What are hazardous working conditions?
The enterprise must receive an expert assessment, and workplaces must undergo certification, based on the results of which the level of hazardous production will be established. Based on the data obtained, benefits and compensation will be assigned to employees, who must be notified of harmful factors and the possibility of contracting an occupational disease.
Working conditions under which:
- the specifics of the work performed involve high loads and a high probability of injury;
- during work there is interaction with viruses, pathogenic bacteria and other biological provocateurs;
- employees work with toxic substances;
- there are physical factors that negatively affect health (vibrations, high noise levels, increased air humidity or pressure, etc.).
How benefits and compensation for harmful working conditions are established
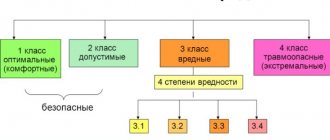
In total, 4 classes of working conditions were identified, namely optimal, acceptable, harmful and dangerous. In the first case, only monitoring is required to ensure that working conditions do not deteriorate. Acceptable working conditions oblige the employer to provide protective equipment and provide employees with additional rest time to minimize the possibility of health problems.
The class of hazardous conditions is assigned only to industries that involve chemicals and radiation, which is not common. But the class of hazardous industries, the third, is the most widespread due to the same harmfulness of many factors, such as fumes, gas welding, heavy dust and others. In this regard, class 3 is usually divided into subclasses, each of which determines the level of influence of a harmful factor on health and prescribes appropriate compensation and benefits for employees.
The main thing that attention is paid to when establishing the required benefits is a special assessment of working conditions (SOUT), which will be issued by the regulatory body after inspecting the company. Rostrud and the labor inspectorate of the region where the company is located are authorized to conduct inspections. Any workers who believe that they are not receiving the benefits they are entitled to can also apply here.
https://youtu.be/3DfYRV64X04
Additional payment for harmful effects: what to expect in connection with the new law?
08/21/201509/06/2018 17:17 Labor consultant
Despite technological equipment being improved every year, it is impossible to completely eliminate all risk factors for specialists in the workplace. This circumstance obliges employers to take measures to compensate for the harm caused to the human body. One of these measures is additional payment for hazardous working conditions.
On January 1, 2014, a new law N 426-FZ came into force, regulating the assessment of the state of the working atmosphere of employees. The concept of workplace certification (AWC) ceases to exist. Special assessment of working conditions or SOUT - this is what is now called a set of measures to identify the negative impact of labor process factors on the health of workers. However, the results of institutions that certified their workplaces before 2014 are valid for five years. The same period is set for a special assessment of working conditions.
Degree of hazardous production
If, according to the results of the SOUTH, the levels of the negative influence of production factors are higher than the permissible standard values, the working conditions are characterized as harmful. In this case, the labor code provides for a number of social guarantees for employees forced to work in unsafe workplaces. This point must be fixed in the employment contract without fail.
According to Art. 14 of the Federal Law, the degree of hazard is classified depending on the level of negative impact of the harmful component in the workplace as follows:
| Classification of working conditions | |
| Optimal working conditions | working conditions under which there is no exposure to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors on the employee or the levels of exposure of which do not exceed the levels established by standards (hygienic standards) of working conditions and accepted as safe for humans, and the prerequisites are created for maintaining a high level of employee performance . |
| 1 class | |
| Acceptable working conditions | working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, the levels of exposure of which do not exceed the levels established by the standards (hygienic standards) of working conditions, and the altered functional state of the employee’s body is restored during a regulated rest or by the beginning of the next working day (shifts). |
| 2nd grade | |
| Harmful working conditions | working conditions under which the levels of exposure to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors exceed the levels established by standards (hygienic standards) of working conditions, including: |
| 3rd grade | 3.1 working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, after exposure to which the altered functional state of the employee’s body is restored, as a rule, with a longer cessation of exposure to these factors than before the start of the next working day (shift), and the risk of health damage increases; |
| 3.2 working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors, the levels of exposure of which can cause persistent functional changes in the employee’s body, leading to the appearance and development of initial forms of occupational diseases or occupational diseases of mild severity (without loss of professional ability ), arising after prolonged exposure (fifteen years or more); | |
| 3.3 working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors, the levels of exposure of which can cause persistent functional changes in the employee’s body, leading to the appearance and development of occupational diseases of mild and moderate severity (with loss of professional ability to work) during the period labor activity; | |
| 3.4 working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors, the levels of exposure of which can lead to the emergence and development of severe forms of occupational diseases (with loss of general ability to work) during the period of work. | |
| Hazardous working conditions | working conditions in which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors, the levels of exposure to which during the entire working day (shift) or part of it can create a threat to the life of the employee, and the consequences of exposure to these factors cause a high risk of developing an acute occupational disease in period of working activity. |
| Class 4 | |
At the same time, the hazard class can be reduced by one step by providing employees with modern certified personal protective equipment.
Requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for organizations
The specifics of the work process, payment calculations and pension contributions, as well as the specifics of providing leave to employees engaged in hazardous work, are regulated by Articles 219, 92, 117, 147 of the Labor Code. Since the entry into force of the law on labor protection on January 1, 2014, corresponding changes have been made to the labor code.
First of all, the employer must include the degree of harmfulness of production, as well as compensation and guarantees in the employment contract. If this has not been done previously, after a special assessment, an additional agreement is concluded with employees, containing information about working conditions and benefits provided. The company's management must take care not only of the regular implementation of SAL, but also of timely amendments to employee employment contracts. Otherwise, the question may arise about the legality of providing certain payments and carrying out work activities.
The right to increased wages, according to Art. 147 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, have all employees employed in production with a hazard and/or hazard class of 3 (3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4) or 4. The minimum percentage of salary increase for such categories is 4% of the same type of work with normal conditions.
In this case, the employer has the right to increase the interest rate in accordance with the terms of the collective agreement. This amount is considered part of the salary, not compensation as such, and is therefore taxed equally.
Why should an employer pay extra?
This salary supplement is one of the social measures to support workers, designed to compensate for the damage caused to human health by harmful technological processes. Along with the additional payment, employees may be provided with other benefits: an increase in the number of days of annual leave, a reduction in the length of the working day or week, early retirement, provision of employees with dairy products and therapeutic and preventive nutrition, etc. The assignment of appropriate guarantees and compensation is made on the basis of labor legislation and the provisions of the collective agreement, the amount of payments and the right to additional benefits depend on the level of hazardous production and are indicated in the employment contract.
More information about therapeutic and preventive nutrition can be found in the article “Special nutrition when working in hazardous working conditions”
Calculation of allowance for hazardous working conditions
Government Decree No. 870 of November 20, 2008 established the minimum bonus rate for employees working in a harmful or dangerous environment; its amount is 4%. After a special assessment, it may be increased. In production, as a rule, provisions for additional payments are included in the collective agreement. When calculating the bonus, the trade union can be guided by the following scheme.
The procedure for determining the amount of additional payment
Due to the lack of modern regulatory documents regulating this area of labor relations, it is customary to use the Standard Regulations on the Assessment of Working Conditions dated October 3, 1986 as the basis for calculating the premium for harmfulness.
- Determination of the hazard class by comparing the maximum permissible values with real indicators of the hazards of production.
- Converting classes to points. According to Appendix N2 of the Model Regulations, the following points correspond to hazard class 3
| Harmful working conditions. Class 3 | ||
| Class 3.1 | Class 3.2 | Class 3.3 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
Subclass 3.4 was first mentioned in 1994 and therefore does not appear in the table. It is logical to assume that it corresponds to 4 points.
Organizations that have introduced hazard class 4 need an emergency set of measures to reduce the negative impact of production factors or reduce the time of such impact.
