What is an audit of an organization's personnel?
An audit, no matter what area it concerns, refers to the verification of mainly paper reports, since this concept comes from the Latin “audieus”, which means “to listen”. The audit has its own goals - identifying possible violations, preventing them, advising on improving efficiency in the area that is currently being audited. The effectiveness of auditing has been noted in many areas of activity, and therefore today it is also carried out in the field of personnel management.
An organization’s personnel audit is a consulting activity through which the company’s personnel potential and its effectiveness are established through expert analysis.
An audit is not only a way of conducting checks (establishing certain facts), but a tool used to solve existing problems in a company, which will ultimately contribute to increasing the profitability of the enterprise.
A specialist (auditor) studies documents related to the selection of employees, their employment, relocation and dismissal in order to check the papers for compliance with the requirements of current Russian legislation
Why order a personnel audit service?
Over the past ten years, with increasing awareness of the importance of “quality” employees for the successful development of a company, the attentiveness and their importance in the company’s activities has been growing. All this affected the development of a special focus for employee performance assessment - personnel management audit. It makes sure that the potential of each of the company’s employees is used fully and effectively. The audit also helps to find out what knowledge the company’s employees lack.
In the West, the importance of the company’s personnel composition and the attitude towards employees as the most important aspect that ensures the profitability of the company’s work is very important. This has been proven by many studies. Competent and motivated employees will work for the development of the company or, on the contrary, provide poor customer service, lose deals and reduce the company’s income.
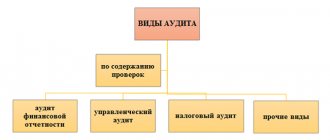
Organizational personnel audit - types of personnel audit
The classification of personnel audits can be done in different ways, depending on the specifics of preparation for this study and how it is carried out:
| Criteria for classification | Types of HR audit |
| In relation to the enterprise |
|
| Frequency |
|
| Research Level |
|
| Scope of Audit Objects |
|
| Method of analysis |
|
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
ON THE ISSUE OF CONDUCTING A HR AUDIT
Despite the fact that the goals of a personnel audit may be different depending on the entities initiating its implementation, it is advisable to establish the most optimal period for its implementation.
Personnel audits in government agencies are usually carried out during the period of comprehensive inspections, which affect all areas of activity of the inspected object and are carried out in accordance with the schedule once every three to five years. Personnel verification can also be carried out during audits of the financial and economic activities of a government body or institution. In addition, targeted inspections may be assigned to analyze the personnel situation in a particular government organization.
Companies whose activities are carried out in stable conditions conduct an audit of the personnel management system every three years, as this allows them to take into account the results of periodic certification of employees. Companies operating in unstable conditions carry out this procedure more often in order to monitor changes in the system, find reserves for increasing the efficiency of personnel management, and also monitor the possible emergence of risks in the field of personnel and labor management.
The timing of the personnel audit is set by the head or higher organization, or inspecting government bodies. The timing depends on the scale of the audit: a comprehensive audit can take place within three weeks, a financial and economic audit can take a month or more. A personnel audit conducted by the labor inspectorate mainly covers personnel records management and lasts about a week. A personnel audit involving independent specialists can take several months [4].
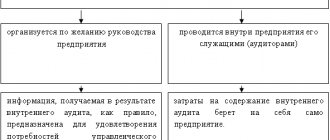
There are three options for performing personnel audits, which have both negative and positive sides.
1. The audit is carried out by the organization itself. For this purpose, a group of auditors is created from employees of the organization, specialists in the required fields. The main advantages of such an audit are that its implementation does not require financial costs and its performers know more about their organization and its problems. The main disadvantages of internal audit are: the expenditure of human resources and time to the detriment of the company's work, lack of experience and professionalism, the risk of leakage of confidential information, and the risk of bias.
2. Involvement of an external consultant. Such consultants can be specialists specially appointed and authorized by a higher organization, independent individuals, small firms, as well as consulting agencies.
The main advantages of such an audit: experience and professionalism of the inspection bodies; quality of work performed; confidentiality; objectivity; recommendations of inspection bodies are more receptive to management.
The disadvantages include: financial costs; the risk of dishonesty of attracted consultants; ignorance of the specifics of the organization; lack of time, which may not allow you to delve into problems.
