According to statistics conducted recently, experts have concluded that VAT accounts for more than 30% of the country's taxes and brings the largest profit in comparison with other taxes. This is probably why this tax is so often subject to changes in terms of calculation by tax authorities.
Often in such situations, the heads of organizations are not the first to learn about changes and because of this, confusion arises. Let's figure out together how value added tax should be calculated in accordance with the law.
VAT – tax deductions
Value added tax is a fee that is paid every month to the tax office, it is not constant, and therefore requires monthly calculations by the accountant in the company.
To do this, the object will need the amount to be accrued, the amount to be paid, as well as the exact tax rate that is in effect in the organization at the time of payment. It is for this reason that this process can take quite a long time. And it’s best to do it throughout the entire month.
It is important to know that despite the fact that payment is made once a month, it must be counted every quarter for the correct deductions.
So, this tax is indirect and builds part of the country’s budget. By law, value added tax is a percentage of what remains over and above your production of goods and services. That is, everything that remains above your standards is value added tax.
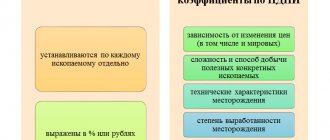
It is important to know that there is no clear framework for what this tax should be, since it depends on many characteristics of the product:
- His price.
- Cost price.
- The material from which it is made.
- Quantity and price of necessary resources.
- Necessary work for the production of a particular product.
If you are an employee of a small company, it will not be difficult for you to calculate VAT, since this indicator does not involve large calculations. But, if your organization employs a large number of people and produces many different goods, it will be better if you use special online calculators that offer many sites for calculating this indicator without errors.
How to calculate value added tax with example
In addition to the VAT tax rates of 0, 10 and 18%, two more rates are applied: 100% * 10% / 110% 100% * 18% / 118%. These tax rates are applied when it is necessary to separate VAT from the amount. Let's look at an example of using these rates. The organization Delta LLC receives payment on account of future delivery in the amount of 177 thousand rubles. In this advance payment, VAT must be allocated and paid to the budget. In order to calculate VAT from the amount, one of the above interest rates is used, depending on the type of goods. Suppose you have received payment for products subject to VAT at a rate of 18%, in order to isolate VAT from this amount, you must use a rate of 100% * 18% / 118%. VAT = 177 thousand * (18*/118) = 27 thousand rubles. Features of the VAT payment procedure. Deadline for submitting a VAT return All organizations have a single reporting period - a quarter.
Also, if you restored VAT that was previously accepted for deduction, then do not forget to add the amount of the restored tax to the total amount of accrued VAT. VAT deduction formula VAT accepted for deduction in a given quarter is calculated using the formula below: If an organization/individual entrepreneur has VAT subject to deduction on construction and installation work performed for its own consumption, then this VAT is added to the total amount of VAT, accepted for deduction in a specific quarter. The final amount of VAT The amount of VAT that needs to be paid to the budget at the end of the quarter is calculated as follows: It is important to note that if, as a result of the calculations, the final value turns out to be zero, then you do not need to pay anything to the budget.
If the resulting value is negative, then you have the right to claim a VAT refund from the budget. How to extract 10% VAT from the amount: example, an individual entrepreneur received an advance payment for the upcoming supply of goods subject to VAT at a rate of 10%. The advance amount is 110,000 rubles, including VAT. In this case, in order to calculate the amount of input VAT, a calculated rate of 10/110 is applied (since the goods are taxed at a rate of 10%). Accordingly, the amount of VAT on the advance will be 10,000 rubles. (RUB 110,000 x 10/110). Formula for accrued VAT To calculate the amount of accrued VAT for a quarter, the following formula is used: If during the quarter construction and installation work was carried out for one’s own needs, an adjustment was made to the sale of goods (work, services) or a sale/adjustment to the sale of the enterprise as a whole as a property complex, then VAT on these transactions is also included in the total amount of accrued VAT.
