Software
20.03.20195168
The need to calculate a percentage of an amount or number can arise for various reasons: someone needs to find out how profitable the discount offered by the store really is; someone needs to substitute the value into the formula. In any case, the sequence of actions is always the same, and people continue to calculate percentages using the same algorithm. Let's try to figure out how this is done.
What percentage is one number greater than another?
To calculate how many percent one number is greater than another, you need to divide the first number by the second, multiply the result by 100 and subtract 100.
Let's calculate how many percent the number 20 is greater than the number 5: 205 · 100 - 100 = 4 · 100 - 100 = 400 - 100 = 300% The number 20 is 300% greater than the number 5.
For example, the boss’s salary is 50,000 rubles, and the employee’s salary is 30,000 rubles. Let's find by what percentage the boss's salary is greater: 5000035000 · 100 - 100 = 1.43 * 100 - 100 = 143 - 100 = 43% Thus, the boss's salary is 43% higher than the employee's salary.
Calculate income tax online
If you want to perform more complex actions, you can use many online services, which are presented on the following pages:
- https://www.calc.ru/kalkulyator-nalogov;
- https://timesnet.ru/calculator/&/?rate=salary9amp;factor=139amp;expect=19amp;amount=10000;
- https://www.rabota-viza-rezyme.ru/Kalkuljatory_onlajn/Kalkuljator_NDFL_onlajn_zdes.html.
In addition to the typical income tax action, there are many more features here. So, you have the opportunity to calculate:
- Tax for a foreigner;
- The amount of salary in hand;
- Dividends;
- Benefits, etc.
Remember that for many categories of citizens there are benefits in this regard. Therefore, do not rush to part with your money. Before you think about how to calculate 13 percent of your salary online, decide on the benefits. You may not be entitled to such tax at all, or you may only be able to pay a limited amount of it.
What percentage is one number less than another?
To calculate how many percent one number is less than another, you need to subtract from 100 the ratio of the first number to the second, multiplied by 100.
Let's calculate how many percent the number 5 is less than the number 20: 100 - 520 · 100 = 100 - 0.25 · 100 = 100 - 25 = 75% The number 5 is 75% less than the number 20.
For example, freelancer Oleg completed orders worth 40,000 rubles in January, and 30,000 rubles in February. Let's find how many percent less Oleg earned in February than in January: 100 - 3000040000 · 100 = 100 - 0.75 * 100 = 100 - 75 = 25% Thus, in February Oleg earned 25% less than in January .
Calculator for calculating salaries, contributions and sick leave 2019-2020
How the amount of benefits is affected by the employee’s insurance experience
Currently, the benefit is issued in the amount of:
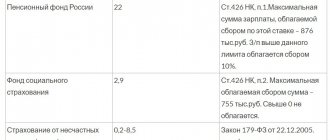
– 100 percent of earnings – to employees with a total insurance experience of eight or more years;
– 80 percent of earnings – to people with five to eight years of experience;
– 60 percent of earnings – to citizens with less than five years of experience.
Employees, regardless of their length of service, who are fired from the company and fall ill within 30 days of dismissal will also receive no more than 60 percent of their earnings. At the same time, we recall that if the employee’s work experience is less than six months, then the amount of the benefit cannot exceed one minimum wage per month.
You need to adjust by percentage as the amount of the benefit, which is calculated based on the employee’s actual earnings. So is the amount of benefits calculated based on the minimum wage.
Calculation of employee's insurance length
The amount of insurance coverage is important for calculating two benefits - for temporary disability and for pregnancy and childbirth.
So, sick leave is issued in the amount of:
– 100 percent of average earnings – for employees with a total insurance experience of eight or more years;
– 80 percent of average earnings – to employees with five to eight years of experience;
– 60 percent of average earnings – to citizens with less than five years of experience or in case of illness within 30 calendar days from the date of dismissal.
These percentages must be used, among other things, to calculate benefits for employees working and living in the Far North and equivalent areas. But only for those of them who began their working career in the North after January 1, 2007.
What periods are included in the insurance period?
Continuity of service is not important for calculating benefits. Only the so-called general insurance experience plays a role. That is, breaks in work can be of any duration.