3. Mixed audit, in which, along with the organization’s specialists, the audit is also carried out by consulting firms. This version of personnel audit is quite common. In this case, part of the work is performed by a division of the company, and part by external specialists.
The advantages include: lower financial costs compared to an external audit; reducing the time required to obtain the necessary information; gaining experience in conducting audits by company employees; higher level of objectivity than with internal audit;
Disadvantages include insufficient confidentiality of information.
When selecting personnel audit performers, they are guided by three main criteria.
The first criterion is professional competence, since the purpose of conducting a personnel audit is not only to check and analyze the personnel situation, but also to provide consulting support to the personnel management system, namely to help eliminate problems and prevent them from happening in the future.
The degree of confidentiality is the second criterion. In cases of high confidentiality, external auditors should be selected.
Their work is more confidential.
The third and important criterion is the amount of financial resources. Depending on how much money is allocated by the organization for conducting a personnel audit, choose one of the given options. If an enterprise cannot allocate a lot of funds to conduct a personnel audit, it is better to involve specialists from your company in conducting it. The best option in this case would be to conduct a mixed audit.
In the process of personnel audit, an analysis is carried out of both the objective aspects of the staff’s work activity (the amount of investment in personnel, the availability of normative and methodological documentation, compliance with labor legislation) and the subjective ones (the degree of staff motivation, the psychological climate in the team, the style and method of leadership) [3] .
The huge amount of information obtained during the audit must be documented. For this purpose, an audit report is prepared. This is a document that is a report on the results of the audit. It contains a description of the procedures performed, results, deficiencies identified during the audit, and recommendations for improving the personnel management system. The purpose of this document is to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise and provide recommendations for improving personnel policies.[1].
The approximate structure of the auditor's report looks like this:
- Introduction. Includes a general description of the enterprise, the goals and objectives of the audit, a description of the object and subject of the personnel audit, the stages of the audit, its schedule, methods of analysis, and the audit team.
- Analytical part. Consists of three subparagraphs: personnel analysis (number of personnel, professional and official composition, job responsibilities, evaluation criteria, motivation system); assessment of managerial potential and personnel processes (general characteristics of line managers, understanding and acceptance of strategic objectives, ability to make coordinated decisions, understanding and acceptance of team work rules and individual responsibility, assessment of the implementation of basic personnel processes); assessment of the organizational structure of personnel management (general characteristics of the organizational structure of management, assessment of interaction between departments, analysis of organizational pathologies).
- Recommendations for improving staff performance. These recommendations indicate strategic errors in personnel management, in setting goals and objectives for line managers, and also provide ways to eliminate errors. For line managers, they summarize their goals and responsibilities, which may include recruiting candidates for positions, training staff, motivating them, and also provide ways to improve productivity. For specialists in the field of personnel management, they indicate weaknesses in the field of recruitment, assessment, training, motivation of personnel and provide recommendations for strengthening these weaknesses.
- Applications. This part of the audit report may contain documents on the basis of which the personnel potential was assessed. These include the results of a questionnaire, a survey of employees, the results of calculations of labor indicators, and efficiency calculations [2].
Personnel audit has a certain range of problems.
One of the significant problems is searching and collecting information. Since information related to the personnel management process is often influenced by subjective factors, personnel is a difficult resource to manage.
The second important problem is reduced work motivation, high staff turnover or a long process of adaptation of new employees to the organization. In this case, it is impossible to objectively assess the effectiveness of personnel policies in the process of personnel audit.
An equally significant problem is the lack of theoretical developments available to users on the use of audit technology in the field of personnel management assessment. Currently, the technology for conducting audits of human resources is not a proven system. There is no specific algorithm for carrying it out. No regulatory documentation has been developed for its implementation.
The fourth problem is the problem of perception of the new system. The introduction of a personnel audit system in some cases causes a state of psychological discomfort among employees, as it can lead to strengthened control measures and increased transparency, which is not always welcomed by the team.
Bibliography:
- Blinov, A.O. The art of personnel management: textbook / A.O. Blinov, O.V. Vasilievskaya; edited by A.O. Blinov. – Moscow: Gelan, 2020. – 411 p.
- Egorshin, A.P. Fundamentals of personnel management: textbook / A.P. Egorshin. – Nizhny Novgorod: NIMB, 2013. – 303 p.
