Who must submit the declaration
A company that imported goods from the territory of the Republic of Belarus or Kazakhstan must draw up and submit a declaration on indirect taxes. The report must be completed for the month in which:
— the organization accepted the imported goods for registration;
— the lease payment period stipulated by the leasing agreement arrives (if goods are imported under a leasing agreement, which provides for the transfer of ownership).
This is stated in paragraph 8 of Article 2 of the Protocol, ratified by Federal Law No. 98-FZ of May 19, 2010, and paragraph 1 of the Procedure approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia of July 7, 2010 No. 69n. If within a month a Russian company has not imported goods and leased items from the territory of the countries participating in the Customs Union (the lease payment has not come due), a declaration on indirect taxes does not need to be drawn up.
Application structure
The application contains 3 sections and 1 appendix:
- in section 1, information is entered by the buyer or intermediary (if, according to the legislation of the state into whose territory the goods are imported, these persons pay indirect taxes);
- section 2 is intended to mark the registration of the application with the tax authority;
- section 3 is not always filled out and not by everyone - only in certain cases listed in clause 4 of the Rules for filling out an application for indirect taxes (Appendix No. 2 to the Protocol on the exchange of information dated December 11, 2009);
- the application is drawn up if the number of delivery participants is more than three.
Fill out a variety of tax applications using materials from our website:
- “Application for transition to the simplified tax system in 2018-2019 (sample)”;
- “We are preparing an application for personal income tax refund (sample, form)”.
How to pay VAT when importing from Belarus and Kazakhstan
An organization applying a special tax regime imports goods from the territory of countries participating in the Customs Union. Special regime officers who imported goods from the territory of the Republic of Belarus or Kazakhstan are also payers of import VAT (clause 1, article 2 of the Protocol ratified by Federal Law of May 19, 2010 No. 98-FZ, clause 1 of the Procedure approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 7 July 2010 No. 69n).
Such organizations are required to calculate VAT, transfer it to the budget and submit a special tax return, attaching all the necessary documents to it (clause 8 of Article 2 of the Protocol, ratified by Federal Law No. 98-FZ of May 19, 2010).
Import VAT: general overview of information
Previously, the current union of states was the Customs Union. Since January 2020, a renewed union of states—the EAEU—has come into force, which currently includes:
- Russian Federation;
- Republic of Belarus;
- The Republic of Kazakhstan;
- Republic of Kyrgyzstan;
- Republic of Armenia.
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs when importing goods into these countries are required to calculate import VAT not to customs, but to their Federal Tax Service, and at the same time display the data in the corresponding declaration.
According to the law, imported goods and imported services into the federal territory are taxed at a calculated rate of 10% or 18%. If the sale of a certain product is subject to taxation at a rate of 18% within the country, then upon import of such a product the tax is paid at the appropriate rate.
In certain cases, the import of goods is not taxed. For example, if medical goods are imported into Russian territory, their sale in Russia is not subject to value added tax.
Absolutely all importers, without exception, are required to pay import tax:
- VAT payers;
- recognized as exempt from the obligation to pay VAT (in relation to tax calculation);
- organizations and individual entrepreneurs under special regimes.
Persons from the second and third paragraphs include import VAT in the cost of services or goods purchased during the reporting period.
When to submit a declaration
The declaration must be submitted no later than the 20th day of the month following the month in which the organization accepted for accounting goods imported from the territory of the Republic of Belarus or the Republic of Kazakhstan. But, let’s say, a company imports leased items into Russia (under an agreement that provides for the transfer of ownership of them to the lessee). Then the declaration must be submitted no later than the 20th day of the month following the month in which the payment due date stipulated by the leasing agreement occurs.
The provisions of Article 163 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which states that the tax period for VAT is a quarter, do not apply in this case. This is explained by the fact that international treaties on taxation issues take precedence over Russian tax legislation (Article 7 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The agreement dated January 25, 2008 refers to such agreements. An integral part of this Agreement is the Protocol, ratified by Law No. 98-FZ of May 19, 2010 (Article 4 of the Agreement of January 25, 2008). The requirements provided for by this Protocol are mandatory for all Russian organizations.
Simultaneously with the declaration, submit to the inspection a package of documents, which is provided for in paragraph 8 of Article 2 of the Protocol, ratified by Federal Law No. 98-FZ of May 19, 2010 (clause 6 of the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 22, 2010 No. 03-07-15/ 101). If the deadline for submitting a declaration and a package of documents falls on the weekend, send them to the inspectorate on the first next working day (clause 5 of the Procedure approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 7, 2010 No. 69n).
Additional Tips
There are several ways to submit your declaration. The most impressive is the electronic version. But printed ones are also common.
The first is best suited for the largest organizations. Their average number of employees must exceed one hundred people. Monopoly enterprises submit declarations exclusively in electronic form. A tax is imposed on profits, the base of which is indicated there.
