Business lawyer > Labor law > Accruals and payments > Allowance for hazardous working conditions: what is it and how to calculate it. Conditions and features of receipt
Despite the fact that progress does not stand still and most enterprises are equipped with the most modern equipment, risk factors for workers in certain types of activities simply cannot be excluded. Therefore, employers are obliged to compensate for the harm that their employees receive, and one of the methods of compensation is a bonus for harm to wages.
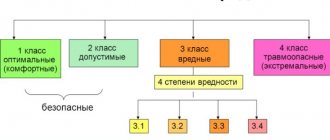
Degree of harmful working conditions
The conditions in which we work can be divided according to the degree of their harmfulness for the worker into optimal, acceptable, harmful and dangerous. What is the difference between them:
What are considered harmful conditions
- Optimal working conditions can be called when the employee is not in danger, or the harm that the employee may receive is minimal. There is also another interpretation of optimality: these are those conditions where the harm caused to an employee is not higher than the level that is safe for the population. In such conditions, the employee is comfortable working, he is productive, all the main environmental parameters (humidity, temperature, etc.) are normal.
- Acceptable conditions are those if after work the employee can recover before starting his shift again. The harm caused to an employee in the workplace should not have a significant impact on his health, nor should it in any way affect the health of his future children.
- Harmful working conditions are no longer safe for a person and even for his future children. Such conditions can be divided into degrees:
- the employee can recover, however, he needs much more time than under acceptable working conditions
- working conditions lead to mild occupational diseases
- can lead to chronic diseases
- possible loss of ability to work
- Extreme working conditions. They occur when during a work shift there is a threat to the worker’s life, as well as a risk of developing lesions.
In general, the vast majority of occupations are those where the conditions do not cause much harm (for example, most office jobs). Ordinary workers in factories are often exposed to hazardous working conditions.
Compensation for harmful working conditions
- exposure to harmful and dangerous production factors exceeding the levels established by standards, namely if the functional state of the employee’s body is restored, as a rule, longer than before the start of the next working day;
- or if harmful factors are capable of causing persistent functional changes in the employee’s body, leading to the emergence and development of initial forms of occupational diseases or occupational diseases of mild severity;
- or if harmful factors lead to persistent functional changes in the employee’s body, leading to the emergence and development of occupational diseases of mild to moderate severity.
- exposure to harmful factors during the working day can create a threat to the life of an employee, and the consequences of exposure to these factors cause a high risk of developing an acute occupational disease
This is interesting: When will the transport tax be abolished in Russia 2020 latest news
Each of the above factors must be reflected in the SOUT act, as well as in the contract.
From the point of view of legislation, the production process includes two parties: the employee and the employer. Determining the harmfulness of the situation at the enterprise affects the content of the employment contract between them. That is, if conditions are harmful to health, then this should be stated in the agreement when applying for a job.
Why should an employer pay extra?
Increased noise levels, low or high temperatures, humidity, working with chemicals, radiation - this is a small list of conditions under which an employee is entitled to a bonus.
Milk for being “harmful”
Each organization is required to conduct a special assessment of working conditions (special assessment of working conditions) once every five years. If, after an assessment, it is revealed that employees are working in harmful conditions, then the employer must compensate them for this and employees may be entitled to the following types of compensation:
- reduced working hours
- additional leave of at least 7 days
- issuing special items (for example, medical nutrition)
- early retirement
- treatment in sanatoriums
- issuance of special clothing
- salary supplement
The duration of additional leave does not exceed 7 days, and in order to receive it, the employee must work in hazardous conditions for more than one year.
Special clothing is required to be issued by the employer at those places of work where the employee is exposed to chemicals, radiation, high humidity, temperature changes and other adverse environmental conditions. The employer, at his own expense, must provide washing, drying and storage of special clothing, and it must also be provided to employees free of charge.
In addition to special clothing, factory workers often receive special food, such as free milk, as compensation. Moreover, at work where working conditions are particularly harmful, therapeutic nutrition should be provided. The norms for issuing and also the rules by which medical nutrition is provided are approved by Order No. 46 of February 16, 2009. Ministry of Health.
Of course, an assessment of how harmful working conditions can be carried out not only by a special commission, but also determined by the employer independently, for example, based on the presence of a particular position in special lists of hazardous professions. Of course, this method cannot be 100% correct and is considered outdated today.
Amount of surcharge for harmful conditions
Supplement amount
Most often, it is the wage supplement that is found, because it is provided for in all categories of conditions under which harm may be caused to the employee’s body.
If an employee performs tasks in harmful or even dangerous working conditions, he is entitled to an increase (at least 4%) to his salary. This payment does not depend on how harmful the conditions are. As working conditions worsen, the employee is given additional leave (usually 7 days), and his work week is shortened (by at least 4 hours).
Compensation for working conditions is regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as some Federal Laws.
If the employer does not pay the appropriate allowances, he is thus violating the law and may be subject to legal liability.
