Home / Other
Back
Published: 04/03/2020
Reading time: 26 min
0
1
- 1 If the agent does the registration on behalf of the principal?
- 2 The reseller acted instead of the principal
- 3 “Utility” for the tenant
- 4 Consolidated invoice for investment construction
- 5 Reissued documents by the commission agent on behalf of the principal
- 6 "Excluded" position
- 7 Purchasing goods for several buyers
- 8 Introductory information
- 9 The intermediary simultaneously sells the consignor’s goods and his own goods
- 10 Re-issuance of payment papers by the reseller
- 11 Conclusion
- 12 The intermediary purchases goods for the principal (principal)
What if the agent does the registration on behalf of the principal?
The most common situation in which over-invoicing is possible occurs during intermediary transactions.
In practice, two situations are possible.
- Goods (work, services) under a commission agreement (agency agreement) are sold by the principal (principal).
In this case, the principal issues an invoice to the commission agent, and he, in turn, reissues it to the buyer.
According to para. 2 clause 24 of the Rules for maintaining logs of received invoices..., approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 2, 2000 N 914 (hereinafter referred to as the Rules), principals (principals) selling goods, works, services under a commission agreement (agency agreement) from the name of the commission agent (agent), invoices are registered in the sales book, which reflect the indicators of the invoices issued by the commission agent (agent) to the buyer. This is one of the grounds for deducting VAT.
- Goods (work, services) under a commission agreement (agency agreement) are purchased by the principal (principal).
In this case, the seller issues an invoice in the name of the intermediary, who purchases these goods and, in turn, on his own behalf, reissues the invoice in the name of the principal.
In this invoice, the intermediary reflects the figures of the invoice received from the seller. In this case, the invoice received from the seller is not reflected in the commission agent's purchase book. In the case of the acquisition of goods (works, services) by a commission agent for the principal at the expense of the principal, when issuing invoices to the principal, a procedure similar to the procedure provided for in paragraph. 2 clause 24 of the Rules.
The purchase of goods, works or services through a commission agent should not deprive the organization (principal) of the right to deduct VAT, which the commission agent paid to the supplier at the expense of the principal's funds.
Both invoices (both those received from the supplier and those issued in the name of the principal) are not registered by the commission agent in the purchase book and the sales book. The Ministry of Finance of Russia explains this in Letter dated November 14, 2006 N 03-04-09/20.
If communication means allow and the capabilities of the parties to the contract are combined, then accounting documentation is exchanged between them in electronic form. The procedure for organizing the transfer of payment papers in electronic form is specified in clause 1 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Documentation is exchanged through telecommunication channels.
Important! According to the commission agreement, the procedure for conducting electronic exchange of invoices is carried out in a certain order.
The commission agent (seller) performs the following functions for organizing electronic document management:
- Formation of payment papers.
- Assignment of an enhanced digital signature.
- Direction through the electronic invoice operator to the buyer's address.
- Waiting for confirmation of receipt of the document.
The commission agreement provides for the need for the commission agent to store payment papers in hard and electronic form. Read about the features of registering and storing invoices here.
Subject to acting on behalf of the principal, the intermediary concludes a corresponding agreement. Under these transactions, obligations and rights arise for the principal. Documentation is drawn up on behalf of or in the name of the principal, principal.
Invoices issued by the agent are drawn up from the principal to the buyer, and the corresponding payment papers are issued to the principal. In general, transactions are carried out with the participation of a reseller, but from the documentary side he does not appear in the process of purchasing and selling services or goods.
VAT accounting for tax agent in 1s
What is an agency agreement? Often, enterprises use the services of intermediaries when selling their products (goods, works or services) or to purchase property, order work or services. All intermediary operations are formalized by appropriate agreements, which can be of three types: orders, commissions and agency agreements. In this article we will consider agency agreements. The legal features of agency agreements are established by Chapter 52 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Article 1005 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation defines an agency agreement as follows: “Under an agency agreement, one party (the agent) undertakes, for a fee, to perform legal and other actions on behalf of the other party (the principal) on its own behalf, but at the expense of the principal, or on behalf and at the expense of the principal. In 1C Accounting, with this work scheme, the following operations are performed:
- Reflection of the fact of provision of services through the preparation and execution of an act confirming the completion of certain works.
- Registration of the invoice provided to the customer.
- Preparation of a report to the principal indicating the amount of remuneration, including VAT, and providing it to the addressee.
- Next, you need to reflect the fact of deduction of remuneration and issue an invoice for agency services.
- The final operation will be the recording in the journal of an invoice from the principal for the work performed by him for the customer.
Registration in the 1C solution Accounting for the provision of services to the customer Reflection in the program of the fact of the provision of services by the agent is carried out by a sales document (act or invoice), which reflects the sale of goods, services or work performed under the commission agreement. The most important thing is to correctly draw up an agreement with an agent in the program. The type of contract must be - With a commission agent (agent) for purchase. The document Write-off from the current account and the result of its execution are shown in Fig. 1.
