It is advisable for every employee, no matter what enterprise he is employed at, to understand the fact that absolutely any professional tasks from the official supervisor of this employee must be performed correctly and efficiently. And if an employee who gets a job in a company at a certain moment suddenly completely ceases to be responsible for the quality of performance of all the tasks assigned to him, stops performing them altogether, or starts slacking, the manager may rightfully decide to reprimand him.
With the help of a reprimand, an employer can only warn his employee, point out all the mistakes and incorrect actions made, however, a reprimand can also be a serious and significant sign of imminent dismissal that needs to be paid attention to.
But what specific number of reprimands can lead to an employee getting rid of him and being fired under the article?
General conditions of dismissal
According to the general approved rule of the labor code of our country, there are only 3 fundamental reasons for the immediate dismissal of an employee from his current work position under the article.
These are the reasons:
- You can dismiss an employee if he himself wants it, that is, the dismissal will take place voluntarily;
- You can fire an employee if the management of the body wants it, that is, dismissal on the initiative of the administration;
- You can fire an employee if the employee wants to leave and the boss shares this desire, that is, dismissal by agreement of both parties.
However, the Labor Code also stipulates the fact that if the quality of work performed by an employee does not completely satisfy the employer, no matter what enterprise he manages in his position, he has the full official right to justifiably point out to the employee his incorrect actions, significant, significant mistakes and attract employee to responsibility of a disciplined nature.
The above rule is indicated and fully described in its wording in Article 192 of the Labor Code of our country.
https://youtu.be/JbchYqa1Q3g
How to reprimand for improper performance of official duties
The official issuance of a reprimand is a legal fact, so this procedure must be properly formalized. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal regulations do not contain regulations that would determine how a reprimand , but, based on practice, this action is recommended to be carried out according to the following algorithm:
- Firstly, the employer must document the fact of failure (or incorrect performance) by the employee of his duties. Most often, this is done by sending a memo to the director of the company by the immediate supervisor of the employee who committed the misconduct. An offense can also be recorded using a report drawn up by a commission formed by the head of the company to evaluate the employee’s actions.
- Secondly, the employer, before issuing a reprimand, must give the employee the opportunity to explain the actions he committed. To do this, it is necessary to send the employee a notice of the submission of an explanatory note.
- Thirdly, the employer needs to wait 2 days - this is how much time the employee has to draw up an explanatory note (Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If he does not do this, the employer should draw up a corresponding act. Further (and also in the event that an explanation is presented, but the employee’s arguments do not look convincing), a reprimand can already be issued.
A reprimand is issued by issuing an order signed by the head of the company.
The order to issue a reprimand must:
- indicate that all the documents that we mentioned above are attached to it: a memorandum of misconduct (or an act of the commission), a notice of the need to submit an explanatory note, the explanatory note itself or an act of failure to submit it;
- indicate the dates and names of the relevant documents.
The order to issue a reprimand must be signed by:
- head of the company;
- by the employee himself within 3 days from the date of drawing up the order.
If the employee refuses to sign the document, it will be necessary to draw up a report about this (Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Information about the reprimand can be recorded in the personal file.
Measures applied to the employee
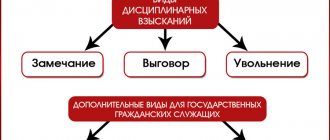
A manager can express specific and justified dissatisfaction with an employee and his actions in relation to his position using such registered, officially accepted means for such cases as
- comment,
- rebuke
- or even the most severe: dismissal of the employee from his current position.
Management is responsible for its final choice; it is management that will always decide what verdict to make, in which of the 3 above forms they will try to call an unscrupulous employee, bring him to disciplinary liability for his actions.
Management will make its final, final choice regarding this issue according to its own internal perception and ideas about the seriousness of the offense committed, as well as according to its perception of the exact circumstances and conditions in which this offense was committed by the employee, and whether the employee can be justified under them.
Legislative regulation
Types of penalties, the procedure for issuing and canceling them are determined by Chapter. 30 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Article 92 of the labor law provides for penalties for failure to comply with labor discipline, which the company administration can use against a worker. This:
- Comment;
- Rebuke;
- Termination of the employment agreement.
It should be noted that the legislation does not establish criteria for when certain types of sanctions can be imposed for non-compliance with discipline. This issue is resolved by the employer independently on an individual basis, taking into account the severity of the act committed and the consequences that ensued.
The question often arises whether someone can be fired for a reprimand. This can be used as a punishment only on the grounds established by paragraphs 5, 6, 9, 10 of Part 1 of Art. 81, paragraph 1, art. 336 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Expert commentary
Kamensky Yuri
Lawyer
The law does not provide for grounds for dismissal for reprimand. Its use is considered a gross violation and may give rise to a legal dispute.
