Working conditions and intensity
To characterize the place of work, determine the standards and area of responsibility of the employer, processes should be divided into classes according to the degree of harmfulness. Determine which jobs are subject to a special assessment of working conditions. Standards are needed to improve production safety and determine the ratio of work and rest time.
The manager, on the basis of Article 212 of the Labor Code, is obliged to organize:
- safe working conditions for personnel;
- safety training for each team member followed by certification;
- access to trained personnel;
- staff work schedule taking into account employment and rest standards;
- reasonable level of work intensity.
The developed measures are aimed at maintaining the employee’s labor activity.
Legislation
All harmful conditions and division into classes are based on the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Several Federal laws that regulate the procedure for conducting special assessments and identifying other characteristics of activities have a great influence. They also determine the procedure for providing benefits and other additional compensation.
Class three, which is also divided into four additional levels, implies hazardous operating conditions. Employees who belong to it are entitled to benefits and bonuses in accordance with the law.
In conclusion, we can say that all hazardous conditions are divided into classes and are regulated by the Labor Code and individual Federal laws in accordance with the type of activity performed.
https://youtu.be/eeZUDxFBHe8
How is the degree of harm and danger determined?
In the process of studying, classes of working conditions are determined according to the degree of harmfulness and danger. The heterogeneity of objects and the nature of work is taken into account. Criteria in different sectors of labor activity are studied:
- without the use of physical force;
- with light and short-term load;
- associated with average physical activity;
- using physical effort and in harmful conditions.
Work intensity is assessed according to state employment standards, workload per shift, and compliance with sanitary standards. The heterogeneity of industrial enterprises and organizations makes the process of developing safe criteria difficult. The following indicators are used as a basis:
- level of physical effort;
- concentration of chemical pollutants;
- biological parameters;
- Features of the workplace associated with intellectual stress.
The degree of danger is determined by prolonged exposure to harmful substances or factors on the body.
Based on the results of an analysis of labor relations in Russia, Federal Law 426 dated December 28, 2013 was issued. Article No. 14 adopts a classification of occupational hazards in enterprises and organizations.
Compensation for employees of dangerous and harmful production areas
The current norms of labor legislation regulate the provision of an increased salary in the event of carrying out production activities with dangerous and (or) harmful working conditions (clause 1 of Article 146 and clause 1 of Article 147).
Employees of enterprises retain the right to additional payment to their salary if it was determined based on the results of workplace certification completed no later than 01/01/2014. Changing the amount of compensation or canceling it is possible only after the employer organizes an SOUT.
Based on clause 2 of Article 147 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the minimum increase in wages for work in unfavorable conditions is 4% of the tariff rate in force for production activities with normal working conditions. An increased amount of payments, approved by the representative body of workers, can be specified in a collective agreement or a local act of the enterprise. It is most advisable to increase payment for work in special conditions through compensatory additional payments, since when determining the increased amount of the main part of the salary, it is difficult to isolate its component in the form of compensation. Reducing or eliminating compensation requires adjusting the terms of the employment agreement. It is carried out by agreement of the parties or in a special manner related to changes in the technological and organizational conditions of labor activity.
Regulatory framework for enterprise organization
Now, for every organizer of the work process in Russia, Federal Law 426 serves as a priority guide. The law defines jobs that are subject to a special assessment of working conditions at enterprises based on the listed criteria.
Article 7 lists requests aimed at reducing the consequences of harmful factors on employee health and the state of the environment. Comprehensive measures are being developed, with the appointment of compensation in the form of increasing tariffs, additional leave, and reduction of length of service. At the same time, contributions for environmental violations to the pension and insurance fund are increasing. That is, conditions are created when it is beneficial for an organization to reduce the classes of working conditions with a special assessment of working conditions.
The Law on the Assessment of Working Conditions has become the main document regulating business relations in Russia. The Labor Code, section 10, and the provisions on labor protection of the Russian Federation are equally valid. To eliminate discrepancies between Federal Law 426 and other Orders and Resolutions of state bodies, Federal Law 421 was issued. It amends laws to eliminate discrepancies.
As stated in the employment contract
A new employee, when signing an employment contract with the employer, has the right to know future working conditions. The agreements have a whole section that describes working conditions, protection, and indicates the class.
ATTENTION! If the type of work activity is dangerous, workers must be warned about this.
The contract does not just indicate the presence of harmful factors - they are described in detail, as well as their impact on health. If an agreement states an optimal or permissible class of conditions, this provision must be respected. If working conditions are violated, you should contact the Labor Commission or the Sanitary and Epidemiological Service.
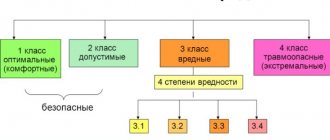
Classes of working conditions
Law of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation No. 33 introduced the SOUT system (special assessment of working conditions) as a control tool. Within its framework, a gradation technique for identifying and measuring harmful factors has been created. The result of the study is the determination of the class of the workplace. Working conditions are divided into 4 classes.
