https://youtu.be/kOFPeFRa5MY
Which categories of employees have the right to choose vacation at a time convenient for them?
Family leave
How to take leave outside the established schedule
An employee requests a postponement of vacation - what to do?
Is it possible to recall an employee from unpaid leave?
Extracurricular rest during the period of dismissal of an employee
Is it possible to send an employee on unpaid leave at the initiative of the employer?
What can affect the duration of administrative leave?
Which categories of employees have the right to choose vacation at a time convenient for them?
Not every person has the right to ask for leave at the most favorable period of time for him, but the employer has every right to refuse the employee upon presentation of the latter’s written expression of will regarding the provision of leave outside the vacation schedule. The only exceptions are situations when a citizen belongs to one of the categories provided with special benefits.
This type of worker includes:
- Minor citizens engaged in labor activities (Article 267 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Women before going on leave in connection with pregnancy and childbirth or upon leaving it (Article 260 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Police officers who did not use days of paid rest time within the time period established by the schedule (Article 57 of the Law “On Service in the Internal Affairs Bodies of the Russian Federation” dated November 30, 2011 No. 342-FZ).
- Spouses of military personnel - they should be given rest time (on their initiative) at the same time as the vacation of the military themselves (Article 11 of the Law “On the Status of Military Personnel” dated May 27, 1998 No. 76-FZ).
- Citizens who were exposed to radiation due to the Chernobyl accident, and liquidators of the consequences of this disaster (Article 14 of the Law “On the social protection of citizens exposed to radiation due to the disaster at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant” dated May 15, 1991 No. 1244-1).
- Persons awarded the “Honorary Donor of Russia” badge (Article 23 of the Law “On the Donation of Blood and Its Components” dated July 20, 2012 No. 125-FZ).
- Heroes of Socialist Labor, Heroes of Labor of the Russian Federation and full holders of the Order of Labor Glory (Article 6 of the law “On the provision of social guarantees to Heroes of Socialist Labor, Heroes of Labor of the Russian Federation and full holders of the Order of Labor Glory” dated 01/09/1997 No. 5-FZ).
- Heroes of the Soviet Union, Heroes of the Russian Federation and full holders of the Order of Glory (Article 8 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On the status of Heroes of the Soviet Union, Heroes of the Russian Federation and full holders of the Order of Glory” dated January 15, 1993 No. 4301-1).
- Employees recalled from regular vacation at the initiative of the employer (Article 125 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- One of the parents (guardians, trustees) raising disabled minor children (Article 261.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Persons listed in Art. 14–19 of the Law “On Veterans” dated January 12, 1995 No. 5-FZ:
- disabled war veterans;
- participants of the Great Patriotic War;
- combat veterans;
- military personnel who performed duties in military units, institutions, military educational institutions that were not part of the active army during the period from 06/22/1941 to 09/03/1945, and/or who were awarded USSR awards for service during the named period of time;
- persons awarded the badge “Resident of besieged Leningrad”;
- persons who were engaged in labor activities during the Great Patriotic War at military infrastructure facilities within the rear borders of active fronts, operational zones of active flotillas, front-line sections of railways and highways.
Any violations in providing guarantees to the above-mentioned employees can be legally appealed by them, including in court.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
RAA Law
Employers, taking into account their production and financial capabilities, can independently establish additional leaves for employees, unless otherwise provided by this Code and other federal laws. The procedure and conditions for granting these leaves are determined by collective agreements or local regulations, which are adopted taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization.
In exceptional cases, when the provision of leave to an employee in the current working year may adversely affect the normal course of work of an organization or individual entrepreneur, it is allowed, with the consent of the employee, to transfer the leave to the next working year. In this case, the leave must be used no later than 12 months after the end of the working year for which it is granted.
This is important to know: Transfer of leave at the initiative of the employer
We invite you to read: Leave for family reasons
Application for transfer of leave for family reasons. Employees are provided with annual leave while maintaining their place of work (position) and average earnings. Annual basic paid leave is provided to employees for 28 calendar days. Annual basic paid leave of more than 28 calendar days (extended basic leave) is provided to employees in accordance with this Code and other federal laws.
Annual additional paid leave is provided to employees engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, employees with a special nature of work, employees with irregular working hours, employees working in the Far North and equivalent areas, as well as in other areas. cases provided for by this Code and other federal laws.
