Leave without pay is considered unscheduled leave for employees of the organization. It is necessary in cases where an employee has any life problems. An employee can contact their manager with a request to allow him unpaid leave if there is truly a good reason for this. The boss has the authority to consider such a request, approve it or deny it if he considers the reasons insufficient. If the organization agrees, a special order is issued.
The conditions for granting leave without pay are specified in Article 128 of the Labor Code of Russia. According to the law, the employee agrees on the duration of time off without pay with his employer. But the employee must understand that vacation without compensation lasting more than fourteen days is not counted in the length of service. Also, because of this, the date of regular paid leave is postponed.
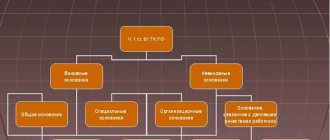
Provisions of the Labor Code on leave without pay at the initiative of the employer
In 1996, the issue of free holidays at the initiative of the enterprise management was considered by the Ministry of Labor.
It has issued clarifications on this issue. After this, a resolution was issued that confirmed them. There, situations were considered when an employee can go on vacation without pay. It was indicated that one of the reasons could be family circumstances. The employee had the right to ask for leave, confirming the reason with relevant documents. In such a situation, it was allowed to take a vacation of up to 5 days.
https://youtu.be/yflimnTttLg
Other options to go on unpaid leave are not prohibited, but can only be carried out with the permission of the boss.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows certain categories of citizens to receive this type of leave at their own request:
- If a citizen is retired but continues to work, he is given this right. However, during the year you are allowed to receive no more than 14 days. You can take vacation days in parts or all at once.
- An employee who is the wife of a deceased military man has the right to take 14 days without pay annually.
- If an employee has a disability, he is allowed to receive 60 days annually at his own expense.
- A student who works is entitled to 15 days of such leave.
- Those who take entrance exams to a university receive 15 days to do so.
- 35 days are given to veterans of the Great Patriotic War.
In addition to those who receive this right on the basis of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, there are other categories whose vacation is determined by other regulations:
- Heroes of Socialist Labor receive 21 days of leave without pay.
- those who were residents of besieged Leningrad have the right to go on unpaid leave for two months;
- Heroes of the Soviet Union are given the right to 21 days;
- Heroes of Russia can receive up to 21 days of unpaid time off each year.
Forced leave at the initiative of the employer can be carried out as follows:
- as a suspension from work;
- as forced absenteeism;
- in the form of downtime.
In the first case, payment is possible only in cases where the suspension was not the fault of the employee. In this case, the payment will be the same as for downtime due to the fault of the boss.
Downtime due to the fault of the boss means that two-thirds of the employee’s average salary will be paid.
In case of downtime due to the actions of third parties, payment will be two-thirds of the employee’s salary.
In all three situations considered, if the employee does not perform work due to his own fault, he is not entitled to payment for this time.
What does the law say about unpaid leave?
In 1996, the Ministry of Labor, in an annex to the labor legislation, provided clarifications on unpaid leave at the initiative of the employer. The explanations were approved by resolution and received an identical name.
They, in particular, said that any employee could go on leave without pay for family reasons: official registration of marriage, birth of a child, funeral of immediate relatives. If such circumstances arise, you can receive maximum leave without pay of up to five days . If there are any other reasons, then you need to separately agree with the employer on the reasons for the leave and the timing.
How and who can take leave without pay?
The Labor Code has identified a separate category of citizens who have the right to take additional days off during the year.
- Retirees who continue to work . They can take either separate days off or several days together, but no more than fourteen days in total.
- Spouses of fallen military personnel are entitled to up to two weeks of leave .
- Working disabled people , with any disability group, can claim sixty days a year.
- students who are also working, as well as individuals entering higher education institutions, are given fifteen days.
- Participants in the Great Patriotic War, according to the labor code, can additionally receive thirty-five days of time off without pay.
To this category of persons defined by the labor code, another list , already regulated by separate laws.
- Law No. 5 of 1997 expands the list by including Heroes of Socialist Labor . Such persons can take additional days off for up to three weeks a year.
- Also the fifth law, but only from the year 1995, gives the right to time off for up to two months to military veterans and those with the status of “Resident of besieged Leningrad” .
- The right to enter the list and receive up to three weeks of unpaid time off was given to Heroes of the Soviet Union and Heroes of Russia . This right was legalized in 1993 in law No. 4301-1.