- Determining the time of exposure to a negative factor. The amount of the premium is determined based on the time of actual stay under the harmful influence of a particular factor.
- Establishing the amount of additional payment for harmfulness. When calculating the interest rate, the sum of all unfavorable factors is taken into account. Clause 1.6 of the Standard Regulations is usually taken as a guideline when calculating
| Working conditions | Actual sum of points according to the degree of harmfulness | Amount of additional payment as a percentage of salary |
| Heavy, harmful | 4 | |
| 2.1-4.0 | 8 | |
| 4.1-6.0 | 12 | |
| Particularly heavy, particularly harmful | 6.1-8.0 | 16 |
| 8.1-10.0 | 20 | |
| >10 | 24 |
In what cases can compensation for harm be cancelled?
A company that has implemented a set of measures to reduce the negative impact of production factors to an acceptable level is exempt from the obligation to pay surcharges for harmful effects. Such measures include, first of all, the improvement of technological equipment and the provision of employees with personal protective equipment that reduces the harmful effects of harmful components.
If, as a result of the reorganization, the harmfulness was not completely eliminated, but its class was lowered, the employer has the right to reduce the percentage of compensation contributions. Cancellation of the surcharge is also possible in the event of an increase in one or another harmfulness coefficient. The amendments made to the Federal Law in January 2014 imply an increase in the lower limit of acceptable values when assessing the harmfulness of production, as a result of which many workers in the industrial and chemical sector may lose additional accruals. At the employee’s initiative, an appeal may be filed with the inspection body with a request to review the results of the inspection.
According to Law N 426-FZ, organizations are required to provide data on the implementation of special assessments or workplace certification completed before January 2014 to the unified information system for recording inspection results by January 1, 2020.
Conducting periodic medical examinations
Periodic medical examinations are also a mandatory measure to identify at an early stage occupational diseases acquired as a result of working in hazardous industries. In addition to standard examinations and laboratory tests, workers in class 3 production facilities must undergo:
- examinations aimed at identifying the development of tuberculosis;
- examinations aimed at preventing the emergence and development of HIV;
- examinations by a psychiatrist.
Insurance against accidents and occupational diseases
Workers involved in occupations that are hazardous to health have the right to claim resort treatment, payment for treatment when an occupational disease is detected or after an injury, as well as the provision of free medications.
As a guarantee in the event of an industrial injury, accident or occupational disease at a hazard class 3 enterprise, the employer is obliged to insure its employees with the Social Insurance Fund.
Types of benefits for employees working in hazardous industries
The state ensures that employers provide the following benefits to workers in hazardous industries:
- additional annual leave (7 days);
- reduction in weekly working hours;
- an increase in salary or hourly pay;
- free regular examinations in medical institutions;
- retirement before reaching retirement age;
- organization of preventive nutrition;
- insurance in the Social Insurance Fund against occupational diseases and accidents;
- refusal to part-time;
- issuance of protective clothing, disinfectants, etc.;
- payment for health improvement and treatment.
Where are compensation for workers in hazardous industries prescribed?
Working conditions in hazardous production must be reflected in the company’s internal documents:
| Document | What information should it contain? |
| Labor regulations | Work schedule, time of breaks and rest (additional annual leave, length of a shortened work week). |
| Regulations on remuneration | Salary bonuses for harmful activities, a clear percentage of additional payments. |
| An employment contract with an employee or an additional agreement to it | Specifics of work, harmful factors, benefits, compensation (payments, additional rest, provision of therapeutic and preventive nutrition, etc.) |
| Time sheet | Shortened working hours. |
Features of taxation of additional payments for hazardous work
For special production circumstances, employees are entitled to additional leave. This is stipulated by law and is not a reason for non-taxation on a general basis, including insurance premiums.
An allowance for hazardous working conditions implies an increase in the tariff rate; it is not compensation, which means that there is no exemption from personal income tax. This does not apply to compensation, which is specified in Art. 164 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This type of employee income exempts the company from tax duty.
