Do I need an invoice if a sole proprietor works without VAT?
In this case, the company will have to pay value added tax for the goods specified in it and generate a corresponding tax return.
Taxation systems Russian regulatory documents consider it possible for firms to use not only the general tax payment regime (OSN) to the treasury, but also simplified systems - UTII, simplified tax system, unified agricultural tax and the patent system. It is advisable to consider each of them in more detail. OSN is a general tax collection regime used in relation to those companies that, during registration or already in the course of their activities, did not express their desire to switch to special regimes. In case of OSN, the following obligatory payments must be made to the treasury: Of all these types of tax deductions, the most significant in terms of the volume of payments and the complexity of administration is VAT. That's why companies are looking to move to simplified systems. Important: This information subsequently goes into your tax return. All LLCs and individual entrepreneurs that, in the course of their activities, make mandatory payments to the treasury on the basis of the simplified tax system are not required to issue invoices (Article 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This is due to the fact that VAT is not charged on their transactions. Attention: At the same time, such agents issue invoices using the simplified tax system for goods that are imported into the customs territory of the Russian Federation (Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Thus, in general, entrepreneurs should not compile this important document, as well as maintain it after its presentation or receipt of the book of purchases and sales. However, in practice there are a number of specific cases that provide for different conditions.
Who issues Initially, you should indicate those companies on the simplified tax system (LLC and individual entrepreneurs) that are exempt from the obligation to prepare invoices. These include (Art.
Exception to the general rule
It is necessary to take into account that, in accordance with paragraphs. 1 clause 5 art.
It is necessary to take into account that, in accordance with paragraphs. 1 clause 5 art. 173 of the Tax Code, in a situation where an organization issues invoices to the buyer using the simplified tax system and allocates the amount of VAT, therefore, these amounts must be paid to the budget in full.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytaboutru
As an example: such a development of events can occur when a government contract for the supply of products is concluded between a customer in a contract system and a company that applies the simplified tax system. The contract price indicates the amount of VAT of 18% and it is stated that payment must be made by the government customer after he receives the acceptance certificate, invoice and invoice from the supplier.
We recommend that companies that participate in procurement for state and municipal needs, while working on a simplified basis, pay attention to the wording in the draft contract at the stage of analyzing the documentation. If it is not indicated that simplified contractors should consider value added tax, then it is necessary to send the customer a request for clarification with a requirement to adjust the provisions of the draft contract.
Can an individual entrepreneur issue invoices without VAT on USN?
Who may not issue an invoice? Depending on the taxation procedure chosen by the individual entrepreneur, payment of VAT may not be provided for; therefore, the question objectively arises about the need to issue invoices to those who are exempt from the “quitrent”. According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax is not paid:
- working in retail trade;
- employed in public catering;
- providing services for cash only;
- operating in the securities market and selling shares and bonds;
- selling goods to consumers who use preferential tax regimes.
Details are provided in Articles 168 and 169 of the Tax Code, which reflect nuances depending on the chosen taxation system. Under the special regime, tax is not paid, which is reflected in the reporting provided.
- home
- For individual entrepreneurs
Companies that apply such a special tax regime as the simplified tax system are exempt from VAT and do not have to issue invoices. However, some simplifiers still have to do this, for example, when they work with counterparties who present such terms of cooperation. We will discuss in detail how an invoice is issued under the simplified tax system with and without VAT in 2020 in the article.
Invoice under the simplified tax system All organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified system are not VAT payers, which means they do not need to issue an invoice. However, if certain situations arise, such a document will be needed. If you nevertheless decide to charge VAT, then here’s another piece of advice: in transactions where you are expected to receive an advance, do not issue an invoice for the advance, do it only after shipment. It is also better to discuss this situation in advance. Otherwise, you will have to report and pay VAT twice: first on the advance invoice, and then on the shipping invoice. The rule here is: you have issued a document with VAT, which means you have transferred the tax. As a result, you will pay the tax twice, since you will not be able to deduct VAT on the prepayment received, because you are not a VAT payer. And also, due to the fact that issuing a VAT invoice to a client is a non-standard situation before the simplification, it is recommended to store these documents for 4 years: the tax office may require them to present it during an audit. VAT Fourthly, the paper must be certified by the signature of the seller, and in the electronic form, also by the electronic signature. A sample of filling out an invoice is attached to this article. Is a zero provided? As mentioned earlier, when drawing up an individual entrepreneur or LLC on a simplified invoice, further preparation of a declaration and payment of VAT to the treasury is required. At the same time, many entrepreneurs are wondering whether it is possible to issue invoices on a voluntary basis, but not pay value added tax? It turned out that this situation is quite real. To do this, you just need to create and present a zero invoice to the buyer. A zero invoice is a document that requires the indication “Without VAT” in the column of the “Tax rate” table. It is important to remember that 0% should be entered in the table. Such a rate will still require the preparation of a declaration.
