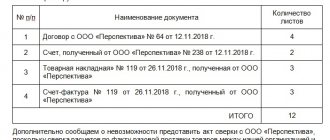
To receive income, you must have primary documentation, that is, you cannot receive money just like that, there must be a justification. At first, this is very unusual, because when you work as an individual, there is no paperwork, but in practice everything is not as difficult as it seems. I’m no longer at all afraid of issuing an invoice or sending a statement, given that I always have all the templates at hand in the accounting service, from where I can always download them.
Primary documentation for individual entrepreneurs
My post was written based on the fact that I chose a simplified taxation system (USN 6%) and perhaps there are some nuances in other systems. Nevertheless, the agreements/acts/invoices/Kudir will be approximately the same for everyone and the essence of the primary documentation also does not change.
Almost all forms and ready-made templates can be downloaded on the Internet if you need them. Since I have been using the My Business service for a long time, I download everything from there. Moreover, I have them there and store them in a completed form. Invoices and acts are the same, but there are many different templates for contracts. I also lead KUDIR in My Business.
Conclusion of an individual entrepreneur agreement or acceptance of an offer
So, before performing any work or providing a service, you need to conclude an agreement, sealed with the signatures of the parties and seals (an individual entrepreneur can only put a signature, a seal is not required). If you enter into an agreement with a company (affiliate) that pays you money, then it will already have an agreement anyway, and you won’t have to invent anything. This is, of course, if there is an option to work the white way with payments to a bank account, and not just to electronic wallets.
Many affiliate programs or services operate under an offer agreement, which can be downloaded as a pdf file to your computer. The offer does not require signing by the parties and during registration (creating a personal account) you agree to it (accept). This is equivalent to you having subscribed. The date of conclusion of the contract is the date of acceptance of the offer.
For private clients, you will have to make the contract yourself. There is a catch, because few users will want to enter into a one-time contract for some small services, such as consultations or creating a blog. The convenience of the Internet is that you don’t need to go anywhere, and the customer definitely won’t want to leave home to the post office to send the original contract. But there is a way out of the situation - the same public offer agreement (example of an agreement). You can post a link to the offer on your website, for example, next to the “Send request” button and sign that when sending such a message the user accepts the offer. You can decide for yourself which action is more suitable and after which the offer is considered accepted by the customer (payment of the invoice, registration on the site, etc.). Thus, everyone is happy: both the customer (his signature is not needed) and you, who did everything within the law.
Certificate of work performed or services provided
After you have completed your work, you issue a certificate of completion of work, or a certificate of services rendered. You will have to send the original of this act to the customer by mail, and he must sign it and send it back to you (this can also be done during a personal meeting). Since not every customer wants to sign something there, usually a line is written in the contract (or offer) that if the customer does not sign the document and send it back, then the work/service is considered to have been performed properly. And in your hands you still have a piece of paper from the post office (you need to send it with a receipt acknowledgment) that you sent the act, that’s enough.
But I described to you the ideal option. Some affiliate programs (we are talking more about freelancing) do not need your reports or they themselves send you a report/report by mail every month (or another period). Rather, the Individual Entrepreneur himself needs the acts to prove that the work was done and the service was provided, if the customer suddenly wants to return the money. A bank statement with your transactions will be sufficient as primary documentation for the tax authorities.
So far I have not found an option so that acts can be issued electronically. Yes, this can be done, and it can be stated in the offer agreement that the act is sent by email, and then the customer must sign it and send it by regular mail, and if he does not do this, then the work/service is considered to have been performed properly. But I was not recommended to do this, because I do not have documentary evidence of sending the act. Or, as an option, do not issue a statement at all and be content with a bank statement showing the fact of payment for the work/service.
Invoicing
Another primary document is an invoice. You issue it after completing the work/service along with the certificate. But the invoice is optional; in fact, it is simply your details, according to which the customer must pay for your work, and the required payment amount. The invoice is often issued by email, on a letterhead or in a more or less free form. However, some companies may still require you to send the original invoice later too.