Figure 1. The principal's funds arrived in the agent's current account. When a bank statement is received, the agent must create a document Receipt to current account with the transaction type Payment from buyer. The agent also needs to correctly draw up the contract with the principal.
The type of contract must be - With the principal (principal) for the purchase. The contract can specify the option for calculating the agency fee. In our case, this is 10% of the purchase amount. Settlement account 76.09 “Other settlements with various debtors and creditors.” The document Receipt to the current account is shown in Fig.
2. Figure 2.
The reseller acted instead of the principal
An intermediary firm or intermediary is an organization or person that represents an intermediate link between consumers and producers of services, works, and goods. These companies promote trade turnover by acting as a catalyst for market relations by solving and identifying problems.
Trade intermediary institutions are those firms that do not depend on the consumer or manufacturer of goods, either economically or legally. The reseller's profit can be accrued in the form of a bonus for the services he provides or as revenue from the difference between the purchase price and the selling price.
Trade and intermediary organizations are classified:
- According to the work performed:
- universal;
- specialized;
- By the nature of operations and type of subordination:
- dependent (from production);
- formally independent;
- independent (full or narrow range of services).
"Communal apartment" for the tenant
A similar situation arises with regard to utilities, which tenants are required to reimburse to landlords in accordance with the terms of the lease agreement.
Let us recall that the Russian Ministry of Finance issued Letter No. 03-04-15/52 dated March 3, 2006. The general meaning of his explanations is that the lessor cannot be a service provider, since he himself receives them from the energy supply organization. Therefore, the supply of electricity under the lease agreement will not be considered a sale.
In Letter dated March 24, 2007 N 03-07-15/39, the Ministry of Finance confirmed its point of view. In it, experts directly stated that if the tenant compensates with a separate amount for utilities (as well as communication services, security, cleaning services), which are not included in the rental price, then the landlord does not issue an invoice for these services, since there is no sale. And taking into account paragraph 1 of Art.
The saddest thing is that some courts take the side of the tax authorities (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga-Vyatka District of May 15, 2006 N A43-33504/2005-31-1070).
Some organizations resort to agency agreements. However, we recommend that they do not indicate that the principal (tenant) purchases utilities through an agent (lessor), since the lessor, even if acting as an agent, cannot, in principle, provide utilities (see above).
"4. When purchasing goods (work, services) through a trustee (agent), the basis for the principal (principal) to deduct value added tax on the purchased goods (work, services) is an invoice issued by the seller in the name of the principal (principal).
- If the invoice is issued by the seller in the name of the commission agent (agent), then the basis for the principal (principal) to accept value added tax for deduction is the invoice received from the intermediary. An invoice is issued by the intermediary to the principal, the principal, reflecting the indicators from the invoice issued by the seller to the intermediary. Both invoices from the intermediary are not recorded in the purchase book and the sales book.”
Therefore, many organizations take a different route. Indicate that the landlord, as an agent, makes settlements with the energy supply organization (and does not purchase electricity for the tenant). In this case, the tax authorities may allow the tenant a deduction based on reissued invoices, but, unfortunately, we cannot guarantee the complete absence of tax risks for the tenant. In this situation, we can only offer options that would minimize tax risks.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Sberbank safe deposit box lease agreement sample
By the way, pay attention to the Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Central District dated November 25, 2005 N A09-5523/05-12. In this document, the judges concluded that the part of the lease agreement that provides for the tenant to reimburse the landlord for 30% of the cost of utilities consumed by the landlord cannot be classified as a commission transaction.
But in this dispute, the lease agreement, apparently, only contained the tenant’s obligation to compensate the landlord’s utility bills, which cannot be considered agency terms. And if the organization had drawn up a separate agency agreement or included agency language in the lease agreement, then perhaps the court would have ruled in its favor.
Sales report to the consignor. 2020 sample
A commission agent's sales report is a document intended to record goods sold by a commission agent. This report is provided to the principal upon execution of the order (Article 999 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Usually it contains information about what transactions the commission agent made and under what conditions. The report may also provide information on expenses incurred in carrying out the assignment. Therefore, the presence of this document facilitates the process of proving the commission agent’s expenses and protects the principal from reimbursement of unreasonably incurred expenses.
Do you want to forget about the problems with preparing the commission agent’s report form and other accounting documents once and for all? MyWarehouse has developed a convenient system for filling out and printing all necessary documents.
But that is not all! The MoySklad online service will help you establish effective accounting in a wholesale company and retail store, including accounting for goods transferred or accepted for sale. To work with it, you only need a computer with a printer and Internet access.
And you will be able to conduct your business, including creating commission agent reports, at any time of the day and from anywhere, wherever you are.
More than 700,000 companies already print invoices, invoices and other documents in the MyWarehouse service Start using
Commissioner's report form
According to Article 999 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the form of the commission agent’s report does not imply certain requirements. Therefore, the report can be of any form, but it must contain all the mandatory details of the primary document, namely:
- Title of the document;
- date of compilation;
- the name of the organization that drew up the document, that is, the commission agent;
- information about the work performed and its results in monetary and in kind terms;
- a list of persons responsible for this (indicating positions) and their personal signatures.
