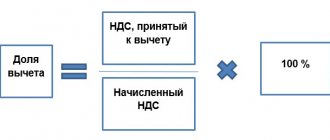
Accounting and legal services
Moreover, if it does not contain all the mandatory details provided for in paragraph 5 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, then the deduction cannot be applied (clause We recommend reading: Commentary on Article 169 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation,
2 Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It’s good if Belarusian suppliers, to please the Russian buyer, issue invoices that meet Russian requirements.
And if not? At the request of our readers, we reviewed the invoices sent to the editor from Belarus.
https://youtu.be/9GjcU47Ict8
VAT on imports from Belarus to Russia: nuances 2020 - 2020
On January 1 of the year, the Agreement dated from this date came into force, relations with Belarus in the field of trade in goods became similar to relations with other foreign countries, that is, Russian goods exported from Russia to Belarus are subject to VAT in Russia at a zero rate, and when importing Belarusian goods into In Russia, the buyer is required to pay VAT to the Russian budget. At the same time p.
How to pay VAT when importing from countries participating in the Customs Union. Moreover, if the supplier from Belarus does not provide you with any documents related to VAT calculations, then you may have problems with deducting the amount of VAT that was paid on the imported goods.
You can get acquainted with the peculiarities of calculating VAT in certain situations on our forum. For example, in this thread you can find out whether transport costs when importing goods from Belarus are included in the VAT tax base. Import from Belarus to Russia: what is submitted to the tax office. Application for import when importing from the Republic of Belarus.
Belarusian invoice
Preparation of corrected and additional electronic invoices. A corrected electronic invoice is drawn up in cases where the payer cancels the indicators of a previously issued invoice. In this case, the corrected electronic invoice will indicate new indicators. When issuing an invoice by an individual entrepreneur, the invoice is signed by the individual entrepreneur or another person authorized by a power of attorney on behalf of the individual entrepreneur, indicating the details of the state registration certificate of this individual entrepreneur. The tax is calculated based on the contract value of the goods, which the supplier also indicates in the shipping invoice documents. Agreement and payment in foreign currency. Article: Settlements with a supplier from Belarus On the one hand, this state of affairs allows us to conclude that the Belarusian invoice is not the only document that gives the right to offset VAT on goods. On the other hand, the majority of our inspectors, referring to the same paragraph. What should an accountant do in this situation? You can proceed in one of two ways.
Purchasing Belarusian goods for - from
For “import” VAT, the tax period is a month, not a quarter.
At the stage of marking the application, difficulties begin. Disagreements arise due to the determination of the ruble value of imported goods, when the Belarusian supplier indicates prices in yuan in the invoices. e. or a currency other than rubles.
But accountants also read the next paragraph of the Protocol on Goods and see that “at the cost of purchased.
The buyer has the right to deduct the VAT paid, but subject to certain conditions. From clause 1 of article 2 of the Protocol of December 11, 2009
We recommend reading: Luxury car tax 2020 calculation calculator
“On the procedure for collecting indirect taxes and the mechanism for monitoring their payment when exporting and importing goods in the Customs Union”
It follows that the payer of “import” VAT is the owner of the goods, who is recognized as the person who has the right of ownership of the goods or the transfer to whom the rights of ownership of the goods is provided for by the agreement (contract).
What is an invoice?
Currently, primary accounting documents can be conditionally classified into 3 groups:
1) document forms with a certain degree of protection (strict reporting forms);
2) primary accounting documents, information about the forms of which is not subject to inclusion in the electronic data bank of document forms and documents with a certain degree of protection and printed materials, but their forms are included in the list of documents approved by Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus dated March 24, 2011 No. 360;
3) other primary accounting documents.
The documents of the third group include, incl. and invoices. Their production, registration, sale, acquisition, use, storage and accounting are not regulated by special legislation. At the same time, when preparing such documents, one must comply with the general requirements for primary accounting documents in accordance with Decree of the President of the Republic of Belarus dated March 15, 2011 No. 114 “On some issues of the use of primary accounting documents” (hereinafter referred to as Decree No. 114).
The invoice is sent to the buyer. Based on it, the latter can make an advance payment (payment). The invoice indicates the purchased goods (work, services) with the total quantity, cost, and, if necessary, VAT.
The invoice is used for settlements and is the basis for the release of goods
To transfer funds in the form of advance payment for goods (work, services) or rent and utility payments, an invoice of form No. 868 or a free-form invoice, developed taking into account the specifics of the organization’s activities, can be used.
The invoice used for settlements is the primary accounting document. It is one of the accompanying documents issued upon delivery of goods (clause 34 of the Regulations on the acceptance of goods by quantity and quality, approved by Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus dated September 3, 2008 No. 1290).
Delivery of goods is carried out on the basis of a contract. In this case, the contract is considered concluded even when only the name of the goods, its quantity and price have been agreed upon between the parties, or the procedure for determining them has been established (clause 3 of the Regulations on the supply of goods in the Republic of Belarus, approved by Resolution of the Cabinet of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus dated 07/08/1996 No. 444, s taking into account changes dated October 11, 2011 No. 1537). When concluding an agreement by drawing up one document, it must, as a rule, contain the following details:
– exact and full name (name), as well as information about the legal address of the parties to the agreement;
– date of conclusion of the contract;
– place of conclusion of the contract;
– proper handwritten signatures of the parties or persons authorized to sign the agreement on their behalf.
Thus, the invoice is part of the contract concluded by the parties, namely an offer.
For reference: an offer is an offer to one or more persons to enter into an agreement on predetermined conditions.
The invoice may specify a specific payment period that is not fixed in the contract. After all, the buyer is obliged to pay for the goods immediately before or after the seller transfers the goods to him, unless otherwise provided by law (clause 1 of article 456 of the Civil Code of the Republic of Belarus).
