Indicators of labor flow
Purpose. The online calculator is used to calculate labor flow indicators.
- Online solution
- Video instruction
In labor statistics, two types of dismissal turnover are distinguished:
- Necessary turnover is the number of employees leaving for reasons of a production or national nature, associated with an increase or decrease in the volume of production work, conscription into the Army, or enrollment in studies.
- Excess turnover is the number of employees who left for personal reasons. Excess turnover represents labor turnover.
Based on absolute indicators according to reporting data, the following coefficients are calculated:
- Admissions turnover ratio = number admitted for the period / average payroll number for this period
- Retirement turnover ratio = number of retirees for the period / average number for this period
- Replacement rate = (number of hires - number of leavers) / average number of employees on payroll
- Turnover rate = number of people leaving for reasons of turnover - this is dismissal of their own free will, for absenteeism and other violations, by decision of the judicial authorities / number of personnel at the end of the period
- Personnel retention ratio = number of employees who worked the entire reporting year / number at the end of the period
Example. The average data for the enterprise for 2002, people are known: Number of employees at the beginning of the year - 400; Hired - 80; Dismissed from work, total - 100; including at their own request, for absenteeism, for violation of labor discipline - 50. Determine: 1. the average number of employees; 2. labor force index; 3. indicator of total labor turnover; 4. admission turnover ratio; 5. turnover rate for retirement 6. labor turnover rate.Solution. 1. absolute indicators of employee turnover. admission turnover - the number of persons enrolled in the period under review by the relevant order for the organization of work; Emergency = 80 turnover on dismissal - the number of employees who left work in this organization, whose departure or transfer was formalized by order, as well as those who left due to death; Chu = 100 total labor turnover - the sum of the turnover of admissions and departures. Cho = 80 + 100 = 180 Necessary turnover - the number of employees leaving for reasons of production or national nature, associated with an increase or decrease in the volume of production work, conscription into the Army, or enrollment in studies. Excess turnover is the number of employees who left for personal reasons. Excess turnover represents labor turnover. In practice, staff turnover usually includes both voluntary dismissal and dismissal at the initiative of the administration in case of violation of contractual obligations between the employee and the administration. Chi = 50 Number of employees at the end of the period T1 = 400 + 80 - 100 = 380 Average number of employees T = (T0 + T1)/2 = (400 + 380)/2 = 390 2. The hiring turnover ratio is equal to the ratio of the number hired per reporting period to the average number of employees Кп = 80/390 = 0.205 3. turnover coefficient for retirement turnover coefficient for dismissal - represents the ratio of the number of people dismissed during the reporting period to the average number of employees Ку = 100/390 = 0.256 4. turnover coefficient turnover coefficient - the ratio of the number of employees who left at their own request and those dismissed for violation of discipline to the average number of employees Kt = 50/390 = 0.128 or Turnover rate = the number of those who left for reasons of turnover - this is dismissal of their own free will, for absenteeism and other violations, by decision of the judicial authorities / number of personnel at the end of the period Kt = 50/380 = 0.132 5. replacement rate Replacement rate = number of hired employees / number of retired employees Kz = 80/100 = 0.8 or Replacement rate = (number of hired employees - number of retired employees) / average payroll number of Kz employees = (80-100)/390 = -0.0513 6. stability coefficient Kst = Number of employees who worked the entire reporting period / number of personnel at the end of the period Kst = 390/(390 + 80-100) = 0.949 7. update scale factor scale factor updates = Number of employees hired in the reporting period / number of personnel at the end of the period Km = 80/380 = 0.211
Certificate of staffing and staffing
Explanation
Staffing of the educational process is considered from the point of view of the level of qualifications, the correspondence of the basic education of teachers to the taught discipline, and staffing.
The qualifications of staff are an indicator of the potential of an educational organization and the effectiveness of the learning process.
Data on teaching, scientific-pedagogical and scientific personnel (hereinafter referred to as NPR) are presented in the form of a certificate in form 14 of the annex to the order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Donetsk People's Republic dated May 4, 2016 No. 502 separately for each educational program , level, type, subtype of educational activity applied for licensing.
Table 14.1 provides quantitative information about teaching, scientific-pedagogical and scientific workers of an educational organization, a structural unit within the organization carrying out educational activities.
The integer value of the rates (column 4) is calculated by dividing the numerical values of the parameter “total number of teaching hours in the curriculum” by the numerical value of the parameter “standard teaching load at the rate” given in one line (rounding to the tenth of the number).
