Calculation of product costs in Excel
It has already been noted that each company will have its own list of costing items. But you can substitute any data into the existing framework, change the formulas if necessary, and get a ready-made calculation.
For an example of costing and selling price calculation, let's take data from the following table:
Costing calculation scheme:
- We calculate returnable waste from the costs of raw materials and materials (we take the specified percentage).
- To determine the additional salary, we take into account the following data: if the basic salary is more than 200 thousand rubles, then the additional salary is equal to 10% of the basic salary; less than 200 – 15%.
- Salary accruals - 30% of the amount of basic and additional wages (the additional 10%, which was introduced in 2020 for an annual income of more than 600 thousand rubles, is not taken into account here).
- Equipment maintenance costs are 5% of the basic salary.
- General expenses – 9% of the average basic salary.
- General production – 18% of (25% OZP + 75% DZP). WZP – basic salary, DZP – additional salary.
- Production cost = the sum of expenses for the maintenance of equipment, raw materials and materials, fuel and energy, components, spare parts and additional parts, accruals for salary, general production and general expenses minus returnable waste.
- Non-production costs (costs) – 3% of production costs.
- Total cost = production cost + production costs.
- We calculate the manufacturer's profit as a percentage of the total cost.
- Wholesale price = full cost + manufacturer's profit.
- VAT is calculated based on the wholesale price.
- Selling wholesale price = manufacturer's wholesale price + indirect taxes (VAT in the example).
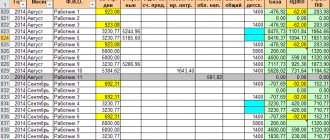
Based on the diagram, we will enter the data and formulas for calculation into an Excel spreadsheet.
Explanations for the calculation of some costing items:
- Returnable waste – =B2*12.54% (percentage taken from the first table).
- Additional salary – =IF(B6
The same principle is used to calculate the cost of products B and C.
You can make Excel take the initial data for calculation immediately in the appropriate tables.
Calculation of estimates for services example | dtpstory.ru
The share of labor costs in total costs in 2015 increased by 1% compared to 2014, and in 2020 compared to 2020 by 0.11%.
The share of costs for social contributions in 2014 was 1.29%, in 2020 - 1.38%, in 2020 - 1.26%. The share of contributions for social needs in 2020 compared to 2014 increased by 0.09%, in 2020 compared to 2020 decreased by 0.12%.
Depreciation in the total cost of the enterprise is 6.55% in 2014, 7.38% in 2020, 6.24% in 2020. Other costs in the total costs amount to 56.85% in 2014, 55.81% in 2015, and 57.82% in 2020.
The share of other costs in total costs in 2020 compared to 2014 decreased by 1.04%, and in 2020 compared to 2020 increased by 2.01%.
Important
Submitting SZV-M for the founding director: the Pension Fund has made its decision The Pension Fund has finally put an end to the debate about the need to submit the SZV-M form in relation to the director-sole founder.
So, for such persons you need to take both SZV-M and SZV-STAZH! Attention
But be careful: the procedure for paying for “children’s” sick leave remains the same!
So who has the right to work without a cash register until the middle of next year?
The concept of product cost
Cost is the current expense of an organization expressed in monetary terms, which is aimed at the production and sale of goods.
Cost is an economic category that reflects the production and economic activities of an enterprise and shows the amount of financial resources spent on the production and sale of products. Cost affects the profit of the enterprise, and the lower it is, the greater the profitability.
Additional agreement to the service contract: legal significance
In accordance with the general requirements of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), each agreement must define its subject, i.e. the main content of the mutual obligations of the parties established as a result of the conclusion of a particular transaction (clause 1 of Article 432 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) . The general norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation are supplemented by special ones relating to the subject of a particular type of agreement.
When fixing the subject of emerging legal relations in an agreement, the parties cannot always describe it in sufficient detail, including due to the specifics of such legal relations. For these purposes, appendices or additional agreements to the service agreement can be used - see below for a sample.
For example, when the same contract involves repeated performance of the same service, but in different volumes or according to a specific schedule (such cases are discussed in the articles “Specification for a product supply agreement (sample)”, “Vehicle charter agreement (sample)” " and etc.).
In addition, using the annex to the service contract - we have provided a sample below - or an additional agreement to the contract, you can:
- change the duration of the contract (for example, extend it);
- introduce new conditions into the main agreement;
- provide qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the services provided and their results, etc.