- And the last number of applicants for unpaid days off are the spouses of active military personnel.
How to arrange a vacation at your own expense?
To get the necessary days off, you must first write an application. The application shall indicate the reason and duration of the leave. If so, you will need to attach copies of documents confirming the reason. The employer's consent is expressed in his order for leave without pay. The employee must be familiarized with the order, after which he signs it.
- The amount of leave without pay is agreed upon jointly with management . If time off without pay is given by law, then the number of days is regulated by law.
- The number of days off without pay, no more than fourteen, must be included in the length of service.
- Days required by law cannot be prohibited by the manager.
- The fate of an employee who takes additional days off at his own expense for a good reason is decided only by his boss .
Positive aspects of additional days off without pay
For an employee, being on leave is a positive thing in terms of solving his problems.
- in the time he requested, temporary difficulties can be solved;
- it is impossible to dismiss him while he is on forced leave, unless during this time the enterprise has been liquidated or its activities have completely ceased;
- the average salary remains unchanged, the time spent on vacation is excluded from the calculation period for calculating salaries;
- the time spent on maternity leave must be paid;
- Tax deductions, regardless of whether wages are paid or not, do not stop.
Negative aspects of additional days off
There are also plenty of disadvantages to forced time off:
- if the time spent on unscheduled leave exceeds the required number of days, then each day exceeding the limit is deducted from the main paid leave;
- sick time on such days off is not paid - only the day following the end of the vacation can be paid;
- The insurance period for this period is not taken into account.
Preface
Leave without pay at the initiative of the employer, which will be discussed, is not provided for by current legislation. However, the provision of such leave to employees has long been widespread, and the action itself has a number of names - such leaves are called “unpaid”, “forced” or “administrative”.
“Leaves without pay can be granted only at the request of employees for family reasons and other valid reasons (Article 76 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), and “forced” leaves without pay at the initiative of the employer are not provided for by labor legislation. If employees, through no fault of their own, are unable to fulfill the duties stipulated by the employment agreements (contracts) concluded with them, then the employer is obliged, in accordance with Article 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, to pay for downtime in an amount not less than 2/3 of the tariff rate (salary).
Despite the fact that both the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the Labor Code of the Russian Federation there are no legal grounds for sending employees on leave without pay in cases where such an initiative does not come from the employees themselves, some employers quite effectively carry out such actions for themselves as way to reduce labor costs.
Maximum period without pay under the Labor Code
The legislation does not distinguish a special category of leave without pay at the initiative of the employer.
Therefore, sending an employee on unpaid leave is possible if management is able to persuade or force the employee to take time off at his own expense.
The duration of unpaid leave will be calculated on a general basis - duration for various reasons.
In general, this type of vacation is arranged in such a way that it is as if the worker himself was the initiator - registration of time off at the initiative of the employee.
Therefore, the maximum duration of rest depends on the reason that will be reflected in the application. For certain categories of citizens, unpaid vacations can be extended for longer periods.
The employer also has other similar tools. In fact, a kind of leave without pay at the initiative of the employer is suspension from work (Article 76 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). There are no specific requirements for the maximum terms of such a measure, because the person is suspended until the cause of this measure is completely eliminated.
However, such a decision requires grounds:
- showing up to work drunk;
- absence of a mark on completion of safety or labor protection courses;
- lack of necessary knowledge to perform certain works (the license has expired, there is a need to take retraining courses, etc.);
- contraindications for health reasons have been received (instead of sick leave, a person will receive a suspension if he is offered to work in another position without identified medical restrictions, and he refuses);
- the employee has not passed a medical examination, including a psychiatrist examination, of course, if periodic examination is required by working conditions.
Important! If an employer offers an employee a fictitious suspension, you should take a close look at the wording, because some of them serve as grounds for disciplinary action up to and including dismissal.
Speaking about the timing, the employee should know that if the leave without pay is more than 14 days in a row, then the time beyond the specified period does not count towards the length of service. How weekends at your own expense are taken into account in your experience can be read here.
Procedure for registering days at your own expense
Taking a vacation at your own expense on the initiative of the employer is a gross violation of the law.
Therefore, formally the procedure is no different from the actions when granting leave at the request of an employee. Therefore, the registration procedure is as follows:
- Preparation of an application by the employee, where he himself asks to be given unpaid days off.
