Major changes in the rules for transferring wages
Now the National Payment System (thanks to the fact that almost all banks have begun working with MIR cards) is ready to begin serving payroll clients throughout the country. For this reason, employees of budgetary institutions and government organizations have been required to receive salaries on MIR cards since 2020. You can easily pay with them on the territory of Russia.
There is one change that affected not only state employees - now each employee can independently choose a bank to transfer earnings. If you work in a government agency, then the card should only be of the MIR system, and if you work for a commercial company, you can use Visa or MasterCard.
This law was dubbed by the media in 2020 as “the abolition of banking slavery.” Almost every Russian previously received a new card upon employment, and after termination of the contract he needed to change the bank or pay money for account servicing (the amount was often greater than for standard debit products).
Features of setting wages
Let's consider the features of determining wages and its dependence on the minimum wage and other indicators.
Can it be less than the minimum wage or subsistence level?
The law specifically defines the minimum wage indicator so that the company administration cannot pay its employees less than this level if they have worked the full working time. This takes into account not only the minimum salary, but also various additional payments.
If the accrued salary is lower than the minimum wage, then it must be raised to this level, otherwise administrative measures will be applied to the company.
In addition, regional authorities have the right to set their own minimum wage, but not lower than the federal value.
Attention! If an employee does not work at full time, then he may receive an accrual amount less than the minimum wage. The most important thing is that when recalculated for the entire bet size, the value corresponds to or is higher than the minimum.
At this time, the Government is gradually increasing the minimum wage to the subsistence level, so that this is consistent with the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The figures are expected to be the same as May 1, 2020.
You might be interested in:
Additional agreement to the employment contract on salary changes for 2020
In the future, the minimum wage will be taken at the cost of living, which was in effect in the 2nd quarter of the previous year. If this indicator decreases, the value of the minimum wage will remain at the same level.
If there is a regional coefficient
An employee can work in territories where special allowances are accepted for working in difficult conditions. They are determined using pre-approved regional coefficients. The list of such territories is fixed by law.
When calculating the amount of earnings, company management must take into account whether a separate minimum wage is applied in this territory or not.
If a separate minimum wage indicator has been adopted for a given region, then employee salaries must be compared with it.
If a separate minimum wage has not been established for this territory, then it is necessary to use the federal value, but adjusted by the regional coefficient. Then the salary of any employee should not be lower than this figure.
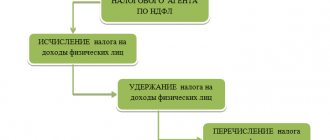
Calculation of personal income tax and minimum wage
The law determines that an employee should not be paid a salary lower than the current minimum wage.
However, when paying it, the employer, as a tax agent, is obliged to calculate and withhold personal income tax. After this operation, the actual amount in hand will be slightly less than the minimum wage.
The law does not define any additional benefits, other than standard deductions, due to the fact that the employee’s salary is equal to the minimum wage. It must be subject to personal income tax in the standard manner.
Is it possible to link wages to the staffing table?
The organization of remuneration at the company must be done so that the staffing table contains all positions with an indication of their salary. This also applies to those who work on a piece-rate payment system - for such, the planned earnings values must be indicated in the document.
However, when hiring a new employee, the amount of his earnings must be reflected both in the employment agreement and in the hiring order. And this should only be done digitally.
If the contract states that salaries are paid according to the staffing schedule, then this will be a reason to invalidate it. This is because salary information is mandatory for this document.
This kind of formulation can only be applied to additional payments - bonuses, additional payments, etc. However, in this situation, it is necessary to familiarize the employee with the documents, which stipulate the procedure for their payments (for example, the bonus regulations), against signature.
Is it possible to calculate wages in foreign currency and pay in rubles?
The Labor Code establishes that the labor agreement concluded between an employee and an organization in Russia must indicate the amount of remuneration in the national currency - rubles.
But in what currency the accrual should be made is not specified anywhere in the law. Therefore, he can make payments in foreign currency.