Read more Neighbors listen to music loudly during the day, what should I do?
Cost formula
The cost price includes the sum of all expenses for the production of goods. To calculate using the cost formula, you need to sum up all the costs that were incurred during the production (sales) process:
The cost formula is as follows:
Full = Spr + Rreal
Here Full is the full cost,
Spr – production cost of a product, calculated by the sum of production costs (labor, depreciation, material costs, etc.),
Rreal – costs of selling products (storage, packaging, advertising, etc.).
If you need to determine the cost of a unit of production, then the formula for the cost of goods produced is calculated by simple calculation.
Costing for accounting purposes
For accounting, calculations are prepared based on the company's current accounting policies. For large customers (especially budgetary organizations) working strictly according to accounting rules and current regulations, estimates are prepared using the base-index method. To do this, each process is priced at the base tariffs of 2001, adjusted for the current price index.
This technique is used by construction and repair organizations that construct and maintain capital construction projects. For these purposes, local, detailed, simplified and object estimates are drawn up. An experienced estimator in any construction company is worth his weight in gold; an ordinary accountant cannot replace him. To simplify its work, special budgeting programs are used that are focused on a specific industry. They are already loaded and regularly updated with tariffs and indices.
Cost structure
The cost formula includes the following components:
- Raw materials needed in the production process;
- Calculation of energy resources (various types of fuel).
- Expenses for equipment and machinery that are necessary for the operation of the enterprise.
- Salaries of company employees, including payment of all payments and taxes.
- General production expenses (office rent, advertising, etc.).
- Expenses for depreciation of fixed assets.
- Administrative expenses, etc.
Compilation instructions and video
Calculations are carried out in accordance with a pre-developed methodology or instructions that describe the calculation algorithm. For example, payment for educational services depends on the number of hours, as well as the degree of qualification of the teacher, which is necessarily prescribed in the relevant methodological recommendations.
Essentially, costing is a detailed description of the costs associated with providing a “unit” of service, which can be measured in various ways:
- An hourly rate is how educational services are measured.
- By describing the result - for example, a cosmetic renovation, indicating the area of the room.
- Using other indicators - transporting cargo over a distance of 45 km.
The cost structure will directly depend on the type of work performed. Therefore, the calculation algorithm will have its own differences. Using the example of calculations related to transport services, the instructions will look like this.
First, the cost of the service is estimated based on wage costs:
- drivers;
- auxiliary workers servicing transport;
- managers, employees and other specialists working at the enterprise.
Next, deductions related to social contributions, as well as expenses for servicing cars and other equipment are taken into account:
- current and major repairs;
- fuels and lubricants;
- depreciation of fixed assets;
- seasonal expenses (oil, tires, etc.).
Then tax payments are taken into account and other indicators are determined:
- Profit according to plan.
- VAT.
- Tariff with and without VAT.
Usually drawn up with a description of a specific service: for example, transporting bricks may cost more than transporting lighter items (hay, pillows, etc.).
The simpler the service looks in terms of its implementation, the simpler the cost estimate itself will be. For example, if we are talking about performances by artists, dance or singing groups, expenses are associated with the payment of salaries, social contributions, as well as the provision of appropriate premises for rent.
When producing goods, it is almost always necessary to take into account not only the cost of producing a unit of product, but also possible losses at different stages of the cycle.
Cost estimates are also prepared for repair work. Typically, the volume of such services is measured by the area of the room and other indicators (for example, slope length, ceiling area). The estimate shows costs per unit of work, indicates a specific type of activity (for example, leveling walls, painting, installing a suspended ceiling, and much more), and then gives the cost for each work and the total amount.
Thus, the calculation algorithm looks like this:
- The unit of service is determined - exactly what volume of work is supposed to be implemented in this case (renovation of 1 apartment, transportation of 5 tons of cargo over a distance of 100 km, provision of tutoring services for 10 training hours, etc.).
- A detailed list of all expenses is specified at their cost.
- They determine the tariff with and without VAT.
- Indicate the planned profit.
Video instructions for compiling
https://youtu.be/VLGnbmkUYTs
The document is usually signed by the chief accountant and the company seal is placed on it. Management is under no obligation to disclose such information to its clients. The legislation also does not provide any guidance as to whether cost estimates need to be attached to contracts with counterparties, so the decision can be made at your own discretion.