How to find out how much VAT is included in the price of a product? If the price is indicated with VAT, then take this price as 118%, find the cost of 1% and multiply to determine how much 18% will be. (1100 rubles: 118 x 18 = 167 rubles 80 kopecks) Every quarter you calculate how much VAT is in all your sold goods and services. You deduct all VAT that you purchased (raw materials, rent of premises, purchase of goods, etc.). And you give the difference to the state - this is your VAT. Bottom line. VAT remitted to the state is calculated as the difference between purchase VAT and sales VAT. Therefore, if you work according to a simplified tax system (without VAT), and your customers are in the classical taxation system (with VAT), then they cannot reduce their VAT by the amount of your VAT (you do not have it). And they are forced to pay more taxes to the state.
Sales ledger The seller must record the invoices that he himself issued to the buyer in the invoice ledger. Although today this is a right, not an obligation. But still, I recommend adhering to the old rules so that it is convenient to keep records, especially since this form has been preserved in many accounting programs.
Next, it must be registered in the sales book. Now this is an important tax document! Based on these documents, you will fill out a VAT return. It may also be required by tax authorities if necessary.
Purchase book In turn, in order to be eligible for VAT deduction, you need an invoice received from the supplier. Payment of VAT upon import must be confirmed by a document that records the payment of tax at customs. “Incoming” invoices are recorded in the invoices received journal and in the purchase ledger.
>VAT payable calculation
1.10. The procedure for calculating VAT payable to the budget
When performing transactions subject to VAT, taxpayers are required to calculate the amount of tax (clause
VAT to be charged
The amount of tax should be the difference between the amount of tax for the entire enterprise and the cost of the goods it produces. It is for this reason that VAT is an indicator that is borne by the buyer.
You have probably seen more than once on tickets or receipts that a separate figure is VAT, which you must also pay. Typically, it is part of the cost of the main product. It is by paying it in stores and for any purchases that you contribute this tax as a payment to the country’s budget.
Calculation of the VAT tax base
The tax base is the cost of products or services, which is determined on the day the goods are shipped or the service is provided or on the day the advance payment is received. The total amount of contributions for value added tax is calculated from the tax base.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
Determining the amount of VAT payable
Thus, in order to determine how much you need to pay as VAT, you need to take the entire cost of the goods that were sold by the organization for a certain period.
After this, you will need to carry out calculations using a simple formula:
VAT = Product price * tax rate for this product
Remember that the last digit can take on three meanings at once, depending on the type of product:
- Medical products, social or financial – 0.4%.
- Children's products and books – 10%.
- Other goods – 18%.
But, before making calculations, check with Articles 149, 150, 160,164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and only then carry out all the calculations. After all, the tax rate will significantly affect the amount you pay.
VAT refund
We can talk about a refund only if, at the end of the tax period, the amount of VAT deductions is greater than the amount of tax accrued for payment to the budget for the same period. The picture is reflected in the VAT return; the return rules for legal entities and individual entrepreneurs are no different.
There are two main points that the person preparing the declaration should have:
- right to refund of tax deductions;
- VAT payer status.
Typically, those who work on the general tax system have VAT payer status. They are required to charge VAT on all transactions that are subject to VAT. Their responsibilities also include submitting declarations, issuing invoices and maintaining a ledger of sales and purchases.
They also have the right to apply deductions in the amount of tax that is presented by suppliers and arises in certain other transactions.
In some cases, defaulters may also be required to pay VAT. But they will not have the right to deduction.
At the same time, a VAT refund implies a series of actions, after which the amount of tax from the budget will be returned to the entrepreneur’s bank account.
A similar situation is faced by exporters who apply a zero rate on goods shipped for export and who are entitled to a tax deduction. The latter is calculated from the amount transferred to suppliers for the purchase of goods, works and services that relate to sales abroad.
Depending on what share of export sales occurs in the total sales volume, the need for a VAT refund may arise each reporting period.
It should be noted that the excess of the amount of deductions over the amount of accrued VAT is not a guarantee of a refund. To return, you must follow the established procedure. The key point in it is the desk audit, which is carried out after filing the declaration.
To do this, a voluminous package of documents is requested, which are divided into two groups:
- confirming the right to apply the zero rate;
- justification for the deduction amount.
