Home / Taxes / What is VAT and when does it increase to 20 percent? / Declaration
Back
Published: September 18, 2017
Reading time: 5 min
0
61
The fine for late submission of a VAT return is imposed in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 119 of the Tax Code and is calculated from the amount of VAT payable.
The amounts of the fine for late submission and the fine for lack of reporting are calculated according to general rules. Failure to submit such a declaration means a zero tax amount, which leads to controversial situations.
- Late delivery
- Failure to submit a declaration
- Extenuating circumstances for taxpayers
- Judicial position on the issue of repeated reduction of penalties
Dear readers! To solve your problem, call hotline 8 or ask a question on the website. It's free.
Ask a Question
Penalty for failure to submit or late submission of a VAT return
Features of filing a VAT return
Penalty for late filing of a VAT return
Submitting an updated declaration as an option to reduce the amount of the fine
Is it possible to reduce the amount of the fine?
If the declaration is not filed with zero VAT
Extenuating circumstances
Features of filing a VAT return
The main purpose of submitting VAT reports to the tax authorities is to transmit information about goods (work, services) sold and purchased for a certain period of time.
The current legislative documents stipulate the tax period for which VAT reporting is provided - a quarter. The deadline for filing a value added tax return is set for the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter. If this date falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is postponed to the next business day.
A fine for a VAT return for failure to submit or late submission is imposed if these deadlines are violated.
All enterprises, organizations and individual entrepreneurs that are tax agents and work with value added tax are required to submit VAT reports.
Since 2020, taxpayers of the Russian Federation are required to submit declarations to the tax service in electronic format. To fulfill this obligation, all declarants must purchase an electronic digital signature with payer information. Specialized software must also be installed. If the taxpayer made errors in the submitted declaration or violated the terms of its submission, the single portal notifies the declarant of the detected problems.
If an organization does not work with value added tax, but provides any services, it must issue invoices.
Penalty for late filing of VAT returns
If an organization does not submit a document within the specified time frame, it is subject to administrative liability in the amount of 5% of the amount of tax that was not paid on time. The fine for late submission of a VAT return is imposed for each overdue month. The payment cannot be more than 30% of the amount of overdue tax or less than RUB 1,000, but it can be reduced if there are extenuating circumstances. These provisions are enshrined in paragraph 1 of Art. 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Don't know your rights? Subscribe to the People's Adviser newsletter. Free, minute to read, once a week.
The fine for failure to submit a zero VAT return will be minimal and amount to 1,000 rubles. for each full and/or partial month of delay.
The person responsible for filing the VAT return receives a warning or must pay a fine of 300–500 rubles, and if the delay is more than 10 business days, sanctions may be applied to the taxpayer’s current account and non-cash money transfers. Even if the delay is one day, the tax office counts this period as one full month.
Submitting an updated declaration as an option to reduce the amount of the fine
You can avoid a fine for a VAT return for failure to submit or late submission by applying the following scheme (in accordance with paragraphs 2–4 of Article 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- Submit an updated declaration before the deadline for submitting the main version. In this case, the original declaration will be considered submitted on the day the updated document is submitted.
- Submit an updated declaration after the deadline for filing the main version has expired, but before the period for transferring VAT to the budget expires. At the same time, the tax service has not yet notified the taxpayer about the shortcomings in the original document and about the on-site audit of the enterprise.
- Pay off accrued arrears and penalties before submitting an updated declaration, which was submitted after the deadline, but before paying the tax. The on-site check did not find any errors.
A fine for an updated VAT return may be imposed if the tax amount in the original report does not coincide with the updated one (20% of the difference), as well as when it is submitted after taxes have been paid to the budget.
Is it possible to reduce the amount of the fine?
The legislation of the Russian Federation provides for the possibility of reducing the amount of the fine for a VAT return for its failure to submit or late submission. The taxpayer must submit an explanatory note to the Federal Tax Service with a detailed explanation of the reasons for the delay in the document. The paper is filled out in free form.
Having studied the text of the note, tax specialists draw a conclusion about the importance of the reasons specified in it. If the reasons are considered sufficiently compelling, the fine may be reduced or cancelled. That is, late submission does not always threaten the imposition of penalties on the taxpayer. But to confirm the information specified in the explanatory note, it must be accompanied by accompanying documents that will prove the importance of the grounds for the delay.