Features of cost calculation
There are several different methods for calculating the cost of a product. They can be applied according to the nature of the work, services or products produced. There are two types of product costs:
- Complete, including all expenses of the enterprise.
- Trimmed cost, which refers to the unit cost of variable costs.
Actual and standard costs are calculated based on the expenses incurred by the company. At the same time, standard cost helps control costs for various resources and, in the event of deviations from the norm, timely provision of all necessary measures. The actual cost per unit of output can be determined after calculating all costs.
What is the cost of goods and services
In an economic sense, determining the cost of services or products means the monetary expression of the costs spent in the process of providing services (production of products or performance of individual works). Any enterprise that provides services or manufactures products faces the need to calculate this value.
The value of this indicator is expressed in cost equivalent: that is, the cost of products, works, services is the sum of the resources expended by the company. These are costs such as labor, materials and raw materials, depreciation, sales, transportation and storage of products, fiscal expenses, etc. The cost of work and services indicator is used by entities for the purpose of competent pricing; financial analysis of activities; determining the level of rational use of resources; identifying savings reserves, etc.
Based on the accrual methods, the cost differs by type - planned (determined according to given standards), calculated (calculated on the basis of technical and economic calculations) and reporting (calculated in comparison with actual costs). Depending on the final goal, there are 2 classification systems - by expenditure items or by economic elements. Taking into account the stages of calculations, there is a full, workshop cost or production cost. To calculate the cost of products, works, and services, several basic methods are used. Let's take a closer look at them.
The total cost of production is determined...
Types of cost
Costs are of the following types:
- Full (average) cost, implying the entire set of expenses, including commercial costs for the production of products and the purchase of equipment. The costs of creating a business are divided into periods during which they are repaid. Gradually, in equal parts, they are added to general production costs.
- Marginal cost, which is directly dependent on the quantity of products produced and shows the cost of each additional unit of goods. This indicator reflects the effectiveness of subsequent expansion of production.
Also, the cost can be:
- Shop cost, which includes the totality of costs of all departments of the enterprise that are aimed at producing new products;
- Production cost, which makes up the workshop cost, including target and general expenses.
- The full cost price, which includes not only production costs, but also expenses incurred by the company in the process of selling goods.
- General business (indirect) cost, consisting of business management expenses and not directly related to the production process.
What is included in the cost - how not to miss anything
Conventionally, all resources used in the provision of services can be divided into the following types:
- Related to the remuneration of a specialist - the so-called “direct”. These are the amounts that an employee receives for his work activities. The hairdresser - for the haircut, the driver - for transportation, the system administrator - for maintaining the local network.
- Related to the purchase of materials or raw materials used within the service. For example, for a hairdresser - hair care products, for a driver - gasoline, for a system administrator - fees for the Internet and licensed software.
- Payment for fixed assets of production - depreciation charges for wear and tear of equipment, maintenance and repair of vehicles, rental of real estate and payment of utilities.
- Remuneration of administrative and management personnel is the cost of work of those specialists who do not directly provide services, but manage the process of their provision or perform another management function.
- Tax and other mandatory contributions to the budget and insurance funds. Any officially registered organization is required to pay taxes, as well as make transfers of funds to medical and social insurance funds. From an economic point of view, it makes more sense to include these costs in the cost price.
- Other expenses. For example, an advertising campaign, payment for communications and travel for employees, etc.
For example, an entrepreneur provides comprehensive services for holding birthdays and anniversaries. For each event, he attracts a host, musicians and a photographer - payment for their labor, as well as tax deductions (if the employees work officially) will be considered direct expenses.
This also includes the cost of renting the premises where the events take place and paying for utilities. But in addition to direct and fixed costs, there will be indirect non-fixed ones, namely:
salary of the organizer himself, decoration of the hall with flowers and balloons.
