What taxes do you have to calculate in Russia?
In any country there are many types of tax deductions. The Tax Code of Russia (TC RF) identifies the following categories of taxes:
- VAT (on value added);
- excise taxes;
- Personal income tax (on the income of individuals);
- on the profit of legal entities;
- for mining;
- water tax;
- fees for the use of biological resources;
- government fees;
- for additional income from hydrocarbon production;
- on the property of legal entities;
- to engage in gambling business;
- for transport;
- to the ground;
- for personal property persons;
- trade fee.
The first nine of them are federal, the next three are regional, and the last three are local. This means that the amount of tax payable will depend on the decision made at the appropriate level, and the funds will go to the appropriate budget.
At the same time, at each level, benefits are adopted for different categories of citizens. Therefore, before calculating the amount of tax, you need to find out whether you have to pay it.
Procedure for determining torque
The procedure for determining the moment is established by Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Thus, clarification of the moment of determining the tax base when selling real estate is carried out based on the fact that the tax base is calculated at the earliest date. This is either the transfer of ownership of real estate according to documents, or the day of payment.
Also, if the moment of determining the tax base is the day of payment, then the moment of transfer of real estate into ownership may also be the moment of determination. This rule is enshrined in clause 14 of Art. 167 Tax Code.
If the tax rate is 0%, and there are no documents allowing the application of this rate in a three-year period, then the moment of determining the tax base is the three-year period after the end of the tax period falling on the day of the transfer of ownership rights from the seller to the buyer for the corresponding product.
Despite the fact that the VAT rate is 0%, the taxpayer is required to submit a declaration to the tax authorities. The moment of determining the tax base gives the right to submit a declaration to the authorities no later than the 25th day of the month after the tax period.
If the customer of the work and services has not drawn up an acceptance certificate, then the moment of determining the tax base is the day the work is performed (services are provided) for tax purposes.
In this case, the date of transfer of goods and rights is the date of drawing up the primary document for them, issued to the customer or to the carrier of the goods to the buyer.
If goods are sold through an online store, then the moment the tax base is determined is the moment the buyer directly receives the goods. Also interesting is the issue of selling goods and works in Crimea.
Thus, until March 18, 2014, the amounts of upcoming purchases are not included in the base, but after receiving goods or payment after March 18, 2014, the taxpayer can easily determine the tax base for VAT.
The Civil Code also regulates the moment of determination - within the framework of Article 861. Based on this provision, all settlements between legal entities and settlements with the participation of entrepreneurs must mainly be carried out in a non-cash manner. Cash order is possible only if it does not contradict certain provisions of the law.
When making non-cash payments, we accept payment by checks, by collection, payment orders and other methods provided for by civil legislation in accordance with modern banking requirements.
When concluding an agreement for goods, work, or services, the parties have the right to independently establish in the agreement a specific form of payment, if this does not contradict the law. Payment forms are given in Article 862 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Under the contract, the buyer undertakes to pay for goods and services before receiving them, or at the time of receiving them from the seller, unless otherwise follows from the essence of the obligation and legal norms. This rule is enshrined in clause 1 of Art. 486 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Where to get basic data to calculate the tax amount
Art. 17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation requires, when introducing a tax, to establish taxation rules. It is necessary to determine:
- taxpayers;
- object of taxation;
- tax base;
- taxable period;
- tax rate;
- calculation order.
These characteristics are indicated in the second part of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. There is a separate chapter for each tax.
Benefits may also be established by law. Those established at the federal level are indicated in the chapter of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation dedicated to each tax. Regional and local authorities can establish their own benefits. Information on the availability and nature of local and regional benefits can be obtained from the legislative acts of the relevant authorities. The Federal Tax Service (FTS) provides the opportunity to obtain information about the availability of benefits on its website.
Checking the need to calculate the tax amount
Before you start calculating, you need to make sure. that this is necessary. In order for you to need to pay, you need to be a taxpayer and have an object of taxation.