- Drawing up an order based on the application.
- Recording days off in the timesheet using special designations.
- Reflection of granted leave without pay in a personal card.
Employee actions
If an employee is forced to take leave at his own expense, he has the right to file a complaint with the Labor Inspectorate. If a violation is confirmed, the management of the enterprise faces liability under Art. 5.27 of the Administrative Code:
- a fine for an official from 1 to 5 thousand rubles;
- the owner of the individual entrepreneur has the same fine or disqualification for 90 days;
- the organization is fined from 30 to 50 thousand or suspended for up to 90 days;
- in case of repeated violation, financial liability increases and the period of disqualification is extended (from 1 to 3 years).
An employee sent on unpaid leave without his consent receives the right to demand in court the payment of two-thirds of his salary, as it should be in case of downtime due to the fault of management.
Of course, such proceedings will most likely lead to the rapid dismissal of the “rebellious” employee, even if the management of the enterprise changes.
To avoid this, it is recommended to file a collective complaint on behalf of the majority of the staff.
Employer steps
The only legal way out of the situation for the employer is to formalize the downtime with the payment of two-thirds of the salary.
Other measures must either be agreed upon with staff or taken at your own risk in violation of the law. How to convince employees to take vacation at their own expense?
To take days off at your own expense at the initiative of the employer, you should be guided by the following arguments:
- Indicate a temporary period of crisis.
- Promise compensation for days off without pay with future bonuses, the opportunity to take annual paid leave in the summer months;
- Explain that the enterprise will go bankrupt if the staff refuses to go on unpaid leave, and people will still lose their jobs;
- Describe the positive side of taking leave at your own expense: maintaining a position without the possibility of dismissing an employee, taking into account length of service for up to 14 days, and so on.
In general, the decision to voluntarily take some employees on unpaid leave at the initiative of the employer should be a compromise. Management should understand that this is a certain sacrifice on the part of the staff for the sake of preserving the enterprise. Therefore, such a solution should be encouraged in the future, but in any case it is not advisable to lead to conflict. Then it will be more profitable to arrange a simple one.
The law prohibits sending employees on leave without pay without their consent.
However, in reality, the state is not always able to control this violation. Workers also fail to restore their rights even in court.
Simple
This situation arises if work was suspended by decision of the employer. The reasons can be not only economic, but also technological, organizational or technical.
Although this situation is similar to an unpaid vacation, there are two important differences:
- if there is downtime due to the fault of management, then the employee receives two-thirds of his average earnings for his entire time;
- During time off, the employee is not at his workplace; during downtime, he must be at work.
Usually the question of where he should be is decided by the manager, taking into account current regulations. If the employee is allowed to leave the workplace, he may have free time.
| Whose fault is it simple | Payment amount |
| Downtime due to the employer's fault | 2/3 of the average employee salary |
| Downtime due to employee fault | days are not subject to payment |
| The blame for downtime lies neither with the employee nor with the employer | at least 2/3 of the tariff rate in proportion to the number of days of downtime |
In a situation where downtime occurs due to equipment breakdown, the employee has the responsibility to report to his boss about the start of downtime.
Vacation without pay according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
There is no direct limitation on this period.
If the law allows the employee to take the leave in question, then the following rules apply:
- If there is a good reason, which is confirmed by relevant documents, then at his request he must be granted such leave for a period of up to 5 days.
- The law provides certain categories of the population with the right to take free vacation at will within the allotted number of days.
- If the law allows an employee to take a certain number of days without pay within one year, he can receive them if his boss does not object.
- If an employee has exceeded his limit, then, in agreement with the director, he can receive the required number of days off, however, all days exceeded will be deducted from the length of service to determine vacation time.
In accordance with Article 128 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, leave without pay can be granted to an employee for family reasons and other valid reasons at the request of the employee, and the duration of such leave is determined by agreement between the employee and the employer.
- participants of the Great Patriotic War - up to 35 calendar days a year;
- working old-age pensioners (by age) - up to 14 calendar days per year;
- parents and wives (husbands) of military personnel who died or died as a result of injury, concussion or injury received during the performance of military service duties, or as a result of an illness associated with military service - up to 14 calendar days a year;
- working disabled people - up to 60 calendar days per year;
- employees in cases of the birth of a child, marriage registration, death of close relatives - up to five calendar days;
- in other cases provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws or a collective agreement.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Product profitability - the formula for calculating realized sales on the balance sheet
Indefinite leave
Today we will talk about the sample and procedure for filling out this order, we will consider the main nuances and features of filling it out. Indefinite unpaid leave for a director The following are examples of similar questions: An employee of the organization has a son who was drafted into the army, and because of this she asked for free leave.