Since there are no specific requirements for the form of the commission agent’s report, in order to avoid disputes in the commission agreement, it is recommended to agree on the condition that it must be drawn up in the form of a document signed by the parties to the commission agreement.
An example of the wording of such a condition: “Upon execution of a commission order under this agreement, the commission agent is obliged to submit a report to the principal in writing.” Moreover, a sample commissioner’s report is included in the commission agreement as an appendix.
Thus, the parties fix its shape.
Based on the data entered into the commission agent's sales report, the commission is calculated. If the principal has objections, then it is necessary to inform the other party about them within 30 days from the date of receipt of the document, unless a different period is established by agreement of the parties (Article 999 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
If the principal has no complaints about the work of the counterparty, then the report is considered accepted. To do this, the principal's representative must sign the commission agent's report form and put a stamp on it. After this, the commission agent can issue an invoice for the amount of his remuneration.
In the online service MoySklad you can free of charge the commission agent’s report and other necessary documents or print them online, taking into account all the rules, without blots and errors. Just use the program and appreciate the ease of designing forms, as well as other advantages of its work.
Download other document forms
Source:
Report to the committent in 1C 8.3 Accounting (purchases)
If, when making a transaction, one party acts on behalf of the other (but on its own behalf) and receives remuneration for this, then such a transaction is a commission. The party giving the order is called the principal or principal, the party executing it is called the commission agent, and the agreement is called the commission agreement.
According to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a commission agent can both sell the goods of the principal (in traditional commission trade) and make purchases for him for a fee. In 1C Accounting 8.3, transactions with the principal are implemented both during sales and during purchases. Let's consider an example when our organization acts as a purchasing commission agent, and the counterparty acts as a consignor.
Conclusion of a commission agreement in 1C for purchases
In the 1C 8.3 “Counterparties” directory, we find or create the required counterparty and create an agreement for it, and the type of agreement should be “With the committent (principal) for the purchase.”
Since our commission will be calculated as a percentage of the purchase amount, we indicate the appropriate calculation method and the amount as a percentage. If you chose another option – “Not calculated” – the amount of the reward would have to be indicated in the documents manually. We write down an agreement with the principal.
Purchase of goods for the consignor
This operation is formalized as a regular purchase: with the standard document “Receipt of goods and services”. Let's create a new document with the view “Goods, services, commission”. We indicate the supplier counterparty and the agreement with him, and enter the purchased goods on the “Products” tab. How will the 1C Accounting program “understand” that they were purchased specifically for the principal?
Let's scroll the table of products horizontally. The columns “Counterparty” and “Committent Agreement” were found. We indicate in them our principal and the contract.
At the same time, an accounting account for purchased goods was automatically established - off-balance sheet account 002 “Inventory and materials accepted for safekeeping.” An accounting account for settlements with the principal has also been established - 76.09 “Other settlements with various debtors and creditors.”
Get 267 video lessons on 1C for free:
After the document was processed, entries were made for the receipt of goods - on the debit of account 002, while the credit account was not indicated, since the goods were put on off-balance sheet accounting. Accounting entries for settlements with the principal and supplier have also been generated.
Transfer of purchased goods to the consignor
There is a special document to reflect this operation in 1C 8.3. It is available in the “Purchases” section, subsection “Purchases” – Transfer of goods to the consignor. Let's create a new document. In the header we will indicate the principal and the agreement. The transferred goods are entered in the tabular section. Here you can auto-fill using the “Fill” button.
If a report has already been entered for the committent, you can use the options “Fill in according to the report...” or “Add from the report...”. In our example, we select the “Fill in balances 002” option. Products that are listed on this account appear in the table.
Let's review the document. It generates an accounting entry for writing off goods from the credit of account 002. The document allows you to print different forms of invoices and UPD.
Report to the committent in 1C 8.3
This 1C program document serves to reflect the commission services provided and calculate the remuneration. The report to the consignor can be completed before the transfer of goods. The document is available in the “Purchases” section (Purchases – Reports to Principals). Let’s create a new document by selecting the “Purchasing Report” type.
On the “Main” tab we indicate the principal and the contract. Since the method for calculating remuneration has already been selected in the contract, it is filled in automatically in the document. In the “Remuneration Service” field, you should select a service from the “Nomenclature” directory, creating a new one if necessary (do not forget to indicate the type of item “Service”).
The income account for the service provided is filled in automatically. If the organization uses item groups, you must also indicate the required item group (subaccount 90.01).
To enter purchased goods and calculate remuneration, you need to go to the “Goods and Services” tab. This section can also be filled out automatically by clicking the “Fill” button. Select “Fill in purchased under contract.”
A line indicating the supplier of goods and the receipt document appeared in the upper part, and lines with goods appeared in the lower part. For each item, the purchase price is indicated and the remuneration is calculated. (If in the filling command you click “Fill by receipt” or “Add from receipt”, you will need to select the receipt document manually).
After entering the goods, the total reward amount will be displayed on the “Main” tab. You can also issue an invoice for the commission there. Let's post the document, it generates transactions for the provision of commissions, you can print out the forms of the act of provision of services and the report to the principal, as well as invoices and UPD.