If the declaration is not filed with zero VAT
Sometimes enterprises have a situation where the tax amount in their VAT reporting is zero. Should a company pay a fine for a zero VAT return if it is not filed? It is impossible to answer this question unequivocally. The Ministry of Finance believes that a minimum amount of 1,000 rubles should be paid for an overdue or unsubmitted declaration. Some officials are pushing for the same approach. Others believe that if no amount is paid to the budget, then, accordingly, there is no need to apply penalties.
But it’s still better to submit all required reports to the tax authorities on time. It must be remembered that in addition to imposing sanctions, the tax service has the right to block the debtor’s access to his current accounts.
Extenuating circumstances
If the taxpayer has any extenuating circumstances to explain why the document was delayed, this may help reduce the amount of the recovery. In paragraph 1 of Art. 112 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation spells out the grounds for a more loyal attitude of the Federal Tax Service towards the taxpayer:
- the offense was committed in connection with difficult family or personal circumstances;
- the violation occurred under threatening influence or coercion, as well as due to material or official slavery;
- the individual facing a fine for violating the law is in a difficult financial situation;
- other circumstances recognized by the court or the Federal Tax Service as mitigating.
During the court hearing, all circumstances that the tax service has already analyzed for pre-trial appeal are considered. The defaulter must declare all mitigating circumstances in court, regardless of whether the Federal Tax Service took them into account when imposing penalties or not. In court, the amount of recovery can be reduced again.
***
Failure to submit or late submission of a VAT return is recognized by tax legislation as an offense and entails the imposition of penalties on the culprit. The fine is 5% of the amount of the overdue tax debt for each overdue month, but cannot be less than 1,000 rubles. The law provides for the possibility of reducing the amount of the fine or canceling it due to the presence of mitigating circumstances. If the violator does not submit a declaration within 10 days after the deadline, the tax authorities have the right to block his current account until the situation is corrected.
The Tax Code stipulates very strict deadlines for filing declarations for each of the taxes prescribed for payment by a particular company or individual entrepreneur. Their violation leads to a number of negative consequences. Moreover, this fully applies to cases when we are talking about delays in the zero report.
How does prosecution work?
The procedure for imposing punishment for tax offenses is provided for by the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This procedure consists of the following steps:
- upon the absence of a declaration within the period established by law, a tax violation report is drawn up;
- a copy of the act is handed over or sent to the payer, who has the right to present his objections regarding the identified violation;
- based on the results of consideration of the act, a decision is made by the tax authority - this document records all the circumstances of the violation, as well as the absence of grounds for exemption from punishment;
- the imposition of a sanction occurs by issuing a resolution - in this document, an official of the Federal Tax Service will indicate the exact amount of the fine that the violator will be required to pay.
To calculate the fine, Article 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is applied. The size of the sanction will be 5% per month of the amount of tax payable for the reporting period.
When assigning a fine, it must be taken into account that its amount cannot exceed 30% of the amount of tax payable under the declaration, but cannot be less than 1000 rubles.
Formally, when imposing a fine for late filing of a zero declaration, similar rules apply. Although the amount of tax payable for the reporting period is zero, the Federal Tax Service specialists impose the minimum possible sanction - 1000 rubles. Judicial practice does not have a clear position on the legality of such a fine. Many courts indicate that due to the absence of an object of taxation, it is unacceptable to apply the general rules for imposing penalties.
If you disagree with being held accountable, the payer can file a complaint with a senior official of the Federal Tax Service, and then with the court. When a complaint is considered by higher authorities, the decision to impose a fine may be canceled completely, or the amount of the sanction may be reduced.
Even if the court agrees with the taxpayer’s position, the head of the enterprise will be held liable for late submission of the declaration form. In this case, the punishment will follow according to the norms of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, and the sanctions include a fine in the amount of 300 to 500 rubles, or a warning.
In practice, a written warning is issued for the first violation, and a fine will be imposed for repeated delays.
A fine is imposed on a manager according to the rules of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. This means that the fact of a violation must be documented in the form of a procedural protocol. The consideration of the case is within the competence of officials of the Federal Tax Service, and the head of the enterprise has the right to file objections to the claims presented.
https://youtu.be/dMxsQF-R7QI
Late with zero report
At the same time, the penalty for delaying a zero declaration is not tied to the amount of tax paid on this report. It is logical that zero reports would then not be filed at all, since any percentage of the zero amount is also zero. Therefore, the legislation provides for a minimum amount of such sanctions - 1000 rubles, which firms or individual entrepreneurs will be required to pay, regardless of how low the calculation base turns out to be.
The principle for calculating this fine is also the same for all reports, that is, the fine for failure to submit a zero VAT return or sanctions for late filing with the Federal Tax Service, for example, calculations for insurance premiums will be the same.