For example, the program has been implemented for 4 years, the volume of implementation of the program according to state educational standards and curricula is 240 credit units, which is 8640 hours. If the full rate of scientific and pedagogical workers is 720 hours, then the program will require 8640/720 = 12 rates.
A characteristic of the sustainability of the work of an educational organization and a guarantee of its stability is the indicator of the number of full-time teaching, scientific and pedagogical workers working in an educational organization, institution, or structural unit.
The main (full-time) teaching staff means teaching staff who have their main place of work in a given educational organization or institution, both full-time and part-time.
The main place of work of a pedagogical worker is considered to be the educational organization where the work book of this worker is kept.
Full-time part-time teaching staff means:
a) internal part-time teaching staff - administrative and managerial personnel of the main (full-time) teaching staff, scientists, and other employees of an educational institution, in addition to the main job responsibilities of those conducting teaching work in this educational institution on a part-time basis;
b) external part-time teachers - persons who lead a teaching load in a given educational institution on a part-time basis, but who have their main place of work in another organization.
The staffing level of teaching (scientific, scientific-pedagogical) workers who have their main place of work in a given educational organization is calculated as the ratio of the number of rates (the share of rates is summed up) of the teaching (scientific, scientific-pedagogical) staff employed by the main (full-time) teaching staff and internal part-time teaching staff to the number of teaching staff positions according to the staffing table of the educational organization, institution (in percentage).
For example, according to the staffing table and curriculum, the integer value of the CPD rates is 12. The implementation of the program applied for licensing in an educational organization is carried out by 6 full-time employees at 7 rates and 8 part-time workers, that is, the actual number of employees is: 6+8 = 14. Thus, the integer value of the rates occupied by the research assistants under this program is equal to: 7+8•0.5 = 11.
The staffing level in this case is: 11/12•100% = 92%, which meets the requirements of the state educational standard for this program.
Explanation
In Table 14.2, the license applicant provides information about teaching and scientific-pedagogical employees of the educational organization. It provides information on all subjects, courses, disciplines (modules) included in the educational program in accordance with the curriculum. For teachers, information is provided about the specialty of each teacher according to their diploma; academic degree, academic title; experience in teaching (scientific and pedagogical) work (including in the discipline taught); main place of work and position held; conditions for recruitment to work.
For part-time workers, the place of main work and the position at the main place of work are indicated.
The educational qualifications of teaching, scientific and pedagogical workers (availability of basic higher professional education, academic degree or academic title) must meet the requirements set by state educational standards for each area (specialty).
For secondary vocational education programs, column 6 indicates the qualification category and teaching titles.
The share of scientific and pedagogical workers (in rates converted to integer values) who have an education corresponding to the profile of the taught discipline (module ) (that is, the profile of the taught discipline corresponds to the teacher’s qualifications indicated in the documents on education, or on qualifications or the profile of an academic degree, title) , in the total number of scientific and pedagogical workers implementing the program is calculated using the formula:
| Percentage of faculty members with education corresponding to the profile of the taught discipline (module) = | The number of hours implemented by research assistants who have an education corresponding to the profile of the taught discipline (module) | x100% |
| Number of hours in OBOP in accordance with the teaching load |
For an educational program with a duration of 4 years and a number of hours of 8640 hours, the number of hours implemented by teaching staff whose education does not correspond to the qualifications specified in the educational documents is 420 hours.
The percentage of faculty members who have an education corresponding to the profile of the taught discipline (module) is equal to: (8640 - 420)/8640•100% = 95%, which meets the requirements of the state educational standard.
In the event that there is no direct correspondence of higher education or an academic degree/academic title to the profile of the discipline being taught, the correspondence of education to the profile of the discipline being taught is established in this situation on the basis of belonging to one enlarged group of education/degree, teacher title and the required education/degree, title. If the discipline assigned to the teacher does not correspond to either education, academic degree, title or the topic of advanced training courses, additional information should be indicated in column 8 confirming the possibility of teaching the specified discipline (articles, publications, etc.).
The share of scientific and pedagogical workers (in terms of rates reduced to integer values) with an academic degree and (or) academic title in the total number of scientific and pedagogical workers implementing the program is calculated using the formula:
| Percentage of faculty members with academic degrees and (or) academic titles = | Number of hours implemented by research assistants with an academic degree and (or) academic title | x100% |
| Number of hours in OBOP in accordance with the teaching load |
According to the data of the educational organization, institution, the number of positions occupied by teaching, scientific and pedagogical workers with an academic degree and (or) academic title, the share of employees with an academic degree and (or) academic title in the total number of teaching, scientific and pedagogical workers is calculated, implementing the program.
