims as justified.
Not all mistakes can lead to the recognition of a contract as illegal (invalid, including void).
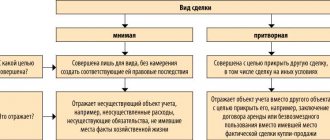
Conclusion of a contract not for the purpose of its execution
In practice, there are cases when an agreement is concluded not in order to fulfill it, but in order to thereby cover up any actions (inaction) of the party (parties) to the agreement, or so that such an agreement is available to third parties.
It should be remembered that these agreements cannot be considered legal. For example, in order not to pay taxes on rental payments, entrepreneurs A and B entered into a free use agreement between themselves. At the same time, it was agreed that for the rent of premises in a building owned by A, B would transfer cash to the owner, without witnesses. Such agreements would be declared invalid.
1. An imaginary transaction - a transaction made only for show, without the intention of creating legal consequences corresponding to it, is void.
2. A sham transaction is a transaction that is made to cover up another transaction, is void. To the transaction which the parties actually intended, taking into account the substance of the transaction, the rules relating to it apply. These provisions are established by Article 170 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Inclusion in the contract of optional conditions that worsen the position of the entrepreneur
First of all, this applies to the conditions providing for property liability for failure to fulfill obligations assumed under the contract. Common measures of such liability are fines and penalties, which are included in almost any business agreement.
The entrepreneur is not obliged to agree with what is proposed to him in the draft agreement. Reason: if fines and penalties are not provided for by law, they can be included in the contract only by agreement of the parties.
Therefore, in the process of concluding a contract, it is necessary, if possible, to exclude from it those provisions that may lead to negative consequences in the future. In addition to penalties and fines, these may include shorter (compared to the law) deadlines for fulfilling obligations, increased requirements for the completeness and packaging of goods, etc. Otherwise, your business may suffer.
Incorrect drafting of the contract
It often happens that an agreement is drawn up correctly, but due to incorrect wording, it is not always possible to establish the true will of the parties. For example, the supply agreement states that the delivery of goods is carried out “based on customer requests, within three days.” This formulation is incorrect, because the contract does not indicate what the customer’s requests should be (oral by phone, written, etc.) and from what moment the three-day period specified in the law begins (from the moment of receipt of the written application, from the moment the customer calls, from the moment the cargo is sent, etc. .d.).
These inaccuracies do not pose a threat to the entrepreneur as long as his work with contractors is based on faith. But when a dispute begins between the parties to an agreement and the law comes into play, it is not always easy to prove your position based on such an agreement, especially if the other party categorically insists on its (opposite) arguments. Therefore, any agreement should be drawn up in such a way that there are as few such “gaps” as possible.
Concluding an agreement by email
It is a common practice in which the parties not only transfer draft agreements to each other via e-mail, but also send ready-made scanned agreements with a signature and seal. Many entrepreneurs naively believe that an agreement concluded in this way can be considered legal.
A scanned signature in a contract is not at all the same electronic signature established by law. In order to obtain the right to electronically sign documents transmitted via the Internet, the interested party must go through a special procedure provided for by Federal Law dated April 6, 2011 No. 63-FZ “On Electronic Signatures” (obtaining special keys, certificates through certification centers, etc. ). Only in this case will the signature under the contract be considered valid and legal, and the contract properly concluded.
You can use e-mail to conclude contracts without the right of electronic signature only in cases where there are no problems between the parties to the contract and they need the contract itself only to confirm the contractual relationship. However, in case of disagreement, referring to such an agreement will be problematic.
Violation of the terms of the contract provided for by agreement of the parties
If the parties to an agreement stipulate the conditions under which, in their opinion, this agreement should be concluded, and one of the parties violates these conditions, such an agreement may be declared invalid in court at the request of an interested party.
For example, in the draft contract agreement concluded between an entrepreneur and an LLC, it was stated that this agreement comes into force from the moment it is signed by the heads of the parties. However, on the part of the LLC, the agreement was signed not by the general director, but by one of the employees by proxy. The manager did not read this agreement. This served as the basis for the entrepreneur to go to court to invalidate this agreement.