Calculation of cost of services - sample
¦The costs of shunting work associated with ¦ ¦¦ ¦supply/removal on/from the track of non-public ¦ ¦¦ ¦use ¦ ¦+—-+———————————————+——— —-+¦ Total ¦ ¦+—————————————————+————-+¦ Profitability ¦ ¦+————————————— ————+————-+¦ Price excluding VAT ¦ ¦+——————————————————+————-+¦ VAT ¦ ¦+—— ———————————————+————-+¦ Price including VAT ¦ ¦L—————————————————+—— ———
DECODING
costs of materials included in the cost estimate
current uncoupling repairs of freight cars
——T——————T———T———-T———-T———¦ N ¦ Name ¦ Unit ¦ Price per ¦ Norm ¦ Amount ¦¦ p/p ¦ materials, ¦ measurement¦ unit of ¦ consumption ¦ costs, ¦¦ ¦ spare parts ¦ ¦ excluding VAT, ¦ by 1 ¦ rub. ¦¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ rub. ¦car, units¦ ¦+—-+——————+———+———-+———-+———+¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦L—-+——— ———+———+———-+———-+———-
Head of department _______________ Full name
Chief accountant _______________ Full name
When pricing, various factors are taken into account. The cost of services plays an important role. It includes all the costs of the contractor, including those not related to the work.
The cost of a service is the sum of the contractor’s expenses incurred during its implementation. The indicator also includes other costs without which the work would not be possible. For example, depreciation of equipment. In the future, the indicator is used to assess the financial condition, performance results and make important decisions for the company.
In what form are estimate documents drawn up?
For different types of work, different forms of drawing up financial documents are used. Let us pay attention to an example of an estimate for design and survey work (design and survey work), which is drawn up in accordance with form 3p. It is an annex to the contract between the parties, the cost here is determined by labor costs. Form 3p estimate is used to calculate the cost of research, design, environmental engineering, engineering and survey work.
Often such estimates consist of two tables. In the first, the level of labor costs is determined, and in the second, the cost of the work performed is calculated. The cost of work is proportional to the time spent on all processes and the remuneration of designers. The second table may also include other costs, such as depreciation, freight and travel costs, and material costs.
For construction work, other forms of estimates are provided:
- Local is prepared for a specific type of work performed; it takes into account the costs of individual sections of construction or repair work.
- The object one is formed within the framework of one object, combining all local estimates and their calculations related to this object. Its adjustment is made based on the data from the working documentation.
- The summary estimate is based on site estimates and characterizes the total final cost of constructing a structure or building.
If it is not possible to draw up an accurate estimate due to the fact that there is no complete clarity on the specification of the materials used or changes will still be made to the project, then local and site-specific estimates can be drawn up. Also often used are estimates drawn up in the form KS-2 (act of acceptance of work performed) and KS-3 (certificate of costs and value of work performed).
Non-profit organizations, including budget ones, are required by law to prepare an annual budget for income and expenses.
Calculation of product costs with an example of calculation in Excel
Fixed costs do not depend on the volume of work, variable costs do the opposite.
What costs will be included depends on the service. The video shows an example of how to calculate the cost of a manicure in a studio:
Material assets may be needed in your work. There are two options for how to proceed: add everything together (relevant if the amount of expenses is small) or take it out of the estimate and charge the client separately for materials. The second option is applicable if the choice is strictly individual and must be made by the customer. For example, it is advisable to include the cost of paper for preparing documents in the cost of accounting services. However, when carrying out repairs, you cannot buy building materials to your liking without agreement with the client, so this expense item is always included outside the scope of the service. But you can include help with selection.
The most obvious way to present costs is in the form of a diagram:
Rice. 1. Determining the cost of IT services
How to make a cost estimate for construction work
https://youtu.be/odYLkkS9czQ
Before drawing up any estimate, cost estimate, specification of materials and other calculations for completed or planned construction and installation work (CEM), it is necessary to consider several basic points in the preparation of project documentation: 1) Basic algorithm for calculating the volume of construction and repair work based on design drawings; 2) Differences between local estimates and calculations; 3) Use of specifications of work and materials when calculating the cost of expenses; 4) Specifics of developing a bill of works and materials; 5) The importance of professional measurements to determine the correct parameters of perimeter, area, mass and other natural indicators. In its usual sense, a quantity survey is a cost estimate prepared to determine the expected costs of construction before it begins.
Calculation example
To calculate the cost of a service, you need to determine what is included in it. For example, to install a ready-made online store based on a standard template, you need:
- register a domain name;
- order hosting;
- buy licenses for the necessary software products (engine, template, plugins, modules, etc.);
- install and configure.