The requirements of Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for the impossibility of multiple penalties for one violation. If a person is reprimanded for an offense, then he cannot be fired for that reason. In addition, there is no need to observe the order of imposition of punishment; there is no obligation to apply their sequence, provided for in Art. 192 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. For example, an employer has the right to terminate an agreement with a person who has committed a gross one-time failure to comply with job duties, even if he has not previously been reprimanded or reprimanded.
Important! The provisions of Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes compliance with the punishment procedure.
When a reprimand is followed by dismissal
The final decision on the subsequent dismissal of an employee employed at any enterprise or other stage of work activity after a reprimand or several reprimands is considered, discussed, and then made directly by management.
It is completely justified and objective, it can be challenged in very rare certain cases.
According to the rule enshrined in the legislation of the Russian Federation, management must first ask the employee for a complete and specific explanation of the reasons for his incorrect behavior, actions, deeds, negligence in relation to work or failure to fulfill direct official duties. But after this, he considers the idea that it is possible to fire this employee or not fire him, according to the article on reprimands.
The employee himself can file a complaint in which he has the opportunity to challenge his superiors’ decision to dismiss him from his former position. This rule is written and officially enshrined in Article 193 of the Labor Code.
In such a situation, it is advisable for management to correctly assess from the very beginning what exactly led to their employee’s negligence: what are his reasons? How objective are they? Can it be mitigating, what does he himself think about this? Before firing him or reprimanding him. This is spelled out and enshrined in paragraph 5 of article 81 of the labor code.
This 5th paragraph tells the citizens of the Russian Federation a lot, and also essentially warns, warns them about the fact that any violations of any conditions provided for in the employment contract concluded between the employee and the employee’s boss were noticed more than once, repeated several recorded times.
An employee’s neglect of his direct job duties must necessarily exceed at least one time.
What are the disciplinary sanctions?
All three types are enshrined in the already mentioned Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Additional types can be applied only if they are provided for by Federal laws in relation to specific categories of employees. But the main ones are:
- A remark is a warning for a one-time violation of discipline. Can be valid for up to 12 months (see Article 194 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- A reprimand is a penalty for systematically committing misconduct. Its validity period is also up to a year.
- Dismissal. In accordance with paragraph 5 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it follows if the employee continues to violate discipline in the presence of penalties.
This article does not say exactly how many reprimands are needed to fire an employee. Failure to fulfill obligations must be repeated, and the penalty must be valid.
How many reprimands does it take to get fired?
The specific number of reprimands to an employee that is necessary for the employer to make a final decision on his immediate dismissal is never prescribed in the labor code by anyone, therefore, after only 1 serious official reprimand, employees who have received a written punishment should specifically think about the possible future consequences and understand that the next reprimand may result in dismissal.
After a subsequent, that is, repeated official reprimand in writing regarding the quality of performance of the employee’s work duties, the employer has every right to decide to dismiss the employee from his current position.
Payments and compensations
Despite the fact that in this case a person is fired for not fulfilling his job duties, he is entitled to both unpaid wages for hours worked and compensation for unused vacation days. If the company owes an employee with accountable funds, then this amount must also be paid. The employee is not entitled to any other compensation.
If on the day of dismissal the employee is not at work, then payments must be made no later than the day following the date of his written request to the administration of the organization with a request to calculate it.
Also, dismissals can be not only for a reprimand, but also in case of staff reduction, liquidation of an enterprise, due to loss of confidence, for absenteeism, for alcohol or drug intoxication.
Dismissal due to reprimands
A full description of cases in which the employer has the officially reserved right to dismiss an employee from his current position without the expressed desire of this employee to leave his current place of employment, due to his negligence in the performance of direct work duties, improper actions during work activities or complete refusal to carry out instructions given to him, tasks from management, is given in Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
But this rule does not mean at all that with all of the above, the opinion of the employee himself, being considered for future dismissal, will not be recognized by the administration in any way, and then taken into account when making a decision on his dismissal. Article 193 of the Labor Code states and also officially stipulates that the employer is required to provide a full, specific, fact-based explanation and substantiation of the reasons for bringing the employee to disciplinary liability in advance.
If the employer has deliberately decided that after taking disciplinary action against the employee, he will be permanently dismissed from his position, a written, fully specified explanation of the claims becomes a great necessity, an officially required obligation of the employer.
Some reasons written in Article 81 of the Labor Code determine the possibility of an employer making a decision to dismiss an employee without any penalties from him, based on a list of other documents submitted, as well as papers.
How to appeal an employer's actions
If an employee is sure that the employer fired him illegally, the employee has the right to go to court to resolve the dispute.