Receiving a commission
This operation is formalized in 1C with standard bank documents of receipt to the current account or receipt of cash, indicating the counterparty and the corresponding agreement. If necessary, you can create these documents from the “Report to the Principal” by entering based on.
Source:
Consolidated invoice for investment construction
The intermediary has the right to issue a consolidated invoice to the principal (principal), including goods purchased from several suppliers. In turn, the principal (principal) has the right to issue a consolidated invoice, including goods that were sold to several customers (see “When trading with several sellers or buyers, principals and principals will be able to issue consolidated invoices”). The procedure for this should be as follows.
If an intermediary sells goods of the principal (principal) to several buyers, he issues a separate invoice in the name of each buyer. These documents are registered in part 1 of the intermediary’s journal with code KVO 27. Also, these documents are registered in the purchase book of each buyer with code KVO 01.
Next, the intermediary informs the principal (principal) of information about all sales, and he issues a consolidated invoice for the goods sold to all customers. The consolidated invoice is registered:
- in part 2 of the intermediary’s journal with code KVO 27. In the columns intended for information about intermediary activities, information about each of the buyers is indicated in separate lines;
- in the sales book of the principal (principal) with code KVR 27. In the columns intended for information about the buyer, information about each buyer is indicated, separated by commas.
If the intermediary purchases goods for the principal (principal), he receives invoices from suppliers and registers them in part 2 of the journal with code KVO 27. Also, invoice data is registered in the sales book of each supplier with code KVO 01.
Next, the intermediary issues a consolidated invoice in the name of the principal (principal) for the goods purchased from all suppliers. The consolidated invoice is registered:
- in part 1 of the intermediary’s journal with code KVO 27. In the columns intended for information about intermediary activities, information about each of the suppliers is indicated in separate lines;
- in the purchase book of the principal (principal) with code KVO 27. In the columns intended for information about the seller, information about each of the suppliers is indicated, separated by commas.
It is possible that several buyers on the same day will make an advance payment to the intermediary against future deliveries of goods belonging to the principal (principal). The intermediary must then issue separate “advance” invoices in the name of each of the buyers. These invoices must be registered in part 1 of the intermediary’s journal with code KVO 28. Also, “advance” invoices must be registered in the purchase book of each buyer with code KVO 02.
Then, when the intermediary informs the principal (principal) of all advances, the principal can issue a consolidated “advance” invoice. This document must be registered in part 2 of the intermediary’s journal with code KVO 28. Also, the consolidated “advance” invoice must be registered in the sales book of the principal (principal) with code KVO 28. In the columns intended for information about the buyer, information must be indicated separated by commas about each of the buyers.
We noted earlier that the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for re-issuance of invoices. However, in paragraph 6 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that the deduction can also be applied by those organizations to which the tax was presented by the customer-developer during capital construction. The customer-developer, as is known, in relation to contracting organizations acts as the customer of design and construction work. Consequently, invoices are issued to him (and not to the investor - the actual “purchaser” of the work).
At the same time, the actual “purchaser” of design and construction work is the investor, because his funds are used to purchase the work necessary for the implementation of the investment project. Consequently, the right to deduction arises not from the customer-developer, but from the investor. In order for an investor to have the right to deduct, a document is required.
Thus, the investor has every right to demand that the customer-developer re-invoice costs. That is, he can demand not only an invoice for the services of the customer-developer, but also a consolidated invoice for the cost of expenses incurred during the implementation of the investment project. This conclusion was confirmed by the Ministry of Finance of Russia in Letter dated May 24, 2006 N 03-04-10/07.
The authors of the letter also reminded that the Rules do not provide for the procedure for issuing consolidated invoices by agents based on several documents received from different principals. Therefore, the agent does not have the right to combine invoices into one and issue a “consolidated” invoice to the buyer (see also “How to issue and register invoices for commission trading”).
*The full title of the document is “On the forms and rules for filling out (maintaining) documents used in calculations of value added tax,” approved. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137.
Filling out a sales commissioner's report in 1C
Any commission trade involves the presence of two actors: the commission agent, who accepted the goods for sale for a fee in the form of a percentage of the proceeds, and the consignor, the person who provided the goods. The 1C Accounting program in version 8.3 allows you to fully reflect all operations occurring in this type of relationship.
As an example, we can consider a situation in which a company transfers a product to a commission agent for sale. The terms of remuneration are 50% of the difference between the purchase and sale prices. The goods were sold in full, the reward was paid.
Transfer of goods to the commission agent
First of all, a new contract is drawn up, and its type is “With a commission agent for sale.” The section devoted to the calculation of remuneration includes the method of calculation and the amount of the interest rate. This will allow you to automate all calculations in the future, and not have to do them manually.
Next, you need to transfer the goods to the commission agent for sale. This type of transaction is registered as “Sales” with the type “Goods, services, commission”.
Information about the counterparty and the agreement with him is entered into the header, after which all product items are listed through the “Products” tab.