When do you need an invoice without VAT?
The obligation to issue an invoice without VAT exists only when the taxpayer-seller has an exemption from VAT under Art. 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 5 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Do not pay VAT under Art. 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, companies or individual entrepreneurs can do so if for three months in a row they receive revenue of no more than 2 million rubles. and do not sell excisable goods. Such taxpayers must:
- notify the Federal Tax Service of your intention not to pay VAT;
- apply the exemption for at least 12 consecutive calendar months, unless conditions for loss of the right to it are created;
- at the end of 12 calendar months, confirm to the Federal Tax Service that during this period they did not lose the right to exemption, and submit a notice to extend the right to exemption from VAT or waive this right.
In other cases, the taxpayer is not obliged, but has the right to create such a document if he considers it convenient (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 15, 2017 No. 03-07-09/8423). For example, if according to Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, not all goods sold are exempt from VAT, but only part of them, then issuing invoices without VAT may make sense in the following situations:
- If the shipment of goods not subject to VAT goes together with the shipment of goods subject to VAT, then the invoice will be common. Based on this invoice, the accounting program will automatically generate an invoice with the same total shipment amount. As a result, this significantly facilitates any data verification when working with documents and their selection at the request of the Federal Tax Service.
- If a separate shipment is entirely made up of goods that are not subject to taxation, then generating an invoice for it will make it possible to maintain compliance with the numbering of shipping documents (waybills, acts) and the invoices issued for them. As a result, for each shipment, easy-to-use sets of documents will be generated in which the numbers, dates and amounts match.
To find out how to be exempt from paying VAT, read the article “How to get an exemption from paying VAT in 2020?”
"Uproshchenets" acts as a tax agent for VAT
Note: A complete list of cases when a payer under the simplified tax system is a tax agent for VAT is given in
Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
.
"Uproshchenets" leases state or municipal property (except for cases when the lessor is a government agency), and the rental price includes VAT- On the day of settlements with the counterparty, calculate and withhold VAT from the income paid to the lessor.
- No later than the next five calendar days, write yourself one copy of the invoice marked “Rental of state (municipal) property.”
- Record the invoice in Part 1 of the Invoice Journal and in the Sales Ledger.
- Based on the results of the quarter in which you transferred the rent to the counterparty, you will pay VAT to the budget. In this case, you can pay the tax in equal installments no later than the 20th day of each of the three months following the expired quarter.
- Include in expenses the amount of tax after it has been paid (if you are using the object of taxation as income minus expenses).
- No later than the 20th day of the month following the quarter in which you transferred the rent to the counterparty, submit a VAT return by filling out the title page and section 2
- On the day of settlement with the lessor, charge VAT on top of the price specified in the contract (exception is the lease of natural objects, such as land, which is not subject to value added tax).
- No later than the next five calendar days, write yourself an invoice in one copy with the note “Rent of state (municipal) property” (if natural objects are rented, make a note in the invoice “Without VAT”).
- Record the invoice in Part 1 of the Invoice Journal and in the Sales Ledger.
- Based on the results of the quarter in which you transferred the rent to the counterparty, you will pay VAT to the budget.
- In this case, you can pay the tax in equal installments no later than the 20th day of each of the three months following the expired quarter.
- Include in expenses the amount of calculated tax after it has been paid (if you are using the object of taxation as income minus expenses).
- No later than the 20th day of the month following the quarter in which you transferred the rent, submit a VAT return by filling out the title page and section 2 (and when renting natural objects - section 7)
- On the day you pay money to a foreign counterparty, transfer VAT to the budget on the cost of goods (work, services).
- No later than the next five calendar days, write yourself one copy of the invoice marked “For a foreign person.”
- Record the invoice in Part 1 of the Invoice Journal and in the Sales Ledger.
- Include in expenses the amount of tax after it has been paid (if you apply the simplified tax system with the object of taxation being income minus expenses).
