What are hygienic standards for working conditions?
Hygiene standards for working conditions are generally accepted indicators from government regulations. If during a work shift the employee is not influenced by harmful factors, then this does not pose a health hazard.
If the opposite happens, a person accumulates substances in the body that can harm health. This happens over the course of a work shift, week, month and year. It turns out that he may have an occupational disease.
The cause of the latter will need to be established. Working conditions are divided into four classes, in turn the third class is divided into subclasses. This is regulated at the legislative level.
The inspection is carried out on a commission by expert organizations together with the management team of the enterprise. In other words, a special assessment of the conditions of the labor process should be carried out for compliance with regulatory parameters.
Acceptable conditions
Acceptable working conditions have levels of environmental factors that should not exceed those established in the hygienic standard.
The working functions of the body must be fully restored after rest by the start of a new shift. Environmental factors should not have an adverse effect on human health even in the long term, as well as on the health of his offspring. The permissible class of conditions must fully comply with the standards and safety of working conditions.
What are optimal working conditions?
If a person works and such conditions do not pose any danger to life and health, then they are called optimal.
To make sure of this, you need to check the following:
- Check vibration level.
- Measure show electromagnetic radiation.
- Assess the impact of harmful factors.
- Measure gas and dust levels in the air.
- Assess the level of noise and illumination using special instruments.
- Conduct a risk assessment from exposure to devices or technical devices installed at the employee’s workplace.
- Other measurements may be made depending on technology and production and the presence of other hazards or equipment.
If after taking measurements according to the established parameters there were no deviations, it can be stated that it is safe to work in this place and this class of conditions belongs to the optimal, that is, the first.
What are acceptable working conditions?
Specialists from an expert organization are invited to carry out instrumental measurements, that is, an agreement is concluded with experts to conduct a special assessment. The following work is carried out:
- The level of noise, dust, gas contamination and other parameters is checked in accordance with production technology.
- Equipment performance is assessed.
- Laboratory tests are being carried out.
- Based on the tests performed, the results obtained are compared with the standard ones.
The regulations specified in the standards show that the results obtained do not exceed acceptable values, that is, there is no negative impact.
This class of working process conditions is considered acceptable, that is, human activity is associated with harmful substances and indicators, but the substances and other indicators determined by measurements do not exceed the maximum permissible concentration or maximum permissible limit. This is the second class of danger.
The maximum permissible values of a harmful production factor for maintaining health, at which its harmful effects are practically absent and can be completely neglected, are usually called hygienic standards (maximum permissible concentration - MPC, maximum permissible level - MPL, etc.). Hygienic standards for working conditions (MPC, MPL) - levels of harmful factors in the working environment, which, when working daily (except weekends) for 8 hours and no more than 40 hours a week, during the entire working experience, should not cause diseases or abnormalities health, detected by modern research methods in the process of work or in the long term of life of the present and subsequent generations. Compliance with hygiene standards does not exclude health problems in people with hypersensitivity. The introduction of MPCs and MPLs made it possible in practice to differentiate between safe working conditions, where concentrations are below MPCs (levels below MPCs), which means occupational diseases are practically impossible, from unfavorable working conditions, where concentrations (levels) are above MPCs (MPCs) and the occurrence of occupational diseases is much higher. more likely. Almost all hygienic regulation of harmful production factors and working conditions is based on this principle.
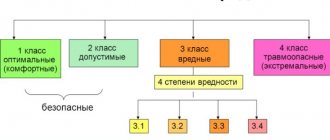
Currently, working conditions are classified according to the hygienic criteria established in Guideline R 2.2.2006–05 “Guide to the hygienic assessment of factors in the working environment and the labor process. Criteria and classification of working conditions”, according to which working conditions are divided into 4 classes: optimal, acceptable, harmful and dangerous.
Optimal working conditions (class 1) – conditions under which the employee’s health is maintained and the prerequisites are created for maintaining a high level of performance.