Taking into account the information about the commission agent entered into the contract, the system accepts the goods specifically for sale, and does not credit them to the balance of the receiving party.
Taking into account the fact that the goods are transferred to the second party on commission, the tabular section contains the column “Transfer Account”. This account is used to reflect all goods transferred to the commission agent. The invoice is issued automatically from the item. If it is placed in the “Product” position, then the invoice is taken as 45.01 “Purchased goods shipped”.
After posting the document, postings are generated reflecting the fact of transfer of goods. For our case, the posting is Debit 45.01 Credit 41.01
Registration of the commission agent's report
After registering the commission agent’s report, the due remuneration is accrued to him. The operation is formalized as a separate document at the address “Sales” - “Sales commission agent reports”, where a new document is generated.
Through the “Main” tab, the counterparty company and the number of the agreement with it are displayed. In the “Commission” section, the relevant information on calculations is entered.
If this information was specified earlier in the contract, then the fields will be filled in automatically.
If desired, the entered data can be adjusted; it is possible to indicate the VAT account and the rate of this tax, as well as register the received invoice.
If the commission is withheld before the revenue is transferred to the principal, the program checkbox “Commission is withheld from the proceeds.” If the principal received the entire amount of the proceeds, and then he himself will settle accounts with the commission agent, then this mark is not affixed.
Next, the invoice and analysis of the costs associated with the remuneration are reflected. In most cases, reflection is carried out under article 44.01 “Distribution costs” and the cost item “Commission agents’ services”.
Through the sales tab you can view all goods sold under the contract. If you have an implementation document, the data can be filled in automatically.
This is done by simply pressing the “Fill” button and selecting the required document from which the data is taken. After this, all presented products will be reflected in the tabular section.
This list can be adjusted manually.
The columns “Transfer Price” and “Price” indicate the prices of receipt of goods and their sale. The amount of the commission agent's remuneration is determined from the difference. Its calculation is carried out for each of the positions separately with the subsequent summation of the data.
The tabular section may display data on the buyer, including if there is an invoice.
The “Returns” tab displays information about goods that, for various reasons, could not be sold and were returned to the consignor.
The “Cash” tab displays data on all receipts of funds from the buyer, and the information is entered into the system manually.
The “Advanced” tab allows you to specify the recipient and sender in cases where their name differs from those entered in the system.
After the document is posted, the following set of accounting entries is generated:
Debit 90.02 Credit 45.01 (writing off cost of goods sold)
Debit 62 Credit 90.01 (revenue)
Debit 44.01 Credit 60.01 (commission costs)
In addition, if there is a condition for deducting remuneration from revenue, additional posting will be generated
Debit 60 Credit 62
Separately, it is necessary to indicate transactions related to the calculation of VAT, both for goods and for remuneration to the commission agent
Debit 90.03 Credit 68.02
Debit 19.04 Credit 60
Payment for goods and rewards
After payment for the goods is received and transferred to the principal, the remuneration is paid. The fact that payment has been received must be reflected.
To do this, it is advisable to use the following procedure “Commissioner’s report” - “create based on”, and then select the required document. Its creation will be carried out automatically with the fields completely filled out.
If remuneration is withheld from revenue, this fact will be reflected in the document.
If the remuneration is paid separately after the principal has received the entire amount, then you can also create a document for payment through the “Commission Agent's Report”.
Source: https://usersv81c.ru/zapolnenie-otcheta-komissionera-po-prodazham-v-1s.htm
Reissued documents by the commission agent on behalf of the principal
The documents accompanying the transaction are drawn up on behalf of the reseller, since he is obligated in this transaction. Algorithm for issuing payment papers:
- The agent issued an invoice on behalf of the principal. The procedure for filling out documentation is carried out in accordance with Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The period from the date of shipment of products is up to 5 days, and upon receipt of an advance payment - on the same day. The reseller provides the number and date.
- The data of these accounting papers is transferred to the principal or principal.
- The principals issue invoices with the indicators reflected in them to the agent first.
- The storage of invoices received from the principal or principal by intermediaries is recorded in the journal of the received settlement documentation.
"Excluded" position
“Invoices in which sellers indicate the work or services of other sellers, paid by the buyer in excess of the cost of the goods, are recorded in the sales ledger only to the extent of the cost of those goods.”
As we can see, the Government of the Russian Federation previously officially allowed the issuance of invoices, which also contained overbilled amounts of expenses. It is logical that the seller of goods did not calculate VAT on these costs. Therefore, the meaning of clause 26 is clear, regulating the inclusion in the sales book only of the cost of goods (without taking into account the cost of work and services of third-party organizations).
But at present this clause is not valid. What does this mean?
It is quite difficult to answer this question. One can only guess that the Government of the Russian Federation, by its actions, actually made it clear that the seller should not overcharge the cost of services and work of third-party organizations to its customers.
A. Isanova
Tax consultant
Date of sale of goods
In a situation where the commission agent carries out an order related to the sale of goods, the report should record the date when the goods were sold.