As a rule, employers almost always try to avoid additional payments to employees. Even if, after carrying out the special assessment, it was revealed that some subordinates need to be paid extra, then employers will pay the minimum, i.e. 4% of wages. However, at state-owned enterprises this percentage is almost always higher due to the fact that they have trade unions that defend the rights of workers and demand that the employer increase the rate (for example, up to 10% of wages).
The established amount of compensation for harm must be specified in the contract with the employee and in all other regulatory documents.
Is there compensation for harmful conditions when working as a plumber?
Good morning! Identification of harmful and (or) dangerous factors in the production environment and the labor process (hereinafter also referred to as harmful and (or) hazardous production factors) and assessment of the level of their impact on the employee, taking into account the deviation of their actual values from established hygienic standards, working conditions and the use of personal protective equipment and collective protection of workers is carried out in accordance with Federal Law dated December 28, 2013 N 426-FZ “On special assessment of working conditions”.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation imposes on the employer the obligation to conduct a special assessment of working conditions to identify harmful factors and their classification (Articles 22, 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This is exactly what the enterprise's labor protection service should do. The identified harmful factors are indicated in the labor protection instructions, which the employee is periodically introduced to during briefings. As a rule, for housing and communal services plumbers, harmful factors include: - infected material and material contaminated or suspected of being infected with microorganisms of 3 - 4 groups of pathogenicity (danger) or helminths; — physical overload (physical dynamic load, weight of a load lifted and moved manually, stereotypical working movements, static load, working posture, body tilts, movement in space) (when working conditions are classified according to these factors based on the results of certification of workplaces for working conditions to a subclass harmfulness 3.1 and higher); - work performed directly on mechanical equipment that has open moving (rotating) structural elements (lathes, milling and other machines, stamping presses, etc.)
This is interesting: If a House is Recognized as Non-Residential, Is the Cadastral Number Removed from Rosreestr?
How to set a premium
In order for the allowance to take effect, the organization must take the following steps:
After the examination
- Determine its size.
- Fix the amount of the allowance in the regulations of the organization.
- Make changes to the contract or agreement with the employee (you can make an additional agreement).
- Pay an allowance.
In order to calculate the premium, you should rely on the following points:
- minimum allowance amount
- industry agreements
- opinion of the trade union (if there is one)
Some industries have special agreements that regulate the amount of the premium (for example, in the coal industry). If the type of activity of your organization is covered by such an agreement, then you should rely on it, and not on the minimum amount of the allowance established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The trade union decision must also be taken into account when deciding this issue.
Payments for harm caused in the workplace are not subject to contributions to extra-budgetary funds, as well as insurance premiums that the employer pays to cover the costs of accidents occurring at the enterprise.
The Labor Code imposes on the employer to prescribe compensation for hazards in the Regulations on remuneration at the enterprise, as well as in the employment contract.
Compensation for unfavorable working conditions can be canceled in an organization if, during the assessment of labor conditions carried out every five years, changes in working conditions for the better are identified to optimal or acceptable conditions.
What compensation is due for harmful working conditions in Russia in 2020
The Labor Code in Article 222 states that a number of workers must be given milk as harmful (or other equivalent food products). The norm for such distribution is 0.5 liters per work shift of any duration.
This is interesting: Payments from Maternity Capital in 2021 in Cash Fresh
Some industries provide for the issuance of dairy products (Article 222 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation No. 45n). Let us remind you that the cost of milk for calculating compensation for harmfulness is determined at the rate of 0.5 liters per shift per employee.
How to calculate the premium
Remuneration can be time-based or piece-rate. Let's calculate the premium for both types. In case of time payment, it can be calculated based on the hourly rate, daily rate and monthly salary.
To calculate wages with hourly wages, taking into account the bonus, we use the following formula:
(Hourly rate + Hourly rate x Percentage bonus) x Number of hours worked = Salary including bonus
When calculating wages taking into account the bonus with daily wages, the formula remains the same, however, instead of the number of hours worked, we multiply by the number of days worked. For monthly salary, use the following formula:
Salary + salary x bonus percentage = Salary
Let's look at the calculation using a specific example. For example, employee N worked in the workshop for 144 hours, this employee receives 120 rubles per hour. The employer has determined that for every hour the hourly rate increases by 15%. From this it follows that the employee will receive in a month:
(120 + 120*0.15)*144 = 19,872 rubles.
Additional Information
Payments for harm caused by work are in no way related to the position the person occupies. It only concerns the work he performs. Moreover, the premium can be expressed not as a percentage, but as an amount that is either the same or different for all workers performing hazardous activities.
The controlling bodies for regulating the payment of bonuses are Rostrud and the Labor Inspectorate.
If an employee believes that he is working in harmful conditions, he can apply to the employer for compensation. If a negative response is received from the employer, the employee has the right to contact the regulatory authorities so that they can organize a check to see how harmless the working conditions at the enterprise are. To do this, you only need an application from the employee, as well as a work book with a confirming record of his device.
Top
Write your question in the form below