However, there is a pitfall here. The fact is that the salary is the amount of the employee’s earnings for the month, clearly indicated in the employment agreement. If the exchange rate falls, which will entail a decrease in the amount of wages paid, this may be regarded by the inspection authorities as a deterioration in working conditions, with management being held administratively liable.
When are payments made?
The Labor Code stipulates that the administration must pay salaries to its employees at least twice a month. At the same time, the exact dates on which this will happen must be fixed in internal documents. The period between issues cannot be more than 14 days.
bukhproffi
Important! Also, the deadline for issuing the advance should not be later than the 30th day of the month, and the second part of the salary - no later than the 15th day of the month following the settlement month.
Is it possible not to pay an advance?
The law determines that an employee must be paid a salary at least every 2 weeks. For violation of this provision, fines of up to 50 thousand rubles may be imposed.
This is precisely the employer’s obligation, and he has no right to violate it, even if the employee personally fills out an application with a request to give him earnings in one amount once a month.
In 2020, the Ministry of Labor issued a letter in which it indicated the case when an advance payment may not be paid to an employee. If he was absent from the workplace for the first 15 days (for example, he was on annual leave or sick), then the organization does not have to make the transfer, since only the time actually worked is taken into account.
Attention! However, if at least one day was worked in this period, then payment for it will need to be issued.
What changes have affected the timing of the issuance of earnings?
The timing of wages has now undergone major changes and has become more severely punished. Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, after the adjustments made, states that wages:
- must be issued at least every six months;
- the interval between payments does not exceed 15 days.
These deadlines cannot be violated even with the consent of the employee. The head of the organization is obliged to take into account the following nuances when choosing the date for transferring salaries:
- the gap of 15 days between salary and advance payments should not be exceeded;
- You should not choose floating dates, as in this case the law may be violated;
- when preparing an order for the payment of wages, you should not use the phrase “no later than ... the dates of the month,” since it sets clear dates for issuing the advance and the main part;
- To make it easier for an accountant to comply with the requirements of the Tax Code and not overwork during the billing period, it is not necessary to set the 15th and 30th for payments.
Form of payment
Remuneration may be piecework or time-based. Let's consider the main nuances of using these systems.
Piecework
In the piecework form, the total amount of funds earned is calculated based on the volume of work performed or products produced.
For piecework wages, wages are calculated using the following formula:
ZP = RI*CT,
- where RI – prices for the production of one unit;
- KT – quantity of products produced.
Consider the following example:
Ivan Ivanovich produced 100 engines in a month. The cost of one engine is 256 rubles. Thus, in a month he earned: 100 * 256 = 25,600 rubles.
Time-based
With time-based wages, wages are determined based on the number of hours actually worked, regardless of how many products were produced and how much work was performed.
Time payment for work:
For monthly salary:
ZP=O*CODE/KD,
- where ZP is wages excluding taxes;
- О – fixed salary per month;
- KOD – days worked;
- KD – number of days in a month.
For hourly/daily fixed salary:
ZP=KOV*O,
- where ZP is wages excluding taxes;
- KOV – amount of time worked;
- O – salary for one unit of time.
Let's look at an example:
Tatyana Ivanovna has a monthly salary of 15,000 rubles. There were 21 working days in a month, but since she took vacation at her own expense, she worked only 15 days. In this regard, she will be paid the following amount: 15,000*(15/21)=15,000*0.71= 10,714 rubles 30 kopecks.
Second example:
Oksana Viktorovna works with a daily salary of 670 rubles. She worked 19 days this month. Her salary will be: 670*19 = 12,730 rubles. As you can see, the formula for calculating wages for this type of payment is very simple.
What responsibility does an employer bear if wages are not paid on time?
For violation of the terms of payment of wages to employees, the employer faces administrative and financial liability. In the first case, he will be responsible to the state, in accordance with the Administrative Code.
According to Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, namely its paragraph 1, for a primary violation an organization may be punished in the form of:
- warnings;
- a fine of 1 to 5 thousand rubles for responsible persons or individual entrepreneurs;
- fine from 30 to 50 thousand for legal entities.