- Kibanov, A.Ya. Personnel management: theory and practice: textbook / A.Ya. Kibanov, L. V. Ivanovskaya; edited by AND I. Kibanova. – Moscow: Prospekt, 2012. – 64 p.
- Rozhkova, N.K. Fundamentals of auditing: textbook / N.K. Rozhkova, N.K. Muravitskaya; edited by N.K. Rozhkova. – Moscow: Forum, 2013. – 272 p.
Objects of audit of the organization's personnel
During a personnel audit, specialists analyze 3 main areas of the company’s activities related to personnel issues:
| Field of activity | What is being checked |
| Staff | The analysis is carried out with an emphasis on checking the sufficiency of staffing levels, the presence of vacancies, the degree of staff turnover, the sufficiency of employee qualifications, and the presence of a personnel reserve. |
| Personnel structures | The effectiveness of the HR department and its relevance to a specific company are checked. Attention is paid to structural units involved in the preparation of future managers, recruitment, selection, training, dismissal and relocation of personnel. |
| HR processes | The analysis here is carried out in correlation of personnel processes with the strategic objectives of the company. During the inspection, the following are assessed:
|
What does HR audit focus on?
Experts carefully study three main areas of the organization’s activities:
- Compliance of HR-related processes with strategic business development objectives: Working with resources. Does the company have enough staff? Is there long-term planning in this area? Is there a succession and employee development system in place?
- Personnel replenishment system. How are candidates searched for vacant positions? What are the requirements for candidates? How is employment organized at the enterprise?
- Adaptation of new employees. Is there an established approach? How effective is it and can it be developed?
- Training, advanced training, certification. Are there such programs? How do they work?
- System of motivation and incentives. Are the methods of monetary incentives, benefits, etc. selected? How effective are they?
- Social and psychological climate. Is the corporate culture formed? Is there social tension? How do these factors affect performance?
- Personnel structure. Is it effective in achieving business objectives?
- How many staff positions are occupied and free? Is there staff turnover? Is there a reserve? Are the staff qualified?
What tasks does the audit of the organization’s personnel set?
In the course of checking personnel documents for the correctness of their execution, as well as studying additional factors reflected in the documentation, the auditor makes conclusions regarding:
- the presence/absence of negative aspects that have a negative impact on personnel efficiency, and the possibility of eliminating them;
- the overall effectiveness of the company’s personnel policy from the point of view of the main goal of the enterprise’s activities;
- finding reserves for improving personnel management;
- correct application of legislative norms;
- objective assessment of the HR department management system and the efficiency of the HR service.
External audit of the company's personnel management system
We will conduct an HR audit tailored to the company’s goals in a short time and provide a report and detailed recommendations for solving problems.
The author's method of 4D volumetric analysis of an HR system is useful for answering many questions from top business officials: - Poor quality selection? — Poor adaptation? — Do we pay little? — Are we motivating incorrectly? — We don’t control it enough? — Don’t we train enough? - WHAT ELSE IS MISSING?! WHY DO THEY WORK LIKE THIS?!
We propose to carry out an assessment from several sides: 1) an audit HR department employees the organization of the HR department’s work; 2) audit of HR business processes in the company : selection - personnel administration - adaptation - training and development - staff motivation - career trajectories and movements - internal communications - internal HR brand - dismissal;
3) audit of the HR function in enterprise management: satisfaction of internal clients with the implementation of basic HR functions in the enterprise, assessment of the involvement of department heads in personnel management, audit of the peculiarities of the corporate culture of the enterprise, audit of staff turnover by department, comparison of the best and worst department; 4) if necessary, assess the labor market and compare with competitors .
For each area, the audit is carried out on 3 points: - description “as is” - existing requirements, standards, established practice - recommendations with examples
A full audit , an audit of individual functions and an express audit are possible .
Over more than 25 years of work, about 200 projects in the field of HR have been successfully implemented, of which more than 20 companies had a turnover of more than 1 billion rubles per year.
Each project began with an HR audit, which identified
- technological chains in HR processes,
- weaknesses and risks of processes,
- suboptimal processes,
- key parameters and KPIs of HR processes,
- real reasons for lack of effectiveness.
The audit technology consists of:
- interviewing the Customer and employees;
- observations and photographs of work shifts;
- analysis of internal documents;
- data analysis and internal statistics, even if you do not keep them;
- process analysis using proprietary checklists;
- competitive analysis;
- benchmarking.
