Features of a one-day business trip
A one-day business trip is the sending of an employee to a locality, from which he can return back to his permanent place of residence. The final goals for daily return are determined by the leaders of the organization:
- Distance of a settlement - from a workplace to a business trip;
- How developed is transport communication between two settlements;
- Is it possible to complete the task efficiently in a short time;
- Does the employee have the right to return home to rest and return to his work assignment the next day?
How to arrange a business trip for one day?
Registration of a one-day business trip is carried out similarly to registration of any other business trip. First you need to decide on the package of documents that are required. So, the registration process is as follows:
- First, the head of the department reports to the employer that it is necessary to send the employee on a business trip.
- If he agrees with this decision, a travel assignment is drawn up. The document has a standard form under the number T-10a. It indicates the main purposes of the business trip.
- Then an order is drawn up on behalf of the manager in form number T-9. Orders are approved by the same resolution as the form for official assignments. If a one-day business trip is arranged, then controversial situations arise. Usually we are talking about the need to create a certificate for a business trip. If an employee is going on a business trip for one day, there is no need for this document. Of course, only if there is an order according to which the employee is sent on a business trip to carry out the order.
Are daily allowances calculated for one day of business travel?
In addition to the Labor Code, payment of travel expenses is determined by the specifics of sending employees on business trips, which are approved by the current decree of the Government of the Russian Federation number 749. This regulatory document does not oblige additional payment of daily allowances if the employee returns home on the same day.
For this reason, if an employee is sent on a business trip for a period of one day, the payment of daily allowance is not considered mandatory. This means that if you send an employee to a company from where he constantly returns home, the payments are not such.
The provisions that payment for one-day business trips does not include daily allowance must be observed as a tax on such payment with insurance premiums. During the inspection, such authorities will insist on the taxation of daily allowances if they are not in the form of payments that are defined by current labor legislation.
In addition, the employee must be reimbursed for any expenses associated with working for another company. But only if the manager agreed to them and provided for them on the basis of local regulations. This is what it says.
Cash is paid by the company for the business trip. Although they are not daily allowances, they represent reimbursement of expenses related to the performance of work duties outside the main workplace. These funds cannot be recognized as income or benefit from an economic point of view. Therefore, they are not subject to personal income tax.
Daily allowance for one day of business trip
If the business trip is only for one day, how is it paid? There are short-distance business trips in which the employee has every opportunity to return home every day - and if he does this, then per diem should not be paid. However, for a one-time trip lasting a day (that is, at least 24 hours), daily allowance must be paid, as well as payment of expenses.
Accountants are often concerned about whether it is necessary to collect personal income tax from the daily allowance for a business trip that lasted only a day? And here it is impossible to give a definite answer. On the one hand, there are known court decisions on the payment of personal income tax for such business trips, since daily allowances were recognized as a source of income from which, accordingly, an individual must pay this tax. On the other hand, directly opposite decisions were made, and the demands of the tax inspectorate were recognized as unlawful. In short, there is no complete certainty on this issue.
The issue of insurance premiums based on the daily allowance is also interesting.
Do I need to accrue them for a one-day work trip? No, there is no such need, they are not paid within the limits established by the Tax Code (up to 700 rubles for business trips within the country, up to 2,500 rubles for trips abroad).
How is one day paid on a business trip?
If an employee goes on a trip, even a one-day trip, he is guaranteed to maintain his average salary. Some managers, in the case of a one-day departure, do not want to calculate the average earnings, so they pay the amount of one day’s wages for that day. To confirm the correctness of such actions, some employees include provisions in employment and collective agreements.
Agreements, labor and collective agreements should not contain requirements that could reduce the level of employee guarantees in comparison with current legislation and other legal norms that contain excerpts from labor law. They are not taken into account at all when performing this or that action.
The key features of payment of travel expenses for public sector organizations are enshrined in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 749 of October 13, 2008. This legal regulation contains not only basic definitions, but also maximum limits on the payment of expenses for business travel.
Let's define the concept
A one-day business trip is the sending of a company specialist to perform a work assignment in an area from where this employee can return to his place of residence daily (Article 166 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Consequently, such trips include not only business trips that last only one day, for example, to submit reports to the head office. But also long trips to places that are in accessible proximity. For example, it is more profitable for an employee to buy a return ticket to his place of residence than to rent a hotel room.
Please note that there are no restrictions on distances for recognizing trips as one-day trips. This decision is made by the manager based on economic feasibility.
Business trip for one day: how is it paid?
Regardless of the duration of the official trip, the employee retains his workplace and position. The employer must also pay him his average salary. Therefore, with a one-day payment:
- One average daily earnings if the UK falls on a working day.
- If the IC falls on a holiday or day off, then make the payment in accordance with the current labor legislation, that is, the average daily earnings in an increased amount. Read more in the material.
In addition to the average salary, pay the employee for all expenses that are documented. For example, payment for travel confirmed by tickets. Also reimburse expenses that the employee made with the permission of the employer.