When licensing the educational activities of religious educational organizations, persons with theological degrees and (or) theological titles are taken into account. Persons who have both academic degrees and academic titles (theological degrees and theological titles) are counted once.
When licensing the educational activities of educational organizations carrying out educational activities that provide for military service and (or) service in law enforcement agencies, teachers of disciplines (modules) of the professional block and the section “Practices and research work” who do not have academic degrees and academic degrees are taken into account ranks with specialized higher education, experience in the troops (navies), headquarters, law enforcement agencies, institutions for at least 10 years, military rank not lower than “lieutenant colonel”, combat experience or state awards, state or industry honorary titles, state awards, and also to teachers who have an academic degree of Doctor of Science and (or) the academic title of professor, teachers of disciplines (modules) of a professional Block who have an academic degree of Candidate of Science and state awards, state or industry honorary titles, state awards (hereinafter collectively referred to as teachers) are equated. . Teachers who simultaneously have academic degrees and academic titles are counted once.
For areas of training and specialties in the field of culture and art, architecture and corresponding areas of training and specialties in the field of education and pedagogy, persons with honorary titles are taken into account. In these organizations, the category of persons with academic degrees and titles also includes persons without academic degrees and titles, but having state honorary titles, laureates of international and all-Russian competitions, laureates of state awards, graduates of postgraduate studies in creative and performing specialties (assistant internships), successful defended their final qualifying thesis. In art universities, the category of scientific and pedagogical personnel with an academic degree of Doctor of Science and the title of professor includes persons without academic degrees and titles, but who have state honorary titles of national significance, members of state academies, and laureates of state prizes.
For areas of training and specialties in the field of physical culture and sports and corresponding areas of training and specialties in the field of education and pedagogy, persons with honorary sports titles are taken into account. Persons who have both academic degrees and academic titles (honorary titles and honorary sports titles) are counted once.
If the program has been implemented for 3-4 years (has a contingent in the final course), then the share of research assistants with academic degrees and (or) academic titles is calculated based on the teaching load for the entire period of study.
For example, for a program with a volume of 8640 hours, the volume of hours according to the curriculum, implemented by research assistants with academic degrees and titles is 6272 hours, which is 8.7 rates.
Then the percentage of faculty members with academic degrees and titles is equal to: 6272/8640•100% = 72.6%.
In the state educational standard of higher professional education for this program, the volume of CPD with degrees and titles must be at least 60%, therefore, this indicator for the program applied for licensing meets the licensing requirements.
The share of employees (in terms of rates reduced to integer values) from among managers and employees whose activities are related to the focus (profile) of the program being implemented (who have at least 3 years of work experience in this professional field) in the total number of employees implementing the program is calculated as follows.
From the total number of positions occupied by teaching staff, the number of positions occupied by employees (in terms of integer values of rates) is identified from among the managers and employees of organizations whose activities are related to the focus (profile) of the program being implemented and who have at least 3 years of experience in this professional field years.
The percentage of employees from among managers and employees of specialized organizations from the total number of teaching, scientific and pedagogical workers implementing OBOP is determined.
At the end of Table 14.2, a conclusion is indicated regarding the compliance of the indicators with the requirements for the program applied for licensing.
Copies of state educational standards, curricula for each educational program applied for licensing
Explanation:
Attached are copies:
state educational standards approved in the prescribed manner for all licensed programs, directions, profiles, specialties, types of additional education and approved in the prescribed manner; ( attached is the state standard approved by the Ministry of Education and Science and a copy of the order)
curriculum developed in accordance with state standards and approved in the prescribed manner for all licensed programs, directions, profiles, specialties, standard programs for types of additional education (copy of the curriculum).
Calculation of the Langelier index and Risner stability index
Langelier index.
In 1936 American scientist WF Langelier proposed using the formula he developed to assess the thermal stability of a solution. The formula is based on determining the degree of saturation of the solution with calcium carbonate. Instability of the solution leads to either scale formation or corrosion. The index is still used by water treatment specialists to this day.
To determine the Langelier index, the following parameters are required:
- pH (hydrogen value) at a temperature of 25C,
- TDS in mg/l or solution conductivity (in mS/m) multiplied by 7,
- solution temperature in degrees Celsius,
- calcium carbonate hardness (Ca2+) in mg/l,
- alkalinity by HCO3- in mg/l.