Maintaining KUDIR
KUDIR is a book of income and expenses where you enter all income and all expenses in chronological order and on the basis of primary documents that support your income (bank statements, contracts, acts). In the case of the simplified tax system of 6%, it is not necessary to mark expenses, they do not participate in the calculation of the tax in any way, but I still do it for my convenience. If you have a simplified tax system of 15%, then you must mark expenses, otherwise you will not be able to calculate the tax.
Previously, KUDIR had to be certified by the tax authorities, but we are lucky and since 2013 this is not required. KUDIR can be maintained on paper or electronically, as you wish, but I am for modern methods. At the end of the tax period (for the simplified tax system a calendar year), the book is printed and stitched, and a new book is opened in the new period. You can download the KUDIR form here.
Stitching is actually not necessary, just like printing. Now, if there is a tax audit, then it will be possible to do this, so why translate the paper once again.
Why are primary documents needed?
An important question: are these documents still necessary? Answer: according to the law, yes, but in reality they will only be required during desk audits (the tax office calls individually). That is, in ordinary life you simply store them, keep them in KUDIR, and don’t hand them over anywhere. As far as I understand from the forums, such checks are very rare when it comes to small individual entrepreneurs with the simplified tax system.
Features of accounting policies under the simplified tax system
If an entrepreneur applies a simplified taxation system, then he pays:
If a company’s expenses make up less than 60% of its income, then of the taxable objects provided for by the simplified tax system, it is more profitable for it to switch to accounting with a simplified tax system of 6% (income) in 2019. It should be noted that this tax regime (USN 6%) has several advantages. When calculating the amount of tax to be paid, only the amount of receipts and payments that can reduce the accrued tax is required. But in this case, special attention must be paid to accounting expenses, since tax authorities check them especially meticulously.
And the transition to accounting under the simplified tax system “income” implies the payment of a single tax on your income, which replaces the profit tax, VAT and property tax, but this does not eliminate the need to pay transport tax, land tax and trade tax. Such taxes depend on the availability of vehicles and the land on which the activity is carried out. If the presence of import operations is implied, then VAT is charged.
Financial result of the activities of the municipal unitary enterprise “Kommunalnik” from the provision of services by type of activity, rub.
Table 3
- reduction of the cost item “accrued for wages” (reduction of the unified social tax rate);
- The economically justified tariff does not contain the VAT rate (if the enterprise uses the simplified tax system).
In addition, the enterprise has an additional hidden reserve for income in that when calculating water supply services, the cost item “Payment for water from outside” (purchased water or rental of wells) includes costs in the amount specified in the contracts (i.e. with VAT ), despite the fact that the company does not pay it.
Reducing costs is the most important reserve for optimizing profits, reducing tariffs and, consequently, increasing the competitiveness and financial stability of an enterprise. Many problems of housing and communal services enterprises can be solved by clearly setting goals, analyzing and optimizing internal reserves, which is the most rational way to achieve set goals.
The 2006 reporting year showed that with self-sustaining tariffs, competent management, and the correct choice of accounting tax policy, an enterprise that operated until 01/01/2006 with losses on its main activities that are socially significant can operate profitably.
Cash and accrual method
Typically, accounting is done on an accrual basis (double entry). But for organizations that have switched to simplified accounting, the current legislation allows for the possibility of maintaining it on a cash basis (clause 12 of PBU 9/99 and clause 18 of PBU 10/99). This is convenient because, according to the provisions of Article 346.24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, this method takes into account paid income and expenses that are used when calculating tax. In this way, they are reflected in the book of income and expenses, which, when simplified, is a mandatory tax register.
The cash method in accounting distorts the real picture of the taxpayer’s economic life, including his financial statements. Thus, accounting is carried out on an accrual basis, and the cash method is left as a method of maintaining tax accounting. But there are still no recommendations for organizing the cash method.
Who can apply the simplified tax system?