The institution sets its own limits for paying travel expenses. Moreover, such indicators should be enshrined in a separate local order of the organization’s management.
Business trip order
To confirm the fact of a business trip, accountants actually have only a few documents left. As before, the most important act to confirm the fact of being sent on a business trip is an administrative document issued by management. Depending on the adopted accounting policy, it is published either according to unified forms or according to the company’s own administrative forms.
We remind you that the storage period for orders and/or instructions on sending on a business trip is 75 years.
For companies that have refused to use a travel certificate due to the fact that it is not necessary, we recommend that the business trip order include as much information as possible about everything related to the planned event.
Regardless of what forms the company uses to issue orders for an upcoming business trip, it is obvious that a number of information must be indicated in it. Thus, such a document must include the following data, in addition to the details generally accepted for orders and/or instructions:
- Full name of the seconded person indicating his position;
- the place where this person is directed;
- period for carrying out a business trip;
- purpose of the order.
It is also advisable to indicate in the order how the seconded person (CL) will get to the place of execution of the official assignment and return from there, and what kind of transport will be allowed to use:
- official;
- public;
- personal.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
How to pay per diem
Daily allowances for one-day business trips in 2020 are paid in a special manner. It is unacceptable to make payments in accordance with the procedure that applies to long-term insurance companies.
Thus, officials found that the amount of payments directly depends on the country:
- Foreign business trip 1 day: daily allowance 50%. That is, if an employee is sent abroad for one day, he will be paid 50% of the current daily allowance rate per day.
- Russian business trip for one day: no daily allowance! With a one-day IC in Russia, the employer is not obliged to pay daily allowances.
In exchange for daily allowance, the employee may be reimbursed for other expenses incurred during the trip. For example, spending on food. The size of such “replacement” payments is not limited. However, tax exceptions apply.
To avoid making mistakes, use the memo on how personal income tax and insurance premiums are assessed on daily allowances for an insurance company for one day.
Travel on behalf of the employer to perform certain tasks can be of varying duration.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how to solve your specific problem
— contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week
.
It's fast and FREE
!
Documenting a business trip for one day raises a number of questions, especially with changes in regulations. Since January 2019, this procedure has been significantly simplified.
What does the law say?
Business travel arrangements must be in accordance with the following legislative regulations:
- all articles of Chapter 24 of the Labor Code;
- approved by the Government, a new regulation on the specifics of sending employees on business trips;
- a local regulatory document that defines the specifics of travel arrangements on behalf of the administration.
Labor legislation defines a business trip as a trip outside a populated area to complete a work assignment. It is subject to mandatory and fixed costs.
Travel by an employee on his own initiative is not considered a business trip and will not be paid for.
It is necessary to distinguish one-time trips from work that is carried out on the road.
For example, a number of professions related to the operation and maintenance of transport, transportation and escort of goods and passengers, and some others.
Such professions include:
- truck drivers;
- conductors of passenger trains;
- forwarders;
- flight attendants;
- sailors;
- long-haul pilots, etc.
For those employees whose main activity is constant travel, travel documents are not issued.
There is sometimes an opinion among employers that a one-day business trip does not require special registration.
The legislation does not limit the duration of work trips to either a minimum or maximum period.
If an employee travels outside the locality on behalf of his superiors and this is not his job responsibilities, then such a trip will be classified as a business trip, even if it lasts less than a day.
Who can I send?
A person who has not entered into a contract with the organization cannot be sent on a business trip, even for 1 day.
The legislation clearly states that the employer has the right to send only “his” employee on a trip. It does not matter what type of employment contract is concluded: , or .
The question that deserves special attention is how to arrange a business trip for an employee working part-time.
If such a need arises, the following steps should be taken:
- take the employee’s written consent;
- issue the employee a certificate, written on the organization’s letterhead and certified by the signature of management, stating that the employee has been sent on a business trip;
- the employee must independently agree on or at the main place of work;
- Further, the preparation of a business trip and report will not differ from the same actions with regular employees.
Employees of organizations have different attitudes towards travel.
For some, this is a reason to improve their professional level, for others it is unnecessary problems. Employers must remember that there are certain categories of personnel that cannot be sent on business trips.
As a last resort, a receipt is taken stating that they were informed of the right to refuse the trip on behalf of the administration.
- workers who have not reached the age of majority;
- pregnant employees;
- employees working under an apprenticeship contract;
- women whose youngest child is under three years old;
- parents or guardians raising a child without a spouse;
- workers caring for incapacitated relatives, subject to a medical certificate;
- disabled people if they are prohibited from traveling for medical reasons.
Do I need a travel permit for 1 day?