Workers working in such enterprises must receive milk or other types of therapeutic and preventive nutrition without payment to strengthen their body. The costs of their acquisition are not subject to taxation.
What is the amount of compensation for hazardous workers?
The amount of benefits is determined based on certain documents:
| Labor Code | Industry and cross-industry agreements | Union consent |
| The Labor Code of the Russian Federation requires from the employer an additional payment to the salary of at least 4% of the salary, additional annual paid leave lasting from 7 days and a working day reduced to 8 hours. | If the industry in which the enterprise is involved has agreements on the amount of compensation and benefits, they cannot be ignored. | If the company has a trade union, the amount and composition of benefits is discussed with it until agreement is reached. |
In some constituent entities of the Russian Federation, special tariffs are provided for hazardous working conditions (for example, in the Urals - 1.15 and 1.2, depending on the city).
How are payments made for special conditions?
The procedure for calculating and accruing additional payments will depend on what specific conditions affect the salary increase.
Abnormal
As mentioned above, most of these conditions are one-time in nature, since the legislator has established restrictions on attracting workers to permanent work in such an environment.
- Working on non-working days.
It is possible to involve employees in work on their legal day off or public holiday, but only with their written consent (a personal statement of consent to such work and the employee’s signature on the Order will be required).
Important! In accordance with Part 4 of Art. 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee has a choice: receive additional pay or take an additional day off on any other day.
And if the employee chose the first option, then the increase is carried out as follows:
- if the day off is worked in full - double salary (double piece rate, double hourly rate, etc.);
- if an employee goes out for several hours, double salary is proportional to the hours worked.
An employee who chooses a day off instead of additional pay will be paid for the working day worked in the usual manner (the amount of 1 salary). The additional non-working day chosen by him is not paid.
- Overtime work.
In accordance with Art. 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, this refers to the work of an employee outside of his working hours at the initiative of the employer. Like work on weekends, overtime work is carried out only with the written consent of the employee.
Overtime is paid as follows (Article 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- the first 2 hours – 1.5 times the salary;
- subsequent hours - at double rate.
The size may be increased by local acts of the organization.
- Night work.
Some activities involve working exclusively at night (from 10 pm to 6 am).
Norm Art. 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes a number of guarantees and restrictions for workers, in particular, a ban on hiring pregnant women, minors, etc. for such work.
The calculation is made according to the rules of Art. 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 22, 2008 No. 554: for each hour of work at night, the salary increases by no less than 20% of the hourly rate.
Harmful or dangerous
Important! In accordance with Part 2 of Art. 147 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the minimum amount of salary increase for work in conditions that pose a danger to the employee or cause harm to him is 4% of the salary.
A different minimum (and in some cases maximum) threshold may be established by other legislative acts regulating certain types of professional activities, for example:
- an additional 50-75% for working with information classified as “top secret” (Government Decree No. 573 of September 18, 2006);
- increasing wages by 50-100% of tariff rates for work related to chemical weapons (Article 4 of the Federal Law of November 7, 2000 No. 136 “On the social protection of citizens employed in work with chemical weapons”);
- an addition of 100% of the salary to police officers, police officers for special conditions (Part 10 of Article 2 of the Federal Law of July 19, 2011 No. 247 “On social guarantees for employees of internal affairs bodies of the Russian Federation...”), etc.
The exact salary amount, taking into account the bonus for harmful or dangerous conditions, is established by local regulations of the organization.
It is important to note that such conditions can be either temporary or permanent. Accordingly, a salary increase will also be accrued either at certain points or constantly.
The degree of harmfulness or danger of conditions is determined as follows.