If the principal uses the accrual method, then on the date of sale of goods by the commission agent, the principal is obliged to take into account income from sales equal to the sale value of the goods without VAT (clause 3 of Article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Let us note that the principal is obliged to notify the committent of the sale of goods no later than three days from the end of the reporting (tax) period in which the goods were sold (paragraph 5 of Article 316 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, on the date of shipment of goods by the commission agent to the buyer, the principal becomes obligated to charge VAT (subclause 1, clause 1, article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 16 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated May 30, 2014 No. 33). The tax base for VAT is defined as the sales value of goods excluding tax (Clause 1, Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Purchasing goods for several customers
The situation becomes somewhat more complicated if the intermediary plays two roles at once: commission agent (agent) and supplier. In this case, he ships to the buyer goods belonging to the principal (principal), and at the same time - his own goods.
We suggest you read How to register a parent from another city
The procedure will be as follows. The intermediary issues an invoice in the name of the buyer for all goods: both his own and those belonging to the principal (principal).
The intermediary identifies himself as the seller. This invoice is registered:
- in the sales book of the intermediary with code KVO 15. In the columns intended for taxable sales and the amount of VAT, information is entered not about the entire product, but only about the intermediary’s product;
- in part 1 of the intermediary’s journal with code KVO 15. In the column intended for the VAT amount, information is entered not about the entire product, but only about the product of the principal (principal);
- in the purchase book from the buyer with code KVO 01.
Connect to the system for exchanging electronic invoices
Then the intermediary informs the principal (principal) of the invoice indicators so that he reissues the document in the name of the intermediary. The reissued invoice will reflect only the goods belonging to the principal (principal). The reissued invoice is registered:
- in the sales book of the principal (principal) with code KVO 01;
- in part 2 of the intermediary’s journal with code KVO 15.
Example 1
Komissioner LLC shipped 20 products to Buyer LLC. Of these, 13 products belong to JSC “Committent” and are sold under an intermediary agreement. The cost of Komitent products is 354,000 rubles. (including VAT 18% - RUB 54,000). The remaining 7 products belong to the "Commissioner". Their cost is 236,000 rubles. (including VAT 18% - RUB 36,000)
LLC "Commissioner" issued invoice No. 365 in the name of the "Buyer" for a total amount of 590,000 rubles. (354,000,236,000), including VAT 18% for the amount of RUB 90,000. (54,000 36,000). This document was registered with the “Commission Agent” and the “Buyer” (see Table 1).
Table 1
Registration of invoice No. 365
| In the sales book of LLC "Commissioner" | |||||
| Column name | Operation type code | Buyer's name | Cost of sales according to the invoice, difference in value according to the adjustment invoice (including VAT) in the currency of the invoice in rubles and kopecks | The cost of taxable sales according to the invoice, the difference in value according to the adjustment invoice (excluding VAT) in rubles and kopecks, at the rate 18 percent | The amount of VAT on the invoice, the difference in value on the adjustment invoice in rubles and kopecks, at the rate 18 percent |
| Column number | 2 | 7 | 13b | 14 | 17 |
| Meaning | 15 | LLC "Buyer" | 590 000,00 | 236 000,00 | 36 000,00 |
| In part 1 of the log of received and issued invoices of LLC "Commissioner" | |||||
| Column name | Operation type code | Buyer's name | Cost of goods (works, services), property rights according to the invoice - total | Including the VAT amount on the invoice | |
| Column number | 3 | 8 | 14 | 15 | |
| Meaning | 15 | LLC "Buyer" | 354 000,00 | 54 000,00 | |
| In the purchase book of LLC "Buyer" | |||||
| Column name | Operation type code | Seller's name | Cost of purchases according to the invoice, difference in cost according to the adjustment invoice (including VAT) in the invoice currency | The amount of VAT on the invoice, the difference in the amount of VAT on the adjustment invoice, accepted for deduction, in rubles and kopecks | |
| Column number | 2 | 9 | 15 | 16 | |
| Meaning | 01 | LLC "Commissioner" | 590 000,00 | 90 000,00 | |
Then the “Committee” informed the “Committent” of the indicators of invoice No. 365, and the “Committent” issued invoice No. 1112 in the name of the “Commissioner” in the amount of RUB 354,000. indicating VAT 18% for the amount of 54,000 rubles. This document was registered with the “Committent” and the “Commission Agent” (see Table 2).
table 2
Registration of invoice No. 1112
Table 2 is provided as a separate file.
It is not uncommon for an agent to purchase goods or services for several principal buyers. In this case, in the invoice reissued to the principal, the quantity of goods (volume of services) will be less than the quantity indicated in the copy of the invoice issued to the agent by the seller. Will this create obstacles to obtaining a VAT deduction? No, it won’t, according to the Ministry of Finance. According to officials, such a discrepancy is not a basis for refusing a deduction from the principal.
| Line number/columns | Content |
| 1 | Date of issue of payment papers from the seller to the intermediary |
| 2 | Seller's name |
| 2a | Seller's address |
| 2b | Checkpoint, seller's tax identification number |
| 3 | Addresses, names of cargo sender |
| 4 | Name of cargo recipients |
| 5 | Dates, numbers of accounting papers issued to the intermediary by the customer, issued to the seller by the reseller are indicated through “;” |
| 6 | Buyer's name |
| 6a | Buyer's full address |
| 6b | KPP, recipient's TIN |
| 1 | Name of services, goods, works |
| 2 – 11 | Data of payment papers issued to the seller by an intermediary |
| Rest | For each item of goods, the corresponding indicators (VAT, cost, units of measurement, etc.) |
This option is simpler. The agreement concluded by the agent with the buyer specifies the action of the commission agent on behalf of the seller.