Remember! As a rule, issues related to:
- failure on the part of the employer to comply with the written form of recording the offense;
- indicating incorrect information in the accompanying documentation, for example the date of violation;
- failure on the part of the employer to request the employee to provide an explanation for his misconduct;
- exceeding the permissible time limits for issuing disciplinary measures.
If an employee was fired for absenteeism, and the court decided that the employer did not have enough grounds to apply this type of penalty, then the absenteeism is considered forced, and the dismissal is illegal.
If the court upholds the employee’s claim, the employee receives a ready-made decision. Based on this document, the employer is obliged to reinstate the person to his previous position and pay wages during downtime.
Please note that you can appeal not only dismissal, but also reprimand. To do this, you should write a complaint to the labor safety inspectorate.
Lawyers advise that before going to court you should always try to resolve the dispute amicably. In addition, you can contact lower authorities, for example the labor protection commission. However, this is an employee’s right, and not at all an obligation, so an employee can bypass unnecessary authorities and immediately go to court.
Watch the video. What to do in case of illegal dismissal:
https://youtu.be/CF1MOMQOnRs
Dear readers of our site! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to find out how to solve your specific problem, please contact the online consultant form on the right. It's fast and free! Or call us at :
+7-495-899-01-60
Moscow, Moscow region
+7-812-389-26-12
St. Petersburg, Leningrad region
8-800-511-83-47
Federal number for other regions of Russia
If your question is lengthy and it is better to ask it in writing, then at the end of the article there is a special form where you can write it and we will forward your question to a lawyer specializing specifically in your problem. Write! We will help solve your legal problem.
For what violations can an employee be fired immediately?
There are circumstances under which management can either reprimand or fire an employee for an employee’s misconduct:
- According to paragraph 5 of Article 81 of the Labor Code, that is, repeated violations of labor duties or their complete failure to fulfill them.
- According to paragraph 6 of Article 81 of the Labor Code, that is, gross violations noticed during the performance of the employee’s duties or violation of the discipline of his work activity, and in this case the remark is sufficient in the singular.
- According to paragraph 8 of Article 81 of the Labor Code, that is, the employee was observed to have committed an act of an immoral nature.
- According to paragraph 9 of Article 81 of the Labor Code, that is, according to an unfounded decision made by management that entailed a harmful effect on the work of the entire company.
“Repeated failure to perform” means that the employee, several times in a row, was careless with the tasks that were assigned to him by his real bosses, and because of these incorrect actions on his part, these bosses lost something or suffered serious losses in the general work business, for example, at the enterprise , where the bad worker is employed.
How disciplinary action can lead to dismissal
There cannot be multiple penalties for the same offense. The punishment becomes more severe as the worker moves from a one-time violation to a systematic one. And depending on their severity, unequal amounts of penalties can be fatal:
- Most often, dismissal follows a third written reprimand, subject to minor consequences for misconduct (for example, for tardiness or neglect of subordination).
- If the reasons are more serious (intentional non-compliance with technological or management standards), a second written penalty is sufficient.
- With one reprimand, the employment contract can be terminated if the person follows it with another violation. For a gross violation of discipline (coming to work drunk, divulging a trade secret, or deliberately damaging property) once is enough, but in this case a reprimand is not issued; dismissal follows as an independent type of disciplinary sanction.
After how many reprimands an employee can be fired is decided by management, based on the conditions of a particular situation. This is strictly stated in Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It is obvious that the consequences, for example, of rudeness and theft, cannot be identical.
Employee negligence
If we talk about the initial appearance of an employee’s negligent behavior: after the initial observed poor performance by the employee of the tasks assigned to him, he cannot yet be fired with only one reprimand, unless, of course, not only negligence is noticed, but a real gross violation. But a normal initial violation is punishable only by a reprimand. If the boss decides to reprimand the employee, it is advisable for him to take into account the employee’s explanations. This is written in Article 193 of the Labor Code.
If we talk about the future negligent behavior of an employee: after a specific superior has repeatedly noticed poor or incorrect performance by an employee of his present tasks in his position, and perhaps complete failure or non-fulfillment, it is already possible to declare with full responsibility that poor performance, violations or failure to perform repeatedly, which means they are repeated for a certain period of time.
But, in this case, it is advisable for absolutely any boss, no matter what enterprise or company he is responsible for, to take into account absolutely all the recent reprimands before finally deciding to fire him. If the reason for the reprimand is precisely negligent performance of work, the boss may not consider a penalty, but immediately dismiss the unscrupulous employee, but there is a condition that no more than 1 year should pass after the initial punishment. This is described in Article 194 of the Labor Code.
Reprimanding an employee: legal consequences for the employer
It happens that the employer comes to the conclusion that the employee was punished unlawfully and wants to remove the reprimand from him. How can I do that?