However, the organization is currently going through a rather difficult time, and it is simply impossible to provide leave at the moment. Is it possible to refuse leave? The usual one is regulated by an article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Due to difficult family or other circumstances requiring presence, or due to other urgent reasons, an employee may apply for time off at his own expense.
But, in addition to inspiring words of support and advice, Habrowers also shared their own similar situations in which their labor rights were violated. The situations were very different: But they were all similar in one thing: Issues of labor legislation Vacation must be agreed with the employer This is the first group of vacations that can be granted if there is a good reason.
The legislation is aimed at maintaining a certain balance between the interests of employees and management. That is, it is assumed that it is possible to indicate different durations of rest, depending on the reasons why it was needed. Corporate interests are also taken into account. Management is responsible for providing vacations. But there are no clear legislative guidelines regarding the duration.
The manager must decide for himself whether the reason is valid. And if so, then by how much. An employee cannot voluntarily refuse to go to work without appropriate grounds.
This will be illegal if the other party simply refused earlier. It is considered that there has been a violation of labor discipline. You can turn to the court if the decision itself on valid reasons seems illegal.
The main thing is to make sure that a formal understanding has been reached. Unauthorized leave can also lead to dismissal. Employers and their responsibilities There are citizens of certain categories who are required to provide vacations under any circumstances. That is, refusals are unacceptable. So, written applications for vacation always require a positive answer when it comes to: WWII participants.
They are given up to 35 days over one year. Pensioners of the appropriate age who continue to perform work duties. They can count on two weeks. Parents and wives of military personnel, or employees of government agencies. Working disabled people are given up to 60 days of rest. Those who have children. Then you can be released for five days.
Suspension from work
This refers to a situation where a manager has suspended a subordinate from work for certain reasons.
This usually happens in the following situations:
- An employee who came to work while intoxicated (it could be alcohol, drugs or any other) is suspended.
- To perform your immediate duties, you must undergo appropriate training in labor safety. If this is not done, dismissal from work is possible.
- Some professions require a mandatory medical examination. Sometimes a psychiatric evaluation is necessary. If an employee evades these procedures, the boss must remove him from his immediate duties.
- Sometimes someone starting a job must meet certain medical requirements. If he does not comply with them, he cannot perform his job duties.
- Failure to have the appropriate qualifications to perform the job, or a license if required, will result in disqualification.
- Removal occurs at the initiative of the boss if there are appropriate grounds. This is done only until the causes are eliminated.
A medical report may cause an employee to be transferred to another location for up to four months. If he refuses to comply, he is removed. At the same time, for the specified period, his workplace remains with him.
It happens that the boss does not have the opportunity to provide the work mentioned. However, in this situation, the employee will be suspended for the specified period.
In the latter case, wages are usually not calculated, but the collective agreement may provide for payment in such situations. Another basis for receiving money may be an employment contract concluded with him.
What should a director do if he needs to send an employee on time off at his own expense?
As mentioned earlier, the law does not regulate unpaid leave granted to an employee at the request (demand) of the employer. In order to send a citizen on vacation without pay, the head of the organization who put forward such an initiative must convince or, alternatively, force him to accept this proposal.
Obviously, the registration of leave at one’s own expense, granted to a worker at the initiative of the employer, will be carried out as if the employee himself had asked for such time off voluntarily. This means that the maximum duration of the vacation period will be determined by the reason specified in the corresponding application of the working citizen.
Thus, for certain categories of workers, vacations provided at their own expense can be issued for long periods (generally binding norms of Article 128 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation apply).
Another way to grant an employee unpaid leave at the initiative of the organization’s management is to apply the specific provisions of Article 76 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which defines the grounds and procedure for removing an individual from work.
The duration is not limited by law, since this measure is applied until the final elimination (cessation) of the circumstances that prompted the employer to use it.
Thus, the manager is obliged to remove the employee from work or, alternatively, prevent him from performing his job duties if the following circumstances exist:
- A citizen appears at work in a state of intoxication.
- The employee did not complete the required training and occupational safety exam.