Calculation example
Let's imagine that you are the owner of a company that earns about 150,000 rubles a month and every month you pay value added tax.
For the purity of the experiment, let's imagine that you produce three types of goods at once, with each type of interest rate. So, you produce medicines, baby food and coffee:
- In the case of a medicine, the tax rate will be: VAT = 150,000 * 0% = 0.
- In the second option, with baby food: 150,000 * 10% = 15,000 rubles.
- In the case of coffee, you will pay the highest amount: 150,000 * 18% = 27,000 rubles.
Despite all this, remember that as the owner of the company, you can return all the money paid to him.
Calculation of the simplified tax system
Determine the amount of single tax payable for the 1st quarter if the amount of income was 350,000 rubles. and the organization paid insurance premiums for compulsory pension insurance in the amount of 15,400 rubles. The organization has adopted a method of paying a single tax based on the amount of income and a rate of 6%.
Solution:
1) The amount of single tax for the 1st quarter is determined
350,000 X 6%: 100% = 21,000 rub.
2) Advance payment cannot be reduced by more than 50%
21000 X50%:100% = 10500 rub.
3) In a given quarter, an organization can reduce the tax amount only by 10,500 rubles, and the amount is 4,900 rubles. (15400 – 10500 = 4900 rubles) remains unaccounted for in the 1st quarter.
The amount of single tax payable in the 1st quarter will be:
21000 – 10500 = 10500 rub.
Payment in foreign currency
But, sometimes, there are situations when the calculation is quite difficult, since the company sells or purchases goods or services in foreign currency, and VAT requires payment in rubles.
So, in order to calculate this amount, you will need to take the exchange rate that was set for the period of shipment of goods. So, in order to calculate VAT, you will need two values at once - the advance received at the time of shipment of the goods, as well as the amount of payments for the goods.
The full procedure for calculating the amount when paying VAT depends on what kind of goods it was and how it was delivered. The legislation of the Russian Federation, namely Article 153, states how to correctly carry out these calculations, taking into account all the points. So, if you are unsure about anything, you better check it out so that you have legal proof.
How to correctly calculate VAT, formula and calculation example. Online calculator.
- What data is needed for the calculation.
- Formula for allocating VAT.
- Formula for calculating VAT.
- Online VAT calculator for the lazy
- Discussion of the article - 8 comment(s)
- X Determine the VAT rate. This information can be found in the above code. The most common: 10%, 18% or 20%.
- X Calculate the amount of the tax base. This procedure is carried out on the basis of the provisions of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This amount is equal to the cost of goods sold, taking into account excise taxes. Calculation date C is the day of transfer of the advance payment for services, the day of actual receipt of payment for the goods or the day of shipment of the goods.
- X Conventionally, the formula for calculating VAT looks like this: tax base * calculated rate. The resulting value must be included in the invoice issued to the buyer or customer. If the goods are sold in foreign currency, when calculating, you need to subtract the ruble equivalent of this value at the National Bank exchange rate, since VAT can only be charged in rubles.
Almost every enterprise that is part of the general tax system is faced with the concept of value added tax. It represents a form of collection into the state budget of added value that arises at each stage of the production process of a product or service. The procedure for calculating VAT is prescribed in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. You can carry out this procedure yourself or use special online accounting programs.
So, in order to calculate VAT:
If you need to allocate VAT
Then the amount is divided by 1+VAT/100. That is, if the amount is 1000 rubles: 1000 / (1+20/100) = 1000/1.2 = 833.33
Next, the original amount is subtracted from the resulting number: 833.33 - 1000 = -166.66.
Since VAT is a positive number, the indicated result is multiplied by -1. We get VAT = 166.66 (rounded to the nearest kopeck).
If you need to charge VAT
Then a simple formula is used - the amount is multiplied by 1.xx (where xx is the VAT rate), for example, by 1000 rubles with a tax of 18%:
1. 1000 *1.20 (if VAT is 20%) = 1120 (amount including VAT)
or
2. Multiply the amount by 0.2 and get the VAT amount, 1000 * 0.2 = 200 rubles (VAT amount)
In addition, you can determine the amount of tax using an online calculator by simply entering the amount, percentage of VAT and the required operation (charge or allocation of VAT) into the appropriate fields.