Family leave
Based on the content of Art. 128 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, unpaid leave outside the schedule for family reasons, as well as other valid excuses, can be granted to a citizen who has submitted the relevant requirements to the employer and has such a right. In this case, the duration of the provided rest is fixed in an agreement between the parties to labor relations on an individual basis.
According to the method of exercising rights, rest days at one’s own expense are usually divided into two categories (depending on the initiative of the parties):
- leave at the discretion of the employer;
- vacation as an integral guarantee of a working citizen.
Vacation at the discretion of the employer
In Part 1 of Art. 128 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation reflects the right of the head of the company to provide administrative (that is, unpaid) days of rest to an employee based on the latter’s application. However, the wording “may be provided” used in the norm gives the employer complete independence in determining the validity of the reasons for the employee who submitted the corresponding application to go on leave and the duration of such leave. It is also worth noting that today the legislation does not contain an exhaustive list of valid grounds that would allow an employer to consider a received application and make an objective decision on it.
It is also not uncommon for subordinates, when submitting an application, not to indicate the reasons why they require short-term unpaid leave. In such cases, consideration of the issue falls exclusively within the prerogative of the manager, therefore, without violating the law, he has the right here to either make concessions and release the employee without prejudice to the work process, or to refuse leave.
Vacation as an integral guarantee for the employee
The categories of citizens to whom the employer does not have the right to refuse to provide unpaid rest time are strictly regulated by Part 2 of Art. 128 Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- persons who participated in the Great Patriotic War;
- age pensioners who continue to work;
- spouses of military personnel, police officers, firefighters, customs officers, employees of institutions and bodies of the penal system, who died or died due to severe wounds, concussions or injuries received in the course of performing official duties, or due to temporary disability associated with service;
- working disabled people;
- employees due to the birth of children, marriage, death of close relatives.
Along with the presented categories, this list additionally includes:
- citizens combining work with higher and secondary education, as well as citizens entering training at the specified educational levels (Articles 173 and 174 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- citizens caring for children (Article 263 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- persons working part-time (Article 286 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Types of vacations at your own expense
To apply for an additional free break, Art. 128 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for a valid reason related to family circumstances.
These reasons include:
- Illness of a relative. Usually this is the first or second degree of relationship - parents, children, grandparents, but, under certain circumstances, may include brothers and sisters.
- Birth of a child. This includes happy fathers of a family whose families have a new addition.
- Domestic home problems. A break in a water supply or gas pipeline, flooding an apartment with water from the top floor, the need to resolve any other urgent household issues, divorce, establishing custody of a child, division of property, and others like that.
- Death of a loved one. The full list of persons to whom this right applies is usually specified in the company’s collective agreement. It may be wider than provided by law.
- Family troubles. The need to take the child to the clinic, to stay with him at home due to quarantine in kindergarten, school (junior grades), vacation periods, personal preparation for passing the exam, diploma (outside the time allotted by law).
- Getting married. Such an event simply will not happen if one of the parties does not show up. Therefore, here it is not a right, but an obligation of the employer to satisfy such a request.
The application is written in the name of the employer. Indicated from whom. The application form contains information about the provision of free holidays. There must be a clear period and reason. The document is dated and signed by the petitioner.
Articles on the topic (click to view)
- Fine for late payment of vacation pay
- What to do with unused vacation
- What to do if your employer does not pay vacation pay
- How long after employment is vacation allowed?
- Is maternity leave taken into account when calculating pensions?
- Accounting for compensation for unused vacation
- Dismissal while on maternity leave
Remember, the wording “family circumstances” has a fairly wide list of reasons to which it can be applied. The main thing is that this is a valid fact that can be documented in the future.
How to take leave outside the established holiday schedule
If there are grounds for going on vacation and there are circumstances that give the right to grant unpaid after-hours leave, the employee can contact the manager in writing at any time convenient for him. In this case, the justification for the need to provide leave outside the vacation schedule is made in an application at the discretion of the employee.
After signing, the document goes to the manager’s desk. If it is satisfied, the employer must impose a resolution on it and issue an appropriate order.
A sample order can be downloaded from the link below.
In case of refusal, indicate in writing on the document the reasons for your decision and, if possible, offer the employee accessible ways out of the current situation.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Read us on Yandex.Zen Read us on Telegram
Important: the boss does not have the right to refuse to grant a subordinate the required extra-curricular leave in the cases provided for in Part 2 of Art. 128 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, since litigation can be much more expensive than the banal absence of an employee from the workplace.