The manager sent the organization's employees on a business trip for 1 day. Do I need to issue a travel certificate for one-day business trips? Is the presence of an order to be sent on a business trip sufficient grounds for compensation for travel expenses if a travel certificate was not issued? Is it necessary to fill out a job assignment (Form N T-10a) if daily allowances are not paid? Having considered the issue, we came to the following conclusion: 1. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the Regulations on the specifics of sending employees on business trips do not allow us to draw an unambiguous conclusion about the possibility of not issuing a travel certificate for one-day business trips. In our opinion, in this case it is permissible to apply clause. Travel on behalf of the employer, to perform any tasks can be of varying duration. Documenting a business trip for one day raises a number of questions, especially with changes in regulations.
InfoS January 2020, this procedure has been significantly simplified. What does the law say? Business travel arrangements must be in accordance with the following legislative regulations:
- all articles of Chapter 24 of the Labor Code;
- approved by the Government, a new regulation on the specifics of sending employees on business trips;
- a local regulatory document that defines the specifics of travel arrangements on behalf of the administration.
Labor Code of the Russian Federation Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 13, 2008 N 749 Labor legislation defines that a business trip is a trip outside a populated area to complete a work assignment.
Decor
The minimum duration of a business trip is not legally defined. It can be either many days or less than a day, without an overnight stay.
Registration of any trip on behalf of the employer must be in accordance with current amendments to regulations.
In 2020, the number of required documents decreased. Before this, the following were required:
- unified order for sending on a business trip;
- travel certificate;
- financial report on reimbursable expenses.
These documents actually duplicated their content and greatly complicated document flow in personnel departments. The decision to simplify travel processing on behalf of the administration was logical and natural.
Currently, a mandatory document for registration of a business trip is. Moreover, it does not have to be in an approved, unified form.
The organization independently decides what types of personnel orders it will use in its work. This must be noted in the documentation instructions.
Regardless of what form of order the enterprise administration chooses, it must reflect the following points:
- number and date of issue of the business trip order;
- surname, first name, patronymic of the posted worker;
- position or place of work of the employee;
- the exact name of the place of business trip (indication of administrative subordination is required);
- days of the start and end of the trip, if the period is less than a day, then there will be one date;
- the purpose of the trip on behalf of the employer;
- organization paying for the trip;
- a note on familiarization with this order from the employee himself and from interested parties.
Unified order forms can be downloaded here:
Registration of a work assignment and travel certificate is no longer mandatory.
If the employer decides that these documents are necessary, then the data from the order is transferred to them. Mandatory use should be noted in the local regulatory document.
Another document that has now lost its relevance is the logbook of seconded employees.
Previously, organizations maintained two journals:
- accounting for employees going on business trips;
- accounting of employees of third-party organizations who arrived on a business trip.
After the adoption of the relevant Government resolution, from August 8, 2020, these journals are closed and archived or destroyed.
It became enough to record employees who left for business trips.
Opposite the employee's last name, under the date of the trip, either the letter K or code 06 is placed. Without indicating the number of hours, even if it is a business trip for one day.
How to arrange a business trip
A one-day business trip should be processed in the same way as any other business trip.
Let's look at what documents are required.
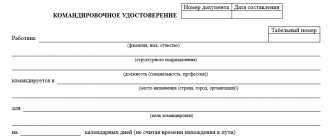
First of all, the head of a structural unit reports to the manager about the need to send an employee on a business trip. If the latter agrees, a service assignment is drawn up. This document has a unified form No. T-10a
(approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 5, 2004 No. 1).
It describes in detail the purpose of the business trip. Next, an order from the manager is issued in form No. T-9
(if one employee is sent on a business trip) and
form No. T-9a
(if several people are sent on a business trip). The orders were approved by the same resolution as the job assignment form.
However, when arranging a one-day business trip, there are controversial issues. This is the need to create a travel certificate. Let us remind you that this document also has a unified form No. T-10. Moreover, even legislators cannot clearly resolve this issue.
If you refer to the Instructions, it is not difficult to come to the conclusion that a travel certificate may not be issued if the employee must return from a business trip on the same day on which he was sent. Which is logical. After all, the purpose of creating a travel certificate is to confirm the time an employee spent on a business trip. Therefore, when an employee is on a business trip for one day, we believe that there is no need for such a document. Provided that, of course, there is an order to be sent on a business trip.
Letters from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 16, 2006 No. 03-03-04/2/244, dated October 24, 2006 No. 03-03-04/2/226 indicate that the order to send an employee on a business trip and the travel certificate have same purpose. Therefore, if an order is issued, issuing a travel certificate is not necessary.
But there is an alternative solution to the issue. Thus, the Regulations note that based on the decision of the manager, a travel certificate is issued to the employee (clause 7). No details are given here. But the requirements still exist, and therefore must be fulfilled, regardless of logic and practical necessity.
It is important
Travel of employees whose permanent work is carried out on the road or is of a traveling nature is not recognized as business trips.
What is the best thing to do in this case is up to the company accountant to decide.
In any case, the employee must submit an advance report. This document is one of the most important evidence of the fact of a business trip. The report has a unified form AO-1, the template of which was approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 1, 2001 No. 55. It must be compiled by the employee within three days upon returning from a business trip. Unless, of course, management has set a different deadline.