Taxpayers are those individuals or legal entities who are required by law to pay contributions. If you are not listed as a taxpayer for a specific tax, you do not have to pay it and you do not need to calculate anything.
The object of taxation is a circumstance the presence of which causes the need to pay tax. The circumstances may be different: receiving income or profit, engaging in a certain type of business, owning certain property, etc. If you do not have an object of taxation - for example, you have not received income - you do not need to pay tax. Only after making sure that you or your organization are taxpayers does it make sense to start calculating the amount of tax.
How to calculate the tax amount
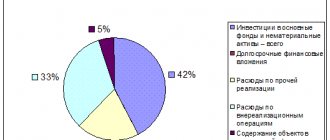
The procedure for calculating a specific tax is set out in the relevant chapter of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In general, the tax base is multiplied by the rate. The result obtained is the tax amount. For example, with personal income tax at a standard rate of 13%, income of 100 thousand rubles is taxed at 13 thousand.
The tax base is a quantitative characteristic of the object of taxation. This could be: amounts of money received as income or profit; units of property, property characteristics (for example, vehicle engine size) and other parameters.
When determining the tax base, an important indicator is the tax period. This is the period for which tax is paid. If, for example, according to personal income tax, the tax period is a calendar year, then all income received in it is included in the tax base.
The tax rate is the amount of tax charged on the tax base. The rate can be expressed as a percentage of income received or as a fixed amount per unit of tax base.
What does it include?
The tax base is determined separately for:
- each period (quarter);
- each tax rate.
The VAT base includes the following costs:
- goods sold (or transferred, including gifts);
- work performed (including free work);
- services provided, also including gratuitous ones.
For the same bet they are added together, but for different bets they are counted separately.
When selling, the value is determined according to the contract, when transferring free of charge - according to the market level. If a product is exchanged for something, the value of the goods received in exchange is taken into account, as far as it can be determined. The same thing happens with works and services.
To correctly calculate the tax amount, it is important to correctly determine to which quarter the received payment is attributed. For this, there are special rules described in paragraph 1 of Article 167 of the Tax Code.
Using benefits when calculating tax amounts
Benefits established by federal, regional or local legislation reduce the amount of tax deductions. This may be a full or partial tax exemption. Other options may apply. For example, when paying personal income tax, the amounts specified in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are deducted from the tax base before multiplying it by the rate.
Tax benefits allow you to save significantly. Therefore, before you start calculating the tax amount, you definitely need to find out whether you have these benefits.
All about income tax
The income tax in Russia is 20%.
But there are categories of taxpayers for which it is different. Article navigation
- What is income tax: we explain it in simple words
- Who should pay income tax
- How to calculate income tax
- Income and expenses - determine the object of taxation
- Formula for calculating corporate income tax
- Calculation example with explanations
- The procedure for submitting a declaration, paying tax and advance payments
- Legal methods of optimizing income tax
Income tax is paid by organizations that use the general taxation system. Its calculation is strictly regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Step-by-step instructions for applying the legal framework when calculating are set out in Articles 246–333 of Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Deviation from the rules is fraught with claims from the tax inspectorate and even fines. Therefore, it is very important to know how to correctly calculate an organization’s income tax.
At the end of the article you will find an interesting and useful video course!
A quick way to calculate your tax amount
There are many calculators on the Internet for calculating tax amounts. We recommend that you use only calculators from government and well-known reputable sites. We offer you links to several such calculators:
- VAT.
- Penalties for taxes and insurance premiums.
- Personal income tax for tax agents.
- Transport tax.
- Land and property tax.
- Personal income tax.
Any of them will help to make or check the calculation of tax deductions. Online calculators take into account most of the necessary indicators, so the results of their work can be trusted.
Sources:
General conditions for establishing taxes and fees.
Tax calculation procedure.
Tax base and tax rate.
Taxpayers.