Acceptable working conditions (class 2) are characterized by such levels of environmental factors and the labor process that do not exceed established hygienic standards for workplaces, and possible changes in the functional state of the body are restored during regulated rest by the beginning of the next shift and do not have an adverse effect in the immediate and long term period on the health status of workers and their offspring. Acceptable working conditions are conditionally classified as safe.
Harmful working conditions (class 3) are characterized by the presence of harmful production factors, the levels of which exceed hygienic standards and have an adverse effect on the worker’s body and / or his offspring. Harmful working conditions, based on the degree of exceeding hygienic standards and the severity of changes in the body of workers, are divided into 4 degrees of harmfulness:
– 1st degree, 3rd class (3.1) – working conditions are characterized by such deviations in the levels of harmful factors from hygienic standards that cause functional changes, which are restored, as a rule, with a longer interruption of contact with harmful factors (than at the beginning of the next shift), and increase the risk health damage;
– 2nd degree, 3rd class (3.2) – working conditions under which the levels of harmful factors cause persistent functional changes, leading in most cases to an increase in occupational morbidity, which can be manifested by an increase in the level of morbidity with temporary disability, the appearance of initial signs or mild forms occupational diseases that occur after prolonged exposure (often after 15 years or more);
– 3rd degree, 3rd class (3.3) – working conditions characterized by such levels of harmful factors in the working environment, the impact of which leads to the development, as a rule, of occupational diseases of mild and moderate severity (with loss of professional ability to work) during work, the growth of chronic (occupational conditioned) pathology;
– 4th degree, 3rd class (3.4) – working conditions under which severe forms of occupational diseases can occur (with loss of general ability to work), there is a significant increase in the number of chronic diseases and high levels of morbidity with temporary loss of ability to work.
Hazardous (extreme) working conditions (class 4) are characterized by levels of working environment factors, the impact of which during a work shift (or part of it) creates a threat to life, a high risk of developing acute occupational injuries (including severe forms). Work in hazardous working conditions (class 4) is not allowed, with the exception of emergency response and emergency work to prevent emergency situations. In this case, the work must be carried out in appropriate personal protective equipment and in strict compliance with the time schedules regulated for such work.
Degrees of harm
Working conditions are divided into degrees of harmfulness:
- Class 1 - these are optimal conditions . That is, the impact of harmful factors on a person is completely eliminated, and his health is safe.
- Class 2 - acceptable . There is exposure to harmful factors during the working day, but everything is within normal limits.
- Class 3 - harmful . These are conditions under which an employee is affected by negative indicators and, after tests, their level is more than normative.
- Class 4 - dangerous . The employee is affected by factors that clearly cannot have a positive effect on his health. The consequences may cause the risk of developing diseases. Such jobs must be eliminated, as it is not allowed to work in them.
4 classes of harmful working conditions
The third class of conditions has four subclasses, namely:
- 3.1 - when exposed to harmful substances during a shift, a person’s health quickly recovers before the start of the next shift. That is, the impact stops and the body’s recovery begins.
- 3.2.- when exposed to such a level of dangers and hazards, permanent changes begin in the body, which can ultimately lead to the development of an occupational disease. It may take about ten to fifteen years for this to manifest itself, but it all depends on the condition of the person as a whole.
- 3.3 - when exposed to harmful factors, there is a deterioration in health, which can lead to mild or moderate occupational disease. The period of disability can last a long time.
- 3.4 - working in workplaces with this hazard class, an employee can get a persistent occupational disease, while persistent loss of ability to work accompanies him.
Depending on the hazard class established by the commission, the percentage of additional payments for hazards is determined. This compensates for the loss of health.
Hygienic criteria for assessing working conditions and factors
To assess working conditions, two parameters are used:
- maximum permissible concentration - this concept is used to assess the concentration of substances;
- maximum permissible level - determines the upper limit of the impact factor, i.e. maximum level.