- No later than the 20th day of the month following the quarter in which you transferred VAT to the budget, submit a VAT return by filling out the title page and section 2
Note:
Invoices are issued
no later than five calendar days, counting from the day of shipment of the goods (performance of work, provision of services) or receipt of an advance towards the upcoming sale (clause 3
Art. 168 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
How to fill out an invoice without VAT
An invoice without VAT for 2020 is filled out according to the same rules that are established for issuing regular invoices containing VAT. These rules are contained in Section 2 of Appendix 1 to Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137 and have been significantly updated since October 1, 2017.
The procedure for preparing the header part of an invoice without VAT does not differ much from the usual one. The only difference is that in the columns of the main table intended to indicate the tax rate and its amount calculated at this rate, in the invoice drawn up without VAT, the entry “Without VAT” is made (subsections “g” and “h”) » clause 2 of section 2 of appendix 1 to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137). Moreover, the entry can be made in any way - on a computer, by hand, using a stamp.
Taking into account the above situations in which there is a need or requirement for issuing an invoice without VAT, there can be two options for issuing it:
- With the entry “Without VAT” in the corresponding columns, all lines of the main table of the invoice and the final part of column 8 for the line “Total payable” are drawn up. This will be the case if all objects of sale or the taxpayer are exempt from VAT.
- With the entry “Without VAT” in one or more rows of the table, despite the fact that in its other rows the VAT rate and amount are present. This can happen when objects that are not subject to VAT are sold simultaneously with goods subject to taxation by taxpayers working with VAT. The final tax amount (line “Total payable”) for this situation will be calculated without taking into account data on lines that contain the entry “Excluding VAT”.
Signatures on the invoice are also prepared in the usual manner. However, faxing them is not allowed.
In compliance with the above features, taxpayers exempt from VAT, if necessary, issue invoices for received advances.
Letter 03-07-11/19048 dated 03/27/2018
If an organization has switched to the simplified tax system, but in order for counterparties to receive a tax deduction, can it submit VAT? If yes, then how?
— when selling goods (works, services), in addition to the price (tariff), present the amount of VAT for payment to buyers in accordance with clause 1 of Art. 168 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
— issue invoices to buyers (clause 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 24, 2008 No. 3-1-11/239).
However, in cases where the counterparty agrees to work with an organization using the simplified tax system only if it receives invoices from it with the allocated amount of VAT, then the taxpayer using the simplified tax system has the right to issue such an invoice to the buyer. In this case, the taxpayer using the simplified tax system is obliged to pay to the budget the amount of tax indicated in this invoice (clause 5 of article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax payment is made at the end of each tax period based on the corresponding sales of goods (work, services) for the expired tax period no later than the 20th day of the month following the expired tax period (clause 4 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The tax period for VAT is a quarter (Article 163 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, the taxpayer using the simplified tax system who issued the invoice is obliged to submit a tax return to the tax authority at the place of his registration no later than the 20th day of the month following the expired tax period (Clause 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The tax return form and the procedure for filling it out were approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 15, 2009 No. 104n. According to clause
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpressru
3 of the specified Procedure, when issuing an invoice to the buyer with the allocation of the amount of VAT by organizations using the simplified tax system, such organizations submit a tax declaration as part of the title page and section 1 of the declaration. The remaining sections of the declaration do not need to be completed or submitted. In this case, in section 1 you only need to fill in lines 010 (OKATO code), 020 (KBK) and 030 (tax amount indicated in invoices issued during the tax period).
If a taxpayer using the simplified tax system has issued an invoice to the buyer with a allocated amount of VAT, then such an invoice is subject to registration in Part 1 of the Logbook of received and issued invoices. The invoice is recorded by the date of issue (that is, the date indicated on the invoice) in Part 1 of the Journal and in the Sales Book. The forms of the Journal of accounting of received and issued invoices and the Sales Book are approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137.
a) register invoices in the Accounting Journal and Sales Book during the quarter according to the date of issue;
b) submit a VAT return for the 2nd quarter no later than July 20. In the tax return on line 030 of section 1, you must indicate the amount of 18,000 rubles;
c) pay a tax of 18,000 rubles to the budget no later than July 20.
Note!
1. In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the moment of determining the tax base for VAT is the day of shipment (transfer) of goods (work, services), property rights. In this regard, the taxpayer under the simplified tax system has an obligation to calculate and pay tax in the tax period (quarter) in which he issued an invoice to the buyer, regardless of the receipt or non-receipt of payment from the buyer for the shipped goods (work, services).