In accordance with Art. 14 Federal Law No. 426 and Resolution of the State Committee for Labor of the USSR, All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated October 3, 1986 No. 387/22-78:
- harmful conditions - class 3 working conditions (3.1 - after exposure, the worker’s body recovers for a long time; 3.2 - risk of developing an occupational disease of mild severity; 3.3 - exposure leads to an occupational disease of mild or moderate severity; 3.4 - risk of developing a severe disease with complete loss of ability to work);
- hazardous conditions – class 4 (high risk of acute occupational disease, threat to the life of the employee).
The hazard class must be converted into points in accordance with Appendix 2 of State Labor Committee Resolution No. 387/22-78.
For harmful conditions:
- class 3.1 – 1 point;
- class 3.2 – 2 points;
- class 3.3 – 3 points.
Class 3.4 was introduced by Guideline 2.2.2006-05. 2.2, that is, later than the above presented Resolution. From a practical and logical point of view, this class of harmfulness is rated at 4 points.
These indicators influence the establishment of a certain percentage of the premium.
Non-standard climatic
Reference. In accordance with Art. 148 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, wages for employees working in areas with a special climate are established by Art. 315-317 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Order of the Ministry of Labor of the RSFSR dated November 22, 1990 No. 2 and individual legislative acts.
As mentioned above, we are talking about the regions of the Far North and territories equivalent to it.
In accordance with Art. 315 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation the following are added to wages:
- regional coefficient (for example, in the Trans-Baikal Territory it varies from 1.4 - 1.2%, depending on the specific locality);
- percentage increase for a certain length of service (after the first 6 months or the first year of work, depending on the region).
For example, throughout the entire territory of the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug there is a coefficient of 2.0. The percentage markup in this region is:
- after the first 6 months of work – 10%;
- every subsequent six months it also increases by 10% until it reaches 100%.
If an employee working in the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug is a young specialist who has not yet turned 30 years old and has lived in such conditions for at least 1 year:
- after the first 6 months of work – 20%;
- for each subsequent six months it increases by 20% until reaching 60%;
- Once the 60% increase is reached, it increases by 20% each year until it reaches a 100% salary increase.
Early retirement due to hazardous work
By law, employees of hazardous industries have the right to retire before reaching the generally accepted retirement age (60 years for men and 55 for women). They begin receiving pension payments at age 55 and 50 , respectively.
The availability of the possibility of early retirement depends on the presence of the position held in special lists of positions, the occupation of which is recognized as harmful and dangerous to health and life, and on length of service at an enterprise in a certain industry with hazardous working conditions.
How to apply for benefits and compensation for harmful working conditions
The procedure for receiving benefits and compensation must be prescribed in a local regulation or collective agreement, and the amount of compensation depends on the hazard class and safety of the workplace. Additional payments are already included in the salary and are indicated in the employment contract.
The basis for the allocation of benefits is the time sheet and management orders to grant leave. It turns out that the employee will be assigned additional days of rest and additional payments, based on the time actually spent at production, without taking into account vacations, sick leave, and weekends.
Procedure for receiving compensation payments
The procedure for receiving additional payment and other compensation for classes 2, 3 or 4 of harmfulness at work is reflected in the collective agreement or in the relevant regulatory local act.
The new monthly wages after the increase are indicated in the employment contract of the individual employee. As a result, a certain additional payment is automatically included in the monthly salary. According to Federal Law No. 426 of December 28, 2013, managers of any industrial enterprise assess current working conditions (SOUT). If, after such an inspection, the workplace is officially recognized as safe, then no privileges are provided and no monetary compensation is paid.
Read also: VAT from January 1, 2020
Required documents to receive benefits
All benefits and compensation will be specified in the employment contract, i.e. they are assigned automatically based on working conditions. No documents are required to submit for payments and benefits. If an employee wishes to replace any compensation with cash, he writes a free-form application addressed to the employer.
If labor standards are not observed and the employee does not receive (or does not receive in full) any additional payments or compensation, he must contact Rostrud or the State Labor and bring:
- application (complaint) to the labor inspectorate;
- work book with a record of employment in an enterprise with hazardous working conditions.