Correction of errors made when concluding a contract
What should an entrepreneur do when an agreement has actually been concluded, but was concluded with violations? Should I immediately demand termination? There is no clear answer to this question. If an agreement is contrary to the law and its conclusion is called into question, then it is best to terminate such an agreement. When an agreement is legally correct, but not beneficial to the entrepreneur, there may be problems with termination if the agreement does not provide for the entrepreneur’s right to unilaterally refuse it.
It will be almost impossible to terminate such an agreement. Based on the provisions of Article 450 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, it is possible to establish two main ways to change or terminate an agreement concluded contrary to the interests of the entrepreneur:
1. By agreement of the parties to the contract . In this case, the entrepreneur is obliged to send a written proposal to the other party to amend the agreement or to cancel the agreement and conclude it in a new edition. A proposal to amend the contract is drawn up in the form of an additional agreement to the contract.
It indicates the numbers of clauses (subclauses) of the agreement and their content in the new edition proposed by the entrepreneur. The additional agreement is drawn up according to the same rules as the main agreement. On the other hand, the agreement itself may provide for additional requirements for the preparation, direction, approval and signing of an additional agreement. The additional agreement in two copies is sent to the other party to the contract, signed and sealed (if a seal is needed in this case). If it is accepted by the opposite party to the contract and signed by it, then the matter can be considered resolved. If the other party does not agree, the agreement will remain in force. Alternatively, the entrepreneur can refuse the contract, but more often this threatens him with big troubles in the form of penalties and lost profits.
2. By court decision. It should be borne in mind that the court will never oblige the other party to agree to change the contract if its provisions, disputed by the entrepreneur, do not contradict the law and the agreement of the parties. That is, if at one time the entrepreneur himself did not notice that his rights under the law were infringed, it will not be possible to correct this in court.
For example, an entrepreneur filed a claim with the arbitration court to invalidate a clause in a supply agreement, according to which the entrepreneur, as a supplier, is obliged to pay a fine of 50% of the cost of the goods for late delivery of goods. The arbitration court rejected the entrepreneur's claims, since this clause of the agreement does not contradict the requirements of the current legislation and was provided for by agreement of the parties, based on the principle of freedom of contract, provided for in Art. 421 Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
If the contract completely or partially contradicts the law or the agreement of the parties, the entrepreneur will have every chance to change it through the court or declare it completely invalid.
In conclusion, we note that having a correctly drawn up agreement is important not only for the purposes of civil legal relations, but also for tax accounting purposes, since errors in the agreement can lead to claims from the tax inspectorate and additional tax charges in the future. Therefore, the terms of the agreement must be worked out and assessed with positions of tax consequences. And one more thing: When using standard forms of contracts, remember that they require individual modification for a specific type of business activity.
photo - plusworld.ru
Let's summarize what has been said:
- There will always be typos and errors in employment contracts; no employer or HR specialist is immune from this. Simply, you need to strive to minimize them or avoid them altogether.
- If they are allowed, then all necessary measures must be taken to correct them, otherwise the employer may face the employee in court.
- Most often, typos in employment contracts are made in: the amount of salary (bonus or allowance), the date of hiring, the duration of the employment contract, working hours, the number of vacation days, in short, in almost everything.
- Everything can be fixed. Depending on the type of typo, you can: conclude an additional agreement to the employment contract, enter information directly into the text of the employment contract itself, or re-sign both copies of the TD with the correct data, of course, with the consent of the employer and employee.
- If it is impossible to reach an agreement with the employee, then in court, additional evidence may include: an order for employment, an application for employment, a staffing table, time sheets, additional agreements, a personal card, personal accounts, witnesses.
Related Posts
- Salary of a part-time worker in an employment contract What salary should be indicated for a part-time worker in an employment contract? Is it possible to set a full salary? Examples from...
- Working conditions at the workplace in the employee’s employment contract Read more about working conditions in the employment contract. Example of wording. Arbitrage practice.
- Changes in labor legislation from 2020! Well, the salads have been eaten, the gifts have been given, we’ve eaten too much candy, it’s time to mentally prepare for the new work...