The final step is to familiarize the employee with the issued order for the provision of leave, which precisely indicates its start and end dates, and the employer’s resolution on it. A mandatory point when resolving the issue of granting leave outside the vacation schedule is to affix the employee’s personal signature on the familiarization sheet (typical for enterprises with a significant number of staff) or directly on the empty space of the order indicating the date.
Read how to create a vacation schedule for 2020 here.
Registration of unscheduled leave
To go on vacation unscheduled, you need to complete several stages of this procedure.
Stage 1 – Receiving an employee’s application for leave.
- The application indicates the start and end dates of the vacation, as well as its duration. If the employee has certain reasons for using leave, in the presence of which the employer cannot refuse to provide it on the specified dates, they must also be provided in the application;
- The application must be registered in a special accounting form designed for registering internal documents, for example in the Employee Statement Register. The application is registered on the day of receipt. The assigned registration number is indicated on the application.
- To make a decision on the merits of the stated request, the application is sent to the head of the organization or other official who has the right to make decisions on granting leave.
- We receive a statement with the manager’s resolution. The resolution of the head of the organization or other authorized official on the application identifies the employee who is tasked with drawing up a draft order for granting leave.
- After the employee responsible for drawing up the draft order for granting leave has familiarized himself with the employee’s application and the employer’s resolution, a mark is placed on the application to send it to the case. It includes the words “For file,” as well as the file number where the document will be stored. The note must be signed and dated by the employee filing the document.
2 – Stage – Issuance of an order to grant leave to an employee unscheduled
- A draft order is being drawn up to grant unscheduled leave.
- The order is signed by the head of the organization or another authorized person.
- The order is registered in a special registration form, for example, in the Journal of Registration of Orders for Granting Leave. The shelf life of the order is 5 years.
- The employee must be familiarized with the order to grant leave against signature.
- An order is sent to the case.
Stage 3 – Drawing up a settlement note.
This document allows you to calculate payments due to an employee during the vacation period. The settlement note is drawn up according to the standardized T-60 form. The form is a double-sided form. On the first side, basic data about the vacation is indicated (dates, start and end of the vacation). On the second side, accounting calculations are made for the due payments.
Stage 4 Registration of a time sheet
The employer is required to keep records of the time actually worked by each employee. For this purpose, a time sheet and calculation of wages is used, which reflects working days, annual paid leave and annual additional paid leave, etc.
Stage 5 Registration of a personal employee card
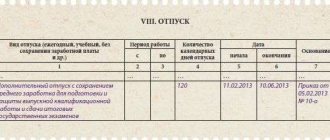
All types of vacations provided to the employee are recorded in section VIII “Vacation” of the employee’s personal card. This section contains information:
- type of leave granted to the employee;
- the period of work for which the leave was granted;
- duration of vacation in calendar days;
- start and end dates of vacation;
- basis (order to grant leave).
Stage 6 – Filling out the vacation schedule.
After the employee is granted leave, the actual dates of its use must be recorded in the schedule. When the actual and planned vacation dates do not coincide, it is necessary to make a note about this in the vacation schedule and indicate the details of the documents according to which the vacation was not granted according to schedule (
An employee requests a postponement of vacation - what to do?
Employee guarantees providing for the right to demand the transfer of the main (paid) rest time to another period of time are reflected in Art. 124 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the provisions of which come into effect in the following situations:
- when the leave coincides with a period when the employee is unable to perform official functions due to illness, pregnancy and childbirth;
- if deductions for the period of annual paid leave are not made in advance or the employee is warned about the beginning of this period less than 3 days or 2 weeks, respectively;
- in case of involving an employee during the vacation period in solving problems of national importance, for the performance of which he was released from work;
- if, due to exceptional reasons, the employer, on his own initiative, but with the consent of the employee, recalls him from the main vacation.
In all other circumstances, the issue of postponing the rest time fixed in the vacation schedule is resolved strictly within the framework of an agreement between the parties. To do this, the employee must write an application for vacation on dates other than those included in the vacation schedule. In this case, the employer satisfies the employee’s stated request solely at its discretion.
A sample employee application for leave is presented below.