2. A taxpayer using the simplified tax system who has issued an invoice with an allocated VAT amount does not have the right to tax deductions for purchased goods (works, services), since only VAT taxpayers who are such in accordance with the norms of tax legislation have the right to tax deductions.
Differences between the Federation Council if there is no taxation on products
To create a document, use the form approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137, with amendments dated August 19, 2017 No. 981, which came into force on October 1, 2017.
An invoice without VAT is issued on the same form and according to the same rules as an invoice with VAT. The only difference is that in columns 7 and 8, where the tax rate and amount are indicated, “Without VAT” must be written.
If all shipped products are exempt from tax, when registering the SF, in all lines in which the names are listed, in columns 7 and 8, you must indicate “Without VAT.” The same entry is made in the line “Total payable” in column 8. If in a sold batch one part of the product is subject to VAT, the other is not subject to tax, the entry “Without VAT” is entered only opposite the corresponding items.
The lines where taxable goods are listed indicate the rate and amount of VAT. In the “Total payable” field in column 8, enter the total tax amount, including only taxable items. Invoices for received advances are issued in compliance with the same rules.
For more information about what an invoice is and when it is used, read our article.
We give a robot vacuum cleaner when you subscribe to Simplified
Simplified companies that issue VAT invoices should not include this tax in their income. This procedure has been in effect since 2016. This amount is also not an expense, because it was returned to the budget in full.
If an organization using the simplified system, on its own initiative or at the request of a counterparty, issues an invoice with the allocated amount of VAT, it must be transferred to the budget (clause 5 of Article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And submit the VAT return in electronic form (clause 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The deadline is no later than the 25th day of the month following the quarter in which such an invoice was issued.
Is SF required if an organization operates without value added tax?
According to paragraph 3 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, VAT payers are required to issue an invoice. SF is not issued if you work as an individual entrepreneur or legal entity that is not a tax payer.
When should such a document be issued?
A taxpayer who is a seller of goods or a provider of services is obliged to issue an invoice without VAT only if he uses the right to exemption from VAT in accordance with Art. 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 5 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This right arises if a legal entity or individual entrepreneur:
- receives revenue of no more than 2 million rubles. for 3 consecutive months;
- does not sell excisable goods.
In other cases, is it possible for organizations that are not tax payers to issue tax invoices without VAT? According to the letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-07-09/8423 dated February 15, 2017, this is not necessary, but there is a right to this matter.
Read about who issues the invoice.
Use Cases
The preparation of such a document is provided if:
- Only part of the goods sold is exempt from tax (Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The company carries out transactions simultaneously with products subject to VAT and not subject to VAT. In this case, the accounting program will generate a general invoice and invoice for the entire batch of goods with the same total amount.
- If the entire batch of products sold is not subject to VAT, issuing an invoice along with invoices and acts makes it possible to create a convenient set of documents while maintaining the numbering.
Who fills out the form?
Only the seller of goods or the provider of services has the right to issue an SF. Thus, he documents the completion of the transaction.
Filling example
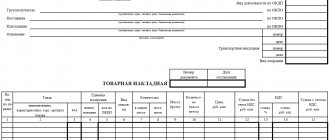
As of October 1, 2017, new requirements for the preparation of this document began to apply. The filling procedure is as follows:
- In line (1) we indicate the serial number and date of issue. For all types of SF there is a common numbering. They are recorded in chronological order (it is allowed to add a letter designation to the number). When making corrections, in line (1a) we indicate the number of the correction; when filling out for the first time, a dash is added.
- Lines (2), (2a), (2b) contain information about the seller:
- for legal entities, it is necessary to indicate the full or short name, detailed address as written in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, identification numbers (TIN/KPP);
for individual entrepreneurs, the full name, address as entered in the Unified State Register of Entrepreneurs, TIN and registration information are entered.
- If the shipper and the seller are represented by the same organization, in line (3) you must indicate “Same.” If the shipper is another company or person, enter the full or short name and address. We put a dash if the invoice relates to work or services.
- In line (5) you need to indicate the payment document number only if there is an advance payment; if there is no prepayment, then this item remains blank.
- Information about the buyer is entered in lines (6), (6a), (6b) similarly to (2), (2a), (2b). If the buyer and the consignee are represented by the same organization, in field (4) you need to put o. If the consignee is another organization, indicate its name and address. If the invoice is for work performed or services provided, a dash should be included.