The insurance period includes the following periods:
– work under an employment contract;
– state civil or municipal service;
— periods of military and other service in accordance with the Law of the Russian Federation of February 12, 1993 No. 4468-1;
– other activities during which the citizen was subject to compulsory social insurance.
Other activities that can be included in the insurance period
Specific rules for calculating and confirming insurance experience are established by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated February 6, 2007 No. 91. The rules clarify what exactly is meant by “other activities”. First of all, this is the period of work as an individual entrepreneur, as well as a notary, private detective or security guard. However, this list is open. The main condition is that the employee at this time must be insured in case of illness and in connection with maternity. That is, the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation must receive social insurance payments for it. And by them they mean:
– for the period before January 1, 1991 – contributions to state social insurance;
– for the period from January 1, 1991 to December 31, 2000 – insurance contributions to the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation;
– for the period from January 1, 2001 to December 31, 2009 – taxes credited to the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation (UST, “simplified” tax, UTII and Unified Agricultural Tax);
– for the period from January 1, 2010 – insurance contributions to the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation.
An important point: in 2001–2002, entrepreneurs did not pay unified social tax for themselves in the part credited to the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation. And only from January 1, 2003 they had the opportunity to transfer insurance premiums voluntarily. Therefore, the period from January 1, 2001 to December 31, 2002, when calculating the insurance period of entrepreneurs, “falls out,” which was confirmed by the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation in its ruling dated February 7, 2003 No. 65-O. And since 2003, the length of service is counted only for those entrepreneurs who transferred contributions.
Documents on the basis of which the insurance period is calculated
The main document confirming the employee’s insurance experience is the work book. If for some reason there are no entries in the work book or there is no book at all, employment contracts will help confirm the length of service.
In addition, you can also use extracts from orders, certificates, personal accounts and even payroll statements. The employee must present these documents to the employer (at the place where benefits are paid). Otherwise, the accountant will calculate the benefit based on the data indicated in the employee’s work book.
An employee who, before being employed by a company, was engaged in entrepreneurial activity, in order to confirm his insurance experience, can submit:
– certificates from archival institutions or documents from financial departments (if the employee was engaged in business before January 1, 1991);
– certificates from the territorial offices of the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation on payment of contributions (if the employee worked as an individual entrepreneur from January 1, 1991 to December 31, 2000 and after January 1, 2003).
How to calculate sick leave if your work experience is less than 6 months
This applies to people whose work experience is just beginning. If a person has officially worked less than six months in total throughout his life and up to the moment of illness, then there is a special limitation for his sick leave. This amount for a calendar month cannot be more than the minimum wage (minimum wage), taking into account regional coefficients.
Currently, the minimum wage is 7,500 rubles. However, if the region has established increasing regional coefficients for wage calculations, the minimum benefit amount must be increased by them.
Please note: payments based on the minimum wage also need to be adjusted depending on the employee’s insurance coverage.
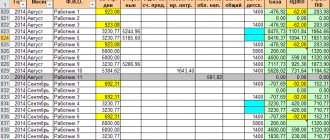
Example 1. At Sokol LLC, Vorontsov S.D. got a job in November 2014. At the same time, this person did not work at other enterprises in 2014. From January 14 to January 21, 2020, Vorontsov was on sick leave.
The employee's total insurance period is 5 years and 4 months, which is significantly more than six months. Consequently, the accountant of Sokol LLC must calculate his allowance based on average earnings.
Example 2. Skorotov P.S. joined Polesie LLC on January 11, 2015. This is his first job. And on February 14 of the same year, Skorotov fell ill and was ill for five calendar days. It turns out that the employee’s total insurance experience is less than six months. Therefore, his benefit cannot exceed one minimum wage for a full calendar month. But it cannot be less than this value (taking into account the coefficient of 60 percent, since the insurance period is less than five years).
More reasons to count according to the minimum wage
A benefit calculated on the basis of the minimum wage must be paid not only if the length of service is less than six months. For example, if a sick employee, without good reason, did not follow the doctor’s instructions or did not show up for an appointment. The benefit based on the minimum will be calculated from the day the violation was committed. In this case, the amount of the benefit must be calculated separately for the days on which the employee violated the doctors’ instructions, and separately for the days when there were no violations. Finally, the results must be added up.
In addition, the minimum, and for the entire period of illness, is received by an employee who falls ill or is injured due to alcohol, drug or toxic intoxication.
