The concept of harmful factors
In many plants and factories, production involves constant exposure of workers to unfavorable conditions. Harmful and dangerous production factors are inextricably linked.
OPF are those factors that, as a result of their long-term or short-term impact on a person, lead to a deterioration in his health or to injury. In industries with such working conditions, various accidents occur quite often.
HMF are factors that, acting on an employee, reduce his performance or lead to various diseases; they are often also called occupational diseases.
It is worth noting that the line between these two groups of factors is quite arbitrary. Under certain conditions, harmful production factors can become dangerous. For example, high humidity refers to unfavorable working conditions; it can cause various diseases of the respiratory system. If a person has to work with electric current in such conditions, then it becomes too dangerous, and not just harmful.
Harmful working conditions by class
List of hazard classes.
- First grade. Conditions are optimal. This category includes workplaces where there are no factors that threaten the life and health of employees. This is a completely safe job;
- second class. The potential for harm to employee health is negligible. Recovery of the body should occur by the beginning of the next working day;
- third class. Working conditions are harmful to employee health. The effect of adverse factors on employee health is significant. The third class of production hazards is divided into four subgroups:
- The first subgroup of harmful working conditions of the third class. The employee’s body is exposed to the harmful effects of working environment factors. Normalization of all body systems does not have time to occur before the start of the next work shift. The health risk is significant.
- Second subgroup. Persistent changes in the employee’s health status begin. They cause moderate harm and can cause various diseases. The employee completely or partially loses his ability to work after fifteen or more years of work in such conditions.
- Third subgroup. Mild to moderate illnesses may occur while performing work duties. The effect of negative factors on the body is persistent and destructive.
- Fourth subgroup. Assumes a threat to the life and health of the employee, loss of ability to work in a given professional field;
- fourth grade. Dangerous working conditions. The employee’s work activity poses a danger to life and health.
In such conditions, chronic diseases may worsen. Serious occupational illnesses appear.
Classification of harmful production factors
All factors in any enterprise can have different origins. You can often encounter unfavorable working conditions that arise due to the fault of management. This issue requires special attention from the inspection authorities.
I would like to hope that most of the dangerous factors are of natural origin, and a person simply needs to take all measures to ensure that their impact is minimal.
GOST divides all harmful production factors into the following groups:
- Physical.
- Chemical.
- Biological.
- Psychophysiological, which include difficult and stressful working conditions.
It can be noted that there is no clear boundary between harmful and dangerous factors; it is always conditional and can be destroyed at any time.
List and classification of professions
The main document that is still used to regulate this area is one of the Resolutions of the USSR Cabinet of Ministers.
This Decree provides 2 lists of professions, which are classified according to a unified system into 24 groups (depending on the field of activity):
- Work in the mountains.
- Preparation, enrichment, roasting of ore rock.
- Production related to ferrous metals.
- Production related to non-ferrous metals.
- Coke and related production.
- Gas production during production processes in metallurgy.
- Activities for obtaining dinas products.
- Various types of chemical industry.
- Obtaining explosives, gunpowder, ammunition.
- Oil refining.
- Metal processing.
- Production and repair of electrical mechanisms.
- Creation of various building materials.
- Creation of products for electronic equipment, radio engineering.
- Glass/porcelain production.
- Creation of artificial polymer fibers.
- Paper production.
- Work in hospitals, hospitals, clinics.
- Creation of medicines, biological materials/preparations.
- Printing.
- Work on transport.
- Work in the nuclear industry.
- Work related to radioactive substances and rare earth chemical elements.
- General professions.
Expert opinion
Salomatov Sergey
Real estate expert
You can find out how to properly organize labor protection at an enterprise here.
List 1
The list contains all professions that are recognized as activities associated with particularly hazardous conditions. Each item on the list has its own unique digital code.
List 2
This list is in many ways similar to the previous one. It contains almost the same professions, and their classification by area also coincides almost completely.