Using formulas, auxiliary coefficients are determined and the intermediate value - pHs - is calculated.
Langelier index formula: pH – pHs.
Its value shows: Langelier index 0, scale formation is observed, no corrosion is observed
Risner stability index.
In 1944 Ryzner noted that a layer of scale on the surface of a metal can prevent corrosion. Based on the coefficients for calculating the Langelier index, Risner proposed his own formula for calculating the stability of a solution.
Formula for calculating the Risner stability index: 2pHs – pH
Its value shows: 2pHs – pH > 6 the solution is prone to corrosion 2pHs – pH = 6 the solution is stable 2pHs – pH Summary table of the values of the Langelier index and the Risner stability index:
| Langelier index | Risner index | Characteristics of the solution |
| 3 | 3 | Extremely high scale formation |
| 2 | 4 | Very high scale formation |
| 1 | 5 | Severe scale formation |
| 0,5 | 5,5 | Tendency to scale formation |
| 0,2 | 5,8 | Light scale formation |
| 0 | 6 | Stable solution |
| -0,2 | 6,5 | Very light corrosion |
| -0,5 | 7 | Light corrosion |
| -1 | 8 | Corrosion tendency |
| -2 | 9 | Very high corrosion |
| -3 | 10 | Extremely high corrosion |
Practical examples of using the Langelier index.
In the example “Features of the use of Aquaclair flocculating devices in Japan”, the value of the Langelier index was:
- make-up water -1.2 (high susceptibility to corrosion);
- circulating water using chemical reagents +1.2 (serious scale formation);
- recycled water with the Aquaclear +1.1 system (serious scale formation).
The value of the Langelier index with the Aquaclair system is closer to the value for stable solutions. This conclusion is confirmed by the observations made. With the Aquaclear system in the cooling system, instead of hard scale, “in some places there was only a light coating of deposits, reminiscent of the finest powder. The plaque can be easily wiped off with a napkin without using any detergents.”
Calculator and tables for calculating the Langelier index.
The Langelier index is calculated using formulas or using tables for express calculation.
Formula: LSI = pH – pHs.
pHs = (9.3 + A + B) - (C + D), where:
- A = (Log10 - 1)/10
- B = -13.12 x Log10(oC + 273) + 34.55
- C = Log10 - 0.4
- D = Log10
Calculation example: pH = 7.5 TDS = 320 mg/l Hardness in CaCO3 = 150 ml/l Alkalinity in CaCO3 = 34 mg/l
In organizations, the movement of personnel is a constant procedure. New employees come in to replace resigning employees. The arrival of new labor has a different impact on the development of the enterprise. In order to analyze the movement of workers, special indicators are used, one of which is the turnover ratio for hiring workers.
What is considered the norm for the staff retention rate?
If the CPC is low, it naturally indicates problems. However, a CPC that is too high, approaching one, does not indicate a good organization of personnel policy - there is stagnation in the organization, a lack of influx of fresh forces and trends towards expansion.
Sooner or later, the personnel core will be forced to give up their positions, and if there are no “young” employees to whom experienced “bisons” can transfer their knowledge and skills, then the company will either cease to exist, or will have to start personnel policy from scratch, replacing them with personnel without any experience in this organization.
It is also possible that employees come to the company, but leave without working for even a year, which indicates obvious or hidden problem situations that need to be identified and resolved as soon as possible.
IMPORTANT! To effectively monitor possible problems, it is better to calculate this coefficient at least once a year.
Calculation example
Let's look at how the turnover ratio formula for hiring employees is used using a specific example.
Let’s assume that the average headcount for 2020 is 700 people. The number of employed workers during this period was 150 people. Substituting the data into the formula, we obtain the turnover coefficient for the reception of workers:
- Cop = 150 / 700 x 100 = 21.43%
To analyze this indicator, it needs to be compared with last year. Let’s say in 2020, the number of employees was 670 people. Only 70 people were accepted in this period. It turns out that for 2015 the turnover indicator for hiring employees was:
- Cop = 70 / 670 x 100 = 10.45%.
Compared to last year, the figure has more than doubled. Accordingly, the HR department urgently needs to take measures to reduce turnover.
It is recommended to carry out such an analysis at least once a quarter, then you can avoid large differences between annual indicators.
By calculating this indicator for different time periods, you can track how changes occur throughout the enterprise as a whole or individually by department.