An entry about an employee’s business trip must be made in the Logbook for employees going on business trips (approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated September 11, 2009 No. 739n).
During the absence of an employee, the letter “K” or the digital “06” is entered in the work time sheet, form No. T-13 (approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 5, 2004 No. 1).
The number of hours worked is not specified, since the employee retains his average earnings during the business trip (Article 167 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
How is a one-day business trip paid?
There are no significant differences in booking a business trip of less than a day from longer trips.
Both in accounting and personnel documents, these days are taken into account and paid in the same way:
- if the day of the business trip falls on a working day, the employee receives the average salary;
- If the business trip coincides with a holiday or weekend, the employee is paid double the average salary.
The main difference in compensation is that daily allowances are not paid for a one-day business trip in Russia.
If an employee travels abroad for less than one day, he is paid half the amount due.
For a trip of several days, the law provides for mandatory compensation, not subject to VAT, these are:
- up to 700 rubles in Russia;
- up to 2500 rubles in the case of , paid in the currency of the receiving party.
However, an employer should not leave its employees without daily allowance or any compensation.
The law does not oblige, but does not prohibit, the reimbursement of expenses to employees for their stay in another area. Typically, such a payment is formalized as compensation and may be equal to the usual amount.
The obligation to return expenses for business trips of less than a day must be specified in.
Otherwise, the manager issues an appropriate order on additional payments to the employee.
The difference between a business trip and a simple trip is the employer’s payment of basic expenses.
Typically, an employee is given advance funds for the following needs:
- travel expenses to and from the business trip;
- additional expenses, they are associated with living away from home, the so-called, in 2020 they remained relevant for long business trips;
- other expenses paid with the permission of the employer - for example, meals or travel on public intracity transport.
When traveling on a one-day trip, the employee must be compensated for the cost of travel.
And in some cases, accommodation, for example, if the time of departure from the business trip is quite late, and the employee needs to rest before the trip. This could be a paid rest room or a hotel room at a train station or airport.
An employee can travel by personal or company transport.
In this case, a memo is drawn up. It justifies the need for this type of travel, prescribes the route and indicates the approximate cost.
The employer compensates for the cost of fuel and lubricants based on kilometers. Receipts from gas stations are presented as proof of spending.
If the day of travel on behalf of the employer falls on a weekend or holiday, then it is paid double. This will be processed as if the work shift fell on a non-working day.
How to pay?
Business trip time is considered working time, therefore a day spent away from a permanent workplace must be paid according to the employee’s average earnings (Article 167 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, in the general case, the following expenses are compensated (Article 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- for travel;
- for rental housing;
- daily allowance;
- other business trip expenses specified in the LNA and agreed with management.
At the same time, housing costs, by agreement with the employer, will be reimbursed if the employee remains away from his place of residence overnight (for example, the transport schedule is such that he does not have time to come home and rest on the eve of the next working day).
As for daily allowances, they are not paid for a one-day business trip in Russia (Regulations on business trips, clause 11, paragraph 4). You can prescribe a special payment for one-day work trips in the local act of the company, without resorting to the term “per diem”. Such a payment can be called “compensation”, but it should be borne in mind that, according to Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation the amount is above 700 rubles. per day can be recognized as the employee’s income and the tax authorities will be required to charge personal income tax, contributions, and additionally accrue profit for the amount of business trip expenses not accepted.
Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation speaks specifically about daily allowances, so the question of whether compensation in this case is considered daily allowance and whether the specified limit applies to it is controversial. The employer makes the decision.
Judicial practice here is ambiguous, however, there is Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court No. 4357/12 dated 11/09/12, which states that the daily allowance for a one-day work trip, prescribed in the LNA, should be included in the costs. After all, an employee goes on a business trip by decision of the employer, and not on his own initiative.
For one-day trips abroad, you need to pay a daily allowance, but in half the amount of the daily norm established by the organization (Regulations on business trips, clause 20). These standards may be fixed for all foreign trips, or they may be set by the company depending on the country of residence. The daily limit, which allows you not to withhold personal income tax and not to accrue contributions, is 2,500 rubles (paid in the currency of the corresponding state).
General rules when sending an employee on a business trip for one day in 2020
- The administration issues a travel order. This can be either a familiar unified form or a free one, but necessarily approved by a local regulatory act;
- The employee is given advance funds to pay for travel and compensation in lieu of daily expenses;
- The HR department employee makes a note on the report card. On the day the employee is absent, an alphabetic or numeric code is assigned, even if the trip falls on a weekend or holiday;
- Upon return, the employee, within three working days, provides documents on actual expenses - checks, travel documents, receipts;
- If an employee travels by personal transport, then upon arrival a memo is drawn up indicating the route and cost of fuel and lubricants.
They are subject to guarantees and compensation regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. These guarantees include payment of expenses associated with traveling to another location for business reasons.