Differences in the lists
In fact, the presented lists are no different. However, List 2 contains only those types of activities that are distinguished by harmful and difficult conditions, but without the characteristic “particularly harmful”. Thus, professions from list 1 involve particularly harmful conditions; this difference affects the benefits provided.
| list 1 | list 2 | |
| privileges | retirement 10 years earlier if you have “harmful” work experience of 10 years/7 years (men/women) | retirement 5 years earlier if you have “harmful” work experience of 12 years/10 years (men/women) |
Along with early retirement, other benefits are provided for both categories of employees:
- free periodic medical examinations at the company's expense;
- provision of special nutrition to minimize harmful factors;
- additional payments to salary;
- additional leave (it is paid in the same way as the main one);
- accident insurance;
- shortened week (36 hours instead of 40).
For its part, the employer can provide additional benefits. Their list is indicated in the individual and/or collective labor contract.
Sources of harmful chemical factors
In production there are always technological processes and equipment that are a source of HPF release. These productions include:
- Cleaning parts using chemicals.
- Painting of equipment.
- Welding work.
- Processes for applying protective anti-corrosion coatings.
- Processing or recycling of metals.
When carrying out all these processes, the release of harmful substances is inevitable, but, as a rule, their increased formation is associated with non-compliance with technologies or their inept use.
Physical factors
In many industries it is simply impossible to avoid the impact of certain factors. Among them, a special place is occupied by:
- Temperature, high humidity and radiation.
- Electromagnetic fields.
- Laser and ultrasonic radiation.
- Vibration.
- Loud noise.
- Lighting, which can be either too intense or insufficient, which is equally harmful to vision.
- Exposure to dust and aerosols.
- Charged air.
- Working parts of equipment.
Each factor individually does not seem to pose a particular danger to human health during short-term exposure. But often an employee is surrounded by them for a long time, and several of them at once, so their influence becomes quite noticeable.
Noise and its impact on humans
At enterprises where machines and other equipment are located in workshops, as a rule, noise cannot be avoided. Constantly operating equipment produces loud sounds that can change in intensity.
If a person is forced to regularly be exposed to such exposure, this will adversely affect his health. Loud noise causes headaches, blood pressure increases, and hearing acuity decreases.
In the end, such conditions cause productivity to decrease, fatigue appears, attention decreases, and this can already lead to an accident.
Managers at such enterprises must take care of their employees in order to try to at least slightly reduce the negative impact of noise on the body. For this you can use:
- Noise silencers.
- Personal protective equipment, such as headphones, earplugs, helmets.
- Soundproof noisy places using protective covers and booth equipment.
- Finishing of premises with sound-absorbing materials.
These measures will help create a more favorable environment for workers.
List 1
The main difference between the two lists is the degree of influence of harmful factors on human health. However, professions and areas can be repeated. The differences will lie in the position and duties performed by the employee. And it is on them that the determination of whether a particular person belongs to these two lists depends. The first list includes particularly dangerous professions. These include:
- employees working in mountainous areas;
- persons who work underground most of the time;
- workers working with ore and similar minerals;
- citizens employed in the field of metallurgical production;
- workers associated with coal processing and mining;
- metallurgical workers;
- persons involved in working with mercury substances, chemical production, as well as ammunition and other explosives;
- citizens engaged in the extraction and processing of gas, oil, shale and coal;
- workers working with power plants;
- employees of metallurgical enterprises;
- persons engaged in the production of electronic equipment, glass, building materials;
- workers extracting peat;
- food and drug industry employees;
- citizens engaged in the production of paints, printing, and the film copying industry;
- workers in communications, healthcare, transport, social professions;
- persons working in the field of nuclear energy;
- workers associated with radioactive elements, as well as the production of synthetic fibers;
- servicing the agro-industrial complex in the field of disposal of animal corpses.
These professions cause serious harm to health, so long periods of work can lead to the establishment of complete disability of a citizen, as well as lead to death. That is why people whose profession belongs to the first group have the right to early retirement 10 years ahead of schedule. This is their fundamental right, which is granted under the following conditions:
- men must work for at least 20 years, half of which will be in a particularly dangerous profession;
- women must work for 15 years, half of which under particularly dangerous working conditions.
If such length of service is available, the employee can apply for early retirement.
Impact of vibration and its elimination
Vibration is included in the list of harmful production factors. It can be classified into several categories:
- By transmission method: general and local.