In case of repeated violation, the punishment is imposed in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses:
- disqualification for a period of 1 to 3 years;
- a fine of 10 to 20 thousand rubles to an official or individual entrepreneur;
- fine from 50 to 70 thousand for a legal entity.
Moreover, in addition to the administrative penalty, which is collected in favor of the state, the employer bears financial liability to its employees. In accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, for each day of delay, the employee must pay 1/150 of the key rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in 2020 of the amount withheld. The compensation is issued along with the salary; no application from the employee is required to receive it.
Who is obliged to index salaries?
Absence in Art. 134 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a clear procedure for indexing salaries leads to the fact that a number of commercial organizations do not increase the salaries of their employees at all.
At the same time, they refer to this same article, which states that employers carry out indexation in the manner established in the collective agreement or other local act. Accordingly, in their opinion, if a local act does not contain a provision on indexation, then it is not necessary to carry it out.
In fact, this point of view is wrong. This has been repeatedly recognized by the Constitutional Court (decision of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of November 19, 2015 No. 2618-O, determination of July 17, 2014 No. 1707-O).
The court explained that the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not allow an employer not related to the public sector to deprive employees of the right to a salary increase. Nor does it allow one to evade the establishment of wage indexation. Therefore, when formalizing an employment relationship, the employer must negotiate with the employee the procedure for increasing his salary. The procedure for indexing wages is determined in a collective agreement, agreement or any other local regulatory act.
At the end of 2020, Rostrud warned employers that the absence of a salary indexation provision in an organization does not exempt the employer from such indexation. If at the end of the year Rosstat recorded an increase in consumer prices, and the employer did not index salaries, he will be fined. If the employer did not approve the indexation provision, he will be obliged to do so.
The Ministry of Labor also recalled the indexation of wages in 2020, clarifying that the employer is obliged to ensure an increase in the real content of workers’ wages.
Thus, all employers without exception are required to index employee salaries. Moreover, regardless of the presence or absence of indexation provisions in the organization.
New rules on advances
In 2020, officials clarified the rules for paying advances. They recommend:
- The size of the advance should not be determined arbitrarily; it should not be a larger or smaller part of the salary.
- It is prohibited to set an advance payment of a fixed amount for all employees.
- Calculations must be carried out in proportion to the working time of employees.
- When determining the amount of the advance, it is necessary to take into account: salary and allowances. In this case, you cannot take into account those bonuses that are included in the final calculation of work for the month: bonuses for completing volumes, incentives for additional or night shifts.
- Incentive and compensation payments are taken into account at the time of salary calculation, that is, wages for the second half of the month worked.
Personal income tax is not paid on the advance amount; it must be deducted from the final salary amount. It is worth remembering that the difference between the advance payment and the final payment cannot be unreasonably increased.
Calculation of vacation pay in 2020 (calculation examples)
Example 1. Accountant O.P. Petrova, according to the vacation schedule, goes on vacation from April 1, 2020 for 14 calendar days. The billing period will be from April 1, 2020 to March 31, 2020. At the same time, Petrova was on vacation in July 2020 (from the 1st to the 28th) and received vacation pay in the amount of 35,000 rubles. In addition, in October 2019, Petrova was on sick leave for 10 days, for which she provided a certificate of incapacity for work. Petrova’s sick leave was accrued in the amount of 10,000 rubles. Petrova’s income minus vacation pay and sick leave for the billing period amounted to 400,000 rubles. The number of days in the billing period was: 10 full months, 3 days in July and 21 days in October.
- Leave is provided to employees according to the vacation schedule. The employer must approve the schedule before the new year, at least 2 weeks in advance. Each employee must be familiar with this schedule.
- The 12 months preceding the start of the vacation are taken into account as the calculation period for calculating vacation payments. If an employee has been working in an organization recently, then he can be granted leave 6 months after being hired.