In this review, we will look at how documents are drawn up during a one-day business trip, and what payments a seconded employee can expect.
Travel expenses
In addition to paying daily allowance, the employer will have to reimburse the expenses incurred by the employee during the trip. What expenses qualify as travel expenses and must be reimbursed?
- Travel costs both to and from the work site.
- Expenses for renting a room or apartment.
- Daily allowance.
- Other expenses that turned out to be necessary to complete the task, made with the permission of the employer.
The last category can include many different things, including entertainment expenses, if business negotiations are expected. In addition, sometimes other expenses can be paid by agreement - for example, meals on a business trip.
Regarding travel costs, there may be different interpretations as to whether they also include costs for traveling within the city itself - in particular, taxi costs. These costs are not included in this category, and the employer is not obliged to pay for them, but can do so by agreement with the employee, and documents confirming the costs must be presented.
There are also expenses that are usually paid by the employer in advance, but sometimes can be paid after. This includes amounts for the preparation of visas and other documents when traveling abroad, entry fees, transit of vehicles and similar costs.
The exact procedure in which expenses must be reimbursed, as well as the amount in which reimbursement is made, are established in accordance with local regulations in force in the company.
If the trip is made on personal or official transport, then a memo is submitted justifying the need to use it, indicating the route and determining the approximate cost. To confirm the expenses, receipts received at gas stations must then be presented, after which the employer will have to reimburse the cost of the fuel.
All documents and checks must be submitted to the accounting department for settlement within three days after returning from a business trip.
As for payment for days spent on a business trip, if it is a one-day trip, the standard rules still apply. That is, if this single day is an ordinary working day, then the employee receives the average wage for it. If it falls on a weekend or holiday, the employee will receive double the amount. We are talking about average wages, not daily wages. If the current one-day earnings are below the average for the period, then paying it instead of the average will be a violation of the law, for which the organization may be held liable under Article 5.27 of the Administrative Code.
Regulatory regulation
The rules for sending citizens on business trips are recorded in the following documents:
- in the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 13, 2008 No. 749;
- local acts and regulations approved at the enterprise.
The preparation of internal and accompanying documents related to sending citizens on business trips is the responsibility of the employer. As a rule, this is the responsibility of or.
One-day business trips are characterized by the following nuances:
- the moment of departure for business reasons to another locality coincides with the date of return, i.e. the actual time spent on a business trip does not exceed one day;
- an employee sent on a business trip does not need to be reimbursed, because he can return to his locality;
- The average salary for a seconded specialist is maintained on a general basis.
If the duration of the trip is several days, the employer is obliged not only to compensate the actual costs of the posted employee (travel documents, costs of renting housing, etc.), but also to pay daily allowance.
- For the state,
the amount of daily allowance is determined at the legislative level and is 100 rubles/day. - For this purpose,
the daily allowance indicator can be approved in local regulations.
The duration of a business trip is less than 24 hours if the employee has an objective opportunity to return to his place of permanent residence on the same day. This means that the official assignment, which was the basis for sending on a business trip, was completed within one working day.
Is it necessary to document the trip with internal documents in this case? Let's understand the rules for sending citizens on a business trip, the duration of which will not exceed one day.
What documents are needed
Even if the proposed business trip lasts only one day, the employer is obliged to document the business trip. The forms that will be filled out at the enterprise include:
- about the need to send a certain employee on a business trip - this document indicates the reason for the trip (for example, notice of a court hearing);
- , which indicates the instructions for the seconded specialist;
- – this document will confirm the validity of the reasons for absence from a permanent workplace, and is also the basis for compensation for travel expenses;
- – this form will contain notes on the dates of arrival and departure to another location.
The need to document a one-day business trip is associated with leaving the main place of work and traveling to another locality or other area. In the absence of an order and other documents, it will be impossible to justify the absence from the workplace.
During a one-day business trip, the employee will use the following documents:
- travel certificate;
- travel documents confirming travel expenses and travel time;
- power of attorney from the employer, if the official assignment is related to the representation of interests;
- other documents, depending on the purpose of the trip.
After returning from a business trip, and put a mark on the travel document. Local acts of an enterprise may establish the obligation to submit a report on the completion of an official task or assignment.
Step-by-step instruction
Based on the rules of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Resolution No. 749, the employer must perform the following actions when applying for a one-day business trip:
- draw up a memo justifying the need to go on a business trip, approve this document with the head of the enterprise and individual structural divisions;
- request the employee’s written consent for a business trip. If such a requirement is specified in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- make a preliminary calculation of travel costs to the place of business trip;
- draw up an order, approve it by the head of the enterprise and register it in the internal document management system;
- bring the order to the dispatched employee against signature;
- issue a travel certificate and funds on account to pay for travel documents.
As a rule, HR and accounting specialists are responsible for preparing documents for business trips. The same departments will be involved in processing documents after the completion of a business trip.