By the way, until 2020, fines for reports on pension contributions not submitted to the Pension Fund on time were calculated using the same principles. The fine for late submission of the zero RSV-1 (the form that was used until the end of 2020) was 1000 rubles, but if the report included the amount of contributions payable, then the delay also cost the contribution payer 5% of this amount per month with a maximum limit of 30 %.
If, based on the results of the declaration, you have no tax to pay
If you did not file a “zero return” on time (a return in which deductions fully covered your income and you do not have to pay tax), then:
- the tax authorities will require you to provide a tax return (particularly to confirm that you actually have no tax due)
- You face a fine of 1000 rubles (Article 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Example: in 2020 Lapin A.K. bought a car worth 400 thousand rubles, in 2020 he sold it for 300 thousand rubles. Since he did not receive income (the sale is less than the purchase) and he still has the documents for the purchase, he does not have to pay tax.
Penalty for late submission of VAT reports
The VAT return must be submitted by the 25th day of the month following the previous quarter (clause 5 of Article 174, Article 163 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the company (IP) is late in submitting the declaration, then it may be held liable.
Companies and individual entrepreneurs - VAT payers or tax agents - must submit a VAT return to the tax authorities (clause 5 of Article 174, subclause 1 of clause 5 of Article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 2 of the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ -7-3/558).
The VAT return must be submitted to the tax office at the place of registration of the parent organization (clause 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Declarations should not be submitted to the tax authorities at the location of the company's separate divisions. This is explained by the fact that VAT relates entirely to federal budget revenues (clause 5 of article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, article 50 of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation).
The VAT return must be submitted by the 25th day of the month following the previous quarter (clause 5 of Article 174, Article 163 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the company (IP) is late in submitting the declaration, then it may be held liable.
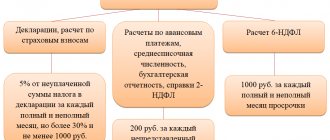
Firstly, the organization may be fined. The penalty amount will be 5% of the tax that is not paid on time. A fine will be charged for each month of delay, regardless of whether it is full or not. In this case, the fine should not be more than 30% of the amount of tax not paid on time and less than 1000 rubles (Article 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the taxpayer has mitigating circumstances, the fine may be reduced (clause 1 of Article 112, clause 3 of Article 114 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Secondly, a company official may be held liable. He may be given a warning or a fine. The fine will be from 300 to 500 rubles (Article 15.5, Part 3 of Article 23.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Finally, if a company has not submitted a VAT return 10 business days after the deadline, the Federal Tax Service may decide to block its current account (clause 2 of Article 76 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Report on time through Kontur.Extern. Three months - free!
Send a request
Questions and answers
- We have not submitted our VAT return, and more than 7 months have passed. What fine will we already have to pay?
Answer: the amount of the fine depends on the amount of VAT indicated in the declaration. It is worth remembering that a fine in the amount of 5 percent of the tax amount not paid within the deadline established by the legislation on taxes and fees, subject to payment (additional payment) on the basis of this declaration, for each full or partial month from the day established for its submission, but not more than 30 percent of the specified amount and not less than 1,000 rubles
We have discovered an error in your tax return and are willing to correct it to avoid a penalty. How can I do that?
Answer: In accordance with Art. 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a taxpayer is exempt from liability if an updated tax return was submitted before the moment when the taxpayer learned that the tax authority had discovered the fact of non-reflection or incomplete reflection of information in the tax return, as well as errors leading to an understatement of the amount of tax payable, or the appointment of a visiting tax audit.
Penalty for late submission of VAT returns
The amount of the fine for late submission of a VAT return, as well as the fine for failure to submit a VAT return, is calculated according to general rules. These rules are contained in paragraph 1 of Art. 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. According to them, the amount of the fine is determined based on 5% of the amount of tax payable for each month (incomplete or full) from the day assigned for submitting the declaration. The amount of the fine cannot exceed 30% of the specified amount and cannot be less than 1000 rubles.
Read more about liability for failure to submit a declaration and questions arising regarding it.
A fine for an updated VAT return can be avoided if:
- submit an update before the end of the deadline for submitting the initial declaration, i.e. on time (clause 2 of Article 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- the clarification is submitted after the deadline for submitting the initial report, but before the deadline for paying the tax, and the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate did not identify errors in the initial declaration or did not have time to inform the taxpayer about the appointment of an on-site tax audit (clause 3 of Article 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- before the submission of the clarification, submitted after the deadline for filing the declaration and paying the tax, the arrears and penalties were paid, and the on-site inspection carried out before the submission of the clarification did not reveal any errors (clause 4 of Article 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The question often arises: if a situation with late submission of a VAT return arises in relation to a report with a zero amount payable, is the minimum fine for an unsubmitted VAT return in the amount of 1,000 rubles charged in this case? There is no single answer to this question.