- The days the employee is on sick leave, on vacation, business trips, caring for disabled children, as well as forced downtime are excluded from the calculation period.
- If salary indexation took place during the billing period, then vacation pay must also be indexed. Indexation is necessary even if vacation pay has already been paid to the employee.
- Personal income tax must be withheld from the calculated amount of vacation pay, as well as insurance premiums must be calculated. The employer is obliged to pay personal income tax and insurance contributions to the budget (
In what case will the weekend be paid?
Another rule for paying salaries in 2020 concerns holidays. It directly affects the income of workers, since the employer is now obliged to provide paid days off required for medical examination. The modified Article 185 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation now obliges enterprises to allocate paid days:
- twice a year - for working pensioners and people who have less than 5 years left before their well-deserved rest;
- once every 3 years - to all other employees.
To receive such a day off, the employee must write an application, agree on the date of absence from the workplace with the boss, and submit a certificate of medical examination to the accounting department. In the timesheet, this day will be reflected according to the average number of hours, and according to this, the salary will be calculated.
Accounting and reporting
| What's changing since 2020 | The essence of the changes | Normative source |
| Accounting statements must be submitted to the Federal Tax Service | Starting with reporting for 2020, financial statements must be submitted not to Rosstat, but to the Federal Tax Service in electronic form (except in certain cases) | Law of November 28, 2018 No. 444-FZ |
| The manager has the right to sign electronic accounting records using an electronic signature | From 2020, the condition that financial statements are recognized as prepared only after they are signed by the manager is supplemented by a new condition? electronic reporting is recognized as compiled after it is signed by the manager using an electronic digital signature | Law of November 28, 2018 No. 444-FZ |
| Will tax authorities conduct GIRBO? State information resource for financial statements | A procedure has been established for submitting reports (including corrected accounting reports) to the State Register of Internal Affairs | Law of July 26, 2019 No. 247-FZ Information of the Ministry of Finance of August 22, 2019 No. IS-accounting-20 “On amendments to the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting” |
| It will be possible to obtain information from GIRBO about other companies or individual entrepreneurs for money | From 2020, access to GIRBO will become paid. For 200 thousand rubles. per year, tax authorities will provide information about counterparties at your requests throughout the year. The Federal Tax Service has already developed regulations for the provision of information from GIRBO. Reports for 2020 and earlier periods will continue to be provided by Rosstat free of charge | Law of November 28, 2018 No. 444-FZ Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of June 25, 2019 No. 811 |
| Accounting reporting forms have changed (valid from 06/01/2019) | All reporting forms now need to be filled out only in thousands of rubles (previously it was possible in millions of rubles), OKVED was replaced by OKVED2, and other amendments were made (mostly of a technical nature) | Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 19, 2019 No. 61n |
| Workers were obliged to comply with the requirements of the chief accountant | From 2020, the chief accountant’s requirements for the correct execution of primary documents will become mandatory for all employees | Law of July 26, 2019 No. 247-FZ |
| Rent must be taken into account according to new rules | According to the Ministry of Finance, companies should now apply either the new standard FSBU 25/2018 or IFRS for leasing (clause 7.1 of PBU 1/2008). And this despite the fact that formally the standard is mandatory for reporting for 2022 (clause 48 of FSBU 25/2018, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 16, 2018 No. 208n) | FSBU 25/2018 “Accounting for leases”, approved. By Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 16, 2018 No. 208n |
| Changed the accounting procedure for state aid | The rules for accounting for state aid have been brought into line with IFRS (IAS) “Accounting for government subsidies and disclosure of information about government aid” | PBU 13/2000 “Accounting for state aid” |
| The rules for accounting for differences in income tax in PBU 18/02 have changed |
| PBU 18/02 “Accounting for corporate income tax calculations” |
| Added to PBU 16/02 “Information on discontinued activities” | Starting from reporting for 2020, information about discontinued operations must include information about the termination of the use of long-term assets for sale | Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 04/05/2019 No. 54n Information of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 07/09/2019 No. IS-accounting-19 “On changes to PBU 16/02” |