Registration of a business trip and accounting for travel expenses are described in the video below:
Who can and cannot be sent
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation lists the circle of persons for whom sending on a business trip is accompanied by additional conditions or a complete ban on business travel. At the initiative of management, any employees can be sent on a one-day business trip, with the exception of the following categories:
- employees who are primarily located - they can be sent on a business trip only with written consent to be recalled from vacation;
- a complete ban on business trips applies to pregnant women, minor employees, as well as employees under an apprenticeship contract;
- When preparing travel documents for persons with family obligations (with children under 3 years of age), it must be explained that no sanctions will follow for refusing a business trip.
If an employee is not on vacation and does not fall into the listed categories, he does not have the right to refuse a business trip. Refusal to travel without legal or valid reasons will be considered a disciplinary action.
Payment of expenses
The procedure for calculating payments for seconded employees is fixed in Resolution No. 749. If a specialist has the opportunity to return from a trip on the same day, this does not happen.
By decision of the management of the enterprise, an employee will be able to receive a daily allowance if the conditions of transport communication and the nature of the assignment do not allow him to return daily without affecting his rest time.
Regardless of the nature of the one-day business trip, the employee retains his average earnings. Also, the management of the enterprise is obliged to compensate for the costs of transport when traveling to the destination of the business trip. Payment is made using travel documents (tickets) and other supporting forms.
Service memo
A one-day business trip in 2020 is documented with documents, including an order to go on a business trip, a certificate, and a job assignment.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how to solve your specific problem
— contact a consultant:
It's fast and FREE
!
The head of the organization signs the documents. Upon returning from a trip, the employee provides a short report on the work done. They send it to the accounting department.
How are travel days paid? Features and Rules
Business lawyer > Accounting > Remuneration > How are travel days paid?
Features and rules When employees are sent to another location to perform a specific task, the manager enters into a special type of labor relationship with them. At the same time, traveling work and business trips are two different things.
About the regulatory framework
Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Business trips are regulated by a whole set of regulatory documents, including:
- Instructions of the Ministry of Finance together with Government Resolutions
- Tax code
- Labor Code
Each of these documents explains certain issues regarding business trips.
What do the payments consist of?
The most important item related to compensation in this case is the group of expenses necessary for the employee to carry out assignments:
- To get to the business trip location
- In connection with registration of lease for residential premises
- Daily nature
- Any other group of expenses, if it is agreed in advance with the management of the enterprise
Calculate based on salary or average earnings?
How exactly are expenses paid in this situation? The average salary is necessarily retained for employees going on a business trip.
The algorithm by which compensation is calculated is reflected not only in regulatory legal acts, but also in the internal documentation of the enterprise.
According to these rules, there is only an exception in the form of time worked on weekends and holidays. Here the calculation is based on an increased salary.
About additional payment for travel allowances
How are additional payments made?
Many managers pay additional amounts to those who go on business trips.
The specifics of the transfer of such additional payments must be reflected in the Business Travel Regulations established for the enterprise. This is especially important for situations where the “salary” payment is higher than the average salary.
Local local acts also stipulate all amounts that are paid in excess of the required minimum.
There are many issues that should be included in local travel regulations:
- Additional standards, if their adoption does not worsen the situation of business travelers compared to current standards.
- Information with rules of conduct individually for those who go on business trips.
- Necessary documents to be provided after the trip.
- Algorithm of interaction between an employee and his managers.
- The amount of payments due, the procedure for their transfer.
The employment and collective agreement may contain additional provisions regarding business travel.
General payment scheme for travel allowances
The employer issues an order or instruction if the employee needs to be sent on a business trip. For this, forms in the form T-9 or T-9a are used.
In 2020, the obligation to fill out the following documents was canceled:
- Travel log
- Travel reports
- Service assignments
- Travel certificates
But in any case, the employee must provide papers confirming his residence in paid housing. To solve this problem, a rental agreement along with a receipt for receipt of funds against this agreement, cash receipts with invoices for the use of hotel rooms, documents for payment of travel to the designated place are suitable.
When an employee returns to his permanent place of work, he must fill out a memo. The document form is free. In the document you must write how long the person was actually on a business trip and confirm the use:
Business trip
- A vehicle transferred on the basis of a power of attorney
- Personally owned car
- Transport owned by the organization
It is mandatory to fill out an advance report with all supporting documents attached. Among them are sales and cash receipts with additional expenses, documents for the consumption of fuel and lubricants, travel sheets along with receipts for housing, and transport tickets.
The number of days on a business trip is the only limiter when calculating daily payments.
The economic service at the enterprise checks the expense report. If everything is in order, the manager approves the document.
After this, they proceed to the recalculation of funds issued earlier. The final result from the report is:
- The employee receives the amount spent in excess of what was previously received
- Employees at the cash desk are returned the remaining amounts of money.