- In line (7) select the name of the currency. Accounting programs automatically enter the digital code.
- Line (8) is for the government contract ID. For other contracts it is not necessary to fill it out.
- The following columns are filled in in the table:
- Column 1 contains the names of goods, works or services.
- Column 1a indicates the product code. This field concerns only deliveries to the countries of the Euro-Asian Economic Union.
- Units of measurement are entered in columns 2-2a in accordance with OKEI. If the invoice concerns work or services, dashes should be added.
- In column 3 we indicate the quantity or volume based on units of measurement. If 2-2a is not filled in, there will also be a dash here.
- In column 4 the price per unit is entered as it is given in the contract.
- The total cost of each item excluding tax is reflected in column 5. The final line will contain the total cost of the entire delivery.
- Column 6 is filled in only for excisable goods. Here you need to indicate the amount of excise tax included in the price. In other cases, the note “Without excise duty” is made.
- When registering a SF without tax, in fields 7 and 8 you need to make the entry “Without VAT”. If some items are subject to tax, the rate and amount are entered opposite them.
- Column 9 reflects the cost of goods, works or services including tax.
- Column 10 must contain the digital product code. Columns 10, 10a, 11 are filled in for goods produced outside the Russian Federation.
- Columns 5, 8 and 9 of the bottom line contain the totals.
In the Federation Council, it is allowed to indicate two addresses (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-07-09/85517 dated December 21, 2017). If the actual address, which differs from that recorded in the register, is recorded in the contract, it should be entered in an additional line.
Invoices without VAT are signed according to general rules. The paper form is certified by the signatures of the manager and chief accountant or authorized persons. If the document is issued by an individual entrepreneur, it must contain the personal signature of the individual entrepreneur or an authorized representative. You can find out more about the invoice for individual entrepreneurs.
Certification of an invoice with a facsimile signature is not acceptable (letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-07-09/49478 dated August 27, 2015). When exchanging documents electronically, a certificate of the electronic signature verification key is required (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated September 12, 2016 No. 03-03-06/2/53176, Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated May 19, 2016 No. SD-4-3/8904).
The invoice is certified only by one enhanced qualified electronic signature of the manager or authorized person. The electronic document does not require the signature of the chief accountant.
You can find out more about filling out an invoice.
From the video you will learn how to correctly fill out an invoice if the company is not a VAT payer:
Invoice under simplified tax system
All organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system are not VAT payers, which means they do not need to issue an invoice. However, if certain situations arise, such a document will be needed.
These include situations where “simplified” people pay VAT: (click to expand)
- Import of goods;
- Operations under a simple partnership agreement, or trust management of property and concession agreement;
- When a company performs the duties of a tax agent, for example, rents state or municipal property.
In all of the above situations, organizations are required to issue an invoice (
"Uproshchenets" fulfills the duties of a VAT payer
“Uproshchenets”, at the request of its buyer, issues an invoice with the VAT amount allocated in it no later than the 20th day of the month following the quarter in which the invoice was issued:- pay the accrued VAT to the budget in full;
- submit your VAT return by completing the title page and section 1
2. “Simpler” carries out operations under a property trust management agreement or a concession agreement on the territory of the Russian Federation and is, respectively, a trustee or concessionaire. Keep separate records of operations under the agreement and all other operations. At the same time, within the framework of the agreement, you need to behave as if you are a VAT payer, namely:
- issue invoices when selling goods (works, services) to customers;
- require sellers to provide invoices for purchases in your name;
- deduct input tax on purchases intended for VAT-taxable transactions;
- maintain a journal of invoices, a purchase book and a sales book;
- pay the calculated VAT on time according to the general rule in equal installments no later than the 20th day of each of the three months following the expired quarter;
- submit a VAT return no later than the 20th day of the month following the end of the quarter, with the obligatory completion of the title page and section 1
Invoice with o
You are not required to issue an invoice from the company using the simplified tax system. Only companies exempt from VAT put this mark. Organizations that are considered exempt from VAT are recognized in accordance with Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Companies that apply the simplified tax system do not qualify as such “exempt” payers, since they are not initially payers of this tax. Accordingly, there is no need to issue a “simplified” invoice marked “without VAT”.
Some counterparties still insist on an invoice. Such companies should keep in mind that they will not receive a deduction for “input” VAT on such an invoice. And why they continue to demand such invoices is not clear.