Types of compensation and privileges “for harmfulness”
Workers are provided with the following guarantees for working in an enterprise with hazardous working conditions:
- reduce the length of the working week (from 40 to 36 hours);
- provide and pay additional leave, the duration of which is at least 7 days;
- an additional payment is added to the basic salary (taking into account regional coefficients, if any);
- provide free annual treatment and medical examination;
- provide the beneficiary with various consumable materials (for example, uniforms).
Additional payment for hazardous working conditions
Important! According to Art. 253, 265, 298 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, some citizens of the Russian Federation are not employed in various hazardous industries. These categories of applicants include teenagers, people with mental health problems, pregnant women and mothers with one or more children under 1.5 years old.
Reduced working hours
According to Art. 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, if working conditions of hazard classes 3 and 4 are present in production, the working day is reduced by several hours. If the working week is 36 hours, then in 1 day they work 8 hours as a maximum. If you work 30 hours in 1 week, then in 1 day - 6 hours as a maximum.
Milk dispensing
According to Art.
222 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in enterprises with various hazardous working conditions, workers are required to be given a certain amount of milk. In this situation, 0.5 liters of such a dairy product are obtained per 1 work shift. Milk is given only to those workers who work in a factory with harmful production factors (Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation No. 45n dated February 16, 2009). This benefit is provided when working with specific metals (aluminum, iron, chromium, etc.), various acids, etc.
Granting a second leave
Providing and paying for additional leave is considered one of the types of compensation for working in an enterprise with various harmful working conditions.
A similar benefit is provided to workers in industries with hazard classes 2, 3 and 4. In this situation, according to Article 117 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, at least 7 days are added to the main vacation. Attention! Additional (second) vacation must be taken in real life. Such vacations are not paid for with money.
However, if the vacation time is 8 days or more, then they receive certain monetary compensation for it.
Read also: Filling out a waybill
Supplement to basic salary
According to Art.
147 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the additional payment to the basic salary is equal to 4% of the salary. However, employers sometimes pay more money. An additional payment equal to 4% of the salary is considered a minimum payment and mandatory monetary compensation. Some organizations have specific allowance amounts. Thus, in the Federal Penitentiary Service, workers who work with HIV-infected prisoners receive the following additional payment - 20% of the basic salary, FSTEC employees - 12%, and crews of ships operating in ice conditions - 12%.
Privileges
According to Art. 30 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2013 N 400-FZ (as amended on March 6, 2019) “On insurance pensions”, employees who work in specific hazardous industries have their retirement age reduced. As a result, women are entitled to a preferential pension at the age of 45, and men at the age of 50.
According to clause 2, part 1, art. 30 Federal Law No. 400 of December 28, 2013, according to list 1, the length of service is at least 10 years, and according to list 2 - at least 12.5 years.
Employment contract
According to Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, certain working conditions are fixed in the employment contract. Such a document contains the following information:
- SOUT results.
- Amounts of certain additional payments, various compensations and allowances.
- Duration of additional (second) vacation.
- Number of working hours per week.
- Types of various compensations and gifts.
On a note! In addition to the benefits described above, they provide two free meals a day for harmful work. However, such a privilege is received only for particularly hazardous work.
Free food
Free two meals a day are provided when working in a specific production facility, where the employee is daily exposed to chemical, bacteriological, radiation and other similar effects. Special tables are set for such workers.
Attention! The type of daily menu depends on the type of specific work performed. It can be hypoallergenic, high-protein, etc. Additional two meals a day are received during the current work shift - at breakfast and lunch.