- The employee has not undergone a regulated medical examination (examination by a psychiatrist), if this requirement is mandatory.
- The employee has medical contraindications.
- Suspension of a citizen’s special right (for example, the right to drive a car) for a maximum of 2 months.
- Authorized officials (official bodies) put forward this requirement.
- Other grounds provided for by law.
Procedure for granting leave
In all cases, the initiative to provide leave without pay must come from the employee. An employer should not influence an employee’s decision, even simply by asking the employee to take unpaid leave.
In the application, the employee must independently indicate the reasons why he needs leave without pay, as well as the duration of such leave. The length of service with the employer does not matter when granting an employee leave without pay.
The employer, in turn, in the absence of an obligation to provide such leave, can satisfy the employee’s request if it considers that the employee’s absence will not have a negative impact on the production process. In other words, granting an employee leave without pay in cases not specified in the law as an obligation of the employer is the right of the employer.
Vacation at one's own expense is granted at the employee's initiative.
And this is not surprising, because, according to Russian labor legislation, this concept simply does not exist. However, such a definition exists in Russian society, albeit unofficially. Often, under difficult, unfavorable circumstances, organizations voluntarily send employees on indefinite leave, until better times come - without pay, but with the hope of returning. True, only a few people who are poorly familiar with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation agree to such conditions.
Such a maneuver allows the employing company to save on employee salaries, respectively, on tax deductions, as well as on the maintenance of workplaces. Meanwhile, we have one law and it says the following. The organization has the right to grant leave without pay only upon a written application from the employee.
Provisions of the Labor Code on leave without pay at the initiative of the employer
One of the reasons for absence from work may be, for example, illegal dismissal. If such a situation occurs, the employee must prove the fact that the dismissal was illegal. In this case, he must be fully compensated for the earnings that he did not receive for this reason. This is stated in Article 234 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It must be taken into account that this period of time must be taken into account when determining the length of service that gives the right to receive basic paid leave in accordance with Article 121 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Negative sides
Unpaid leave at the request of the employer
The legislation does not provide for the option when a boss requires a subordinate to take leave without pay.
If we are talking about a request from a boss to his employee, then the latter has the right to voluntarily agree to such a development of events. In this case, leave at your own expense is issued in the usual way. The only peculiarity is that, in case of agreement, the duration of the rest is automatically agreed upon.
Sometimes the employer may offer the employee to take time off without pay in the form of suspension from work. At the same time, the employee must be careful - the fact is that this action in the future may become the basis for disciplinary action.
Application Form
To receive unpaid leave, you must correctly fill out an application. Let's consider the algorithm for writing such a statement. In the upper right corner you need to write in whose name you are writing this application. For example: “Director of the private enterprise Gaus Ivanov I.I.” Below you indicate who wrote this application, that is, indicate your position, surname and initials. Next we move on to the main part of the statement. In the middle, in large font, you need to write the word “Statement”, and below is the entire text. An application of this kind will have a main part, which should contain the text of the appeal itself - here you should indicate the reason why you are asking for administrative leave within the period you specified. Below you need to indicate the current date and sign. After the appeal is drawn up and signed, the HR department issues an order in the T-6 form. You can write the application by hand, but you can also type it on the computer. The main thing is that you put your signature under the text of the statement itself. It will be better if you bring your application to the employer in person. If you do not have the opportunity to appear at work, then it is best to ask a colleague to hand over the document to the employer.
You can view a sample application, as well as a sample protocol, on our website; you can also download this sample as a separate file, in just one click and completely free of charge.
Remember, if your request was ignored and leave without pay is not provided, this is a gross violation of the provisions of the Labor Code. It may seem that a few days off is not a reason to start a dispute with your superiors. But in reality, people face many problems due to this.
- Leave without pay granted for an insufficient period;
- Refusal to grant leave without pay due to minor errors in the preparation and submission of the application;
- Refusal to give leave without pay due to imaginary reasons (lack of staff, workload at work, etc.);
- Unspoken “harassment” of an employee after he legally took leave without pay.
How to send an employee on vacation at your own expense
The law answers this question unequivocally: the employer does not have such a right. However, in real life this is not so rare. In fact, there is a request from the boss to the subordinate about this. Moreover, it is very difficult to refuse in this situation.
Typically, such situations arise in cases where the company, for some reason, does not have enough money to pay salaries. If employees go on leave without pay, the salary fund for the corresponding month will be significantly less.