Attention! To have the right to use such manipulations, the seller must take care of issuing a power of attorney, ensuring the right to represent interests.
You will learn more about filling out an invoice in our article.
Invoice under a commission agreement with the principal
→ → Update: October 6, 2020
Our organization sells goods through a commission agent. Who should we issue invoices for goods sold to and how do we fill them out?
You need:
- issue an invoice to the intermediary for the advance payment he received from the buyer or for the goods sold by him. Data from intermediary invoices dated on the same date can be reported in one consolidated invoice, , .
- obtain copies of invoices issued by the intermediary to the buyer before the end of the quarter in which the intermediary received an advance from the buyer or shipped goods to him. The obligation of the intermediary to provide you with copies of such invoices within a certain period, for example, within 3 calendar days from the date of their preparation, can be enshrined in the commission agreement (agency agreement);
EXAMPLE.
If your company (principal) sells goods through an intermediary (commission agent or agent) acting on its own behalf, the intermediary issues invoices to buyers.
The consignor fills out an invoice for goods shipped by the intermediary Alpha LLC (commission agent) and Beta LLC (seller, consignor) entered into an agreement for the sale of wall clocks. On November 10, 2016, Alpha LLC (commission agent) shipped 100 pieces of wall clocks worth 118,000 rubles to the buyer Gamma LLC.
(including VAT RUB 18,000). Alpha LLC (commission agent) provided Beta LLC (committent) with a copy of the invoice issued to the buyer. Beta LLC (committee) prepares an invoice for the sale of goods as follows.
INVOICE No. 155Committent
Introductory information
Modern VAT verification is a cross-check of suppliers and buyers participating in the same transaction. Tax officials study the information entered in the purchase books and sales books, and in case of intermediary transactions, also in the journal of received and issued invoices (hereinafter referred to as the journal).
If the data for all counterparties is consistent, the inspectors admit that there were no violations. Otherwise, the transaction falls into the category of suspicious with all the ensuing consequences (read more about this in the articles “VAT “under the hood”, or a general cameral” and “VAT return for the 3rd quarter: what the tax authorities will check and how to avoid common mistakes when filling out the declaration").
Carry out automatic reconciliation of invoices with your counterparties
As part of cross-control, inspectors, among other things, study such details as the type of operation code (KVO). The list of codes was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3 / [email protected] (see “From July 1, new transaction codes will need to be indicated in the books of purchases, sales and the invoice journal”). The commented letter describes what values of the KVO and other “key” details must be indicated during various intermediary operations so that the transaction does not arouse suspicion.
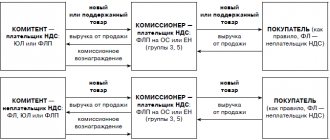
Sales of goods by the commission agent - his own and the principal's
Accounting, taxation, reporting, IFRS, analysis of accounting information, 1C: Accounting
03/29/2016 subscribe to our channel
We have already talked about the reflection in “1C: Accounting 8” edition 3.0 of operations for the sale of goods through a commission agent and the use of “consolidated” invoices (No. 5 (May), p. 25 “BUKH.1S” for 2020 and No. 6 ( June), pp.
15 "BUKH.1S" for 2020). From this article by 1C experts, you will learn how to take into account in the program the sale by the commission agent of his own goods and goods received from the principal, and to register a “mixed” invoice issued upon shipment. Using a practical example, the sequence of operations is shown, starting with the receipt of goods from the consignor and ending with the reflection of the formation of a log of invoices, books of purchases and sales, and a VAT declaration.
Chapter 51 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation is devoted to the commission agreement. One party (the commission agent) undertakes, on behalf of the other party (the principal), for a fee, to complete one or more transactions on its own behalf, but at the expense of the principal (Clause 1, Article 990 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The principal pays the commission agent remuneration in the manner and amount established in the commission agreement (clause
1 tbsp. 991 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Things received by the commission agent from the principal are the property of the latter (Clause 1 of Article 998 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation)
The intermediary simultaneously sells the consignor’s goods and his own goods
The commission agent or agent who, on his own behalf, sold goods belonging to the principal or principal must issue an invoice in the name of the buyer. An intermediary must be specified as the seller. The intermediary records this invoice in part 1 of the journal. This invoice is not recorded in the intermediary's sales book. This document is also recorded in the buyer’s purchase book.
Then the commission agent or agent must inform the principal or principal of the invoice so that he can reissue the document in the name of the buyer. The reissued invoice is registered in the sales book of the principal (principal) and in part 2 of the intermediary's journal.
