About unconfirmed expenses
If the papers were still present, but were lost, then it is possible to reimburse expenses, but only under the following conditions: if the agreement (collective, on business trips, etc.) provides for reimbursement or compensation (corresponding to the legislation of the country, in this case the Russian Federation), when the employee , lives or lived without documents that would confirm housing expenses. In 2020, you will need to pay additional insurance premiums.
Comparison: with and without documents
If there are documents:
If the employee (taxpayer) provides the employer with all the necessary documents for housing expenses, then he pays the employee everything except the daily allowance. For example: in one day, he can pay an employee located within the country no more than 700 rubles, and outside the country no more than 2,500 rubles per day in 2020. Plus expenses for travel and other services, including for renting residential premises (paid baggage allowance, communication services and similar secondary expenses).
If there are no supporting documents:
If the employee (taxpayer) does not submit papers confirming the expenses for housing, since there are none, then the amounts of all the above payments for accommodation without supporting documents on a business trip are immediately exempt from any taxation. The rest remains the same: within the country, the employer can pay no more than 700 rubles, and outside the country no more than 2,500 rubles per day in 2020. But you can hardly expect money for additional expenses, but sometimes you can.
Here you can clearly see that only the payment for the conditions of being on a business trip changes.
Business trip and daily allowance standards
The term “daily allowance” is given in Art. 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which establishes legal standards for reimbursement of travel allowances to employees. Daily allowances are mentioned in Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 3, as one of the compensation payments not subject to personal income tax.
Limits have been established for tax purposes: expenses within the country - 700 rubles. per day, and for foreign business trips – 2500 rubles. per day. The lower limit of daily allowance is stated in government decree No. 729 dated 02/10/2002 and is 100 rubles. per day in Russia. The document concerns employees of state budgetary institutions, however, commercial structures should also be guided by this lower limit in payments - a deterioration in the position of an employee of a private company, compared to a government agency, may provoke an inspection by Rostrud or a lawsuit against a commercial company.
For employees of government agencies going abroad, daily allowances are calculated according to the norms of Resolution No. 812 of December 26, 2005 and are calculated in foreign currency.
Important! The basic general principles and requirements for calculating daily allowances are set out in government document No. 749 dated 13/10/2008.
The company must develop and adopt a local RA for business trips or take into account all the nuances of the procedure and amount of reimbursement of daily expenses to an employee in the collective agreement. A state institution or municipal institution must be guided by the regulations of the authorities at the appropriate level.
In the LNA, the daily allowance can be specified in any amount, but if it exceeds the maximum norms, the difference is subject to personal income tax. In excess of the established limits, daily allowances and insurance contributions are subject to (Article 422-2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Contributions “for injuries” are considered in connection with daily allowances according to the rules of Federal Law-125 of July 24, 1998, Art. 20.2-2. Contributions are not subject to all amounts provided for by the employer's LNA.
In practice, when establishing daily allowance standards, employers often take as a basis the maximum limits specified in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation regarding personal income tax in order to minimize the difference between accounting and tax accounting, the number of accounting errors and problems with the tax authorities.
The employer may not take one-day business trips around Russia into account when calculating daily allowance. At the same time, it is quite possible to register something like this in the LNA and compensate the employee for even one day.
Note that the issue of withholding personal income tax from the amount of such a one-day payment is controversial:
- The Ministry of Finance believes that it is illegal to tax income, for example, food expenses in the range of 700 and 2500 rubles, respectively (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 03-04-07/6189 dated 01/03/13).
- The Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation believes that daily allowances are not the employee’s income and should be compensated to him without personal income tax (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court No. 4357/12 of 09/11/12).
- Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation, guided by Art. 122, 123 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, may charge the employee, in addition to tax, a fine and penalties for the “extra” paid day.
The choice of what to do is left to the taxpayer.
If an employee goes abroad, he must be compensated for a one-day trip in the amount of 50% of the daily payment amount established by the company (Post. 749, clause 20). When calculating income tax or “simplified” tax, daily allowance expenses are taken to reduce the base in full (Article 264-1-12, 346.16-1-13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the LNA establishes the calculation of daily allowances for foreign business trips in foreign currency, when calculating the tax base, a recalculation is made at the rate on the date of recognition of the expense (Article 272-10 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), i.e. approval of the advance report (clause 7, paragraph 5 of the same article).
When leaving on a business trip, the employee’s daily allowance is advanced: it is calculated in advance and issued. The planned number of business trip days is taken by the accountant from the organization’s order. Upon return, the daily allowance is recalculated depending on the actual duration of the business trip and either additional payment is made to the employee, or they are put on mutual settlements with the subsequent deduction of the overpaid amount.