This situation usually arises if the workload of subordinates is insufficient. Since it is impossible to send an employee on unpaid leave, we can say that there is downtime.
We invite you to read: Additional leave for a single mother - Human Rights
Thus, the employee will receive two-thirds of his salary during this time. Of course, in this case there will be some savings in the salary fund, but it will be much less than in the case of taking unpaid leave at will.
The financial difficulties of an enterprise fall under the category of business risk, which is borne by the employer, and not by his employees.
Employer motivation
So, the employer does not have the right to force employees to take leave without pay, i.e. send them on “forced” leave. So for what reason do employers, in violation of the procedure established by law, send employees on such vacations? The answer is simple - saving money.
Let's imagine a situation where an organization does not receive the necessary financing, for example, due to the insolvency of the main customer of the products or due to the bank's refusal to issue a loan for the purchase of the necessary raw materials. As a result, the employer is unable to provide workers with work and pay them wages.
It should be noted that if an employer cannot provide employees with work due to non-receipt of funds from customers, judicial practice proceeds from the fact that circumstances related to the lack of financing, even due to unfavorable market conditions, price changes, or failure to fulfill contractual obligations by counterparties, should be considered as fault employer, since such difficulties fall into the category of business risk, for which the employer carrying out business activities is responsible, which means downtime in such a situation must be paid in the amount of at least two-thirds of the employee’s average salary.
The above position corresponds to Article 2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, which states that entrepreneurial activity is an independent activity carried out at one’s own risk, as well as Article 401 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, according to which a person who has not fulfilled or improperly fulfilled an obligation when carrying out entrepreneurial activities, bears responsibility unless he proves that proper performance was impossible due to force majeure, that is, extraordinary or unavoidable circumstances under the given conditions.
Thus, with the exception of the cases specified in Article 401 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the employer can be found not guilty if he has taken all measures to prevent downtime.
When is unpaid leave possible?
Most often, an employer offers its employees to go on unpaid leave due to downtime.
Important! Formally, a temporary suspension of work or the provision of services due to technical, organizational, economic or other problems does not provide grounds for sending personnel on leave without pay.
Downtime does not provide for the absence of people from the workplace, but does imply a reduction in their wages (Article 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- by a third (the average salary is taken for calculation), if the downtime arose due to the fault of management;
- 67% of the “bare” salary is paid if production stopped due to an objective factor, and not due to the fault of the employees and management of the enterprise;
- payments stop completely if there is downtime due to the employee’s fault.
This provision in some cases makes it beneficial for both staff and management to take leave without pay.
Responsibility
If an employer, on his own initiative, sends employees on leave without pay, his actions can be qualified as a violation of labor and labor protection legislation, for which Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation provides for liability in the form of an administrative fine. officials in the amount of one thousand to five thousand rubles;
for persons carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity - from one thousand to five thousand rubles or administrative suspension of activities for a period of up to ninety days; for legal entities - from thirty thousand to fifty thousand rubles or administrative suspension of activities for a period of up to ninety days, and violation of labor and labor protection legislation by an official who was previously subject to administrative punishment for a similar administrative offense - entails disqualification for a period of one year up to three years.
At the same time, employers should keep in mind that in accordance with Part 3 of Article 2.1. Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses, in the event of a legal entity committing an administrative offense and identifying specific officials through whose fault it was committed (Article 2.4 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation), it is allowed to bring to administrative liability under the same norm both a legal entity and the said officials.
Since the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses does not provide in this case any restrictions when imposing an administrative penalty, the judge has the right to apply to a legal entity or official any measure of punishment within the sanction of the relevant article, including the maximum, taking into account mitigating, aggravating and other circumstances affecting the degree of responsibility of each of these persons (clause 15 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 24, 2005 No. 5 “On some issues that arise for courts when applying the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses”).
Actions of the employer, initiated by him independently and related to sending employees on vacation without preserving their earnings, are qualified as a violation of labor legislation. For committing this offense, the employer is subject to liability established by the provisions of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, which provides for the application of an administrative fine of the following amount to the guilty subject:
According to those recorded in paragraph 3 of Art. 2.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation provisions, the application of administrative sanctions to a legal entity does not entail automatic release from liability for the said offense of the guilty individual and vice versa.
https://youtu.be/z4iRGmj7N30
Due to the fact that the provisions contained in the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation in the mentioned cases do not establish any restrictions when determining punishment, the judge is vested with the right to use any of the prescribed penalties (including the maximum) against guilty subjects within the framework of the sanction established by the relevant article , taking into account circumstances that have both a mitigating and aggravating effect on guilt.