Not everyone has the right to apply the simplified tax system. Thus, they cannot apply simplification, in particular:
- organizations with branches;
- organizations and individual entrepreneurs that produce excisable goods;
- organizations in which the share of participation of other organizations is more than 25% (except for contributions from public organizations of disabled people under certain conditions);
- organizations and individual entrepreneurs whose average number of employees exceeds 100 people;
- organizations whose residual value of depreciable fixed assets exceeds 150 million rubles.
In paragraph 3 of Art. 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, you can find a complete list of persons who cannot use the special regime in the form of a simplified version.
Peculiarities of accounting for individual entrepreneurs in a simplified manner
Individual entrepreneurs are luckier than legal entities: they do not have to do accounting. For them, there is a choice among free programs for maintaining accounting for individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system. Federal Law No. 402-FZ exempts individual entrepreneurs from accounting reporting. However, if you want to take into account the facts of economic activity, you can use any convenient rules; no one checks their compliance with the law.
For individual entrepreneurs, only tax accounting is required. It includes primary accounting documents, such as cash registers, an income book (or income and expenses), and tax returns. In addition, you must report to the Federal Tax Service on insurance premiums (if you have hired employees).
Accounting for the receipt of fixed assets in excess of the fund
Methods for accounting for fixed assets received in excess of investments in the authorized capital are not defined by law. To account for income, it is allowed to use account 83, which consolidates information about additional capital. Property is accounted for separately from other fixed assets in the context of objects.
The municipal unitary enterprise received property from the owner in excess of the value stated in the constituent documents. The cost of the property received was 51,000 rubles. After retrofitting with spare parts worth 2,000 rubles, the main asset was put into operation. The accounting of the enterprise reflects the operation:
- The receipt of property was taken into account: Dt 08 Kt 83 in the amount of 51,000 rubles;
- Additional equipment taken into account: Dt 08 Kt 10 in the amount of 2,000 rubles;
- The registration of fixed assets is reflected: Dt 01 Kt 08 in the amount of 53,000 rubles.
On the possibility of changing the amount of additional capital, the corresponding provisions are included in the constituent documents. When returning the property, the value of the additional capital will be reduced.
Simplified accounting forms and forms, relevant in 2019
Bookkeeping on the simplified tax system from scratch usually begins with the questions: what accounting documents should an LLC have under the simplified tax system, what forms and forms of documents to use. Federal Law No. 402-FZ has granted broad powers to economic entities in this area, which the Ministry of Finance regularly confirms. For example, instead of a consignment note, it is convenient to use a universal transfer document (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 21, 2013 No. ММВ-20-3 / [email protected] ). This is what the UPD form, a universal transfer document, looks like:
Basic rules for primary and accounting and tax accounting registers:
- Only events that took place are recorded; the law specifically stipulates liability for records of imaginary transactions.
- All forms are approved in the accounting policy of the organization.
- The documents for which the Federal Tax Service has developed an electronic format have an established structure, but differences in appearance are allowed and have an expanded set of indicators.
- Some primary documents are unified (cash, bank). In addition, accounting, for example, in a travel agency or concert box office in a simplified manner, encounters ticket forms, in laboratories or research centers - with centralized forms of reports and protocols, etc. There are no unified registers.
Accounting for fixed assets in municipal unitary enterprises
The property is classified as depreciable fixed assets (clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). To account for fixed assets, the enterprise issues an accounting card No. OS-6. The register indicates the initial cost, group and rate of depreciation, period of use, date of registration. Depreciation in MUP is accrued according to standard accounting rules - monthly, reflected in a separate account. The amount is included in the taxation of the enterprise to reduce the base.
The owner of the property may not establish the value of the property in the transfer deed. Enterprises have the right to register in an amount corresponding to the market value (clause 10 of PBU 6/01). Obtaining data is possible after the assessment. Read also the article: → “Accounting for fixed assets” (PBU 6/01).”
Enterprises have the right to construct a fixed asset at their own expense, using their own funds. After acceptance of the fixed asset, the object is transferred to the municipality (the owner of the municipal unitary enterprise). Expenses incurred during the construction process are not taken into account for tax purposes (Clause 16, Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Financial statements of an organization using the simplified tax system in 2020: document forms
The LLC accountant's calendar on the simplified tax system for 2020 includes only annual reporting. This is not required from the individual entrepreneur either. Interim reports (monthly, quarterly) are relevant only if they are specified in the accounting policy.
The deadline for submitting annual reports is March 31. Composition - only the balance sheet and financial statements with attachments. In case of significant deviations from industry averages or losses over several years, tax authorities have the right to demand explanations for the balance sheet. The form is paper or electronic, not unified. The recommended format for submitting financial statements in electronic form is approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 20, 2017 No. ММВ-7-6/ [email protected] Place of submission - Federal Tax Service and Rosstat.
This is what the form of simplified annual financial statements looks like, which small businesses submit to the simplified tax system.
In recent years, the number of reports to other departments has increased significantly: SZV-M reports must be submitted monthly to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, and personal income tax declarations must be submitted quarterly. In this regard, although small businesses are allowed to conduct accounting in a simplified form, the total volume of accounting work has not become smaller, and the cost of outsourcing accounting services in an LLC using the simplified tax system does not decrease.
Who is entitled to keep simplified records and who is not?
Let us immediately note that there is no desire to keep records in the book of income and expenses of organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified taxation system (hereinafter referred to as the book of accounting under the simplified tax system), the form of which is established by the resolution of the Ministry of Taxes, the Ministry of Finance, the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection and the Ministry of Statistics of April 19, 2007 No. 55/60/59/38 “On establishing the form of a book for recording income and expenses of organizations and individual entrepreneurs using a simplified taxation system, and on some issues of filling it out” is not enough. To carry out accounting in the accounting book under the simplified tax system, an organization must comply with the requirements of Article 291 of the Tax Code, namely:
a) have an average number of employees for the period from the beginning of the year to the reporting period inclusive of no more than 15 people and an accrual amount of gross revenue from the beginning of the year of no more than 410,000 rubles. (Part one of paragraph 1 of Article 291 of the Tax Code). During the year, the above criteria should be monitored, since if they are exceeded, you will have to switch to accounting from the month following the reporting period in which such an excess occurred (part six of paragraph 1 of Article 291 of the Tax Code);
b) not exceed in 2020 the criteria for the number and gross revenue specified in paragraph “a” (part six of paragraph 1 of Article 291 of the Tax Code). Please note that part six of paragraph 1 of Article 291 of the Tax Code does not stipulate what tax system the organization switching to the simplified tax system should have applied in the previous year. This means that both the organization that applied the simplified tax system in 2020 and the organization that applied the general taxation procedure in 2020 must check themselves for compliance with the criteria for headcount and gross revenue for the purpose of applying the simplified tax system. It must be said that such a rule was introduced into Article 291 of the Tax Code on January 1, 2020, and previously, organizations moving from the general procedure to the simplified tax system, in order to keep records in the accounting book under the simplified tax system, did not need to analyze whether they fit into the criteria for the number of employees and by gross revenue;
Example
Situation 1. LLC (number of employees - 13 people) in 2016 used the simplified tax system with accounting. Gross revenue for 2020 amounted to RUB 500,000. From January 1, 2017, this organization does not have the right to switch to keeping records in the accounting book under the simplified tax system.
Situation 2. A private enterprise (number of employees - 8 people) in 2020 applied the general taxation procedure and received gross revenue in the amount of 430,000 rubles for the year. From January 1, 2020, the company switched to the simplified tax system and is required to continue maintaining accounting records.
If in 2020 LLCs and private unitary enterprises do not exceed the criteria for maintaining an accounting book under the simplified tax system, then these enterprises will have the right to switch to keeping records in the accounting book under the simplified tax system from January 1, 2018.
c) not be:
- a business company in respect of which Belarus and (or) its administrative-territorial unit, having shares (shares in authorized funds) or in another manner that does not contradict the law, can determine the decisions made by this business company;
- an organization implementing investment projects in accordance with investment agreements concluded with Belarus.
And I would like to draw your attention to one more important point: switching to keeping records in the accounting book under the simplified tax system is possible only from January 1 (part one of paragraph 1 of Article 291 of the Tax Code). By the way, there is no need to report the decision to switch from January 1, 2020 to keeping records in the accounting book under the simplified tax system in the Internal Revenue Service: this information is reflected in the tax return (calculation) for tax under the simplified tax system in line 9 “Procedure for keeping records by organizations” of section III “Others” intelligence".
About the advantages of a book over accounting
In the table below, we have systematized the main differences between two types of accounting: accounting and accounting in the accounting book under the simplified tax system, which will help the accountant make an informed choice of one or another accounting system.
| No. | Index | Type of accounting under the simplified tax system | A comment | |
| accounting | accounting in the accounting book under the simplified tax system | |||
| 1 | Method for determining revenue | According to the accrual principle, that is, on the date of shipment of goods, performance of work, provision of services, transfer of property rights (part two of paragraph 2 of Article 288 of the Tax Code) | According to the principle of payment, that is, as payment is made for goods shipped, work performed, services rendered, transferred property rights (part two of paragraph 2 of Article 288 of the Tax Code) | When non-payments from partners increase, it is beneficial to use the “on payment” method of determining revenue. If the revenue is received, there is a tax; if it is not received, there is none. True, VAT payers, when keeping records in the book, must remember that the moment of sale is the day the money is received, but no later than 60 days from the date of shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights (part one of paragraph 1 of Article 921 of the Tax Code) |
| 2 | Accounting policy of the organization | Formation of accounting policies in accordance with Article 9 of Law No. 57-Z dated July 12, 2013 “On Accounting and Reporting” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 57-Z). The accounting policy of the organization in accordance with paragraph 4 of Article 9 of Law No. 57-Z includes: ● types of accounting valuation used by the organization; ● chart of accounts for the organization's accounting; | Formation of accounting policies in accordance with part three of paragraph 2 of Article 291 of the Tax Code. The accounting policy reflects only tax aspects in cases where the Tax Code provides for the option of accounting for indicators that form the tax base for a particular tax | When keeping records in the accounting book under the simplified tax system, it is mainly VAT payers who encounter variations in the accounting of indicators, so the formation of an accounting policy is important for them. Some organizations that keep records in the accounting book under the simplified tax system may, in their accounting policies, determine the date of shipment of goods, performance of work, provision of services (parts six and ten of paragraph 5 of Article 288 of the Tax Code). In addition, organizations conducting accounting, as a rule, submit accounting policies to the Tax Inspectorate along with annual reports, but organizations maintaining records in the accounting book under the simplified tax system do not. |
| ● forms of primary accounting documents developed by the organization; ● the procedure for conducting an inventory of the organization’s assets and liabilities; ● other methods of organizing and maintaining accounting | ||||
| 3 | Annual financial statements | Paragraph 1 of Article 14 of Law No. 57-Z establishes the obligation to prepare annual reports, which are submitted to the Tax Inspectorate no later than March 31 of the year following the reporting year (subclause 1.4 of Article 22 of the Tax Code) | Preparation of annual reports is not required by law | The absence of the obligation for organizations keeping records in the accounting book under the simplified tax system to prepare and submit annual reports to the tax authorities significantly simplifies the work of an accountant |
| 4 | Cash book | It is required (part one of paragraph 50 of the Instruction on the procedure for conducting cash transactions and the procedure for cash settlements in Belarusian rubles on the territory of the Republic of Belarus, approved by Resolution of the Board of the National Bank of March 29, 2011 No. 107; hereinafter - Instruction No. 107) | May not be carried out when the appropriate decision is made by the management of the organization (part two of paragraph 50 of Instruction No. 107) | Maintaining a cash book during accounting obliges organizations to use receipts (for posting money to the enterprise's cash register) and expenditure (when issuing money from the enterprise's cash register) orders in their activities, which increases the document flow in the enterprise. The ability not to maintain a cash book greatly facilitates the work of an accountant when maintaining records in the accounting book under the simplified tax system. |
| 5 | Qualification requirements for chief accountant | The chief accountant must meet the requirements established by paragraph 3 of Article 8 of Law No. 57-Z | There are no requirements for the chief accountant by law | Organizations that keep records in the accounting book under the simplified tax system have the right to hire a specialist to the position of chief accountant who does not meet the requirements of paragraph 3 of Article 8 of Law No. 57-Z (for example, this may be the founder of a private unitary enterprise without special accounting education) |
| 6 | Accounting objects | All assets and liabilities are subject to accounting in accordance with Law No. 57-Z | Accounting objects are listed in paragraph 1 of Article 291 of the Tax Code, and among them there are no such things as, for example, goods, finished products, raw materials and materials | The need for maintaining and the form of accounting for certain objects not mentioned in paragraph 1 of Article 291 of the Tax Code is determined independently by the organization keeping records in the accounting book under the simplified tax system, which greatly simplifies accounting |
Zhanna Dibrova, economist
Procedure for applying the simplified tax system: regulatory framework
The main regulatory document regulating the procedure for applying the simplified tax system is the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It is in its provisions that the basic rules and restrictions for simplified taxation system officers are recorded. In addition, the activities of the simplified taxation system officer are regulated by relevant laws, orders of ministries and departments, as well as letters and explanations of individual situations. More details in the table below.
| No. | Regulatory document | Description |
| 1 | NK chapter 26.2 | All the main provisions concerning the mechanism of transition to the simplified tax system are described in the Tax Code (Chapter 26.2). This document also sets out the procedure for accounting for income/expenses, the tax calculation scheme, features of registration and submission of reports, etc. |
| 2 | FZ-401 dated 11/30/16 | The regulatory act fixes an increase in the income limits allowed for simplified taxation system officers, and also increases the residual value of the operating system both for the transition to the “simplified system” and for maintaining the regime. |
| 3 | Order No. 698 dated 03.11.16 | A regulatory document issued by the Ministry of Economic Development fixes the coefficient for calculating the simplified tax system (deflator) for 2017. |
| 4 | Federal Law-248 dated 07/03/16 | The law regulates the use of codes for classifying products and activities within the framework of tax regimes, including the simplified tax system. |
| 5 | Order No. 2469-r dated November 24, 2016 | According to the regulatory document, new classifiers have been introduced to determine the group of household services, which will allow tax authorities to apply tax benefits. |
| 6 | Letters from the Ministry of Finance with explanations | Additional information regarding the clarification of certain aspects of the application of the simplified tax system is described in letters from the Ministry of Finance. In particular, letter No. 06-04-11/01/49770 explains the procedure for applying the BCC for the “STS 15%” scheme. Letter No. GD-4-3/12023 dated June 24, 2014 describes the mechanism for terminating activities within the framework of the simplified tax system. |
How to switch from simplified tax system to another mode
As a general rule, you can change the simplified tax system to another tax regime only at the end of the year. If you decide to renounce your status as a simplified tax system officer in 2020, then you need to submit notification 26.2-3 by December 31, 2017, where you indicate the new tax regime. In this case, the regime change will take place from 01/01/18.
An alternative option for changing the simplified tax system is the loss of the status of the simplified tax system operator due to violation of the requirements for the payer. For example, if in Q3. 2020 You exceeded the income limit, then in the same period you are recognized as an OSNO taxpayer. The transition occurs automatically; there is no need to submit any notifications to the Federal Tax Service.
If, in addition to the simplified tax system, you are planning activities within the framework of UTII, then you have the right to combine both tax regimes from the moment the UTII activity arises. At the same time, do not forget to fill out the appropriate notification and submit it to the Federal Tax Service (UTII-1 for legal entities or UTII-2 for individual entrepreneurs).