What transaction type code should be specified when registering the above invoices? From the commented letter it follows that in the sales book of the principal (principal), and in the buyer’s purchase book, and in both parts of the intermediary’s journal, the same KVO is entered - 01.
Example 1
Table 1
table 2
Invoice under the commission agreement from the commission agent
» » When selling goods (works, services) of a principal - a VAT payer, you must issue invoices to buyers on your own behalf. You hand over copies of these invoices to the principal, and he issues invoices to you based on them. Invoices that you issued to the buyers and which you received from the consignor, register invoices in the journal. When purchasing goods (work, services) for the consignor, sellers issue invoices in your name. You reissue these invoices to the principal. Register the invoices that you received from sellers and which you reissued to the principal in the invoice journal. When selling goods (works, services) of a principal who is a VAT payer, you must draw up and issue invoices to buyers on your behalf. Give copies of these invoices to the principal.
The principal will take from the copy information about the buyer, goods shipped or advances received, issue an invoice on his behalf and give it to you. Register all invoices that you issue to customers and that you receive from the principal in the invoice journal. There is no need to register them in the sales book or purchase book. You need to issue invoices and keep invoice journals, even if you are not a VAT payer (clause
3.1 Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For example, if you are on the simplified tax system. If you are a VAT payer, you must also issue invoices to the committent for your commission (including those paid to you in advance) or for other income that you receive for your services.
Re-issuance of payment papers by the reseller
When issuing invoices to the principal (principal), the intermediary (agent or commission agent), purchasing goods, work, services or property rights on his own behalf, indicates the full or abbreviated name of the seller, who is a legal entity, or the last name, first name and patronymic of the seller - an individual entrepreneur. In this case, the specified invoices are signed by the agent.
However, as the authors of the letter noted, the agent can additionally indicate his name, address and INN/KPP in such an invoice. It is safer to enter this information after filling out all the necessary details (see “Additional invoice information is best reflected after specifying all the required details of this document”).
We invite you to familiarize yourself with a sample loan receipt for another person
The reissued invoice must be registered in part 1 of the journal of received and issued invoices (clause 7 of the journal rules). No entry is made in the sales book, because the agent has no obligation to charge VAT (clause 20 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book). In addition to the re-issued invoice, the intermediary gives the customer a copy of the original invoice issued by the supplier, certifying it with his signature (subparagraph “a” of paragraph 15 of the Rules for filling out an invoice).
Tax legislation in the case of the acquisition of services, works or goods under commission agreements regulates the procedure for the actions of intermediaries in clause 24 of the Rules. According to this, when selling services, works or goods, it is necessary to re-issue a commission invoice to the agent in the generally established manner. The reseller must provide the customer with the appropriate payment papers of this sample.
| Line number/columns | Content |
| 1 | Chronological order number, same date |
| 2 | Seller's name |
| 2a | Name of the seller, location according to the constituent documentation, checkpoint, tax identification number |
| 2b | |
| 3 | Addresses, names of cargo sender |
| 4 | Name of cargo recipients |
| 5 |
|
| 6 | Buyer's name |
| 6a | Information about the principal (principal, agent) |
| 6b | |
| 1 | Name of services, works, goods |
| 2 – 11 | Payment paper data from the intermediary |
| Rest | For each item of goods, the corresponding indicators (VAT, cost, units of measurement, etc.) |
The signing of such an invoice is carried out simultaneously by the chief accountant and the founder of the intermediary. These payment papers are filled out in this order, despite the lack of information about the intermediary.
Important! If this is not done, the agent will not accept the amount of VAT for payment, which is indicated in the invoice to the principal from the commission agent.
Commission remuneration
The amount of commission is a mandatory detail in the commission agent’s report. The commission agent must reflect the amount of the commission excluding VAT in the income taken into account in the income tax base (clause 1 of Article 248, clause 1 of Article 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, income is reflected on the date of approval of the report if the commission agent uses the accrual method (clause 3 of Article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the commission agent uses the cash method, then income is taken into account on the day of receipt of funds from the principal or when repaying the debt in another way (clause 2 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The principal has the right to take into account the amount of remuneration (excluding VAT) in expenses that reduce the tax base. If the commission agent sells goods belonging to the principal, then the amount of remuneration is reflected in the costs associated with the sale (clause 1 of Article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), or as part of other expenses (subclause 3 of clause 1 of Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Let us remind you that according to clause 4 of Art. 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the taxpayer has the right to independently assign to one or another group expenses that simultaneously belong to several groups. If a commission agent purchases goods or other property for the principal, then the principal has the right to include the amount of remuneration in the cost of this property (clause 1 of Article 268, clause 2 of Article 254 and clause 1 of Article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When applying the accrual method, expenses are taken into account on the date of signing the commission agent's report (clause 1 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), when using the cash method - on the date of payment of remuneration (clause 3 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Note that the amount of remuneration can be set by the parties as a fixed amount or in an amount depending on the indicators adopted in the contract. In the case where the amount of remuneration is calculated based on the cost of goods sold or purchased, it is advisable to show in the report the calculation of the amount of remuneration.