During the last two calendar years, was the employee on parental leave for up to three years or maternity leave?
If the employee was on maternity or children's leave during the two years included in the calculation, one or both years of the calculation period can be replaced with the previous ones. Of course, if it’s more profitable for the employee. To do this, she must write a special application. But keep in mind: real payments are taken into account and are not indexed in any way.
Example: V.S. Mikhailova, an employee of Vector CJSC. I got sick in April 2015. In June 2014, she returned from maternity leave, which she had been on since March 2011. The employee has been working for this company since March 2008. Thus, 2013 is “empty” for her, and 2014 is “half empty”.
In this case, the benefit can be calculated based on earnings for the two years preceding the maternity leave. These are 2009 and 2010. And if it is more profitable for the employee, she can leave 2014 and add 2010 to it. The main thing here is that the amount of benefits in the end be the largest.
Note that this is the only exception to the general rule. In all other cases, benefits must be calculated based on earnings for the last two calendar years.
The calculation includes all payments for all places of work for the last two calendar years for which insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund were calculated. But in practice, it is quite possible that the employee had no income during the estimated two years. In this case, the benefit must be calculated based on the minimum wage. This rule applies even if the employee had earnings in the year in which he fell ill.
Employer's actions during downtime
When the moment of disruption to the work schedule occurs, the employer is obliged to perform a number of sequential actions:
- Find the culprit behind the production stop.
- Take measures to stop downtime.
- Draw up the relevant documentation and familiarize it with employees against signature.
- Accrue and pay wages in accordance with Art. 157 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It is sometimes quite difficult to identify those responsible for the suspension of production activities. For example, when equipment breaks down, it is possible that each party is at fault: the equipment broke down due to missed scheduled maintenance - the employer is to blame; due to the rules of violation of operation - the employee is guilty; due to marriage is a circumstance beyond the control of the parties.
When taking measures to restore production, the employer must ensure that there is evidence confirming its actions, for example, in the absence of materials, negotiations or correspondence with suppliers.
An employee who, for any reason, cannot perform the function assigned to him by the employment contract must notify the employer of the fact of downtime. After notification, the date and time of downtime must be documented in the prescribed form - by order, or some other document provided for by the organization’s office management rules.
During the entire period of downtime, a mark is made in the work time sheet with the letter designation “RP”, “NP” or “VP”.
Depending on who is to blame for the suspension of the production process, wages are calculated in different ways.
Downtime notification
If downtime occurs, the employee must notify management about this (Part 4 of Article 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The requirement for written notification is not established by law. Therefore, an employee can inform about the beginning of downtime both orally and in writing (for example, submit a memo). An exception to this rule is forced downtime during a strike. Employees who do not participate in the strike, but are forced to stand idle in connection with its conduct, must notify the organization’s management about this in writing (Part 6 of Article 414 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Situation: is it necessary to notify the employment service about downtime?
The answer to this question depends on whether the downtime is related to the suspension of production or not.
From the literal interpretation of paragraph 2 of paragraph 2 of Article 25 of the Law of April 19, 1991 No. 1032-1, it follows that the organization must notify the employment service in two cases:
- when introducing a part-time working day (shift) and (or) part-time working week;
- when production is suspended.
Thus, you only need to notify the employment service about downtime if the downtime is related to the suspension of the organization’s production. This must be done no later than three working days from the date of the decision on the relevant measures (paragraph 2, paragraph 2, article 25 of the Law of April 19, 1991 No. 1032-1). The unified form of information is not approved by law. In some regions, employment services independently establish the form for submitting information and communicate it to organizations, in particular, on information sites on the Internet. If the form for submitting information is not established, send information about the suspension to the employment service in any form. Please indicate:
- the reason for the suspension of production;
- the start date and end date of the downtime (if its duration is known), recorded in the organization’s administrative documents;
- number of employees who will be affected by the downtime procedure.
Attention: administrative liability is provided for failure to provide information to the employment service authorities (Article 19.7 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Penalties – warning or administrative fine in the amount of:
- for an organization – from 3,000 to 5,000 rubles;
- for officials (for example, the head of an organization) - from 300 to 500 rubles.
In other cases, when the downtime is not related to the suspension of production (for example, when a car breaks down, when one employee has downtime), there is no need to notify the employment service.