Changing the vacation schedule
The vacation schedule is subject to mandatory change if, for some reason, one of the employees received vacation outside the established vacation schedule. The change occurs as follows:
- first, based on the employee’s application and the order of the head of the organization, a change is made to the schedule regarding the period of time in which the employee will use his leave;
- after changes have been made to the schedule regarding the calendar period of time, it is necessary to approve it by re-signing such a schedule;
- as measures to approve a new vacation schedule, a new certification of the drawn up schedule should be considered in the form of affixing the signature of the head of the organization and his personal seal with the signature “I approve.” The issuance of a new order to approve the changes made is not required.
Dear readers, each case is individual. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, call:
Or on the website. It's fast and free!
The legislation does not provide for a unified sample application for changing the vacation schedule, however, in practice, a list of data required to indicate has been developed:
- Full name, employee position;
- Full name, position of the head of the organization;
- the subject of the application is a request to transfer the dates established in the vacation schedule to new ones and the reason for the transfer;
- date, employee signature.
If the employer, having assessed the current state of affairs of the company and established the possibility of transferring vacation to other dates, satisfies the employee’s request, he issues an order to change the vacation schedule. Next, the HR department enters new data into the relevant documents.
Please note that the employee should wait for the official response from the employer and only then leave the workplace. Otherwise, absence from work without a vacation agreed by the employer may be regarded as absenteeism.
We suggest you read: Forgery of documents to obtain a loan liability
You will find additional information in the article “How to write an application for transferring vacation - sample.”
In addition to the application for changes to the employee’s vacation schedule, changes are also possible at the will of the employer.
The transfer of leave by decision of the employer must be caused by production needs and agreed with the employee. The law identifies 2 cases of changing vacation time at the initiative of the employer:
- Preliminary. Before the planned vacation begins, the employer agrees with the employee on the postponement to a later date, until next year.
- Subsequent. Recall from vacation with the consent of the employee.
In both cases, it is necessary to formalize the mutual will of the employee and the employer in the form of an order to transfer the vacation dates agreed upon in the schedule to new ones, indicating the reasons for the transfer and the visa of the employee whose vacation is being postponed.
Is it possible to recall an employee from unpaid leave?
At the moment this issue is not covered by law. However, it is more appropriate to recall an employee from administrative leave in a similar manner to the procedure for recalling an employee from annual paid leave, the legal aspects of which are enshrined in Art. 125 Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- Obtain consent from the subordinate to terminate vacation at the employer’s suggestion.
- Having obtained one, issue an appropriate administrative document, which should indicate the reasons for the recall and the date the employee returns to work.
A feature of the procedure for recalling an employee from unpaid leave is that the remaining unused rest days are not subsequently added to the main leave and are not provided at a convenient time for the employee during the current year.
Registration procedure
- The employee must make a statement stating the reasons in writing.
- The employer decides on the advisability of providing leave.
- In a personal conversation with the employee, the terms and conditions are discussed (in some cases, the average salary is retained during the vacation, if this is established in local regulations).
- The manager issues an order to the personnel department to create the appropriate order.
- The personnel department is preparing an order, after signing which the employee will have the right not to go to work for a specified period. The order can be issued in any form or in the T-6 form.
This is important to know: Part-time parental leave
Extracurricular rest during the period of dismissal of an employee
If an employee submits a resignation letter, it is necessary to carry out the calculation procedure correctly and provide the accumulated vacation days in proportion to the time worked. If the dismissed employee has unused rest periods and wishes to take them off outside of the schedule before the dismissal procedure, it is advisable to refer to Art. 127 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
According to this article, upon dismissal, an employee may be provided with both monetary compensation for unused days of paid leave and rest followed by dismissal. In this case, the employee’s last day of work is recognized as the last day on vacation. The procedure for determining the number of days when calculating compensation for unused rest periods is set out in the letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated 05/07/2005 No. 4334-17.
Vacation pay not according to schedule
When granting vacation to an employee outside of the schedule, he is subject to the requirements for the procedure for paying vacation pay provided for by current legislation.
Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation determines that funds due to an employee must be paid to him no later than three days before going on vacation. Current legislation allows for the payment of vacation pay at an earlier date.
Employers whose employees go on vacation unscheduled may be faced with a situation where the employee submits an application for leave less than three days before the planned start date of the vacation.
