Concept and types of disciplinary sanctions
What is disciplinary action?
Disciplinary action is a penalty for discipline. It's simple. But what actions or behaviors violate discipline?
An employee of a simple company can violate labor discipline. A striking example is being late for work or, conversely, leaving the workplace before the end of the working day without a good reason.
In order to impose a penalty on an employee for violating the working day, there must be a reason. This is primarily reflected in the internal regulations and other regulations of the company.
Do not forget that according to the legislation of the Russian Federation, disciplinary action is the same type of liability as criminal or material.
Internal local acts of the company must not violate the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Many large structures are developing regulations on disciplinary action.
This is common among military personnel, medical workers and other public sector workers.
How can an employer punish for violation of discipline?
Several types can be used.
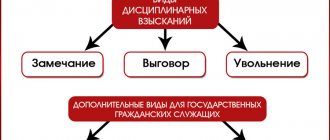
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that disciplinary action can be of 3 types:
- comment;
- rebuke;
- dismissal.
No local act of regional or local government can expand this list. And especially the company.
If a company has developed a system of fines for being late for work or, in general, for any irregular departure from work, then this is illegal. Contact the labor inspectorate.
The system of disciplinary sanctions is well developed among military personnel. For violation of discipline they apply:
- Rebuke;
- Severe reprimand;
- Reduction in rank;
- Dismissal;
- Deduction;
- Arrest.
In order to apply a penalty, the manager must find a basis when explaining the reasons for the behavior of the offending employee in writing. Only after this is a reprimand applied.
For systematic violation of discipline, he may ultimately be fired. The dismissal order must specify all the reprimands for which the employee is dismissed.
If the employee was not informed that he was reprimanded, then the dismissal is also illegal.
After all, he did not know that he was violating labor discipline and could not correct his behavior.
Rules for drawing up a document
We propose to consider several examples of documentation that appear when issuing a disciplinary sanction against employees who have committed serious or moderate violations.
Sample explanatory note:
A sample of an act drawn up in cases where an employee does not agree with the charges:
An order form for disciplinary action is available.
Application procedure
The employee is required to provide an explanation.
To initiate disciplinary proceedings, it is necessary to require the employee to provide a written explanation of the reasons for his behavior.
He has 2 days to submit an explanation. If he does not do this, then a special form of act of refusal to provide explanations is drawn up.
After this, the production itself occurs. The circumstances of the misconduct, the severity and consequences for the company of such employee behavior are studied.
Evidence is also collected that the misconduct took place. This can be obtained from the head of the department in which the offender works. If the company keeps records of employee arrivals/departures, request an extract for a specific employee.
If the organization has trade unions that protect the rights of workers, then without their opinion the production cannot be closed and a decision cannot be made.
The guilty employee is a full-fledged person in the production. He has the right:
- study materials;
- demand new materials;
- give your assessment;
- demand audits and inspections;
- involve third-party specialists and trade unions.
If a penalty is nevertheless applied, an order to apply a disciplinary sanction is drawn up. The employee is required to familiarize himself with it.
The basis for review is the employee’s signature on the document. If within 3 days the employee is not familiarized with this order, then a report is drawn up. This period does not include the time of his excused absence.
Only one penalty can be applied per offense. If an employee commits the same type of misconduct, but regularly, this is considered several misconducts.
Dismissal as a disciplinary sanction may be applied in the following cases:
- Repeated violation of discipline;
- The only gross violation;
- Unreasonable decision (for a manager);
- Actions that resulted in loss of trust.
Dismissal for violation of discipline can only be established by a court (Article 391 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If an employee does not agree with the decision made or the evidence base for applying a penalty, he can appeal this to a superior manager or contact the Labor Inspectorate.
Disciplinary offense. What does this mean?
Limits of disciplinary offense
A disciplinary offense is considered non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment of those duties that are directly related to the performance of work activities. Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation determines that this includes violation of established norms of labor legislation, non-compliance with job descriptions, terms of the employment contract (ET), etc.
The resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court determined that disciplinary offenses include:
- Absence from one's workplace without permission from superiors or other valid reasons. This act can be imputed only when the subordinate has been indicated in writing where his workplace is located. In the absence of such instructions, a work place may be considered to be the place where the employee is obliged to come to perform his duties.