“Simplers” are not obliged to fulfill such a request. They have the right to explain to their counterparties that in order to post the purchased goods, documents such as an invoice for payment, an invoice and a statement will be sufficient. And if the counterparty continues to insist and it is impossible to convince him, then you can issue the required document. Please indicate that the purchase does not include VAT.
Such registration of an invoice will not entail obligations to pay tax, as well as the preparation and submission of a VAT return, since the tax will not be highlighted in the invoice (
Should a simplifier pay VAT if...
A simplifier does not have to pay VAT. The company can revoke an erroneous invoice if it sends a letter to the buyer requesting it. In this case, the company is not a VAT payer, since the requirements of paragraph 5 of Article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not met (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated December 29, 2009 No. F09-10483/09-S2). If the accountant has already registered an erroneous invoice in the sales book, then cancel the entry (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated April 30, 2015 No. BS-18-6 / [email protected] ).
There is no need to pay VAT or submit a return. Although the simplifier issued an invoice, he did not highlight the tax amount in this document. This means that the company does not become a VAT payer (clause 5 of Article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
You need to pay VAT to the budget. A universal transfer document with status 1 replaces two documents at once - a delivery note and an invoice. This means that the simplifier actually issued an invoice including tax. Therefore, pay VAT no later than the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter. Within the same period, submit your declaration to the tax office via the Internet (clause 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In the declaration, fill out the title page, sections 1 and 12. Transfer the entire amount of tax from the UTD to the declaration.
From 2020, strict standards for submitting VAT returns will be introduced. From January 1, 2020, in almost all cases, tax agents must submit VAT returns exclusively electronically - regardless of the number of employees.
Simplified tax agents on the simplified tax system - tax agents who issue and receive invoices when carrying out business activities in the interests of another person on the basis of intermediary agreements, from January 1, 2020, are required to submit a VAT return to the inspectorate only in electronic form (paragraph 3, paragraph 5 Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the simplified person does not issue invoices with allocated VAT, then he has no obligation to submit a VAT return - neither in paper nor in electronic form. And if a simplifier voluntarily issued a VAT invoice, then he must submit a VAT return. And only in electronic form from 2020!
If you issue an invoice with VAT
Some organizations, on their own initiative, may issue invoices, highlighting VAT. In this case, they are required to pay tax to the budget and also submit a VAT return to the Federal Tax Service. This must be done before the 25th day of the month following the quarter in which the document was issued. For example, a company issued an invoice using the simplified tax system on February 10, 2020; accordingly, it must submit a VAT return by April 25, 2020.
It is important to understand that issuing an invoice with allocated VAT does not give the simplifier the right to a tax deduction on purchased goods. Only VAT payers have the right to such a deduction, and organizations using the simplified tax system are not such.
>Issuing individual entrepreneur invoices using the simplified tax system
For entrepreneurs using the simplified system, the same requirements for issuing invoices apply as for organizations using the simplified tax system.
>Legislative framework
Legislative act
Invoices are required to be issued only by VAT payers, to which organizations applying the simplification do not belong (clause 2 of Article 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). That is, for an organization that has switched to the simplified tax system, the requirement to issue an invoice is not based on the law. For information on the consequences of exposure, see the material below.
The rationale for this position is given below in the materials of the Lawyer System and the GlavAccountant System.
Recommendation. What should an organization do on a simplified basis that has issued an invoice with allocated VAT?
“If, on its own initiative or at the request of a counterparty, an organization (including an autonomous institution) has issued a simplified invoice with an allocated amount of VAT, this amount will have to be transferred to the budget (clause 5 of Article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And not only in cases where the invoice was issued for the sale of goods (work, services), but also when the organization issued an invoice for the amount of the prepayment received. Simplified organizations do not have the right to deduct VAT from the prepayment received after shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services). This was stated in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 21, 2012 No. 03-07-07/53.*
No later than the 25th day of the month following the quarter in which the invoice with the allocated tax amount was issued, the simplified organization must draw up a VAT return in electronic form and submit it to the tax office via telecommunication channels (clause 5 of Art. 174 Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
An example of the calculation and payment of VAT by an organization in a simplified manner. After switching to the simplified system, the organization issues invoices to customers with the allocated tax amount
The Alpha organization carries out contract work. From January 1, 2020, Alpha switched to a simplified system, but continues to issue invoices under the agreement concluded with Proizvodstvennaya OJSC in 2014.