A thorough analysis of changes in the indicator makes it possible to take timely measures to reduce turnover in the company. If you periodically calculate such an indicator, you can get a general idea of the dynamics of hiring workers.
What is the employee turnover rate
This is an indicator of the constant and frequent change of specialists of the enterprise; it is this that makes it possible to determine how high the percentage of “turnover” is in the enterprise and how effective the internal personnel management policy applied by the employer is.
Important: it is defined as the ratio of those who left to the average number of employees.
It is this indicator that makes it possible to determine the number of employees who left for one reason or another during the selected period.
When calculating it, absolutely all workers who took part in the production process are taken into account, and not those who remained according to the list at the enterprise, which makes it possible to see the overall picture.
How staff turnover and persistence rates are used - see this video:
Calculation of the turnover ratio for hiring employees
When calculating the turnover ratio for hiring employees, you must be guided by the following formula.
Turnover ratio for hiring employees = (number of hired employees for the analyzed period (month, quarter, year) / average number of employees on the list in the analyzed period) * 100%
In the formula for the turnover ratio for hiring employees, the number of hired employees is calculated based on the number of hiring orders issued in the period under review. Orders to hire part-time workers, as well as persons with whom civil law contracts have been drawn up, are not taken into account. The indicator in the denominator - the average number of employees on the list in the analyzed period - is nothing more than the average number of employees.
To determine the average headcount, you will need to know the number of employees for each day of the analyzed period. Data can be obtained from a time sheet, which reflects the number of employees and the hours they worked.
The average headcount for the month is calculated as follows. The number of employees for each calendar day of the month is summed up and divided by the number of calendar days in the month. Similarly, the average headcount for a quarter, half-year or year is calculated as the sum of the average headcount for the months included in the analyzed period, divided by the number of months (3, 6, 9 or 12).
Features of applying the coefficient in the healthcare sector
That is why in the legislative framework there are certain norms and regulations governing the provisions of part-time work specifically for employees of medical organizations.
In 2003, the Ministry of Labor adopted Resolution No. 41 of June 30, which provided for the rules of part-time work for workers in the educational, pedagogical and medical fields of activity.
The concepts of “staffing” and “staffing” are not approved at the legislative level.
One should approach the qualitative assessment of statistical calculations on personnel composition very carefully.
An example of calculating the turnover ratio for hiring employees
An example of calculating the turnover ratio for hiring employees.
| Index | Number of employees, people |
| Average headcount | 500 |
| All accepted, including: | 50 |
| - accepted by the employer | 10 |
| — accepted by transfer from other organizations | 20 |
| - accepted in the direction of the employment service | 20 |
Turnover ratio for hiring employees = (50 / 500) * 100% = 10%
By calculating the turnover ratio for hiring employees for different periods, you can see how the situation is changing for the company as a whole or for its individual divisions. Analysis of this indicator allows the enterprise’s personnel service to timely develop a set of measures to reduce turnover, motivate employees, and move employees within the company. If you calculate this indicator regularly, you can get a clear picture of the dynamics of hiring employees in the company.
By analyzing the dynamics, you can assess whether the growth rate of hiring new employees is justified, whether the increase in new employees corresponds to the real needs of the company, or whether it is caused by other reasons. It is advisable to compare the turnover rate for hiring employees with the rate of employee departure. If, against the background of a high turnover rate for hiring, there is also a high rate of employee attrition, then we can talk about high staff turnover. The HR service, using indicators that are easy to calculate, has the opportunity to analyze the reasons for the dynamics of employees in the enterprise.
Calculation of the part-time ratio in healthcare
There is nothing complicated in calculating the part-time ratio, since this is done by taking the number of occupied positions in the clinic and dividing it by the number of doctors who are physically present in the clinic:
= number of occupied medical positions (paramedics) / Number of individual doctors (paramedics) at the end of the reporting period
The resulting coefficient shows how filled vacancies in a medical institution are, as well as whether the head physician needs to take any measures to expand the staff.
Example:
In the regional clinic, according to the job description, there are 58 doctors and 69 representatives of junior medical personnel, but in fact there are 44 doctors and 52 nurses in the clinic.
Using the formula for calculating the part-time ratio, the head physician can see that the indicator for doctors is 1.3 (58/44 = 1.3), and for junior staff 1.1 (69/58 = 1.1).
The value of this coefficient allows you to determine how many rates one medical worker works on average.
At the same time, its value of 1.4 is considered quite high, and 1.5 is generally the maximum permissible, since this state of affairs indicates that the staff is significantly overloaded.