Using, for example, the 1C:Enterprise software, VAT is calculated by generating an invoice indicating the cost of the goods. Next, this accounting application automatically produces the result, independently determining the tax rate.
Calculating VAT is not easy, because value added tax is one of the most complex taxes. In large organizations, calculation, accrual and accounting for VAT is carried out by an accountant specially hired for this purpose. Taxpayers of value added tax (clause 1 of Article 143 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) are: * organizations; * individual entrepreneurs; * persons recognized as VAT payers in connection with the movement of goods through the customs territory of the Russian Federation. Please note that organizations and entrepreneurs can receive an exemption from VAT if certain conditions specified in Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are met. According to paragraph 1 of Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the following transactions are subject to taxation under value added tax: 1. sale of goods, works and services in the territory of the Russian Federation; 2. transfer of goods on the territory of the Russian Federation (performance of work, provision of services) for one’s own needs, expenses for which are not deductible when calculating corporate income tax; 3. carrying out construction and installation work for own consumption; 4. importation of goods into the customs territory of the Russian Federation. According to Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, those who pay VAT are required to issue invoices to buyers and customers, maintain books of sales and purchases, as well as logs of issued and received invoices. Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation specifies transactions that are not subject to VAT, and Article 150 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation lists goods for the import of which VAT is not required to be paid. When selling goods (works, services), VAT is calculated as follows. The tax base for VAT is defined as the cost of goods (work, services) sold based on sales prices including excise taxes, but excluding VAT (Clause 1 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). More details about how VAT is calculated in some specific situations can be found in Articles 154 - 162.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The moment of determining the tax base for VAT is the earliest of the dates (clause 1 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation): 1. day of shipment of goods (provision of services, performance of work); 2. the day of receipt of payment (partial payment) on account of upcoming shipments. The VAT tax base includes the amount of advance payment received for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services). Many accountants ask how to calculate VAT when receiving an advance. The formula for calculating VAT can be as follows: Amount of VAT = Amount of advance received: 118 x 18. How to calculate the amount of VAT if goods taxed at a rate of 10% are shipped. The formula is as follows: VAT amount = Amount of advance received: 110 x 10. Let us remind you that when receiving an advance, you must issue an invoice to the buyer or customer. The tax period for VAT is quarterly. VAT rates are specified in Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The organization acts as a tax agent
There are cases when an organization is foreign and therefore cannot be registered for tax purposes. But, despite all this, it must pay VAT, like any other company located within a given country.
In such cases, they resort to the services of a tax agent:
- It is important to know that if a foreign organization is official, it had to go through the process of registration with the tax office, and therefore pay VAT and other payments itself. If it has not been registered, finding it becomes unrealistic for everyone. It is for this reason that the value added tax from a foreign organization must be paid by the one who is, as it were, the counterparty of this organization in this country.
- It is important to know that if both the sender and the recipient are foreign citizens who have not been registered with the tax service, the payment will have to be handled by an organization that is in some way connected with the details of one of them. So, for example, this could be the production and transfer of any materials, etc.
This method is quite strange. After all, on the one hand, in this way the Russian state is trying to force a foreign object to register. But, on the other hand, it does not do this itself, but with the hands of third parties who have absolutely nothing to do with the profits of this organization, but must pay their taxes for them.
Procedure for paying VAT
Clause 1 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation talks about the procedure and deadlines for paying VAT. Payment is made during the quarter in equal installments. Then, when the deadline falls on a weekend, payment is transferred to the nearest working date. The law provides for accelerated tax payment. It is quite possible to pay the entire amount at once.
A very important factor is checking the details of the tax authority that receives the amount of money. Because there are times when they change, then you have to deal with the bank:
Then, when a company is late in payment, tax officials will impose a fine on it. Tax agents are an exception. They must pay the tax before the purchase is paid for, otherwise the bank does not have the right to accept payment.