Days are counted according to the calendar, from the day of departure until arrival at the place of permanent work, including weekends and holidays. The day is taken up to 0 o'clock, i.e. from zero hours it is considered that a new business trip day has begun. For each day, a full payment is issued, without proportional calculations by hour.
If a citizen returns from a business trip on the same day and is simultaneously sent on another business trip, he must receive the daily allowance twice. If an employee travels abroad, he is paid a “Russian” daily allowance until the day he crosses the border with Russia, after which the “foreign” standards established by the company are applied, and upon return they do the same. The moment of crossing can be tracked in the international passport or, if we are talking about the CIS, where crossing the border does not require such marks, using travel documents.
Local NAs may specify different daily allowances for different countries visited by the business traveler. If a business trip involves traveling to several foreign countries, the daily allowance is calculated based on the end of the day and the country visited.
Attention! An employee who, according to the terms of the employment contract, constantly performs his duties on the road or has a traveling nature of work, is not recognized as a business traveler and is not paid daily allowances.
Lack of documents for renting housing from private individuals
Documentation
Renting an apartment, room from a private person or living together with him also requires a written agreement (document), which must indicate: rental payment (cost), term (for which it is rented), responsibilities and various rights of the landlord. And to conclude an agreement, you only need the passport of both persons.
It is highly recommended to check all the landlord’s documents and make sure that this is his apartment or room, ask for an extract and a document on ownership rights. Problems with all this should not arise if the landlord turns out to be a conscientious person, and even if this is not the first time he is renting out an apartment, then he is already accustomed to such questions and requests and this is normal for him.
Accountants who represent the organization in which the person taking the hire works want him to be sure to issue all powers of attorney to conclude an agreement in the name of that very organization. But more often than not, this is not necessary. If there is an order specific to this topic from the director of this company, which states why, where and for what purpose the employee went, for what job, etc., and a housing rental agreement, which is given for a certain time (how long it is valid given order), the accountant will not have any claims against you.
Lack of documents for hotel accommodation
Documentation
We sorted out the rental of housing, but what happens if the person who lived in a hotel on a business trip does not bring any documents: no check, no receipt, etc.?
Of course, if the documents were accidentally lost, you can easily request a certificate or any other document that confirms the fact of residence by calling the hotel.
There is one thing that is worth paying attention to - the certificate from the hotel must describe in detail what services the hotel provided, etc., but the company that sent the employee must provide documents that will establish how long the employee was on site, and exactly what hotel he was in.
And then, the tax service may not be very satisfied with some points. To do this, the company should prepare for unforeseen disputes, because it can win the dispute.
Payment
Be sure to request payment for all services provided at the place of residence, that is, at the hotel. By call or other means.
VAT
If the costs of renting housing will reduce taxable profit, deduct the input VAT on them from the budget (clause 7 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Situation: what documents should be used to confirm the right to deduct VAT on expenses related to an employee’s accommodation during a business trip?
The right to deduct VAT on an employee’s living expenses during a business trip can be confirmed:
- a strict reporting form (the form must be drawn up in accordance with the requirements of the Regulations approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of May 6, 2008 No. 359);
- an invoice, to which is attached a document confirming payment for services (for example, a cash receipt).
This conclusion can be drawn from the provisions of paragraph 7 of Article 171 and paragraph 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as well as paragraph 18 of Section II of Appendix 4 to Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137.
The tax amount in these documents must be highlighted on a separate line. And the invoice is issued in the name of the organization that sent the employee on a business trip (for this you must present a power of attorney).
A similar point of view is shared by the Russian Ministry of Finance in letters dated February 25, 2020 No. 03-07-11/9440, dated July 19, 2013 No. 03-07-11/28554, dated November 21, 2012 No. 03-07-11 /502, etc.
Advice: there are arguments that allow organizations to deduct VAT even in the absence of an invoice or strict reporting forms. They are as follows.
Arbitration courts recognize the legality of a VAT tax deduction on the basis of other documents (in addition to invoices and strict reporting forms) confirming living expenses. The main thing is that from the documents submitted by the employee it is clear that the amount of tax is included in the cost of services and paid (clause 7 of Article 171, clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For example, the basis for deducting VAT may be:
- a strict reporting form with an unallocated amount of VAT (see, for example, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated January 13, 2005 No. F09-5754/04AK);
- another document (for example, an invoice for payment of hotel services in an unspecified form) both with and without highlighting the VAT amount in a separate line (see, for example, resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated July 26, 2011 No. KA-A40/6657 -11, Volga District dated February 7, 2008 No. A57-597/07, Central District dated June 21, 2004 No. A62-1547/03, dated May 25, 2007 No. A48-2510/06-8, East Siberian District dated November 20, 2007 No. A33-9940/06-F02-8607/07, West Siberian District dated February 7, 2006 No. F04-133/2006(19416-A45-27)).