And the more the coefficient value differs from 1.5 upward, the lower the quality of work of employees in the organization becomes.
The administration of the institution (clinic or hospital) must remember this and promptly take appropriate measures to solve this problem.
Causes of personnel shortage
Problems of education
Due to the spread of commercial universities, higher education has become accessible and easy to obtain, but the level of knowledge and skills of graduates often does not satisfy employers. In addition, there is no adequate and practical system for further employment of graduates and motivation of personnel to work in a particular position.
According to the President of the RSPP (Russian Union of Industrialists and Entrepreneurs) Alexander Shokhin, the personnel shortage is currently one of the three most pressing problems. After completing their studies, 31.3% of university graduates and 40.5% of technical school graduates work outside their specialty.
Lack of qualified specialists in certain areas
Russian higher and secondary educational institutions in some areas train a limited number of personnel. For example, only a small number of universities graduate specialists in metallurgical, agricultural and other industrial specialties. If we take into account that not every certified specialist is truly qualified, then the circle of potential candidates for an open vacancy narrows even further.
Inflated salary expectations of candidates
Representatives of the professions most in demand on the market set the salary bar high. Not every company can meet high expectations, so the shortage of personnel in some areas is only increasing.
For example, IT specialists today value their work quite highly for the Russian personnel market. According to the international recruiting company Hays, in 2020, there were from 2 to 7 offers of potential jobs per IT specialist.
Outflow of qualified personnel to other regions or other areas of activity
Holders of rare specializations often retrain and move to other industries due to more attractive salary offers. Often, good specialists also move to large cities with a population of over a million, and in remote regions of the country with a lack of qualified personnel, the problem becomes more acute.
For example, the Far East does not lack specialists in the oil and gas industry, but at the same time a catastrophic situation is developing in the field of medicine, education, and social services.
General demographic situation in the country
According to Rosstat, the economically active population today makes up about 52% of the total number of citizens of the Russian Federation. This is significantly less than in other European countries. This factor also affects the personnel shortage in the state.
You can view statistics on unemployment and employment in Russia on the Rosstat website – www.gks.ru.
About 84% of Russian companies faced a staff shortage for various reasons in 2020. Every year, the shortage of personnel in Russia is increasing, and therefore many organizations are implementing strategies to overcome this trend.
Eliminating personnel shortages can be done through:
- Investing in internal corporate programs for personnel training, advanced training or retraining of its employees.
- Recruiting personnel from related fields and training them on site.
- Hiring workers from other regions of the country or even foreign specialists with payment for relocation and rent of an apartment at the expense of the company.
These are just some of the ways to overcome the personnel shortage; we will look at them in more detail later.
Why is their calculation necessary?
Indicators of staff turnover and stability need to be regularly analyzed in any organization in order to correct mistakes when hiring new specialists.
After receiving unsatisfactory results, any responsible manager will think about why this is happening, why people do not like working in this company, are not satisfied with their working conditions, wages or work schedule. All these questions can be answered after analyzing the indicators under consideration.
How personnel records are carried out in an organization - see this material. Read about how to correctly create an inventory of transferred documents here.
Areas of employment where staff shortages are common
At a certain point, the Russian personnel market became oversaturated with lawyers, economists, accountants, PR specialists, marketers and representatives of other non-technical specialties.
Today in the market there is an acute shortage of qualified:
- IT specialists;
- web designers;
- technologists for various areas of production;
- workers of agriculture and agro-industrial complex;
- insurance specialists;
- medical workers and pharmacists;
- engineers and skilled workers;
- specialists in the field of sales and procurement;
- specialists in the field of finance.
Most citizens strive to obtain higher education in management and administrative specialization. At the same time, the demand for skilled workers is practically not satisfied.
In Russia there is still an acute shortage of bus drivers, salesmen, turners, gas welders, cooks, seamstresses, builders, and plumbers. And foreign workers from neighboring states of the former USSR are most often low-skilled, poorly trained, do not know Russian well, and have problems with the migration service. All this complicates the work of many industrial, construction enterprises, the housing and communal services sector, etc. At the same time, due to the high shortage of personnel, employers are now ready to offer decent wages to qualified workers.
Why is there such an imbalance of supply and demand in the personnel market? Experts explain this by the fact that there are always more workers with a humanities education compared to specialists in technical fields of employment. At the same time, most companies are interested in personnel with technical education; it is easier for such specialists to find employment.