Failure to submit a declaration
Officials take the position that a taxpayer cannot be exempt from a fine for failure to report VAT, even if the tax amount is calculated and paid on time. This rightly equates to a fine for late submission of reports. This point of view is also shared by the courts.
For a declaration that does not have the amount of tax payable, it is impossible to calculate the penalty using the percentage method, but it must be imposed. Some judicial practices still oblige you to pay a minimum penalty equal to 1000 rubles.
There is also a completely different position on the issue of late submission of the declaration. According to many courts, which refer to the provisions of Article 119 of the Tax Code, the amount of the penalty should be calculated taking into account the tax amount payable. Based on this, there is no single fixed fine, and liability will depend directly on tax liability.
In this case, if a declaration submitted at the wrong time results in a zero amount of tax payable, the penalty for ignoring the deadlines will also be zero.
Penalty for failure to submit a return with a missing tax amount payable
The position of officials is that a taxpayer is not exempt from a fine for failure to submit a VAT return, even if it does not indicate the amount of tax payable and there is no arrears. The fine for such a violation is provided for in Art. 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 22, 2014 No. SA-4-7/16692, Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 23, 2011 No. 03-02-08/121 and October 27, 2009 No. 03-07-11/270, Federal Tax Service of Russia on Moscow dated March 16, 2009 No. 20-14/4/ [email protected] ). Accordingly, this fully applies to the fine for late submission of a VAT return with a missing amount for payment.
The opinion of officials is mostly supported by the courts (resolutions of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation “On some issues arising when arbitration courts apply part one of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation” dated July 30, 2013 No. 57, the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated June 8, 2010 No. 418/10 in the case No. A68-5747/2009, Arbitration Court of the North Caucasus District dated 04.29.2016 No. F08-2313/2016 in case No. A32-42102/2014, FAS West Siberian District dated 02.16.2012 in case No. A03-7357/2011 ( By ruling of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 31, 2012 No. VAS-7486/12, the transfer of this case to the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation, FAS North-Western District dated January 25, 2011, in case No. A26-5027/2010, FAS West Siberian District dated September 7, 2010, was refused. in case No. A75-9192/2009).
Since it is not possible to calculate the fine for a VAT declaration based on a report that does not have an amount payable, but it must be applied, in this case the amount of the fine for late submission of the declaration is considered equal to the minimum penalty - 1000 rubles. (decrees of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Central District dated March 23, 2012 in case No. A35-6471/2011, FAS Volga-Vyatka District dated February 15, 2010 in case No. A31-7500/2009, FAS Northwestern District dated February 25, 2009 in case No. A56- 28215/2007, FAS East Siberian District dated February 28, 2007 No. A19-20250/06-52-F02-674/07-S1 in case No. A19-20250/06-52).
Read about the situations in which it is possible to reduce the amount of sanctions in the following materials:
- “Mitigating circumstances will help reduce the fine by more than half”;
- “Is missing the deadline for filing a return for the first time a mitigating circumstance?”
Violation of the procedure and deadlines for submitting the declaration. Calculation of the fine
If the procedure and reporting deadlines specified above are not followed, including complete failure to provide reporting, the company will incur tax liability in the form of a fine, as well as administrative and even criminal liability.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
If, based on the results of the declaration, you have tax to pay
If, based on the results of the declaration, you have tax to pay, but you have not filed a declaration, then:
- According to Article 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (“Failure to submit a tax return”), you face a fine of 5% of the tax amount for each month of delay (starting from May 1), but not more than 30% of the total amount
- If you have not filed a declaration and also have not paid the tax by July 15, then you face a fine of 20% of the tax amount under Article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (“Non-payment or incomplete payment of tax amounts (fees)”). It is important to note here that this penalty can only be applied if the tax office has discovered non-payment of tax. If, before notifying the tax authority, you discovered it yourself, paid the tax and penalties, then the tax authority does not have the right to apply this fine to you. Note: this same article of the tax code may entail a fine of 40% of the tax amount (instead of 20%) if the failure to pay was committed intentionally. However, in practice, it will be quite difficult to prove the intentionality of non-payment to the tax authority. Please note that this fine can only be issued if the tax authority itself has discovered that you have not filed a return. If you filed a declaration and paid the tax and penalties before he sent you a notice, he has no right to issue a fine for concealing income.