Article 14 classifies the features listed in the table.
| Class Working conditions | Characteristics of the workplace determined on the basis of characteristics |
| I Normal | No or minimal environmental exposure. Favorable conditions. |
| II Acceptable | The level of environmental pollution is moderate, fatigue is low during the shift, and there is enough time for rest. |
| III Harmful | Excess of factors affecting health. Gradation into subclasses 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4 depending on the possible consequences for the body. |
| IV Dangerous | High level of danger. Cumulative exposure to risk factors can lead to disease. |
It is clear that even in hazardous industries there are work areas of all categories. If working conditions class 2 is defined, what does this mean? There is an adverse effect, but it is within tolerance. A person will have enough time between shifts to fully recover.
Working conditions of the third class, according to the SOUTH, are divided into 4 subclasses of hazards:
- 1 – to recover from the effects of work characteristics, a break between shifts is not enough, there is a risk of deterioration in health;
- 2 – risk of occupational disease without loss of ability to work;
- 3 – the consequence of work can be chronic diseases;
- 4 – high probability of exacerbation of diseases and disabilities.
Before the implementation of SOUT, monitoring and certification of workplaces (AWS) was carried out on the basis of Order 342 of the Russian Federation dated April 26, 2011, order of the Ministry of Health. The difference between the AWP and SOUT methods is in the regulations. The classes of working conditions are identical, certification of workplaces according to AWS, carried out before December 28, 2013, remains in force for the next 5 years.
Procedure for assigning a hazard class
The SOUT inspection is carried out by a licensed organization upon request from the head of any structure. For an uncertified workplace, the manager faces penalties. Within 6 months after the establishment of the enterprise, the manager is obliged to initiate an SOUT. This will determine into which classes the working conditions at a given enterprise are divided.
The SOUT expert must have a certificate. The commission, chaired by the head, includes a labor protection engineer and members of the trade union committee.
Commission functions:
- Prepare documentation for each workplace to be assessed.
- Make a work schedule.
- Check the actual names of professions with the All-Union Classifier and bring them into compliance.
- Evaluate measurements of physical and chemical parameters by a certified laboratory.
- Develop measures to eliminate harmful and dangerous factors.
- Approve the report to the Labor Inspectorate.
- Familiarize the employee with the result against signature.
Based on the results of a comprehensive check, a SOUT card with an identification number is drawn up. The results of an organization's audit are valid for 5 years.
Possible downgrading
Unfavorable workplace conditions are financially disadvantageous to the organization. In connection with such conditions, the employer must:
- increase contributions to the pension and insurance fund;
- raise the worker's pay;
- add days to vacation.
Extra expenses are a direct incentive for the manager to introduce new technologies and work methods. If working conditions have improved significantly, the manager can initiate an unscheduled inspection of the workplace and raise the indicator to the second class.
In May 2020, the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation is introducing a methodology for reducing the subclass of hazard class 3, using modern personal protective equipment, and improving working conditions. At the same time, a commission is created and objectively evaluates the positive aspects of reducing the hazard class. The work is carried out in accordance with accepted regulations.
Occupational injury hazard assessment
In the new law, the risk of injury, the use of personal protective equipment and the hygiene component are excluded from the special safety regulations, contrary to the logic and proposed amendments during the discussion of the draft law. The legislator considered that injuries due to safety violations cannot affect the inclusion of a workplace in the list of benefits. The risk of injury was determined in the automated workplace and classified into three levels.
Hygienic criteria and microclimate indicators of the workplace
The measurement methodology is Appendix No. 1 to Order No. 33 of the Ministry of Labor. The physical parameters of the microclimate and vibroacoustic loads on the body are of decisive importance for comfortable work. In the automated workplace, these indicators were subject to measurements in all places. SOUT provides for measurements only in cases of installation of technological equipment. In one workshop, with hazardous working conditions of class 3, this indicator will be measured in the immediate area of its action.
Workplace illumination is a standardized indicator. By order of the Ministry of Health, under the automated workplace the factor was considered mandatory, in the SOUT it became selective.
Until February 2013, electromagnetic radiation was monitored at all workplaces; according to the SOUTH, the indicator was left for specialists involved in electronics. The class of working conditions according to the AWS determines more factors than the SOUT. The abolition of automated workplaces led to the loss of important hygienic indicators from the assessment of workplaces.
Workers' compensation
There are several ways to compensate for the harmfulness of working conditions. They are established by law.
The employer can only increase the amount of compensation; he does not have the right to reduce the approved standards:
- Under 3rd class working conditions, additional paid leave of at least a week may be provided.
- The working week can be reduced to 36 hours.
- In third class, an additional payment of 4% of earnings is also possible.
- Milk (from 1.5 liters per day) and other products are provided to those whose professions are included in the list of Government Decree No. 168.
- Regular medical examinations, including additional ones to detect tuberculosis and HIV.
- Workers with working conditions of the 3rd hazard class are provided with insurance. When an insured event occurs (injury, for example), a payment is issued for treatment and rehabilitation.
It is possible to retire earlier than the standard age. The list of professions that require early retirement due to harmful working conditions is established by Federal Law No. 400. According to it, women retire at 50 years old, men at 55 years old.