Sanitary rules are developed for each type of enterprise separately. There is no single regulatory document, therefore, when examining the level of negative impact of production factors on a person, you should study the provisions for a specific organization. For example, the requirements for noise levels in a medical institution and in a factory will be different, and the regulations for the level of illumination in an educational organization will be different than in a catering establishment.
Harmful factors
Harmful factors come in different directions, these include:
- Chemical and biological substances . When exposed to the body in the maximum permissible concentration, they do not have a harmful effect, but if the concentration of these substances is at a level that exceeds the limit, then the body has a negative effect.
- Noise . If the limit exceeds 80 dB, then your health is at risk.
- Electromagnetic radiation . When exposed to humans, it can cause radiation sickness, so you should carefully consider this issue. Check the grounding device and other mandatory measures.
- Dust in the air shows that a person's lungs are under a lot of stress and after this the soft tissues become rough.
Class assignment
Expert organizations that operate accredited laboratories can classify labor as hazardous. This procedure is performed during a special assessment of working conditions.
Attribution algorithm:
- Measurements are taken, and the instruments used in the work must be verified and the laboratory assistants certified.
- After measurements are taken, analyzes are carried out.
- Based on the tests carried out, it is established how many times the maximum permissible concentration exceeds the standard value.
- The obtained data is entered into the protocol, and then into the certification card.
- Based on the results obtained, the percentage of additional payment to employees is established.
At-risk groups
If workers are exposed to harmful influences during their shift, they can be classified as high-risk. That is, hygiene standards are exceeded. Working in such conditions contributes to the development of occupational diseases.
Lists of professions No. 1 and No. 2 have been adopted, which include workers associated with metallurgical production.
Employees working in extreme conditions include persons whose health condition may suddenly deteriorate.
Hygienic assessment of work
Based on the developed methods and other regulations, a hygienic assessment of working conditions is carried out. The main goals of the event are:
- Ensuring control over the state of health and safety based on accepted standards. Enterprises are developing a production control program. Depending on the class of harmful substances, the frequency of measurements is established. The latter can be performed by employees who have certificates. Audits are carried out by employees from other higher organizations, such as Rospotrebnadzor and expert companies.
- Determining which activities need to be carried out first, including assessing the effectiveness of completed tasks.
- Creation of a data bank on the conditions of the labor process at enterprises.
- Analyzing the health status of employees, conducting special examinations and establishing diagnoses. Organizations are required to conduct medical examinations annually, that is, if deviations in health status are detected, the presence of occupational diseases is determined.
- Conducting an occupational risk assessment if an employee performs production tasks in hazardous conditions.
If any regulatory indicators are violated, the responsibility of the facility manager is to urgently take measures to eliminate such cases. Excesses of hazardous factors must be eliminated, if possible, or reduced to a minimum level.
What harmful factors do doctors (surgeons) encounter?
The activities of surgical specialists consist of diverse elements. Doctors examine patients, participate in some diagnostic procedures, prepare patients for surgery, make dressings after operations, and regularly make rounds. Doctors spend a lot of their working time preparing related documents, scientific conferences, consultations, consultations with highly specialized specialists, discussing proposed interventions, and issuing recommendations to patients and their relatives. At the same time, operating activities occupy the predominant part of the working time of surgeons, due to which they stand out from the entire category of medical workers.
One of the harmful factors in the sanitary and hygienic working conditions of a surgeon can be called night shifts. The higher the doctor's qualifications, the lower their frequency. Novice specialists are on duty on average 4-6 times a month. Moreover, this applies to obstetricians-gynecologists, ophthalmologists, and otorhinolaryngologists. With the participation of on-duty specialists, ambulance teams visit patients, perform diagnostic procedures, surgical interventions and other emergency measures to save the lives of patients in serious condition.
In comparison with the sanitary and hygienic characteristics of representatives of the professions discussed above (miners and drivers), the working conditions of a doctor can be considered the most favorable, despite shortcomings in the organization of working time and the uneven distribution of professional workload.