In March 2020, for the upcoming work, Alpha received from Master a 100 percent prepayment in the amount of 118,000 rubles. (including VAT – 18,000 rubles). An invoice was issued for the amount of the advance received with the tax amount allocated. On April 20, Alpha submitted an electronic VAT return for the first quarter of 2020 to the tax office. On the same day, VAT in the amount of 18,000 rubles. was transferred to the budget.
In May, the work under the contract was completed. On May 14, the parties signed an acceptance certificate, and Alpha issued an invoice for the cost of work performed in the amount of 118,000 rubles. (including VAT – 18,000 rubles). On July 20, Alpha filed a return for the second quarter of 2020 with the tax office. On the same day, VAT in the amount of 18,000 rubles. was transferred to the budget for the second time.
The provisions of paragraph 8 of Article 171 and paragraph 6 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation do not apply to organizations using the simplified tax system. Therefore, Alpha cannot deduct the amount of VAT paid to the budget from the prepayment received.
An exception to this rule are intermediaries who use simplification and act on their own behalf. When selling goods (works, services) under intermediary agreements, commission agents and agents acting on their own behalf are required to issue invoices to buyers with allocated VAT (clause 20 of section II of Appendix 5 to Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137) . They do not have the obligation to pay tax to the budget (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2010 No. 03-11-11/123). However, they must submit logs of invoices received and issued as part of intermediary activities to the tax office (clause 5.2 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Intermediaries who apply the simplification and sell goods (work, services) of foreign organizations that are not registered in Russia with tax authorities are recognized as tax agents for VAT. Consequently, they must transfer to the budget the amounts of tax withheld from the income of foreign organizations. In relation to these amounts, such intermediaries are required to submit VAT returns to the tax authorities. This follows from the provisions of paragraph 5 of Article 161, paragraph 5 of Article 346.11 and paragraph 2 of paragraph 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Situation: should an organization transfer VAT to the budget in a simplified manner if the buyer has allocated the tax amount in the payment order. The organization did not issue an invoice to the buyer
No, you shouldn't.
Organizations (including autonomous institutions) using the simplification are required to transfer VAT to the budget only in the following cases:
- import of goods (clause 2 of article 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- issuing invoices to the buyer with the allocation of the VAT amount (clause 5 of Article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- fulfillment of duties as a tax agent for VAT (clause 5 of Article 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the organization did not issue an invoice to the buyer, then there is no need to pay VAT. Even if the buyer indicated the tax amount on a separate line in the payment order. A similar point of view is reflected in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 18, 2014 No. 03-07-14/58618″.
How can a “simplified” accountant of expenses reflect “input” VAT in the Accounting Book?
The fact that the seller indicated the cost of the goods including VAT in the contract using the simplified tax system, and the buyer, when paying for the goods, indicated the amount of tax in the payment order, does not mean that the “simplified” person must pay VAT.
This obligation only arises if an invoice has been issued. The Russian Ministry of Finance recalled this in letter dated June 22, 2018 No. 03-07-11/42820. Buyers - “simplified” buyers with the object “income minus expenses”, who from October 1 entered into an agreement with sellers not to prepare invoices, will be able to take into account “input” VAT in expenses based on primary documents. Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 09/08/14 No. 03-11-06/2/44863.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytdevru
On October 1, 2014, a new version of subclause 1 of clause 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation came into force, which allows the seller not to issue an invoice if goods (work, services, property rights) are sold to counterparties who are not VAT payers or are exempt from the obligation to calculation and payment of VAT. In this case, a written agreement must be concluded between the seller and the buyer regarding the non-drafting of invoices.
According to tax legislation, payers of the simplified tax system with the object “income minus expenses” have the right to take into account the costs of paying taxes and fees (subclause 3, clause 2, article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, they are required to keep records of income and expenses in the Income and Expense Accounting Book (KUDiR) of organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified taxation system. Clause 2.5 of the Procedure for filling out the Accounting Book stipulates: in column 5 the taxpayer reflects the expenses specified in Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, when filling out the Income and Expense Accounting Book, the “simplified” person must indicate the VAT amount in column 5 as a separate line. All transactions recorded in this document must be confirmed by primary documents. Such documents include payment documents, cash receipts or strict reporting forms with a separate line for the VAT amount. The absence of invoices (subject to the written consent of the parties to not prepare them) is not an obstacle to writing off VAT in expenses.