Of all this, the client himself pays the cost of the domain, hosting, license at the price of the suppliers. The installation company may add additional costs for ordering services from suppliers or adding them to the setup price. One employee can cope with such work, so only his time is taken into account in the calculation. However, if you take the development of an online store from scratch and on a turnkey basis, it requires the involvement of different specialists.
| Variables | Permanent |
1. Salary:
2. Postage expenses |
|
How much can the cost of developing an online store cost? It is better to calculate the costs of attracting specialists based on the time they spend on work.
| Employee | Salary per month with taxes and fees | Number of hours per month* | Number of hours per project | Specialist costs |
| Project manager | 164,25 | |||
| Designer | 164,25 | |||
| Designer | 164,25 | |||
| layout designer | 164,25 | |||
| Programmer | 164,25 | |||
| Tester | 164,25 | |||
| Content manager | 164,25 | |||
| Total |
* Based on the 2020 production calendar with a 40-hour work week.
To calculate the full cost of the project, you need to take into account all other expenses. For example, if there is one specialist on staff, the team can develop 5 online stores per month, if there is not much distraction from other work.
| View | Based on 1 unit. | Number of units | Total |
| Variables | |||
| Salaries for specialists | |||
| Sending documents | |||
| Permanent | |||
| Office rental | |||
| Communal payments | |||
| Outsourced accounting | |||
| Administrative expenses | |||
| Advertising and Marketing | |||
| Equipment depreciation | |||
| Total: | |||
Rice. 2. Company spending structure
Thus, in monthly terms, the company’s costs for developing the IM will be 139,120 rubles. Accordingly, the cost of one service is 27,824 rubles.
Questions and answers on the topic
No questions have been asked about the material yet, you have the opportunity to be the first to do so
Download construction cost estimate
- calculation Page 1 of 2 In this table you can see what it is and how it is compiled and download the calculation of labor costs and wages. Costing is a document that displays the work that needs to be performed during construction, its volume, time standard and price.
Based on these indicators, labor intensity and wages are calculated. Builders most often use only a few areas, for example, excavation work, installation of metal structures, carpentry, carpentry, roofing, finishing, insulation, flooring. From them you can find out the composition of the unit that is optimally suited for performing a particular task.Having decided on the work that needs to be done to erect the structure, we begin to search for the corresponding work in the enir.
Example and sample
Let's consider an example of determining the cost of providing eyelash extension services.
So, for this you need special artificial hairs. You need to calculate the prices of eyelashes per person.
If the cost of 1 pack of hairs is about 4,000 rubles, there are 4,000 units in a box, and 100 pieces are needed per client, then you can calculate the cost of the hairs:
It is simply impossible to increase the volume and length of eyelashes without using special glue. For this reason, there is a need to calculate the volume of this material.
Glue volume 5 ml, price – 3500 rubles. About 0.2 ml must be spent on each cell. Using this information it is easy to make a calculation:
For this kind of procedure there is no need to purchase any additional equipment, since you can only get by with a brush.
A set of brushes – 500 rubles, quantity per package – 50 pieces.
Additionally, you should use medical adhesive tape, the cost of which is 400 rubles, length - 6 meters. Moreover, only 10 centimeters are needed per client.
Next, you need to sum up all the costs received and get the cost .
The example considered is rightfully considered simple, since it did not take into account the cost of renting any premises, tax fees, wages to employees, possible payment for utilities, and so on. This calculation can only be reliable if the entrepreneur works for himself and the services themselves are provided at home.
Moreover, there is no need for any advertising campaigns and so on.
The methodology for calculating the cost of work or services is presented in this video.
Procedure for compilation
To correctly calculate the cost of services, you need to follow the methodological instructions for the industry. In addition, the initial competent distribution of expenses among accounting accounts is very important. This will allow you to accurately assess the cost of services and perform pricing. And such posting is made to the accounts on the basis of primary documents, which make it possible to determine the production and non-production nature of the expenses.
Costing example
As for the costing process itself, it includes two main stages :
- Initially, you should decide on direct and indirect costs. This is most conveniently done using accounting data, where the entire grouping of expenses according to this criterion occurs in accounting accounts;
- Then, based on the adopted calculation method, costs are distributed. This is very important, especially if several types of services are provided. Here it will be necessary to determine the amounts of general business, general production and commercial expenses, which are either subject to distribution between types of services in relation to some attribute (for example, salaries of main workers), or to be attributed without distribution in full to revenue.