How violations are detected
Holding employers liable in connection with granting employees leave without pay on the initiative of the employers themselves is very rare, since such situations in practice are virtually unprovable, except in cases where the employees themselves file a complaint or during an inspection, documentary evidence of such “pops up” violations.
For example, a written request from the employer to employees with a proposal to submit an application requesting to use leave without pay, or the presence of applications from employees requesting leave without pay with the wording “due to a decrease in production volume” or “due to the impossibility of paying me wages."
Proof of offenses is possible if there is documentary evidence
It is possible to hold an employer accountable for granting, on his own initiative, leave to employees without paying them the salary due to them only if there is documentary evidence of this violation of labor legislation. This type of confirmation can be:
- Written orders or proposals from the employer for employees to submit applications for leave at their own expense.
- Applications from employees for the provision of the said leave, containing reasons such as the inability to pay wages, a decrease in the overall productivity and profitability of the company, etc.
We suggest you read: Dismissal after maternity leave
The mentioned documentary evidence of violations must be presented either by the employees themselves when they send relevant complaints to the State Labor Inspectorate or the Prosecutor's Office, or identified during an inspection of the employer by regulatory authorities.
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl Enter to let us know.
Design features
When carrying out registration, the following features take place:
- If an employee plans to take unpaid leave, he must first determine whether he is entitled to it by law. If the law gives him such a right, then the employer is obliged to provide him with leave. If the situation is different, then you need to coordinate this issue with your boss.
- The first 14 days are included in the length of service, the subsequent ones are not.
- Having received free leave, an employee has the right to interrupt it at will and go to work. At the same time, he must notify the manager about his decision.
Registration of free vacation occurs in this way:
- The employee writes an application addressed to the boss with a request for leave.
- The manager issues an order to provide him with the required number of days.
- The employee goes on vacation.
- Such days are marked in the report card with appropriate symbols.
In accordance with legislative norms, the initiator of registration of leave without payment of wages is solely the employee himself. The employer does not have the right to either offer the employee to take such leave or in any way influence him for this purpose.
In a handwritten statement, the employee must state the reasons that prompt him to take leave without pay, and also indicate its duration. The presence or absence of an employee’s work experience does not affect the granting of leave without pay.
In cases where the employer is not obliged to provide said leave to the employee, the granting of his request will depend on whether the employee's absence will have any adverse effect on the overall work activity. Thus, it can be stated that in cases that are not defined by law as the direct responsibility of the employer, providing an employee with leave without payment of earnings is precisely the right of the employer.
Basic provisions
The discussion and subsequent consolidation of the decision on the issue of granting leave at one’s own expense takes place in the form of collective agreements, that is, in the form of concluding some kind of oral agreement directly between two parties - the employer and the employee. Next, this agreement must be enshrined on paper.
The only thing that determines an employee’s ability to leave without paid leave is one or another valid reason that requires the immediate presence of a person.
However, labor regulations do not clearly indicate who or what determines whether the reason cited by the employee is sufficiently valid. Therefore, this issue rests on the shoulders of the employer, and he decides whether to let his subordinate go or not. However, his powers in this matter are limited if the employee is on the list of people who are entitled to such rest by law. An employer’s refusal may be perceived as an administrative offense.
Rest periods are most often tied to one or another event that was considered respectful enough by the employer to let his subordinate go (funeral, farewell to the army, etc.). Often the duration is specified separately.
This type of rest does not contradict or conflict with receiving the main one. However, the same rules may apply to it as to the main one. For example, it can be used to recall an employee. If he falls ill during the period of administrative leave, then sick leave is not paid to him, since this period falls into the category excluded when calculating benefits, etc.
Request and registration of this is possible only unilaterally - on the part of the employee. The employer's demands to send someone on leave without pay are not justified and are not enshrined in law. Therefore, when a company, due to economic or other reasons that impede work (for example, repairs in the organization), sends its staff on administrative leave, it is acting unlawfully. From a legislative point of view, in this situation the so-called idle time, compensated to employees from the employer’s funds.