An audit carried out in this way allows, in a short period of time, to identify both the causes of inefficiency and the strengths of the company’s HR system, and to determine the existing potential.
Reviews, recommendations and cases of my clients who passed the HR audit, upon request.
I. HR department audit
- assessment of the qualifications of HR department employees
- staffing of the HR department
- organizational structure and management of the HR department, powers and areas of responsibility
- technical and technological equipment of the HR department
- audit of the HR department budget and its execution
- working conditions for HR department employees
II. Audit of business processes “Human Resources Management”
- audit of mass recruitment technologies (demand planning, recruitment funnel, job requirements, etc.)
- audit of hand-hunting technologies for key specialists
- audit of HR records management and administration technologies
- audit of staff motivation technologies used
- audit of adaptation and mentoring technologies
- audit of employee training and development technologies
- audit of internal communications technologies
- audit of internal HR brand management technologies
- audit of outplacement technologies
III. Audit of HR functions in enterprise management
- the role and place of the HR service in management
- audit of internal customer satisfaction with the implementation of basic HR functions at the enterprise
- assessment of the involvement of department heads in personnel management
- audit of the features of the corporate culture of the enterprise
- audit of staff turnover by department, comparison of the best and worst department
IV. Competitors in the labor market
- who are the competitors in the labor market, selection criteria
- criteria for comparison with competitors in terms of HR functions
- working conditions in comparison with competitors (wages, working hours, workplace comfort, provision of tools, workload, etc.)
- requirements for accepted employees during recruiting
- positioning of the company in the labor market and external HR brand
V. Labor market
- regional labor market potential
- movement in the regional labor market
Other consulting services
Related publications:
- Corporate Code of the company The Corporate Code is a set of principles, norms and rules of conduct for the company’s employees, based on the strategy,...
- Program “Implementation of the Corporate Code” Introduction In order for the Corporate Code to be understood and, most importantly, accepted by managers and employees...
- Game mechanics in personnel management Game mechanics in personnel management are increasingly used. We present to you a list of forty-seven...
- What are the KPIs for your chief accountants? In one of the Facebook HR groups, a question arose: what KPIs do your chief accountants have? As it turned out,…
- Training for managers “Tools of operational management” in Surgut Training “Tools of operational management” was created for managers involved in operational management. This training program is mandatory…
Does it make sense to conduct an audit of the organization’s personnel?
There are a number of cases in which it is advisable for a company to spend time and money researching the personnel situation. An audit of an organization’s personnel will bring tangible benefits to the enterprise if:
- sudden unexpected dynamics of personnel (mass dismissal from work, etc.);
- change of leadership;
- major changes in laws governing employment and termination;
- transfer of personnel affairs to the management of a secretary, accountant or other specialist of an inappropriate profile;
- formation of a database of personnel documents for the purpose of their archival storage;
- dismissal of personnel management;
- preparation for an external audit, which will be carried out by representatives of regulatory authorities.
Audit of organization personnel - stages
HR audit in a company is carried out in several stages:
| Audit stage | Description |
| 1 – Preparation | The purpose of the audit is determined. The responsible person(s), timing of the activities, methodology, and sampling are established. An order (instruction) of the management is issued. |
| 2 – Data collection | Documents are studied, observations of the work of employees are carried out, surveys are conducted, questionnaires are distributed (in order to collect the necessary data). Next, an initial check of the information received is carried out. |
| 3 – Interpretation of the information received | Grouping information into a convenient form for further analysis (charts, graphs, tables, lists). Conclusions are drawn, research results are compared with previously obtained indicators (or with indicators of other companies). |
| 4 – Final | Drawing up a report, results, recommendations for further actions. |
A personnel audit is a periodically conducted examination of the state of affairs in an organization in the field of personnel management, including a system of measures to collect information, analyze it and evaluate on this basis the effectiveness of the organization’s activities in using the organization’s labor potential and regulating social and labor relations. In other words, personnel audit is a system of consulting support, analytical assessment and independent examination of the organization’s personnel potential.
