What refusal is considered unfounded?
Provisions of Art. 64 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provide grounds for distinguishing unjustified refusal into three types:
- failures that do not have an indication of the cause;
- refusals, the reason for which is prohibited by law (an example would be a discriminatory criterion that is a violation of human rights);
- refusals containing a reason not related to the employee’s qualities related to his position or profession.
The groundlessness of the refusal and restriction of the rights of persons applying for employment is established by the court, for which the procedure for judicial proceedings is observed. In practice, a refusal can be recognized as justified only when it is based on the absence of the necessary business qualities of the employee. Only this basis is not a violation of the rights established for workers by industry legislation
https://youtu.be/f1YVL4oY77U
Mandatory guarantees for the employee
When concluding an employment contract, guarantees for the employee are mandatory in the text of the contract itself. This is necessary, first of all, so that the hired employee has an idea of what he can count on in the event of high-quality and conscientious performance of his duties.
All guarantees provided to an employee upon concluding an employment contract are divided into two groups - mandatory and additional.
Mandatory guarantees include:
- guaranteed payment for work performed . This means not only that the work of a particular employee must be paid without any deductions if he performs his duties in full and does it efficiently. When forming a mechanism for remunerating the labor of a particular person, it should be taken into account that the final amount of material compensation for work performed should not be less than the currently established minimum subsistence level;
- formed working day regime , which provides for the presence of not only a formed general working time regime for the employee, which will be recorded in the employment contract (for example, the use of a flexible schedule or a rotational method), but also an indication of breaks within the working day for the direct implementation of work activities, and also for rest, including eating;
- the employer's obligation to make transfers to various funds , which give an officially employed employee the right to receive certain social guarantees. Thus, mandatory transfers include transfers to the Pension Fund of Russia and the Social Insurance Fund for the formation of pension savings, as well as for registration and regular use of medical insurance opportunities, including in the event of permanent disability due to industrial and domestic injuries.
Who cannot be refused to sign an employment contract?
The possibility of refusing to accept a position is limited by the legislator. Refusal cannot take place if:
- in relation to the employer there is a procedural decision obliging to conclude an employment contract with the person specified in it;
- the candidate must be employed within the framework of legislative quotas;
- the employee was invited to the position according to the transfer rules and reported to the new place of work within a month. The duration of such a period is established from the date of termination of the employment relationship at the previous place of performance of professional duties;
- the employee actually began to perform labor functions even before the official registration;
- the employee was elected to the position as a result of competitive procedures.
An applicant for a position who considers the refusal to employ him to be unfounded is given the right to protect his rights in court proceedings. The decision by which the plaintiff's demands are satisfied is binding on the employer.
Commentary on Article 64 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
According to Article 64 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, unjustified refusal to conclude an employment contract (including depending on the age of the employee) is prohibited. We have already mentioned labor discrimination in the commentary to Article 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In general, an unjustified refusal to conclude an employment contract should be considered any circumstances referred to by the employer, if they are not related to the professional qualities of the employee. Such circumstances include direct or indirect restriction of rights or the establishment of direct or indirect advantages in relation to individuals (categories of persons) when concluding an employment contract, depending on gender, race, skin color, nationality, language, origin, property, social and official status. position, age, and place of residence (including the presence or absence of registration at the place of residence or stay).
At the same time, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation contains specific regulations prohibiting refusal to conclude an employment contract with certain categories of persons. In particular, Article 64 of the Code of the Russian Federation prohibits refusing to conclude an employment contract for women for reasons related to pregnancy or the presence of children (primarily minors).
The same article contains a prohibition on refusing to conclude an employment contract to an employee who was previously invited in writing to work by way of transfer from another employer, provided that the latter applied to the new employer within one month from the date of dismissal from the previous place of work. After this period, the employer has the right to refuse to hire this employee.
On the other hand, in a number of cases provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to refuse to conclude an employment contract to the person who has applied to him. Thus, in accordance with Article 331 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, persons for whom this activity is prohibited by a court verdict or for medical reasons, persons who have had a criminal record for certain crimes, as well as persons declared incompetent in the manner prescribed by federal laws cannot be allowed to engage in teaching activities. laws.