- In its direction: vertical and horizontal.
- By exposure time: temporary and permanent.
As a result of constant exposure to this factor, not only the nervous system begins to suffer, but also the musculoskeletal system and the analyzer system. Workers who are forced to work in such conditions often complain of headaches, dizziness, and motion sickness.
If we add the influence of accompanying factors, such as humidity, high temperature, noise, then this only increases the harmful effects of vibration.
To protect against it, the following measures can be proposed:
- Replacement of equipment with more technologically advanced ones.
- Use of soft coatings on vibrating parts of instruments or equipment.
- Installation of units on a solid foundation.
Chemical factors
Substances from this group can be distinguished into the following categories:
1. According to their effect on the human body, harmful and dangerous production factors of a chemical nature are divided into:
- Toxic. They have a negative effect on the entire body, such as carbon monoxide, mercury, and lead.
- Annoying. Substances such as acetone, chlorine, and nitrogen oxides cause irritation of the mucous membranes.
- Carcinogenic. Chromium oxides and beryllium with their compounds can lead to the development of cancer cells.
- Causing allergic reactions.
- Mutagenic. They provoke changes at the cell DNA level.
- Affecting reproductive function.
2. By route of entry into the body:
- Through the respiratory system.
- Through the gastrointestinal tract.
- Through the skin and mucous membranes.
Also, these harmful factors in the working environment have varying degrees of impact, depending on which they are distinguished:
- Extremely dangerous.
- Highly dangerous.
- Moderately dangerous.
- Low risk.
If the use of protective equipment is sufficiently effective in hazardous enterprises, then workers will be exposed to hazardous substances to a much lesser extent.
Who is entitled to early retirement pension?
Legislatively, the right to early retirement is secured for citizens by Law of December 28, 2013 No. 400-FZ “On Insurance Pensions”. In particular, Article 30 of this law, which contains an exhaustive list of professional categories of citizens entitled to early retirement due to age.
Some categories of citizens working in certain professions with dangerous and harmful working conditions are entitled to early retirement benefits.
Such harmful and difficult work includes the following industries: mining and underground work (including mineral extraction);
metallurgical production (ferrous and non-ferrous metals);
production of explosives (gunpowder and ammunition);
oil and gas, coal and shale processing;
chemical production;
production of electronics and radio equipment;
production of building materials;
pulp production;
glass production (including porcelain and earthenware);
nuclear energy, etc.
Work in these industries is accompanied by the presence of harmful working conditions, which is associated with special danger, increased severity, the presence of injuries and other factors (gas pollution, background radiation, noise level, lighting, etc.), which can lead to occupational diseases, complete or partial loss ability to work.
In order to implement Article 30 of Law No. 400 dated December 28, 2013, the Government of the Russian Federation adopted Resolution No. 665 dated July 16, 2014 (hereinafter referred to as Resolution No. 665). Paragraph 1 of this resolution defines the types of work and production, professions and positions that are used in determining the length of service for the corresponding types of work for early retirement.
A complete list of industries, professions, positions and indicators with harmful and difficult working conditions, employment in which gives the right to an old-age pension on preferential terms, is indicated in Lists No. 1 and No. 2, which were approved by a resolution of the USSR Cabinet of Ministers of January 26, 1991 No. 10.
Depending on the type of work performed and its assignment to a particular list, different conditions for the appointment of early pension provision are established.
List No. 1 (in everyday life, the “first grid”) identifies industries and professions for the early assignment of old-age pensions to persons who worked in harmful and dangerous working conditions, in hot shops, and in underground work. According to the specified list, professions with a special (critical) degree of harmfulness and danger are pensioned.
The professions and positions specified in List No. 1 do not include periods of work provided for in List No. 2, “small” lists and other periods of work with special working conditions.
List No. 2 (or the “second grid”) identifies industries and professions for the early assignment of old-age pensions to persons who worked under difficult working conditions. To determine the right to early pension provision, it is allowed to add the periods of work provided for in List No. 1 to the periods of work activity according to List No. 2.
Example
A man aged 54 years has 4 years of work on List No. 1 and 9 years on List No. 2, as well as 26 years of total insurance experience. In accordance with the law, there is no right to retire in old age according to List No. 1.
When adding the periods of work in List No. 2 to the periods of work in List No. 1, the result is a preferential length of service equal to 13 years, which gives the right to retire at 55 years in accordance with paragraph 2 of part 1 of Law 400-FZ.
The procedure for conducting a special assessment of working conditions (SOUT) is legislated by Law of December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ “On the special assessment of working conditions.” The assessment is carried out by the employer together with the specialized organization involved. The commission created to carry out the assessment should directly involve specialists from the department or occupational safety service.
The purpose of conducting such a special assessment (inspection) of working conditions is to identify and measure potentially harmful and hazardous production factors present in certain industries and affecting the health of persons working in the identified areas.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0bapUlnLA90
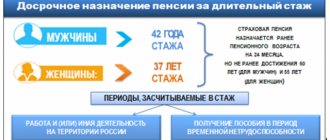
To establish an early old-age insurance pension, three main conditions are legally defined: reaching the established retirement age;
availability of full insurance (work) experience;
duration of special (preferential) experience.
Conditions for early retirement by age for men and women in accordance with Lists No. 1 and No. 2 are given in the table
Condition of appointmentMen
Women
According to List No. 1
Retirement age 50 years
45 years
General insurance experience of at least 20 years
at least 15 years
Special experience*10 years
7.5 years
According to List No. 2
Retirement age 55 years
50 years
General insurance experience of at least 25 years
at least 20 years
Special experience *12.5 years
10 years
Reducing the age according to List No. 1 by one year for each full year of preferential work
Reducing the age according to List No. 2 by one year for every 2.5 years of preferential work
for one year for every 2 years of preferential work
Periods of work, according to clauses 1 and 2, part 1, art. 30 of the Law of December 28, 2013 No. 400-FZ, which occurred after January 1, 2013, are counted towards special experience subject to the following conditions: payment of compulsory health insurance (insurance) contributions at additional rates established by Article 33.2 of the Law of December 15, 2001 N 167-FZ ;
compliance of the class of working conditions in the workplace with the established standards based on the results of the special labor assessment.
In 2020, insurance premium rates were increased for employers who have harmful and dangerous working conditions in their production. Namely: 9% - from payments in favor of employees from list No. 1;
The basis for calculation is the income (salaries and other payments) received by employees who are employed in positions considered difficult and harmful.
SPsk - the amount of old-age insurance pension;
IPC - individual pension coefficient (determined individually for each of the acquired pension rights);
SPK is the cost of one pension coefficient (PC) as of the day from which the payment is assigned (this is a fixed amount, determined by Government decree). In 2020, from January 1 - 81.49 rubles.
Many of our citizens who officially carry out their working activities ask the same question: when does the right to retire on preferential terms begin?
What do the professions on the first or second list mean? Who is included in them? How are pension benefits processed? How is it calculated?
Let's consider all these exciting questions in more detail.
To receive a preferential pension, a citizen must accumulate a minimum work experience. In addition, you must meet the following requirements:
- Accumulate a sufficient number of pension points.
- Reach the age at which an employee who puts his life and health at risk can retire early.
- Achieve the minimum “preferential” length of service.
Failure to fulfill one of the conditions will be the reason why a person will be denied a disability pension.
In order to apply for early retirement under the new law from 2019 in connection with work in difficult and hazardous working conditions (the so-called preferential pension for hazardous work), several conditions must be met. We will explain what these conditions are in this article.
For Russian citizens working in difficult and hazardous working conditions, in underground work or in hot shops (the so-called list No. 1, list No. 2 and “small lists” of hazardous professions in the Russian Federation), the legislation provides for the possibility of early retirement if they have a specified amount of special length of service
Thus, in order to apply for an early old-age pension under the new law from 2020 in connection with work in difficult and hazardous working conditions (the so-called preferential pension for hazardous work), several conditions must be met:
- Reach the retirement age established for a specific category of professions.
- Work for the required number of years in hazardous production - i.e. have the required quantity:
- special work experience in harmful (difficult) working conditions;
- general insurance experience.
- Have the required number of generated pension coefficients (IPC).
For Russians working in hot shops, in hazardous, difficult working conditions, in underground work, including for citizens of certain professions (the so-called “small lists”), an old-age pension is assigned early - i.e. before reaching the generally established retirement age.
This possibility is provided for in Part 1 of Art. 30 of Law No. 400-FZ “On Insurance Pensions”.
However, in order to become a pensioner early, it is necessary to have the duration of harmful work experience prescribed by law - time spent working according to the lists of hazardous professions established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 665 of July 16, 2014.
| Conditions for preferential retirement | According to list No. 1 | According to list No. 2 | ||
| Women | Men | Women | Men | |
| Retirement age (years) | 45 | 50 | 50 | 55 |
| Required specialized experience (years) | 7,5 | 10 | 10 | 12,5 |
| Required total insurance experience (years) | 15 | 20 | 20 | 25 |
If the harmful experience indicated in the table was not completed in full, then you can count on a reduction in the generally established retirement age in proportion to the accumulated special experience.
Factors of the labor process
Psychophysiological factors include the severity of working conditions and its intensity. When we talk about hard work, we mean:
- Large load on the musculoskeletal, cardiovascular, and respiratory systems.
- The magnitude of the static load.
- Number of identical movements.
- The amount of loads that have to be lifted.
- The worker's posture during the process.
By work intensity we mean the load on the nervous system and sensory organs (mostly analyzers). These include prolonged mental work, monotony of processes, and emotional overload.
All these are harmful production factors, which, if you look at them, almost every one of us experiences in our workplace to one degree or another.
List of professions with hazardous working conditions according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in 2020 – Social assistant
This meant and means that people work in enterprises and production where there are high health risks. The negativity that a person receives from such work was smoothed out, at least with free milk (we are talking about the Soviet Union, where milk was given out free of charge, according to the established norm, depending on the impact of the aggressive environment on a person).
Today, they don’t give milk for being harmful, but “for being harmful” they are entitled to other additional payments and benefits that compensate for hard and harmful work.
List of professions with hazardous working conditions | List No. 1, List No. 2
The list of professions with hazardous working conditions establishes benefits and compensation for employees whose working conditions are fraught with health risks. We will tell you what the criteria are for including a profession in the list, how to comply with all legal requirements and ensure that workers’ rights are respected.
Harmful working conditions - list of professions 2018
Working conditions at the enterprise are recognized as harmful based on the results of a special assessment. The SOUT expert will verify the presence or absence of a position in the List. If the position is present in it, then based on the results of the special assessment, he can no longer determine the optimal or acceptable TS.
https://youtu.be/nf4nsgKkWtA
The list of professions with hazardous working conditions has been adopted by law and has been updated and supplemented for many decades.
Harmful conditions are conditions that can harm the health of workers, affect reproductive function, reduce immunity, lead to occupational diseases, and negatively affect a person’s mental state.
The list of professions with hazardous working conditions is divided into two different documents, this somewhat complicates the task for both the occupational safety specialist and the HR department. We will tell you more about these lists and their contents below, as well as about the compensation that employees are entitled to.
The main benefit under both lists is the right to early retirement. In addition, for working under difficult working conditions, an employee can receive: additional days of paid leave, an increase in salary, a reduction in the working week, free additional meals, free trips to sanatoriums and health centers, etc.
Legislative framework and regulation
Providing specialists in professions with hazardous working conditions with preferential pensions and other bonuses has a long history in our country.
So, both lists that we mentioned above were compiled in the Soviet Union - by Resolution of the USSR Cabinet of Ministers of January 26.
1991 No. 10 “On approval of lists of production, work, professions, positions and indicators giving the right to preferential pension provision.”
Source: https://xn—-gtbho2aetb.xn--p1ai/kompensatsii/perechen-professij-s-vrednymi-usloviyami-truda-po-tk-rf-v-2019-godu.html
Impact of harmful factors on humans
In any enterprise, in order to create favorable conditions for employees, it is necessary to try to provide a comfortable environment. This concerns, first of all, the cleanliness of air in production premises.
Sanitary and hygienic services divide the main harmful production factors into chemicals and industrial dust.
The first, in turn, are divided into:
- Industrial poisons that are often used in production.
- Pesticides for agriculture.
- Medications.
- Household chemicals.
- Poisonous substances.
A large amount of dust is also a pressing problem in the mining, metallurgical, engineering, and agriculture industries.
The negative impact of dust is that it can provoke the development of lung diseases.
At any enterprise, workers are exposed to harmful production factors from several groups at once, that is, complex. That is why the issue of providing protection from their negative effects is quite acute in the production sector.
Protecting workers from hazardous substances
Despite all the measures aimed at neutralizing the harmful effects of factors, it is impossible to achieve ideal working conditions. This is not possible due to the peculiarities of technological processes, products and raw materials for its manufacture.
Therefore, for managers, protection from harmful production factors is a top priority.
In this case, it is necessary to be guided by the following priorities:
- Eliminate the hazard or reduce the risk of exposure to it.
- Use safe work practices.
- Fight against the dangerous factor and its source.
- Effectively use personal protective equipment.
It often happens that all the measures taken cannot ensure completely safe working conditions; in these cases, it is simply impossible to do without the use of PPE.
Among them are the following categories, which are the most common in use:
- Anti-vibration products can be: mittens, handhelds, gloves. Since such protection can reduce labor efficiency due to inconvenience of work, additional breaks must be provided.
- Noise protection headphones. But they can reduce a person’s ability to navigate in space and provoke headaches due to compression.
- Respirators and gas masks. It is very difficult and inconvenient to work in them for a long time, so you should look for alternative means of protection.
It can be concluded that personal protective equipment, on the one hand, reduces the impact of harmful factors, but on the other, can create other dangers to the health of the worker.
Analysis of methods of protection from exposure to harmful and dangerous production factors
There are many different examples of how to reduce the impact of dangerous and harmful production factors; the main thing is to select them correctly, ensuring the maximum level of protection for workers, because the presence of occupational diseases and injuries depends on this.
And the examples given in the article show how important it is to protect against the negative consequences of exposure to HFPF, and it gives a good effect only if the workers themselves strictly adhere to the rules and regulations of occupational safety and health.
Regular real-life briefings on labor protection, constant monitoring of compliance with safety rules when performing work, work and rest schedules will help you here; the latter plays a significant role in reducing the time and degree of exposure to harmful factors.
The use of preventive measures, according to the results of the SOUT (milk, therapeutic and preventive nutrition, vitamin preparations, etc.), helps to neutralize the harmful effects of harmful and dangerous factors and increases the resistance of the workers’ body to their effects.
And, of course, a huge role, if not the most important one, is played by protective equipment, clothing and footwear, which helps reduce dangerous and harmful production factors or prevent injury to a person, as well as safety signs, posters, warning painting, protective fencing of equipment and much more.
But in any case, it is necessary to understand and convey to workers information that there are no sufficiently reliable means of protection from the effects of some harmful production factors and it is impossible to ensure the ability of the human body to withstand their effects, and not all occupational diseases caused by working conditions can be completely cured.
That is why all those working in harmful and dangerous working conditions should be provided with the compensation provided for by law, based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions.
Security measures
They are aimed, first of all, at preventing harmful production factors from exerting their dangerous effects on humans.
For this purpose, any enterprise must conduct safety training. The date and content are recorded in a special journal with the signature of all those instructed and the person who conducted the instruction.
In total, there are several types of such work:
- Induction training. It is mandatory for those hired. Age, length of service or position does not matter here.
- Primary. It is carried out already at your workplace, it is usually carried out by a foreman or the head of a given department or workshop.
- Repeated. It is carried out for all employees without exception every six months.
- Unscheduled. It is carried out if:
- The rules have changed.
- The technological process has changed.
- We purchased new equipment.
- Cases of violations of safety regulations by workers were identified.
- After long breaks from work.
Quite often you can find in practice a situation where workers are simply allowed to sign safety logs without any instructions. This is simply unacceptable. Any accident in this situation will be entirely on the conscience of such careless managers who work only for show.