In this case, administrative liability measures will not be applied to the employer who failed to comply with the deadlines for paying vacation pay established by law. Rate the quality of the article. Your opinion is important to us:
Is it possible to send an employee on unpaid leave at the initiative of the employer?
Very often, especially nowadays, the labor inspectorate receives complaints from workers that some employers are forced, under threat of dismissal, to write applications for leave without pay. For such a violation of the requirements of labor legislation, the employer may be held liable under Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, and he may ultimately face not only a fine or disqualification.
During the consideration of the case, the judicial authority has the right to evaluate the period of the employee’s stay on forced unpaid leave as a temporary suspension of work due to the fault of the employer or an attempt to save money by paying the employee. If such circumstances exist, the court will hold the employer financially liable and collect the accumulated wage arrears with full compensation for the moral damage caused.
Thus, M. filed a claim in the court of first instance for recovery from P. LLC. arrears of wages, compensation for unused vacation, severance pay for 3 months, compensation for moral damage, expenses for paying for the services of a defense lawyer and issuing a power of attorney for him. By the decision of the Verkh-Isetsky District Court of Yekaterinburg dated March 10, 2016, M.’s stated claims against LLC “P.” were fully satisfied.
In satisfying M.’s demands for the collection of the above payments, the district court proceeded from the fact that the organization’s announcement of downtime in relation to the plaintiff was contrary to current legislation and violated her labor rights. After all, downtime in this case is not caused by the suspension of work activity, as reflected in Art. 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, but is associated solely with the employer’s desire to reduce the cost of paying her labor, which does not correspond to the basic principles of legal regulation of labor relations.
The court of appeal considered these conclusions of the district court to be correct, since they correspond to the facts established in the case and the evidence base collected and do not contradict the provisions of the law regulating labor relations. Based on the above, the panel of judges left the final document of the first instance court unchanged, and the defendant’s complaint without satisfaction (appeal ruling of the Sverdlovsk Regional Court dated May 21, 2016 in case No. 33-9840/2016).
Can the bosses refuse and not let me go on forced leave to do my business?
If an employee asks for leave, the reason for which is specified in the labor code or in a legal act, then the management cannot refuse him this. If the director did not sign the application and refused to provide days off, then the employee must act on the basis of the law:
- write an official application for leave without pay;
- give it to the secretaries and demand that the incoming document be registered;
- management is obliged to grant a shift refusal to the employee’s request;
- file a complaint with the labor inspectorate, and attach a photocopy of the application and refusal.
- wait until the check is completed.
Expert opinion
Lebedev Sergey Fedorovich
Practitioner lawyer with 7 years of experience. Specialization: civil law. Extensive experience in defense in court.
Of course, it is better not to spoil the relationship with the employer and not to immediately submit complaint documents to organizations for the protection of labor of citizens. The first thing you need to do is try to talk to your boss in person, citing the norms and laws of labor law.
This is important to know: Application for director's leave: sample 2020
In cases where vacation is issued without circumstances regulated by law, management may not sign the application and refuse days off.
Is it possible to keep wages during vacation days?
According to the law, additional days off for family reasons do not imply continued pay. The organization does not make contributions to the Pension Fund for the employee at this moment, so you should not count on payment for these days.
But not all organizations adhere to this rule. The management itself can decide whether to grant leave with pay to the employee or not. The organization’s documents may state that leave for serious reasons can be paid. In this case, the employee’s wages for the weekend are calculated on a general basis, based on the average wage.
In addition, the organization may provide compensation in the form of monetary assistance or a gift.
Sometimes an employee may ask to keep his salary during forced additional leave if he has overtime. That is, the employee worked for several days on official leave.
If we consider this issue at the legislative level, it is worth noting that the concept of leave with pay is not spelled out in more than one act. Labor laws only talk about basic holidays that are paid:
- annual for planned vacation;
- additional leave with pay;
- study leave.
Moreover, each type of vacation has its own payment rules. In the employment contract of each organization you can find all the nuances and rules for granting vacations and pay.
Let's look at an example: according to the law, days off for a wedding do not imply the possibility of maintaining the employee's pay, as with leave due to the birth of a child. But the organization’s contract may indicate otherwise - maintaining wages for a period of several days. If we consider study leave, then the preservation of wages can only be for students who study by correspondence. Those who study full-time may not count on receiving money after such a vacation.