Let us add to what has been said that, at the request of a person who has been refused to conclude an employment contract, the employer is obliged to inform him in writing of the reason for the refusal, for example, indicating as such the lack of necessary professional qualities in the applicant. At the same time, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not contain any instructions regarding the period of such a message, which in general, we recall, should not exceed 30 days calculated from the date of the application.
A refusal to conclude an employment contract may be appealed by a person not hired in court if the latter considers such a refusal to be unfounded. The right to go to court in connection with an unmotivated refusal to hire is retained by the employee for three months from the day he learned or should have learned about a violation of his right.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with the law?
If the employer does not comply with the requirements of Art. 64 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, then he faces the following types of liability:
- Administrative. This type of violation is punishable by a fine of 5–50 minimum wages. If this is a repeated engagement, the manager will be disqualified for 1-3 years.
- Material. In this case, the manager is obliged to pay the injured party material damage.
- Disciplinary. Here the manager may face a disciplinary sanction, reprimand, reprimand or dismissal.
- Criminal. In case of non-compliance with Art. 64 of the Labor Code, the head of an organization can pay in cash in the amount of 200-500 minimum wages or by corrective labor for 120-180 hours. For very serious violations that result in the death of an employee, the manager can receive up to five years in prison.
Guarantees for the employer
If the fact of employment is officially registered, then guarantees are provided not only for the citizen, but also for the organization. First of all, this concerns the fact that the company will not be left without employees. This is due to the fact that labor legislation stipulates the citizen’s obligation to inform the management of the enterprise about the termination of the employment relationship in advance. Often this time period is used by the company to find a new employee.
In addition, the execution of the agreement provides a guarantee that all requirements established by the company will be met. The company's management has the opportunity to clearly describe the duties of employees and prescribe responsibility for their violation. This is especially true for material liability.
In particular, when a citizen’s work involves expensive equipment. When drawing up an agreement, there is reason to believe that employees will treat the property of the enterprise with care. If not, compensation will be paid.
What is discrimination?
According to Art. 64 of the Labor Code, an employment contract is concluded on the basis of a person’s professional qualities. And if a situation arises that the employer refuses to hire you, he must explain the refusal in writing.
The manager is responsible for discrimination based on gender, skin color, nationality, etc. Criminal liability is assumed if a pregnant woman or a woman with small children is not hired. It is prohibited not to employ people with HIV and their family members.
Despite the fact that Art. 64 of the Labor Code implies a ban on certain facts during employment; there are nuances in work that are not considered discrimination. For example, preference for more qualified specialists.
Reasons for refusal to hire
Despite the provisions of the Labor Code, refusal to conclude an employment contract occurs in the following cases:
- The candidate's age does not fit within the limits established by law.
- The applicant does not have the necessary skills and abilities, and also does not have the necessary qualifications.
- The applicant's business qualities do not meet the requirements of the vacancy.
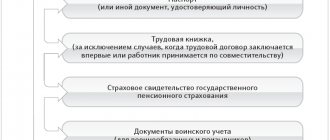
- The applicant cannot provide the necessary package of documents to conclude an agreement.
- The applicant refuses to comply with mandatory requirements for employment (for example, passing a medical examination).
Arbitrage practice
The activities of the judicial authorities give reason to believe that not in all situations the guarantees entitlement to a person under legislative acts are fulfilled. It is important to note that labor legislation does not provide a clear definition of what should be understood as business-type qualities. This opportunity can be used by odd companies to cover up the illegal fact of refusing to hire.
The Resolution of the Plenum of the RF Armed Forces states that from a legal point of view such a refusal is fully justified. At the same time, judges establish what must be understood as business qualities. This also applies to abilities aimed at performing labor functions. The reasons in this case are:
- availability of training and qualifications in a certain specialty;
- health compliance;
- the presence of certain qualities of personal significance.
It is worth noting that such an indication does not make it possible to fully use the guarantees reflected in the law. Citizens quite rarely turn to the judiciary to challenge the refusal.