In order to avoid any troubles with the tax service, you must clearly know the rules and procedure for paying value added tax. It is also important to submit the declaration on time, then the entrepreneur will avoid paying large fines and the ensuing consequences.
- Accounting for interest on a deposit: postings and examples
- Updated (adjustment) VAT return: features of filling out
- VAT 10 percent: list of goods, in which cases it applies
- Income tax return: how to check whether it is filled out correctly
Import
In addition to the fact that it must be paid by the buyer, it is also imposed on the objects when importing or exporting certain goods and services. To avoid confusion and lengthy calculations, the legislation of the Russian Federation has clear limits on what the VAT rate should be, depending on the product and its characteristics.
So, for example, if your product is included in the list of goods or services useful for the country, it will range from 0 to 10%, but if it is widespread, the tax on it will be 18% of the cost of your product.
Calculation of tax included in the price
In some cases, for example, when the goods were purchased and shipped or work was carried out earlier, VAT may already be included in the price. Then you need to calculate it differently.
This usually happens in the following cases:
- when making advance payments for future delivery of goods/services or work provided;
- if the contract indicates the cost, provided that VAT is already included in it, but its amount has not been calculated.
In this case, there are two formulas for calculating VAT:
- multiplying the transaction value with tax by 20 and dividing by 120;
- multiplying the tax value by 0.2 and dividing by 1.2.
Another way is to take 16.6666...% of the amount, the resulting number is rounded to the nearest kopeck. Based on this calculation formula, you can understand how to calculate the amount excluding VAT.
Sales of precious metals
It is important to know that according to the legislation of the Russian Federation, those organizations that are engaged in the sale of precious metals have special tax rights, or rather, its rate of 0%. So, according to the same law, these include:
- Gold.
- Silver.
- Platinum.
- Palladium.
- Iridium.
- Osmium, etc.
It is these metals that should not be taxed upon purchase or sale.
According to the laws, VAT is not obligatory for companies to pay, but in practice few people turn to the tax service to return it. After all, this action promises not only money, but also lost time and nerves.
It is for this reason that many organizations pay this tax, while others do it out of ignorance. But, regardless of the reason why this happens, it is worth considering the fact that you can always return this money.
VAT calculation errors
Incorrect calculation of VAT entails the imposition of penalties on the organization. But often erroneous calculations still occur:
| Error | A comment |
| Advance payments are not included in the tax base | In accordance with Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, advance payments are subject to VAT calculation. |
| Accepted for accounting for input VAT in case of an incorrectly drawn up invoice | This error may cause suspicion and mistrust of the tax authorities. Incoming invoices must be closely monitored. |
| There is no separate accounting | If an organization refuses to keep separate records of transactions subject to VAT and non-VAT, VAT will not be deductible. |
| VAT refund for fines or penalties | A fine or penalty is not considered to be goods, work, or services, and therefore VAT refunds cannot be made. |
An example of calculating VAT payable to the budget (VAT)
· veterinary drugs that have passed state registration with the authorized federal body and are included in the State Register of Veterinary Drugs developed for use in animal husbandry on the territory of the Russian Federation, bottled in containers of no more than 100 ml;
Excise tax is an indirect tax included in the selling price of products. The following goods (products) are subject to excise taxes: ethyl alcohol from all types of raw materials, alcohol-containing products with a volume fraction of ethyl alcohol of more than 9%, alcoholic products (drinking alcohol, vodka, alcoholic beverages, cognacs, wine and other food products containing ethyl alcohol more than 1.5% of the volume of a unit of alcoholic products, with the exception of wine materials), beer, tobacco products, cars, motorcycles with an engine power over 112.5 kW (150 hp), petroleum products (motor gasoline, diesel fuel, motor oils for diesel and (or) carburetor engines; straight-run gasoline), household heating fuel produced from diesel fractions of direct distillation and (or) secondary origin, boiling in the temperature range from 280 to 360 degrees Celsius.
Also read: During the Inventory of Property, the Debtor Must Be present