Situation. Issue of goods based on an invoice
The organization's accountant is presented with TTN-1 for accounting for receipt of inventory items, in which an invoice is indicated in the column “Base for release”.
Is such a reason allowed?
An invoice can be the basis for the release of valuables along with a contract, application and other document (clause 6 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Economic Council of the Republic of Belarus dated December 5, 2012 No. 12 “On some issues of consideration of cases arising from contracts for the supply of goods”).
Filling out the line “Base for leave” in TTN-1 or in TTN-2 is mandatory, since the primary accounting documents must indicate the content and basis for the business transaction (subclause 1.4, clause 1 of Decree No. 114).
How to issue an invoice
We will consider the procedure for issuing an invoice based on the procedure established in the regulatory documents of a number of departments.
Let us turn to the Instructions on the procedure for selling goods from retail trade networks to legal entities and individual entrepreneurs, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Trade of the Republic of Belarus dated 06/08/2005 No. 22 (hereinafter referred to as Instruction No. 22). When releasing goods for which payment is made by bank transfer, the seller issues an invoice in 3 copies, one of which is transferred to the buyer, 2 copies remain with the seller. The invoice provided to the buyer is the basis for payment for the purchased values. One copy of the document issued by the seller is transferred to the warehouse and serves as the basis for the formation of the quantity of goods to be released after payment by the buyer.
The validity period of the invoice is set by the seller, but not less than 5 working days from the date of its issue. Execution of other documents in place of an invoice is not permitted.
In addition, issued invoices must be registered daily in the register of issued invoices for the sale of goods by bank transfer to legal entities and individual entrepreneurs. The form of such a register is as follows:
Please note that the invoice must be signed by the head and chief accountant of the supplier organization or another person (persons) authorized to do so by order (instruction) of the head of the organization or a power of attorney on behalf of the organization. Signatures must have a decryption (initials and surname). The invoice is certified by the seal or stamp of the seller.
In a number of cases, you can use the invoice form (housing and communal services), approved by order of the Ministry of Housing and Communal Services of the Republic of Belarus dated 01.06.2011 No. 74 “On approval of forms of accounting documents in organizations of the housing and communal services system” (Appendix 2). An invoice (housing and communal services) is an act of services rendered (work performed). The transfer of an invoice (housing and communal services) by the seller to the buyer can be done both on paper and in electronic form.
How long to keep an invoice
Invoices should be kept for 1 year after the tax authorities have carried out an audit of compliance with tax legislation, subject to the completion of the audit carried out within the framework of departmental control (clause 218 of the List of standard documents of the National Archival Fund of the Republic of Belarus, generated in the course of the activities of state bodies, other organizations and individual entrepreneurs , indicating storage periods, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Justice of the Republic of Belarus dated May 24, 2012 No. 140). Let us remind you that a similar retention period is established for powers of attorney.
VAT without invoice
By virtue of Art.
172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when importing goods into Russia from the territory of Belarus, the basis for deducting VAT paid upon import of goods is a contract, transport documents confirming the movement from the territory of Belarus to the territory of Russia, as well as documents confirming the actual payment of VAT. When importing Belarusian goods into the territory of the Russian Federation, an invoice is not issued by Belarusian sellers and is not the basis for deducting VAT paid by Russian buyers when importing Belarusian goods into the territory of the Russian Federation.
VAT on export of goods
Thus, the invoice for shipped goods may not contain the following:
- line (5) - number and date of the payment order - is filled in only in case of payment for goods in advance (clause 4, clause 5, article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- Column 1a - product type code - is filled in only when exporting to the EAEU. The codes are taken from the Commodity Code for Foreign Economic Activity of the EAEU (clause a(1) clause 2 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 01/09/2018 No. 03-07-08/16);
- columns 2, 2a, 3 and 4 - unit of measurement, price and quantity of goods - are filled in only if the contract for the supply of goods provides for a price per unit of goods, and this unit is in sections 1 or 2 of the OKEI (paragraphs "b" - "d » clause 2 of the Rules for filling out an invoice);
- columns 10, 10a and 11 - information about the country of origin of goods and the customs declaration - are filled out only when selling imported goods (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 26, 2018 No. 03-07-08/4259).
Thus, in letter dated January 26, 2018 No. 03-07-08/4259, specialists of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation explained the following: the seller of imported goods is responsible only for the compliance of information about the country of production and the customs declaration number in invoices with the information contained in the invoices received by him -invoices and shipping documents.
Thus, columns 10, 10a, 11 are filled in only when selling imported goods. In this case, these columns indicate a digital code, a short name of the country of origin of the goods according to OKSM and the registration number of the customs declaration under which the shipped goods were imported into the territory of the Russian Federation (clauses “k”, “l” of paragraph 2 of the Rules, letter from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 02/22/2018 No. 03-07-08/11477). Accordingly, dashes are placed in columns 10-11:
- if Russian-made goods are shipped;
- if the invoice of the supplier from whom the organization purchased the imported goods does not contain the necessary information.
We also note that the norms of paragraphs. “k” and “l” of clause 2 of the Rules, indicating additional information in invoices is not expressly prohibited.
Therefore, in this situation, it is best for a Russian supplier shipping goods to the Republic of Belarus to meet the Belarusian buyer halfway and indicate in the invoice for goods produced in the Russian Federation, in column 10 - the digital code of the Russian Federation 643 and in column 10a - the name of the country of origin of the goods: Russian Federation. Since the Belarusian buyer is an importer of these goods and, accordingly, the issue of documenting the deduction of VAT on imported goods remains relevant and important for him.