About payments and grounds for them
A business trip order must contain information on:
- Source where the funding came from
- Ways of transportation
- The total time within which the task must be completed
- Arrival date
- The place where the business trip is taking place
- The task from production, its main goal
- Personal information of the employee himself
- Registration number along with the date of the document
- Statutory details of the organization
Accrual of the advance amount for the upcoming trip is the responsibility of the accounting department and its employees. When transferring a sum of money with the appropriate amount, they rely on cash orders.
The basis for receiving additional payments is recalculation of amounts that were previously allocated.
About specific days and their payment
Advance report
The time for paying the daily allowance is calculated based on documents along with the advance report. It is easy to find information on arrival and departure dates and period of stay in your hotel bill. Travel documents perform the same function.
Daily allowances are paid on individual days of the trip. This means that only the days actually spent at the place of stay are taken into account.
As for payment at the average level, it is calculated according to the work schedule. Only the receiving party fills out such a schedule.
We calculate average earnings
In this case, actions are performed in the sequence determined by regulations:
- The total salary amount is calculated based on the previous 12 months preceding the business trip.
- If there are deductions that are not included in the salary, they are excluded from the formula. This applies to sick leave and vacations.
- Based on the last 12 months, the days actually worked are determined. With the exception of absences from work.
- Average wages are the result of dividing the total earnings for one year by the days worked over the same period of time.
About daily allowances. time tracking
When an employee arrives at a business trip, he is subject to the internal regulations in force at the receiving party.
When the employee returns, he submits his time sheet. The document is filled out at the place of business trip.
In this case, the individual work schedule drawn up for the employee at the main place is taken into account.
Fixed amounts are transferred to such employees for each day. This is one of the mandatory guarantees.
To calculate the total by number of days, include the following information:
- Every day while the employee was at work. Not excluding weekends and holidays.
- All days that the employee was at the place of arrival.
The legislation establishes the minimum required daily payment amount - it is equal to 700 rubles. For business trips abroad, payments increase to 2,500 rubles.
The management of the enterprise may pay daily allowances higher than those established by the standards. The main thing is that the amounts of additional payments are fixed in local acts. Travel employees do not report on used daily allowances.
Expenses. How to properly reimburse?
Travel expenses
Monetary compensation is expected only for expenses within reasonable limits, with documentary evidence. In addition, compensation is paid for expenses that were not planned in advance. In this case, it is important to confirm the need for them.
Cash registers and gas station receipts are presented in situations involving the use of personal transport. If the travel employee used other means of transportation while traveling, the appropriate tickets must be presented.
There is no separate item for food in the lists of expenses. Such expenses belong to the group of so-called “daily allowances”.
There are no established standards for housing that is rented during a business trip. But there is one condition that is important for this group of expenses - economic benefit.
Even the insurance fee may be accepted for payment. Although it is not on the list of mandatory expenses, this investment is taken into account when calculating tax fees.
As for reimbursement of the cost of luggage, this is a purely individual matter.
Each case is considered individually, taking into account production needs and the economic benefits of the solution.
Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
Source: https://PravoDeneg.net/buhuchet/oplata/kak-oplachivayutsya-komandirovochnye-dni.html
Peculiarities
A business trip differs from a regular trip in that the employee’s employer:
- travel costs to the appointed place and home;
- accommodation;
- other expenses - food, travel around the city.
Rules for sending an employee on a business trip for 1 day:
- Published. Use the usual approved form or a simple free one, but always approved.
- The employee receives an advance payment for transport travel and compensation funds instead.
- The HR department employee makes a note on the report card. On the day of absence, a code of letters or numbers is entered.
- When the employee returns, he must issue a travel and expense report within 3 days. These can be checks, receipts.
If the employee traveled, then upon his return he writes a note indicating his route.
When choosing a one-day business trip, the employer is guided by the following information:
- what is the distance from the workplace to the place of business trip;
- how developed is the infrastructure between these cities;
- whether the employee will complete the assignment in such a short time.
Features of a 1-day business trip:
- to send an employee on a business trip, only an order from the head of the institution is enough;
- on the same principle as for a multi-day trip;
- until the employee leaves, he needs to pay an advance - the cost of travel in both directions;
- if an employee travels abroad, he is paid a daily allowance - half the norm;
- within 3 days after the trip, the employee is obliged to present all receipts;
- if there is unspent money left, it is returned to the organization’s cash desk;
- if the employee paid personal money, the employer is obliged to reimburse this amount.
Who can I send?
Despite the fact that the business trip is one-day, an employee who has not entered into an employment contract with the organization cannot be sent on it.
Legislative acts state that the agreement can be fixed-term, indefinite or part-time.
The following categories of employees are not sent on business trips:
- persons who have not reached the age of majority;
- pregnant women;
- employees working under an apprenticeship agreement;
- women with children under 3 years of age;
- parents or guardians who are raising a child without a spouse;
- employees who care for incapacitated relatives must be confirmed with a medical certificate;
- disabled people.
Before this, it is necessary to obtain their consent to travel.