Very simple. All that is required to cancel a reprimand is to issue an appropriate order from the head of the company. It can be drawn up at any time (Article 194 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The employee himself or his immediate superior can also apply to have the reprimand lifted.
The order to remove the reprimand must contain a reference to the order to issue the reprimand, indicating its date and number.
An employee is considered to have a disciplinary sanction after it has been issued for exactly 1 year, if during this time he does not commit other offenses, followed by other disciplinary sanctions (Article 194 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this regard, there is one more option for removing a reprimand from an employee - wait for its automatic cancellation.
A reprimand is a legal fact, and it must be correctly executed. Many people forget that, for example, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for any severe reprimands. The employer has no right to officially use this phrase. If he nevertheless gives the employee a severe reprimand, then the labor inspectorate (if the employee complains there) can:
- firstly, impose an impressive fine on the company based on clause 1 of Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation;
- and secondly, to cancel the order imposing a severe reprimand.
In addition, the employer has the right to impose any disciplinary sanction, including a reprimand, only if the employee fails to perform or performs his job duties incorrectly. However, these responsibilities must be recorded somewhere: in a contract, job description, labor regulations.
Dismissal on the basis of a severe reprimand, other non-existent disciplinary sanctions, as well as when the reprimand is issued outside the regulatory framework, can be successfully appealed by the employee in court with a high probability of success. As a result, the court may oblige the employer to reinstate the person at work. And immediately.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Request not to leave the place for which crimes it applies
When is a reprimand issued?
A reprimand, like any other disciplinary sanction, must be issued by the employer within a month after the employee’s misconduct is revealed. The company has no right to punish the employee later. This period may be extended if the employee is absent from work due to being on sick leave or on vacation (including study).
The maximum period within which an employer has the right to issue a reprimand is 6 months. However, if a misconduct is revealed during an audit (for example, an audit), a reprimand can be issued no more than 2 years from the established date of the commission of this misconduct.
We announce a reprimand or reprimand
Important Necta [e-mail hidden] Russian Federation, Blagoveshchensk #11[260103] September 29, 2011, 11:49 Quote: the employee immediately loses his bonus for a year. I do not agree that this works automatically. Such conditions should be enshrined in the bonus regulations. The employer may specify such a condition for calculating the bonus, or may not charge the bonus only for the period in which the penalty was imposed. As far as I remember, the security forces and emergency services do not give quarterly bonuses if the recovery is in this quarter. Info For the rest - charged. They have this spelled out in the bonus regulations. I want to draw the moderator's attention to this message because: A notification is being sent... Alex Russian Federation #12[260146] September 29, 2011, 12:43 pm Olga in syt is right. Everything is spelled out in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. That is, if the bonus is monthly, then the employee misses the bonus only in this month. If this is an annual bonus, then it flies away with the annual one. This, by the way, happens most often.
The employee was late for work in February, and the following January did not receive his 13th salary. 2. Bonuses of all types are not awarded until the expiration of the disciplinary sanction. Yes, no questions asked. A year without bonuses. If I don't take it off sooner.
But bonus policy is the employer's business. It is not regulated by the Labor Code. On whatever terms I want to encourage an employee, these are the terms I will use.
And talking about bonuses outside the terms of the bonus regulations is generally pointless. Because bonus conditions are determined only by the bonus regulations. And nothing more. I want to draw the moderator's attention to this message because: A notification is being sent...
Deadlines for applying penalties
1 month to issue a reprimand or reprimand to the employee, or rather to issue an appropriate order . 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, that is, from the day when the violation became known to the immediate supervisor of the offending employee (for example, the head of a department), p. 34 Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court dated No. 2.
Monthly period 34 Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court dated No. 2:
- extended for the duration of the employee’s illness or while he is on some kind of leave (annual paid, additional, educational, at his own expense, etc.);
- is not extended for days on which the employee was absent from work for some other reason, for example, for additional days off.
WE TELL THE MANAGER
Even if it is obvious that a particular employee has committed a disciplinary offense, he cannot be reprimanded or reprimanded outside the statute of limitations for bringing disciplinary action.
At the same time, it will not be possible to issue a reprimand or reprimand if 6 months have passed since the date of the disciplinary offense. 193 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The six-month period increases to 2 years if the misconduct is revealed as a result of an audit or audit (for example, during the inventory, a shortage of goods and materials was discovered due to the fault of the storekeeper).
The mentioned deadlines are preemptive for the employer and cannot be restored. Their omission excludes the possibility of applying disciplinary sanctions to the employee, see, for example, Appeal Rulings of the Novgorod Regional Court dated No. 2-5088-33-2076; Omsk Regional Court dated No. 33-5026/2013.