Procedure and terms for providing benefits
The law establishes the following rules for remuneration of personnel in hazardous production:
| Benefit or compensation | Procedure and deadline for provision |
| Salary supplement | As a percentage of the salary amount (at least 4%) monthly (indicated on the payslip as a separate line). |
| Shortened working hours | The duration of the shift is increased to the general norm at the request of the employee; if the employee refuses to shorten the shift, compensation is paid. |
| Additional rest | Every year, according to the vacation schedule for the time actually worked, simultaneously with the annual paid vacation. |
| Therapeutic and preventive nutrition | Hot breakfast at the beginning of the work shift, milk or fermented milk products, vitamin supplements for first and second courses. |
Legislative acts on the topic
| Article 210 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation | On preserving the life and health of employees through improving working conditions, ensuring safety at work and assigning compensation for harmful working conditions |
| Art. 212 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | On the creation of a labor protection service at the enterprise |
| Federal Law of December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ “On special assessment of working conditions” | On conducting an assessment of working conditions |
| Government Decree No. 188 dated March 29, 2002 (as amended on October 8, 2014) | List of areas of activity and specialties associated with hazardous working conditions |
Labor and collective labor agreements
First of all, working conditions, including in positions, workshops and production facilities with hazardous working conditions, are fixed either in collective or individual labor contracts.
Conditions mean:
- The result of the workplace assessment by the SOUT commission.
- Amounts of compensatory surcharge and allowance.
- Amounts of additional leave.
- Number of working hours per week.
- Obligations of the employer to provide employees with personal protective equipment.
- Conditions for compensation payments in case of exceeding maximum permissible working hours.
- Types of compensation (milk, etc.).
The legislation of the Russian Federation establishes the following types of compensation measures for harmful working conditions, which must be notified in an individual or collective labor contract:
- Mandatory bonus for hazardous working conditions in the amount of at least 4 percent of the salary.
- 36 hour maximum working hours per week.
- Mandatory additional payment for overtime hours. A maximum increase is possible up to 40 hours per week. Overtime compensation is set by industry agreements in the range of 20-50% for each hour of overtime over the 36-hour maximum.
- Additional paid leave for employees engaged in hazardous work. The minimum duration of additional leave is set at 7 calendar days.
- Providing milk, personal protective equipment, additional nutrition, as well as receiving free spa treatment.
- Possibility of replacing milk and food with their monetary equivalent.
Video - Benefits, guarantees and compensation for harmful working conditions
https://youtu.be/-_vuk4h77mk
Common mistakes
Error: The X-ray room employee is not paid compensation for harmful working conditions.
Comment: Medical workers forced to work in hazardous conditions (immune laboratories, dispensary employees, etc.), along with employees of other harmful and dangerous industries, have the right to benefits and compensation. Read about this in the article ⇒ “Benefits for medical workers for harmful working conditions.”
Error: A hazardous production worker asks to replace the additional 7-day rest with a cash equivalent.
Comment: Cash compensation is allowed to replace only days of additional rest beyond the first 7 days required for time off.
Legislative regulation of the issue
The rules for establishing various benefits (guarantees), the amounts and the official procedure for paying bonuses and other monetary compensation for work in harmful and various hazardous working conditions are specified in the following legal acts:
- Resolution of the USSR Council of Ministers No. 1173 of August 22, 1956;
- Resolution of the USSR Council of Ministers No. 369/P-16 of November 1, 1977;
- Resolution of the USSR Cabinet of Ministers No. 10 of January 26, 1991;
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 870 of November 20, 2008;
- Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation No. 45n dated February 16, 2009
Such information is reflected in Federal Law No. 426 of December 28, 2013. In short, this law is called “SOUT”.
Answers to common questions about benefits and compensation for hazardous working conditions
Question No. 1: If an employer, at its discretion, assigns additional payments to employees involved in hazardous production, will the salary supplement be subject to personal income tax?
Answer: Since the law does not force the employer to establish such payments, personal income tax will be collected from them in the general manner as from income.
Question No. 2: Are insurance premiums and personal income tax withheld from monetary compensation for workers in hazardous industries?
Answer: No.
But if it is possible to eliminate negative factors of production, then personal income tax is withheld from compensation payments. Rate the quality of the article. Your opinion is important to us: