Business trip on a weekend - features
Current legislation establishes that a business trip is a trip by a company employee to an area determined by the company’s management to achieve the goals and objectives set for him.
Depending on them, the duration of a business trip can take a fairly significant period of time.
It may include weekends and holidays. Please note: in most cases, weekend travel dates fall at the beginning or end of a business trip. The legislation establishes that these days must be agreed upon with the management of the company and formalized accordingly.
An employee goes on a day off
In practice, a situation often occurs when an employee on a business trip must begin completing the task assigned to him by management at the beginning of the week.
Therefore, in order to be at the destination on time, he must go on a trip on a day off. The legal requirements are such that management must give permission for this, and the employee must agree to start work on a day off.
To do this, these days must be reflected in the order for the business trip so that the employee takes advantage of the existing guarantee - appropriate payment or a day of rest. The employee must provide his consent to go on a business trip on a day off in writing.
Attention: the business trip order must accurately record the days that fall on weekends, and, if necessary, the hours. This must be done so that the employee can correctly pay for travel expenses, payroll, etc.
For example, in order to be on time at the destination on Monday, an employee needs to fly out of his city at 23-30 on Sunday. To be at the airport by this time, the employee must leave home at 22-00.
In order for an employee sent on a business trip to have their salary calculated correctly for two hours of work on Sunday, it is necessary to record that this person is going on a business trip on Sunday at 22-00.
Important: if you do not do this, but simply indicate that the business trip begins on Sunday, the employee will have to pay for the entire day.
Do not forget that the company employee chooses the type of compensation for working on weekends independently. He can request either double payment for this period or the provision of any day of rest for him.
It is important to remember that daily allowances on weekends are paid in full. They should not be recalculated taking into account the time worked.
Attention: the situation may turn out to be such that an employee goes on a business trip without permission on a day off. Then the administration can pay him for this day in a single amount as a simple working day.
Day off during a business trip
A business trip may cover a long period of time, which includes weekends. For example, an employee went on a business trip to Central Asia and returned the following Tuesday. During his business trip, he has days off.
In this case, payment is made only if the employee performs the official tasks assigned to him on the specified weekends.
Just as in the previous case, the involvement of an employee in work must be provided for by order of the manager. Also, the administration must agree with the employee, obtaining his consent.
Attention: if the documents confirming the trip do not indicate that the employee must perform his duties on a day off, then there is no need to pay for them.
In this case, only daily allowances for business trips in 2020 are required to be paid. Their size must be fixed in the internal documents of the organization.
For the purpose of calculating income tax, the daily allowance should not exceed 700 rubles if traveling within Russia, and 2,500 rubles if traveling outside the country.
Attention: in addition, when traveling on a business trip, travel expenses for travel, accommodation and other allowable expenses must be compensated.
Returns on the day off
If the day an employee returns from a business trip falls on a weekend or holiday, then such a day must be taken into account in the same way as departure on a weekend.
Thus, if an order was issued in advance, according to which work on a day off should be carried out only for the hours actually worked during which the trip occurred, then payment should be made only for them. If there was no such order, then you will have to pay in full for the whole day.
Attention: the procedure for paying for days off must be determined in advance and carried out on the basis of a previously issued order.
What if an employee himself wants to leave early on a day off?
The law stipulates that the employee and the administration must agree on the start and end days of a business trip. After this, they must be secured by issuing a travel order in T-9 format.
However, a situation may arise when an employee, on his own initiative, wants to go on a business trip on a day off in order to start work in a new place on Monday.
Attention: the law establishes that the day of the start of the trip will be considered the day indicated in travel documents, receipts for housing, etc. Therefore, you cannot simply ignore this. But in order not to pay for these days as work on a day off, in the report card they are o instead of “RV”.
The employee remains on vacation at the place of business trip
- Lawyer consultation
- Articles
If the cost of a ticket is recognized as employee income, insurance premiums and income tax are charged. Amounts related to travel expenses are subject to VAT deduction. Free transfers (up to RUB 4,000) are not subject to insurance premiums.
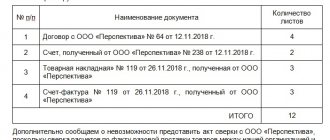
per year), formalized by a gift agreement. Example: Manager N.I. Kulikova was on a business trip from June 14 to June 24, 2020 in Krasnoyarsk.
Upon completion of work, with the consent of management, she stayed for paid leave for:
- 2 days (weekend, June 25-26);
- 20 days (from June 25 to August 15).
Upon returning, Nadezhda Ivanovna provided an advance report. The cost of a round-trip ticket was 10,000 rubles (excluding VAT). Do I need to withhold personal income tax and in what amount? Solution:
- Since the employee stays for a short period of time on weekends, the organization must reimburse travel costs.
Financiers do not give a clear answer, arguing that if an employee returns from a business trip later than the established date specified in the business trip order, payment for his travel in some cases cannot be considered as compensation for expenses associated with a business trip. As a criterion for assessing the targeted nature of travel expenses from a business trip, it is proposed to use the length of the period of time for which the employee stayed at the place of business trip.
In particular, if the period of stay at the place of business trip significantly exceeds the period established by the order on the business trip (for example, if immediately after the end of the business trip the employee is granted leave, which he spends at the place of business trip), the employee receives economic benefits provided for in Art.
Payment for travel: business trip or personal interest
In particular, if the period of stay at the place of business trip significantly exceeds the period established by the order on the business trip (for example, if immediately after the end of the business trip the employee is granted leave, which he spends at the place of business trip), the employee receives economic benefits provided for in Article 41 Code, in the form of payment by the organization for travel from the place of free time from work to the place of work. In this case, payment by the organization for the employee of a return ticket with an arrival date later than the end of the business trip specified in the business trip order, in accordance with subparagraph 1 of paragraph 2 of Article 211 Code is recognized as his income received in kind.
As noted in the report card
Under normal conditions, in order to mark work on a business trip on a day off on a time sheet, the letter code “РВ” or the numeric code “03” is used.
If going on a business trip on a day off is not a production necessity, but the desire of the employee himself, then this day is marked in the timesheet using the letter code “K”, without using the code “RW” (work on a day off).
This step allows you to pay for these days not at double the rate, as would be required by law, but at single rate, based on average earnings.
Is time off provided for a business trip - what does the law say?
In general, in the Labor Code there is no such thing as “time off”. But in practice, many employers and employees encounter it. Time off means an additional day off, which is provided to employees of an enterprise for overtime.
Moreover, if the employee’s working time falls on an employee’s day off, then he can receive compensation from his superiors in two formats:
- increased wages for this period;
- provision of additional days off - time off.
However, such compensation for a business trip can only be provided if the person actually worked on a day off.
In short: time off is usually provided for business trips on weekends. That is, the person had to work on his day off. Moreover, at this time he can only be on his way to the place of business trip or, conversely, returning from a business trip.
To receive time off, you will need to follow a work schedule during your business trip. Only then can you choose the format of your own compensation. Moreover, the right to choose remains with the employee himself (Article 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
How is a business trip paid on a day off?
If an employee is on a business trip for a long time, some days will necessarily fall on weekends. However, payment for them is calculated based on what part of the trip they occurred.
If an employee comes to an organization and its work schedule is built according to a standard scheme with two days off, then there is no need to pay for these days. But there is an exception to this rule - if a visitor needs to carry out his duties on a day off, even though he is not a worker.
But in this situation, the personnel department of the receiving party must issue an appropriate order, and a copy of it is handed over to the traveler.
After the employee returns to his permanent place of work, he transfers this order to his accounting department, and there, based on it, payment is made for days off on a business trip. This can be done in two ways, enshrined in the law - pay twice the amount, or pay once with the provision of additional rest.
Attention: if weekends fall on the days of departure or return, they are always considered working days, and the company must act according to the standard scheme for this case.
Are there days off after a business trip?
In accordance with Law 76-FZ “On the status of military personnel” dated May 27, 1998, military personnel undergoing military service on conscription, as well as military personnel undergoing military service under a contract in military professional educational organizations and military educational organizations of higher education, formations and military units of permanent readiness and training military units are provided with at least one day of rest weekly. The rest of the military personnel performing military service under a contract are provided with at least one day of rest weekly, but not less than six days of rest per month.
This means that weekends are not necessarily Saturday and Sunday. It all depends on the documents approved by the organization. In our situation, this means that the weekends of the sending organization may well not coincide with the weekends of the receiving organization. What regime should a business traveler follow?
Is it possible to make up for a lost day off?
If an employee worked on a business trip on a day off, and during this day he performed his duties, then the administration must provide compensation for this day. The law specifies that this can be done in two ways.
In the first option, the employee is paid for a given day at a double rate.
If you choose the second option, then for a given day he will be charged a simple payment, as for a normal working day. However, he must still be given an additional day off at the employee’s discretion.
In order to confirm your choice, after returning from the trip you must fill out an application addressed to your manager. It must indicate the day that the employee wants to receive as an additional day off for work on a business trip.
As soon as the application is signed, the personnel service formalizes the specified day as a day off by issuing an order.
Attention: in addition, the company in internal documents (for example, Regulations on Business Travel) may indicate other methods of payment or compensation for a lost day of rest. However, the law determines that the new conditions must be at least no worse than those proposed by the Labor Code.
Should I have a day off after a business trip?
If no work activity was actually carried out, a standard mark is affixed. There is no payment for this day, but the person will be able to receive daily allowance and accommodation compensation. Time Off During Business Travel There is no provision in the law regarding the provision of time off during travel to perform an organizational assignment.
Representatives of interested parties from the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Labor of Russia objected to the satisfaction of the citizen’s demands. In court, they explained that the provisions of the contested regulatory legal act do not contradict the current legislation of the Russian Federation and do not violate the rights of workers sent on business trips.
Situation 1. An employee goes on a business trip using personal transport
A typical situation often arises in small and medium-sized companies that use OSNO or simplified tax system. Main questions:
- whether organizations have the right to take into account the actual costs of fuel and lubricants in expenses for income tax or tax under the simplified tax system or only within the limits of the standard;
- which document in the latter case regulates the standard;
- Are such payments subject to personal income tax?
Decision
An employer, when sending an employee on a business trip, is obliged to compensate him for business trip expenses, in particular, for travel to the place of business trip and back (clause 12, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, expenses for compensation for the use of personal cars for business trips are accepted within the limits established by the Government of the Russian Federation (clause 11, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).