The moment of determining the tax base is the earliest of the following dates:
1) the day of shipment (transfer) of goods (work, services), property rights; 2) the day of payment, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights.
In cases where the goods are not shipped or transported, but there is a transfer of ownership of this product, such transfer of ownership is equivalent to its shipment. When a taxpayer sells goods transferred to him for storage under a warehousing agreement with the issuance of a warehouse certificate, the moment of determining the tax base for these goods is determined as the day the warehouse certificate is sold.
When selling goods (work, services), the moment of determining the tax base for these goods (work, services) is the last day of the quarter in which the full package of documents is collected.
The moment for determining the tax base when performing construction and installation work for one’s own consumption is the last date of each tax period.
The moment of determining the tax base for the transfer of goods (performance of work, provision of services) for one’s own needs, recognized as an object of taxation, is determined as the day of the said transfer of goods (performance of work, provision of services).
The accounting policy adopted by the organization for tax purposes is approved by the relevant orders and instructions of the head of the organization.
The accounting policy for tax purposes is applied from January 1 of the year following the year of its approval by the relevant order or order of the head of the organization.
If the taxpayer - manufacturer of goods (work, services) receives payment, partial payment on account of upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), the duration of the production cycle of which is more than six months, the taxpayer - manufacturer of these goods (work, services) has the right determine the moment of determining the tax base as the day of shipment (transfer) of the specified goods (performance of work, provision of services) in the presence of separate accounting of operations performed and tax amounts for purchased goods (work, services), including fixed assets and intangible assets, property rights used to carry out operations for the production of goods (works, services) of a long production cycle and other operations.
Upon receipt of payment or partial payment by the taxpayer - manufacturer of goods (work, services), a contract with the buyer is submitted to the tax authorities simultaneously with the tax return, as well as a document confirming the duration of the production cycle of goods (work, services), indicating their name, production date, name of the manufacturer, issued to the specified taxpayer-manufacturer by the federal executive body exercising the functions of developing state policy and legal regulation in the field of industrial, military-industrial and fuel and energy complexes, signed by an authorized person and certified by the seal of this body.
If the moment of determining the tax base is the day of payment, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services) or the day of transfer of property rights, then on the day of shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services) or on the day of transfer of property rights on account payment received earlier, partial payment also arises when the tax base is determined.
When selling real estate, the date of shipment is the day of transfer of real estate to the buyer of this property under a transfer deed or other document on the transfer of real estate.
TAX BASE AND PROCEDURE FOR CALCULATION AND PAYMENT OF VAT
The tax base
The VAT tax base includes all income received from the sale of goods, works, and services. The tax base also includes the following amounts:
· Received advances
· Received financial assistance
· Interest received on bonds, bills, trade loans
· Payments received under insurance contracts against the risk of non-fulfillment of obligations
· Consisting of the customs value of the imported goods, import customs duties and excise taxes
The tax base for VAT is determined on the earlier of the two dates below:
· on the day of payment, partial payment on account of upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services)
· on the day of shipment (transfer) of goods (works, services)
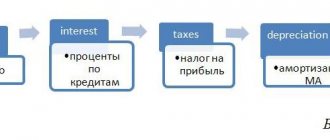
The procedure for calculating (calculating) VAT tax
The formula for calculating VAT is as follows:
VAT payable to the budget = VAT calculated upon sales – “Input” VAT accepted for deduction
VAT calculated on sales is calculated by multiplying the tax base by the tax rate.
Procedure and deadlines for reporting
The VAT return must be submitted to your territorial tax office no later than the 20th day of the month following the expired tax period:
· For the first quarter – until April 20
· For the second quarter – until July 20
· For the third quarter – until October 20
· For the fourth quarter – until January 20
It is necessary to submit a VAT return regardless of whether there is an object of taxation or not. That is, even if the organization did not have any economic activity, the declaration must be submitted.
Attention! From January 1, 2014, VAT returns must be submitted only electronically , through special communication operators.