In countries with a market economy, personnel audit emerged from management audit into an independent direction, first in the form of a consulting service, and soon (80s of the twentieth century) into a mandatory diagnostic procedure, subject to all the canons of auditing (legal support, methodological apparatus, staffing) . Since the mid-90s. Russian consulting firms also began to offer personnel audit services. But in most cases, they have the nature of narrowly focused studies of the psychological characteristics of staff, the compatibility of work groups, staff motivation, the presence of conflict situations, leadership style and are one-time. The services are poorly formalized, are not comprehensive and long-term in nature, and do not cover the diagnosis of socio-economic indicators of work with personnel and the connection of this work with the development strategy of the organization. This niche in the consulting services market is quite free. The development of personnel audit in Russia is also hampered by the position of many heads of organizations who do not understand the usefulness and even the necessity of conducting a diagnostic examination of the personnel management system and do not see it as an important tool for increasing organizational efficiency.
However, the importance of personnel audit is constantly increasing. This is due to a number of objective reasons:
— the role of the enterprise’s personnel service in the implementation of the strategic goals and objectives of the organization is increasing;
— investments in human resources are increasing, which makes the problem of their recoupment important;
- in conditions of fierce competition for the development of new markets for goods and services, the need to gain popularity among consumers, organizations are beginning to care more and more about creating a positive image of the enterprise. And it also consists of the organization’s attitude towards its employees, compliance with their rights and guarantees.
The essence of a personnel audit comes down to diagnosing the causes of problems arising in an organization, assessing their importance and possibilities for resolution, and formulating specific recommendations for the organization’s management. Personnel audit is carried out using diagnostic research methods of the personnel management system. Its distinctive features:
— focus on overall organizational efficiency;
— a strict form of the inspection program, procedures and conclusions;
— independence of the auditor in relation to the organization;
— professionalism in performing the inspection;
- reliability;
— comparability with international law.
The object of the personnel audit is the personnel management system of the organization as a socio-technical system; the subject of a personnel audit is the effectiveness of the system for the formation, use and development of the organization’s labor potential or the effectiveness of the personnel management system.
The main question of a personnel audit within the framework of a management audit is: what should be the organizational forms of a business entity, what quantity of personnel and what quality must the organization have in order to effectively and cost-effectively implement the chosen strategy?
The purpose of a personnel audit is to improve the efficiency of the personnel management system. Based on this, the tasks of personnel audit can be formulated as follows:
— finding problems in the field of personnel management;
— ensuring compliance of the HR strategy and policy with the strategic goals of the organization;
— formation of effective methods of personnel management; ensuring the effectiveness of their use;
— determining the correspondence of efforts at the strategic, linear and functional levels of personnel management to each other;
— integration of elements of the personnel management system as a whole into the organization’s development strategy;
— implementation of long-term planning of the organization’s personnel management system;
— establishing compliance of personnel policies with legal requirements;
— optimization of personnel management costs (through the introduction of more effective methods and procedures);
— support and creation of a better organizational environment for the perception of changes in the field of personnel management;
— determining the contribution of the personnel management service to the effectiveness of the organization as a whole;
— clarification of the duties and responsibilities of the personnel management service;
— strengthening the professional image of the personnel management service;
— encouraging greater responsibility and professionalism among personnel management employees;
— increasing the efficiency of the information system of the personnel management service.
Similar to an audit of the financial or tax activities of an enterprise, a personnel management audit aims to assess and provide an opinion regarding the compliance of the ongoing personnel work with the intended goals and objectives, identify existing problems and outline ways to improve it.
Various employees are usually involved in conducting the audit.
Table 20.1
Subjects of audit of the activities of the enterprise’s personnel service
| Parties involved | Characteristics of the parties |
| Internal audit | § Heads of the organization § Line managers § All employees |
| External audit | § Representatives of trade unions § Employees of audit (recruitment) agencies |
| Self-audit | § Enterprise HR specialists |
The complexity and versatility of the object and goals of personnel audits require the use of a variety of methodological tools for inspection and analysis. Typically, three main groups of methods are used in audit practice:
1) organizational and analytical
, involving verification of documentation and reporting, analysis of labor indicators indicating the effectiveness of the organization and its personnel. At the same time, from the total number of labor indicators, only those that have the greatest impact on the efficiency (profitability) of the organization should be highlighted. These include indicators of the use of labor, working time, quality of labor, its productivity and payment, etc. The sources of this information are the documentation and reporting of the organization, including the balance of the organization’s labor resources, description of work and specifications, job descriptions, data on costs hiring, dismissal, training and retraining of personnel, questionnaires and tests of candidates for vacant positions (jobs), the level of occupational diseases, industrial injuries, turnover, etc.;
2) socio-psychological methods
, consisting of conducting independent sociological surveys, questionnaires, individual and collective conversations, interviewing workers of various levels and categories. This group of methods is most effective for assessing job satisfaction, attitude to work, relationships in the team, motivation to work, the effectiveness of management and the reward and compensation system, etc.;
3) economic methods
, allowing to assess the competitiveness of an organization in the labor market, the effectiveness of the functioning of personnel management services and the effectiveness of the personnel audit itself by comparing the economic and social indicators of the organization’s activities with legally established norms and standards, or with average or best indicators in the industry.