The imbalance is also explained by the fact that in the work of humanitarian specialists little has changed over the years, while precision technologies are developing very quickly. Therefore, there are not enough specialists with the necessary knowledge in technical fields; often they are simply not yet trained in universities. It turns out that the functionality is already in demand, but officially there is no such profession yet.
In what cases is it used?
To answer the question in what cases and how the calculation of the coefficient is used to determine part-time doctors, a few words should be said about the features of part-time work for doctors.
The following important points should be highlighted here:
- Medical employees have the right to work part-time not only in other clinics (external part-time work), but also at their main place of work (internal part-time work).
- When working under reduced working hours, doctors are allowed to register as part-time workers, provided that they do not participate in activities that are subject to sanitary and hygienic restrictions.
- The maximum time of part-time work for doctors cannot exceed more than ½ of the standard working time, calculated on the basis of the approved working week (for the main job). Moreover, such requirements apply not only to junior, but also to middle and senior medical personnel, therefore, regardless of the doctor’s qualification level, the employee must be registered within the framework of the current legislative norm.
A doctor has every right to work at his main place of work, holding a part-time position there (internal part-time job).
Taking into account the fact that some doctors have multiple qualifications, it is quite possible for them to work in this way, since it is fully permitted by law.
When a doctor works simultaneously in several clinics, this will be considered an external part-time job, which for medical workers is limited by sanitary and hygienic requirements.
The list of such types of work that cannot be performed by medical workers part-time due to sanitary and hygienic restrictions is not established by Russian legislation.
The possibility of performing such work by medical staff in each case requires an assessment of these sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the compatibility of both the main job and part-time positions.
Is part-time teaching allowed? Read about it on our website.
Is it possible to work part-time without a main place of work? Find out .
How many bets can you take part-time? See.
How to determine personnel shortage: calculation formula
Calculation of personnel shortages can be made if the number of employees of the company is known.
The formula used is:
Shch = Oz / Nf x Kn
- Shch – staffing number.
- Oz – total costs for the volume of work per year, hour.
- Nf – standard working time fund for one employee per year, hour.
- Kn is a coefficient that takes into account the planned absences of employees during vacation, illness, etc.
In practice, the concept of staffing is also used in personnel work. Staffing means that for every staffing unit indicated in the staffing table there is a real employee. The absence of gaps and open vacancies indicates that the enterprise is fully staffed.
For clarity, you can also calculate the percentage of staffing in the company. It is calculated by the formula:
Qs = Шч / Срч x 100 (%)
- Qs – staffing level (%).
- Shch – staffing level or the required number of employees according to the staffing schedule.
- Average number of personnel for the reporting period.
In approximately the same way, you can calculate the quantitative staffing ratio. To do this we use the formula:
Qk = Шч / Срч
- Qk – staffing ratio.
The formula for calculating personnel shortages and staffing levels is applied both for the enterprise as a whole and for its individual structural divisions. Also, analysis of personnel shortages can be carried out for certain positions and specialties. This will help to timely identify weak personnel areas in the enterprise, competently form a personnel reserve, move employees within the company, train and improve the qualifications of subordinates.
A high percentage of staffing and, accordingly, a low deficit (its absence) indicate a sufficient number of qualified employees, which means that the company can quickly and effectively solve strategic problems.
What does headcount calculation look like?
Like that.
The data you enter allows you to calculate the target number and workload for the amount of work you define and compare it with the actual number of employees.
Do not forget about the principles of calculating the number that you should have read about in the article about the 8 basic principles of calculating the number - all calculations were made in accordance with them.
If the calculator’s algorithms suddenly fail, a cell highlighted in red with the amount of “lost” hours will appear to the right of the “Control” inscription.
Personnel shortage: solving the problem
Let us examine in detail how a company can solve the problem of staff shortages on its own. Let us list real ways to eliminate the personnel shortage.
Hiring missing personnel for the company
If there is a shortage of specialists in a particular field, HR workers can independently select personnel. When supply in the market is low, an employer can attract candidates with various advantages, for example, a high wage rate, bonus payments, a favorable social package and other working conditions. If necessary, retraining or advanced training of new employees may be required.
Restructuring within the team
This method does not require expanding the company's staff or searching for new specialists. An employer may attempt to redistribute work time and responsibilities among already employed employees. In this case, an increase in the workload and overtime of employees is likely, which can be fraught with conflicts, discontent among subordinates, and errors in the redistribution of wages. In addition, the employer will likely incur large costs for retraining and training its employees.