1. A fixed asset or intangible asset has been acquired, the cost of which includes VAT, and in accordance with paragraph. 9 clause 3 art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 8 PBU 6/01 “Accounting for fixed assets”, clause 8 PBU 14/2007 “Accounting for intangible assets” VAT is included in the initial cost of the object. Therefore, do not reflect the VAT amount in a separate line in the Income and Expense Accounting Book (KUDiR)
2. Goods, materials, work or services were purchased, the price of which includes VAT. According to Sub. 8 clause 1 art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, show in the Income and Expense Book the “input” VAT on the specified purchases separately from the purchase price
Should I issue an invoice using the simplified tax system?
Our organization uses a simplified taxation system (STS), but our clients ask, in addition to invoices, to issue them invoices for products sold and services provided. Do we need to issue an invoice to clients, if yes, then in how many copies should we issue an invoice?
In accordance with clause 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the obligation to issue invoices is provided only for VAT payers. The Methodological Recommendations on VAT (approved by Order of the Ministry of Taxes of Russia dated December 20, 2000 N BG-3-03/447) say that organizations and entrepreneurs for those types of activities for which they do not pay VAT should not issue invoices to buyers - invoices (an exception is made only in the case when organizations act as tax agents).
In accordance with Article 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, organizations using the simplified taxation system (STS) are not recognized as VAT payers, with the exception of VAT payable in accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation when importing goods into the customs territory of the Russian Federation.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for the issuance by taxpayers using the simplified tax system of invoices indicating in a certain column “Without tax (VAT)”. In general, an invoice serves only to deduct VAT. According to an invoice indicating in a certain column “Excluding tax (VAT)”, the buyer has nothing to offset, therefore the so-called A “zero” invoice is essentially useless to him and a burdensome waste of paper and time for your organization.
Thus, you do not have the obligation to issue invoices, and your clients, but only those who have qualified accountants, do not need invoices from organizations applying a special tax regime - a simplified tax system.
Features of the design of the invoice
346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In the book of income and expenses, input tax must be shown as a separate line*. The cost of raw materials and supplies is included in expenses as these values are written off for production (subclause 1, clause 2, article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Accordingly, according to the Ministry of Finance, VAT on material costs is also taken into account in expenses at the time of release of raw materials and materials into production.
It turns out that the moment of recognition of these expenses is the same. This means that the option of including input VAT in expenses - separately or in the cost of raw materials and materials - does not matter. Therefore, in the book of accounting for income and expenses, VAT can not be highlighted as a separate line, but can be written off together with the cost of material assets.
An UNP expert found out in the department of special tax regimes of the Russian Ministry of Finance that this procedure for accounting for input VAT can also be applied when writing off the paid cost of purchased goods. “VAT on purchased goods can be taken into account as part of their cost. Accordingly, when they are implemented, the tax will be included in expenses,” the ministry confirmed to us.
The Code allows you to write off immediately. Note that the Tax Code allows you to write off input VAT immediately after payment. This is a general condition for recognizing expenses (clause 2 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The paid cost of raw materials and materials, as well as the paid cost of purchased goods, are taken into account as expenses according to special rules.
They are recognized accordingly as they are released into production or sold (subclauses 1, 2, clause 2, Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). There are no conditions for including VAT in expenses other than payment. However, if a company writes off input tax as expenses before accounting for material costs or the cost of purchased goods, this may cause claims from the tax authorities.
For those companies that do not want to argue with tax authorities, the Ministry of Finance offers a simplified option for accounting for input VAT - in the cost of material assets. It will allow you to avoid difficulties with calculating the amount of VAT to be written off if the input tax rates are different for the raw materials used to produce products.
The Ministry of Finance clarified when a supplier under the simplified taxation system is obliged to pay VAT to the budget, as well as when it is necessary to draw up an invoice to close a government contract.
03/27/2018 The Ministry of Finance in letter No. 03-07-11/19048, answering the question when a company that applies the simplified tax system should issue an invoice for the sale of goods and services, indicated that by virtue of clause 2 of Art. 346.11 of Chapter 26.2 of the Tax Code (TC), companies that operate under the simplified tax system are not recognized as payers of value added tax. At the same time, according to paragraph 3 of Art. 169 of Chapter 21 of the Tax Code, taxpayers of value added tax are required to draw up invoices.
Organizations that apply the simplified taxation system do not have to issue invoices when selling goods.