Depending on the number of factors, several types of personnel audits are distinguished (Table 20.2.).
Table 20.2
Classification of types of personnel audit
| Classification sign | Type of personnel audit | Main characteristics |
| 1. Frequency | Current Operational Regular Panel | Conducted according to pre-established regulations for a certain period of time Conducted according to operational orders of management Conducted at certain intervals Conducted with a certain frequency, with unchanged methodology and tools on the same groups of people and the same objects |
| 2. Completeness of coverage of the objects under study | Full Local Thematic | Covers all objects Covers a separately selected group of objects or one object Includes all objects but on the same topic |
| 3. Method of analysis | Complex Selective | The entire arsenal of methods is used. Employees selected using a special method - sampling - are analyzed. |
| 4. Level of implementation | Strategic Managerial Tactical | The assessment is carried out at the level of senior management. The assessment is carried out at the level of line managers. The assessment is carried out at the level of the personnel management service. |
| 5. Test method | External Internal | Conducted by third-party specialists Conducted by employees of the organization itself |
Carrying out an audit involves dividing the work into four stages.
At the preparatory stage, the following are carried out: formalizing the idea of conducting an audit, determining its goals, and the expected effectiveness for the organization; selection of personnel (inside or outside the organization) to organize the inspection, training if necessary; development of an internal document (order, instruction) outlining the deadlines, tasks of performers and participants of the inspection, briefing of performers and participants; development of a plan for collecting, providing and reviewing the analyzed information.
At the information collection , the following are carried out: checking documentation and reporting, personnel monitoring, observation, surveys, questionnaires, conversations with employees, preliminary processing of statistical data, arrangement of accounting and other information. It should be taken into account that statistical and other indicators become more accessible and meaningful from the point of view of analysis if computer equipment and modern information technologies are used for their collection, storage and processing.
At the stage of information processing and analysis, the information obtained during the inspection is processed and formalized in the form of tables, diagrams, diagrams, graphs and other forms of data presentation convenient for evaluation, and is entered into a computer; at the same stage, according to the developed algorithm, data on the activities of personnel is analyzed and assessed by comparison with similar particularly successful organizations, scientifically based norms and standards, through the use of expert assessment methods, etc.
At the final stage - the stage of summarizing and presenting the assessment results, conclusions and recommendations - the final material is prepared, which usually includes a report on the results of the audit. The parameters for auditing HR processes are given in Table 20.3.