But if the organization does not intend to sue, use a non-cash form of payment with the hotel. In this case, the hotel is obliged to issue an invoice to the organization for the services provided (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Then there should be no problems with VAT reimbursement (clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
An example of how expenses for renting housing during a business trip are reflected in accounting and taxation. The hotel invoice has a VAT amount allocated. The organization applies a general taxation system
General Director of Alpha LLC A.V. Lvov returned from a business trip. The duration of the trip was 4 days (from February 9 to 12). On February 13, the advance report was approved.
Along with the expense report, Lvov submitted documents to the accounting department that confirmed his expenses. They include a hotel bill (strict reporting form) in the amount of 5,310 rubles. The invoice indicates that the cost of services includes VAT at a rate of 18 percent in the amount of 810 rubles.
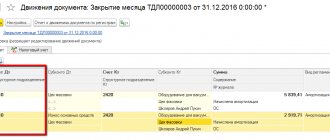
Alpha's accountant made the following entries in accounting:
Debit 26 Credit 71 – 4500 rub. (5310 rubles – 810 rubles) – expenses for hotel accommodation in Lviv are written off;
Debit 19 Credit 71 – 810 rub. – VAT is allocated from the cost of hotel accommodation services;
Debit 68 subaccount “Calculations for VAT” Credit 19 – 810 rub. – accepted for VAT deduction based on the hotel invoice.
When calculating income tax for February, Alpha's accountant included 4,500 rubles in expenses.
An example of how expenses for renting housing during a business trip are reflected in accounting and taxation. The hotel invoice does not include VAT. The organization applies a general taxation system
General Director of Alpha LLC A.V. Lvov returned from a business trip. The duration of the trip was 4 days (from February 9 to 12). On February 13, the advance report was approved.
Along with the expense report, Lvov submitted documents to the accounting department that confirmed his expenses. They include a hotel bill (strict reporting form) in the amount of 5,310 rubles. The invoice states that the cost of services includes VAT at a rate of 18 percent. The VAT amount is not allocated.
The following entry was made in the organization's accounting records:
Debit 26 Credit 71 – 5310 rub. – Lvov’s expenses for hotel accommodation were written off.
To determine the cost of services, which reduces taxable profit, the Alpha accountant allocated the amount of VAT by calculation: 5310 rubles. × 18/118 = 810 rub.
When calculating income tax, expenses for hotel services are taken into account in the amount of 4,500 rubles. (5310 rub. – 810 rub.).
The organization’s accounting reflects a permanent tax liability:
Debit 99 subaccount “Continuous tax liabilities” Credit 68 subaccount “Calculations for income tax” - 162 rubles. (RUB 810 × 20%) – reflects a permanent tax liability on housing rental expenses that do not reduce taxable profit.
On the possibility of including in the calculation of taxable profit the amount of VAT (its equivalent) paid to foreign counterparties under the laws of other states, see How to take into account other expenses associated with production and sales when calculating income tax.
About accommodation services provided by the company itself
It may be that business trips from the company are always assigned to the same place, and for this the company rents an entire apartment building or separate, multi-room apartments.
In this case, the company itself pays for all accommodation, but the following question may arise: does the organization take into account all taxes for the costs and profits of renting apartments? The answer will be yes, but only for a certain period of actual residence.
If the contract is concluded, for example, for a year, then the period for all employees participating in the business trip, who take turns living in this place, will be 11 months, and the remaining twelfth month will be considered an unreasonable expense of the company.
Advantages of renting an apartment
The issue related to the preparation of reporting documents when renting an apartment on a daily basis is considered important and increasingly popular. The main positive characteristic is not only the ability to obtain the necessary documents, but many other important factors.
Currently, the choice of apartment is carried out not only by employees, but by management. The reason is the elementary cheapness of rent. The reduced cost is based on the absence of the need to pay for third party services.
Hotel rooms can take up a significant portion of a company's budget. This is especially evident when it is necessary to send employees on long business trips. Speaking about savings, it should be noted that this is a direct opportunity to save on food. You don't have to visit restaurants. You can cook your own food.
In addition, the option of daily rental housing provides greater comfort. A person who is on a business trip can choose the most convenient accommodation for him. If you contact specialized companies, you can get an apartment with such advantages as:
- Freshly renovated;
- New modern furniture;
- Installed double glazed windows;
- Equipment with household appliances;
- Availability of a large LCD TV.
Each such rented apartment has a kitchen equipped with the necessary appliances and other equipment. For people who want to feel at home on a business trip, a daily or long-term apartment is an ideal option.