Personnel outsourcing
This is another effective way to overcome the problem of personnel shortage. Outsourcing implies the delegation of certain tasks or part of the functions to a third party under the full control and responsibility of the third party.
As a rule, such a third-party contractor is a highly qualified professional who has a narrow specialization and understands the nuances of a particular job. Outsourcing is not associated with the physical movement of personnel from the contractor’s company to the customer’s company. The actual place of work for the employee remains the same.
When outsourcing, the customer can only evaluate the result of the service itself, but not the process of the contractor’s employees. They are not under his control or management. In fact, these are ordinary civil relations between two legal entities.
Outstaffing of personnel
Another way to solve the staffing problem. Differences from outsourcing:
- When outstaffing under a contract, there is a transfer not of personnel, but of functions that were previously carried out by the customer’s internal divisions, or business processes.
- In outstaffing, tasks are assigned to employees by the customer's employee; in outsourcing, tasks are assigned by the contractor.
- With outstaffing, the customer himself is responsible for the results of the work of the provided workers. He can make claims to the contractor only if he provided him with personnel untimely or in insufficient quantities. With outsourcing the situation is different. Here the customer can make claims to the contractor for the final result.
- When outstaffing, the calculation of payment under a contract is usually based on the employee’s rate, which may include his salary, benefits package and other similar expenses. In outsourcing agreements, payment is most often tied to the quality of the result and the volume of work.
Outsourcing and outstaffing allow the customer to free up financial, human and organizational resources in order to concentrate on carrying out the core activities of the organization.
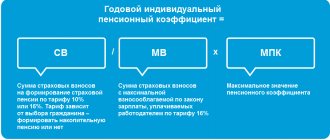
Replacement rate formula
What functions are not part-time?
Speaking about medical workers, it should be made clear that not all jobs here can be part-time.
According to Regulation No. 41 of June 30, 2003, this includes:
- Conducting accounting, medical or technical examination. Almost always, such work is one-time in nature, and is paid individually and is not regular. In addition, we are not talking about performing regular duties, as prescribed in Art. 282 of the Labor Code, since the work is aimed at a specific one-time result.
- Consultation by highly qualified doctors - professors and doctors of science. Such work also does not fall under the category of regular work, since it can be performed at different times and with different intensity of consultations. You need to understand that the doctor’s duties do not include counseling, but he has the right to do so, and there is also no system of subordination of the subjects of the relationship. Such relationships are of a civil law nature, therefore the consultation function does not apply to part-time work.
- Performing specific duties without holding a full-time position in a medical institution. An example of such work is duty, which is established in addition to the main working hours and in accordance with Art. 99 of the Labor Code belongs to the category of overtime.
If we take a closer look at the work that medical employees can perform without holding a full-time position, we can confidently conclude that this is a combination.
This is due to the fact that duty is often carried out simultaneously with the main job, and therefore does not apply to part-time work, since such work is performed in free time from the main job.
Any work performed by a doctor at a time beyond the regular schedule falls under the category of overtime, and therefore is paid in accordance with Article 152 of the Labor Code of Russia.
Such work is usually formalized by an additional agreement to an existing employment contract, which also specifies the scope of work, the amount of additional payment and the specifics of the function performed.
An example of such a document:
Sample additional agreement on combination
How to correctly calculate the percentage of staff turnover example
On this page:
- Fluidity is not the opposite of stability
- Does any layoff affect turnover?
- Types of staff turnover
- Formula for calculating staff turnover rate
- Absolute and relative rates of turnover
- Example of calculating the turnover rate
If you try to assess the efficiency of staff, the most significant indicators will be the cost of wages and various benefits, time spent on personnel paperwork and the turnover rate. Of these indicators, the last one represents one of the greatest difficulties in calculations and influence on it; there are many objective reasons for this.
Let's consider what the staff turnover rate is, what algorithms are used to calculate it, and what factors can influence it. Women's Questions 11 Strange Signs That Indicate You're Good in Bed Do you also want to believe that you give your romantic partner pleasure in bed? At least you don't want to blush and apologize... Sexuality Our ancestors slept differently than we do. What are we doing wrong? It’s hard to believe, but scientists and many historians are inclined to believe that modern man sleeps completely differently than his ancient ancestors. Originally... Dream of 10 charming star children who look completely different today Time flies, and one day little celebrities become adult personalities who are no longer recognizable. Pretty boys and girls turn into... Celebrities What to do after intimacy: 9 rules You're done having sex. Maybe it was good, maybe it was bad, but that's not the point. The process is over.