Simplified rules for sending on business trips since 2015
According to the new rules for processing a business trip, a number of documents are no longer mandatory and are not required for sending on a business trip. Which documents were needed before January 8, 2015, and which were no longer required, are shown in the table below.
| Title of the document | what happened before | what is relevant now |
| order | V | V |
| job assignment | V | |
| travel certificate | V | |
| trip report | V | |
| advance report with travel documents attached | V | V |
| memo | V | V |
| logbook for business travelers | V |
From this table it is obvious that the document flow regarding the procedure for sending on a business trip and reporting on it has been simplified. There is less work for HR officers. But the position of the accounting service, for which documentary evidence of the completed business transaction is still of great importance, has become somewhat more complicated.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
One day business trip
Often an employee is sent on a business trip to an area from where he can return home every day.
The payment procedure is influenced by where the employee is sent - within Russia or abroad.
Across Russia
When sending an employee on a business trip around Russia for 1 day, the employer must take into account the conditions of transport links, the complexity of the assignment and the need to provide recreational conditions.
Daily allowances are not paid for such trips. The prohibition on the payment of daily allowances is compensated by reimbursement of expenses associated with the business trip.
These payments are not subject to tax.
Money paid for a one-day business trip does not relate to the economic benefit (income) of the employee. But amounts within the normal limits are not taxed - in the Russian Federation this is 700 rubles. The remaining amount is subject to personal income tax. The exception is the provision of checks or receipts.
Also, insurance premiums are not charged on this amount. In this case, it is necessary to comply with the following conditions:
- the payment is not framed as daily allowance, but as other employee expenses;
- the employee's expenses are confirmed by receipts;
- the amount of payment is established by the organization’s documentation.
Abroad
In case of a foreign business trip, even if the employee returned home on the same day, daily allowance is paid. They amount to 50% of the employer's standard for foreign travel.
This payment is not subject to tax if it does not exceed the norm - 2500 rubles.
A business trip is also formalized by order. The document indicates the country and place of business trip, the assignment and the deadline. The employee is given an amount that will be enough for the trip.
It is issued in the currency that is national in the country where the employee is sent. Additionally, rubles are also issued for expenses before crossing the border.
All information regarding the business trip is recorded in the report card. After returning home, the employee draws up a report.
Registration procedure
Registration of a daily business trip must be completed in compliance with the norms of current legislation. This year the registration procedure has become simpler.
The order remained a mandatory document. It must display:
- when was it created?
- number;
- what position does the employee hold;
- where he is sent and for what purpose;
- duration of business trip;
- who will pay for the trip?
The order must be signed by the employee. This is proven by the fact that he was familiar with the business trip in advance.
The second stage is issuing an advance to pay for small expenses. The employee is given cash or money is transferred to a card.
Are daily allowances paid?
In accordance with the general rules, per diem is not paid in 2020, since the employee returns home every day and does not live at the place of business trip. But the employer is obliged to compensate for travel costs.
Payment of daily allowances for one-day business trips should be mentioned in the collective agreement or other type of internal documentation.
The employee is required to present documents confirming expenses when traveling on a business trip. He is reimbursed for expenses and paid an average salary per day.
The inspection service may not recognize food costs as additional expenses, even if they are supported by documents.
Payment of daily allowance
When traveling on business to an area from where the employee (based on transport conditions and the nature of the work performed on the business trip) has the opportunity to return daily to his place of permanent residence, daily allowances are not paid.
Daily allowances are paid to cover the employee’s personal expenses for the duration of the business trip. Travel to the place of business trip and back to the place of permanent work is also paid, and expenses for renting living quarters are reimbursed. The legislator made the payment of daily allowance conditional on the employee residing outside his place of permanent residence for more than 24 hours (resolution of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of March 4, 2005 No. GKPI05-147).
However, if the company has decided to pay daily allowances, then the next question arises: should they be subject to personal income tax? There is a dual position on this issue.
There are court decisions in which arbitrators decide that taxes must be withheld. For example, in the resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated December 14, 2011 No. A27-2997/2011, the servants of Themis indicated that the daily allowances paid by the company to employees on one-day business trips were income for the latter and, therefore, should be subject to personal income tax.
There are also decisions indicating that personal income tax in this case does not need to be withheld. For example, the resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated February 8, 2011 No. A56-12834/2010 noted that the tax inspectorate accrued additional personal income tax unlawfully. To substantiate their position, the tax authorities indicated that the place of business trip is significantly remote from the employee’s permanent place of residence. The daily return of an employee from a business trip to home is difficult and requires a significant amount of time. Therefore, the payment of daily allowance in this case is justified and personal income tax does not need to be withheld. All types of compensation payments are not subject to personal income tax within the limits established in accordance with the law (clause 3 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, with such an approach, daily allowances can easily be “driven” into the income tax base and not be subject to insurance premiums (Clause 2, Article 9 of Law No. 212-FZ of July 24, 2009).