- If you did not file a declaration and also did not pay the tax by July 15, then you will also have to pay an income tax penalty in the amount of 1/300 of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for each overdue day (after July 15)
- If you had to pay tax in the amount of more than 600 thousand rubles. (for example, you sold an apartment received as an inheritance for 5 million rubles), but did not file a declaration and did not pay the tax before July 15, then you may also fall under Article 198 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation (Tax evasion and (or ) fees from an individual)
Example: in 2020 Muromtsev A.I. inherited an apartment and immediately sold it for 3 million rubles. The amount of tax that Muromtsev had to pay upon sale: 3 million rubles. x 13% = 390 thousand rubles. Muromtsev did not know that he had to file a return with the tax authority and pay income tax, and, accordingly, did nothing.
At the end of July 2020, Muromtsev received a notification from the tax office that he must declare the sale of the apartment.
If Muromtsev immediately after receiving the notification files a declaration and pays tax (with penalties), then he only faces a fine of 5% of the tax for each late month after filing the declaration: 3 months (May, June, July) x 5% x 390 thousand .rub. = 58,500 rub.
If Muromtsev does not submit a declaration, then the tax authority will also have the right to hold him accountable under Article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and collect an additional fine of 20% of the tax amount (78 thousand rubles)
Penalty for incorrect reporting format
If tax reporting is submitted in an incorrect format, liability is provided for this in accordance with Art. 119.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The fine is 200 rubles. for each case of non-transfer of reporting.
At the same time, there is a possibility that the reporting will not be accepted even if the company complies with all the rules for its presentation. The fact is that due to technical failures in telecommunication data transmission systems, reporting may also not reach the tax office. If declarations are submitted at the very last moment, there is a risk that the company will be fined for being late.
You can challenge such a decision of the tax inspectorate through the court. However, this may take a long time. In addition, it will be necessary to provide evidence that the taxpayer did not submit reports precisely because of a technical failure in the system.
Penalty for non-payment and late transfer of VAT
You will be fined if VAT is not paid due to an understatement of the tax base, incorrect calculation of the tax amount or your other illegal actions (inaction) (clause 1 of Article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The fine for non-payment of VAT does not apply if:
- you correctly calculated the amount of tax and indicated it in the declaration, but did not pay it to the budget (clause 19 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 30, 2013 N 57);
- you have an overpayment of VAT for previous quarters, its amount is equal to or greater than the arrears and this overpayment is not offset against your other debts (clause 20 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 30, 2013 N 57).
Despite the fine issued, you will also have to pay arrears and penalties (clause 5 of Article 108 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Responsibility for understating the tax base for VAT
Understating the tax base for VAT may entail such types of liability as gross violation of accounting rules (Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) or non-payment of tax (Article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The fine for gross violation of the rules for accounting for income, expenses or taxable items is 20% of the amount of tax debt, but not less than 40,000 rubles. (clause 3 of article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
A gross violation of the rules for accounting for income, expenses or taxable items includes the following situations (Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- you late or incorrectly reflected business transactions in accounting and (or) tax accounting and reporting. Such mistakes may result in a fine if you make them more than once during a calendar year;
- you do not have primary documents, invoices, accounting or tax registers.
The fine for non-payment of VAT due to an understatement of the tax base will be 20% of the amount of arrears or 40% if the tax is not paid intentionally (clauses 1, 3 of Article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For example, such an underestimation may be due to an arithmetic error.
If the tax base for VAT is understated, you cannot simultaneously fine under Art. 120, and under Art. 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 2 of Article 108 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Determination of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated January 18, 2001 N 6-O).
Penalties are also charged for arrears (Clause 1, Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It does not matter, according to Art. 120 or Art. 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, you are fined.
Penalties for late payment of VAT begin to accrue from the day following the established tax payment date (Clause 3, Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For example, if the 3rd VAT payment for the third quarter of 2020 was not made, then from December 26, 2015, penalties begin to accrue.
- the amount of tax that was not received into the budget on time;
- period of delay;
- refinancing rate in effect during the period of delay.
Penalties can be calculated using ours and transferred to the budget yourself. Or you can wait until the tax authorities send you a demand for payment. However, if you are submitting a VAT update for the previous period, where the amount of tax payable has increased compared to the initial declaration, then before submitting the updated return you need to pay penalties and pay additional tax yourself. Otherwise, tax authorities will fine you for late payment of tax (clause 1, clause 4, article 81, clause 1, article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).