Table 20.3
HR Process Audit Options
| HR processes | Contents of HR process audit |
| 1. Formation of the organization’s personnel policy | 1) Assessing the current state of personnel policy, the degree of its coordination with the goals of the organization, and its development strategy. 2) Assessing the degree of connection between personnel policy and the specifics of the organization and external conditions. |
| 1. Workforce planning | 1) Assessment of available resources, goals, conditions and prospects for the development of the organization, future personnel needs. 2) Evaluation of programs in terms of compliance with goals, organizational culture, and development prospects of the organization. |
| 2. Recruitment | 1) Assessing the prospects of internal and external sources of staffing from the point of view of the current situation and the enterprise development strategy. 2) Assessing the adequacy of the recruitment methods proposed for use in terms of personnel requirements, personnel strategy and tactics of the organization. |
| 3. Personnel selection | 1) Assessing the effectiveness of the developed program of assessment procedures. 2) Analysis of changes in the organization’s human resources potential. |
| 4. Development of an incentive system | 1) Assess the compliance of the developed principles, salary structure and benefits with labor market conditions, productivity and profitability of the organization. 2) conducting comparative studies, determining an effective reward system. |
| 5. Personnel adaptation | 1) Assessing the effectiveness of existing methods of personnel adaptation. 2) Formation of a field of problems that arise during the adaptation period. |
| 6. Staff training | 1) Evaluation of programs in terms of training effectiveness, practical orientation, formation of motivation to work, creation of a favorable atmosphere in work groups. 2) Development and testing of alternative programs. |
| 7. Assessment of work activity | 1) Assessing the effectiveness of using methods. 2) Adaptation of effective assessment techniques. |
| 8. Promotion, demotion, transfer, dismissal | 1) Assessing the effectiveness of the personnel monitoring system used, adapting computer methods of personnel monitoring. 2) Assessing the effectiveness of career planning methods. 3) Assessing the adequacy of personnel development programs to the goals, strategy and state of development of the organization. |
| 9. Training of management personnel | 1) Analysis and design of management activities in the organization. 2) Assessing management potential and determining the need for training of management personnel. |
| 10. Monitoring the socio-psychological situation and organizing communication within the enterprise | 1) Diagnostics of personnel processes and socio-psychological climate, assessment of the level of social tension in the organization. 2) Diagnostics of organizational culture, type of management team, assessment of the level of their compliance with other elements of the organization (goals, structure, technology, finance, management system, personnel). 3) Determining the need for the preparation and implementation of programs for the development of intra-organizational communication. |
Results of the audit of the organization's personnel
After the specialist submits a report on the HR audit, the company’s management will have the opportunity to draw a conclusion regarding:
- the causes of negative factors, ways to eliminate problems;
- sufficiency of staff;
- potential for career advancement at various job levels;
- quality of personnel management in the company;
- needs for staff development;
- prevailing management style;
- opportunities to introduce any innovations;
- internal climate in the team.
Since 2020, we have been issuing state diplomas. sample
Now with Eduson you can get a professional diploma. retraining of employees and a certificate of advanced training in management and sales. The advanced training program is designed for 150 hours of training. Prof. retraining of employees - 250 hours of training.
If you want to train a group of employees of 30 or more people, write to
Common mistakes
Error:
The company's management decided to transfer authority to resolve personnel issues to the company's accountant. An audit of the organization's personnel has never been conducted.
A comment:
In cases where personnel matters are not transferred to a personnel specialist, it is advisable to regularly conduct personnel audits.
Error:
There is a mass layoff at the enterprise, management does not take measures to find out what caused the unexpected sharp dynamics in personnel.
A comment:
The reasons for the lockout can be clarified based on the results of a personnel audit.
Express HR audit: algorithm, checklists and difficulties
HR expert Anastasia Novoselova again helps us (and you) understand difficult HR concepts and processes. This time we’ll talk about an express HR audit, the algorithm for conducting it and its pitfalls.
“An express audit of HR processes is carried out when it is necessary to determine tasks for the near future and find out what the company’s weak points are. HR audit is not an end in itself. It is extremely rare that the owner decides to carry it out without any specific pain. As a rule, such an order is based on a specific request, the need to change or improve something in the HR system or the business as a whole.
If we talk about an express audit - that is, one that can be done in a period of several hours to several days - then you first need to ask the customer the question: “Why do you want to conduct an audit, what was the reason?” .
The answer is very important, it is this request that you need to focus on. After all, before taking measurements and diagnosing the system, you need to understand what caused the audit, what the “symptom” is. It’s like a doctor: first the patient tells him what and where it hurts, and then the doctor finds out the reasons and diagnoses the disease.
That is, for example, if a customer says that the recruitment process is not going well, or the best employees are constantly leaving – these are all symptoms. We need to formulate these symptoms, write them down and form hypotheses (why this happens), which we will then confirm or refute during the audit process by conducting diagnostics.
Express audit technology
The first step is to work with the numbers and statistics in the field of HR. Remember that numbers are the most telling thing in an audit. Working with processes is also important, but it is the numbers that give an objective picture. Therefore, it is necessary to collect statistics and figures on HR processes , to understand what indicators are available for analysis. The more such indicators we collect, the better. Because often our perception is distorted by emotions, ideas about how it should be and how we want to see it. So the customer does not always see an objective picture. If there are no statistics, then there is no need to specifically collect them for an express audit. We will operate with the data that we have.