The second option is more often used by smaller firms. It must be provided in an approved form that is computer oriented. The declaration is filled out manually or printed on a printer. In this case, correction of records and double-sided printing are not allowed.
Sometimes it can be difficult to correctly determine the tax base.
When registering goods that are subject to excise taxes, it is formed by the following articles:
- the estimated value of the cost of goods that were sold within the allowable period;
- volume of products sold in kind;
- a combined tax amount collected from fixed percentages.
In other situations, the tax base is formed on the basis of the cost indicators of imported products. If the goods are the result of the fulfillment of contractual obligations, then the costs of the entire transaction are recognized as the cost. Certain expenses can increase the tax base.
What does the declaration consist of?
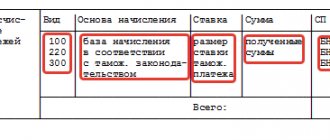
The indirect tax return includes:
- title page; — Section 1 “The amount of VAT payable to the budget in relation to goods imported into the territory of the Russian Federation from the territory of the member states of the Customs Union”; — section 2 “The amount of excise duty payable to the budget in relation to excisable goods imported into the territory of the Russian Federation from the territory of the member states of the Customs Union”; — an appendix to the declaration “Calculation of the tax base by type of excisable goods.”
The specifics of filling out sections and appending a special declaration on indirect taxes are given in the Procedure approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 7, 2010 No. 69n.
All organizations must submit the title page and section 1 of the declaration:
— who in the reporting month registered goods imported into Russia from countries participating in the Customs Union (regardless of whether these goods are subject to VAT or not); — for whom in the reporting month the lease payment term stipulated by the leasing agreement has come.
The total amount of VAT calculated for payment to the budget for goods imported from member countries of the Customs Union is reflected in line 030 of section 1 of the declaration. It must correspond to the amount of the tax deduction reflected on line 190 of section 3 of the general VAT return. If the organization imported excisable goods into Russia, it is additionally necessary to fill out section 2 and the appendix to the declaration.
General rules for filling out indirect tax returns
- The pages of the document are numbered consecutively; the serial number of the page is entered starting from the title page, regardless of the presence or absence of sections.
- Fields of any values are filled in from left to right, starting from the first familiarity.
- Free spaces in the fields are filled with a dash or the value “0”.
- Text values are filled in capital block letters, cost indicators are indicated in full rubles.
- The use of corrective means is not allowed in the declaration; corrections are made in pen and signed by the taxpayer.
- The declaration must not be sealed with any means that could damage the paper.
In accordance with the current procedure for filling out a declaration, the day of submission of the declaration to the tax authorities is recognized as:
- the date of receipt of the document by the inspectorate when presented in person by the taxpayer or his representative;
- date of sending the declaration by registered mail with an inventory as an attachment by mail;
- date of sending the declaration using a telecommunication channel, if there is confirmation of such sending (receipt of receipt of the document in electronic form).
What documents are submitted to the tax office along with the declaration?
The following must be attached to the declaration:
— application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes on paper (in four copies) and in electronic form; — bank statement confirming payment of VAT to the budget; — transport and (or) shipping documents; — invoices for shipment of goods; - an agreement on the basis of which goods are imported into Russia (purchase and sale agreements, leasing, trade credit (commodity loan), agreements on the manufacture of goods, - on the processing of customer-supplied raw materials); — commission agreements, assignments or agency agreements (if they were concluded); - an agreement for the purpose of fulfilling which imported goods were purchased under commission agreements, mandates or agency agreements (if intermediaries do not pay VAT).
Let’s say that goods are imported from the territory of Belarus or Kazakhstan, and the seller is a representative of another state, including one that is not a member of the Customs Union. Then the inspectors need to submit another document. We are talking about an information message from the supplier of goods about the person from whom they were purchased.
Please note: sometimes not all specified documents need to be submitted to the tax office. For example, if the preparation of invoices, commodity and shipping documents is not provided for by the national legislation of the union states, your inspectors cannot require these papers.
All documents, except for the application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes, can be attached to the declaration in the form of copies certified by the head (chief accountant) and the seal of the organization.
Tax base of indirect tax
When considering the general case, the tax base of indirect tax is determined on the basis of the cost of goods purchased. If we are talking about goods that are the result of work performed under a contract, the value is determined by the transaction price payable by one of the parties to the supplier for the goods. At the same time, the tax base may be increased by certain expenses (unless otherwise provided by the inclusion of these expenses in the transaction price), for example, such as:
- sum insured;
- costs of delivery of goods;
- the cost of packaging, including the cost of packaging materials.
Important! The tax base for indirect taxes includes the amount of excise taxes that are payable on excisable goods.
When selling or receiving excisable goods, the tax base is determined as:
- estimated cost of sold excisable goods;
- volume of excisable goods sold in their natural form;
- a combined tax rate that includes a percentage rate and a flat rate rate.