The second step is actually an audit of HR processes . I recommend that you first highlight all the typical HR processes that the company has. These are HR strategy, organizational policy, recruitment and selection of personnel, adaptation, administration of labor relations, personnel records management, training and development of personnel, development of corporate culture, motivation system (material and non-material). Not all processes exist in every organization, so the audit, of course, should be carried out only on those that are present in the company.
To do this, you need to select a group of employees who are involved in a certain process and conduct a short survey, asking literally three questions. “How effectively do you think this system works?” “What problems are there in the system?” “At what points can the system work better?”
Third step. We take special checklists that I compiled for conducting an express HR audit. With their help, we carry out assessments in each area. Checklists work simply: there are statements, and employees need to put pros or cons for each - what is and what is not in the company. It literally takes ten minutes.
So, we have statistics, answers to questions from participants in the process and completed checklists. this information into a matrix for each of the processes. We can immediately digitize this data, draw up graphs and draw conclusions for the manager: what HR processes are in place in the company, what works, what is considered a problem. And these will not be general words, but specific elements. For example: “Staff training needs have not been identified; Individual employee development plans are not developed; there are no criteria for evaluating candidates during the probationary period.”
these findings to the initial audit request. The identified problems may just be the reason why the manager initially turned to HR.
After such an audit, we can immediately propose a program to eliminate deficiencies .
So, in a maximum of four days (and in a small company an express audit can be carried out in a day), we diagnose the problems of the HR system and develop recommendations directly on the audit points. At the same time, I propose to introduce a methodology for monitoring the effectiveness of these indicators, so that subsequently the manager himself can periodically conduct such an express audit using checklists.
Underwater rocks
Any HR audit is just the beginning of the work. Prepare for the fact that managers will be unpleasantly surprised by its results and problem areas that they were not even aware of. Therefore, it is necessary to explain to the customer: yes, a certain element may not work perfectly, but if this is not the cause of the problems formulated in the request, then this problem can be solved in the second place.
This approach is a risk assessment. There is no point in telling the owners that everything is bad in the company. Speak their language – about risk assessment and problem areas. Explain that first-level risks are those that directly affect profits and revenue, and they need to be addressed first. And risks of the second and third levels are resolved in a longer term.
The task of HR is to make sure that, based on the results of the audit, the manager wants to change something and invest in the HR system. He must understand what result this will bring. Clients are more willing to accept the approach of dividing risk levels.
Remember that making changes to the HR system without diagnostics is dangerous. This could lead to negative consequences for the company."
Other articles from Anastasia on our blog: Mass selection: instructions for a recruiter. Stages, life hacks, mistakes Guide to HR freelancing Drawing a funnel for mass recruitment of employees Closing unusual vacancies Trends in developing material motivation for personnel: considering the economy
Answers to common questions about auditing an organization's personnel
Question #1:
Is it necessary to conduct regular scheduled audits of company personnel? Does a personnel audit make sense if it is carried out situationally?
Answer:
In some cases, it is recommended to regularly audit the organization’s personnel, for example, in large companies and enterprises that experience staff turnover. But an audit can be carried out by order of management (operational), and in relation to a “focal” group of employees (panel), and regularly (permanent).
Question #2:
Is it necessary to involve third parties to conduct personnel audits?
Answer:
No, in addition to the external audit, an internal audit of the organization’s personnel can also be organized, which is carried out by full-time employees of the enterprise.
How often are staff skills assessed?
An audit of sales skills of managers is a scheme of various procedures carried out from time to time to collect information, research it and evaluate the performance of company employees. The purpose of a personnel audit is to resolve issues related to sales managers, coordinate their actions and improve business processes. For example, most often an audit of staff sales skills is carried out to find out how effectively the company's sales managers are able to work with clients. Are they cheating clients or being rude? Or maybe they don’t know how to competently present the benefits of a product/goods/services and thus don’t convince you to place an order. The client leaves for competitors, and the company suffers losses. The manager thinks that they need to give even bigger “discounts” and lose more profit from the goods, but it turns out that managers simply do not know how to sell “expensively” and convince customers with the right arguments. That is, when conducting an audit of sales department employees, you can find out the following facts:
- Why are customers given discounts left and right, reducing profitability?
- Problems in sales techniques of sellers
- How well do salespeople know how to properly negotiate with clients?
- The level of real knowledge of your managers
- Identify hidden problems of falling sales and ways to prevent it.