- Refusal of a subordinate to perform the duties prescribed in the job description. The TD or job description clearly defines what exactly the subordinate is responsible for during the work process and for what he will receive a salary, and if he refuses to do this, this is regarded as a direct violation of labor discipline. If the employee’s refusal is based on a change in the conditions of the labor contract, then this behavior is not regarded as a guilty act.
- Refusal of subordinates to undergo the required training in safety, labor protection, etc., if this is one of the mandatory conditions for admission to the performance of their direct duties.
- Refusal of subordinates to sign a document on partial or full responsibility, if this was previously agreed upon when registering a person for a position and this is provided for by current legislation.
The Labor Code stipulates that a misdemeanor can arise due to the intentional actions of the employee, or due to negligence. In any of these cases, he bears responsibility, regardless of the form of guilt. The only exceptions are those cases when nothing depended on the subordinate (lack of raw materials, onset of illness, etc.).
A disciplinary offense is considered in the following cases:
- Actions/inactions are committed by a person who is in an employment relationship with the management of the organization.
- The actions committed are not classified as socially dangerous, since otherwise they would be considered criminal offenses.
The actions of a subordinate, which were carried out taking into account legal norms and rules, cannot be regarded as a guilty act. Thus, an employee’s refusal to be transferred to another type of work if his consent is required for this is legal. In the same way, refusal to leave vacation early at the request of the management of the enterprise organization is considered lawful.
Disciplinary offenses do not include refusal to fulfill the obligations assigned to him, if this threatens his health or life, until the possible danger is eliminated.
https://youtu.be/qr5MMWyUmKo
Terms of application of disciplinary sanctions
Misdemeanors have an expiration date.
Penalties can be applied within a limited period. Each stage of production has its own time frame.
It applies no later than 30 days from the moment the violation is discovered. This period does not include:
- employee sick days;
- employee leave.
No more than 180 days must pass from the day the offense was committed; if audits and inspections of the company’s activities were carried out during the proceedings, then the period increases to 2 years.
After all deadlines have expired, the penalty should not be applied, that is, no order for disciplinary action is issued.
In this case, the employee is not considered guilty and can safely work in this company.
Office hours are not included in this period. It turns out that this can last a very, very long time.
Validity period of penalties
From the date of issue of the order, the penalty is valid for one year. After the end of this period, it is withdrawn automatically; no additional withdrawal instructions are required.
The manager can remove the penalty early on his own initiative or at the request of the head of the department, the trade union or the employee himself.
The stigma of a “guilty person” implies its educational nature.
Thus, the employee who has been disciplined tries to correct his behavior and follow labor discipline.
Order on application of penalty
An order is issued containing some information.
If a disciplinary sanction is decided to be applied to an employee, an order is drawn up. There is no strict form of the order, but many use a unified form developed by the Russian government.
The fact is that the order must strictly reflect important aspects:
- Type of violation;
- Time of violation (date);
- Detection time;
- Proof;
- Type of recovery.
In order not to waste time developing their own form, many people use a ready-made, standard form.
The order is issued in one copy and several copies are made: one for a personal file, the other for the employee personally.
Simply issuing an order and filing a case is not enough. It is mandatory to familiarize yourself with the employee’s order and have a signature on the order. If the employee is not informed within three days, then a report is drawn up.
The act reflects all the facts of the moment the employee refused to read and sign the order. Who was present, what time it was, reasons for refusal (if possible).
https://youtu.be/XKGgYbPj9PI
How to apply
Procedure for filing a disciplinary sanction:
- Calling the employee to the director or head of a department or division.
- Obtaining explanations from the offending employee, finding out the reasons for his actions, etc.
- The employee must write an explanatory note.
- If you refuse to submit an explanatory document, the employer draws up an act of insubordination.
- An order to impose punishment is drawn up. Deadline – no later than 3 days in working hours.
- The employee must sign the order.
- In case of refusal to sign the order, an act of disagreement is also drawn up.
If a subordinate categorically refuses to write an explanatory note, then monetary penalties in the form of a fine may be applied to him.
Here another order comes into force:
- The employee is given another 2-3 days to think about it.
- Then an act of refusal to explain what happened or the violation was drawn up.
- He must sign the document.
- If the act is not signed by the employee, then the penalty is imposed on him anyway.
According to Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in cases of an employee’s refusal to explain the reasons for the misconduct, the employee’s opinion will no longer be taken into account. Therefore, the employer has every right to determine the extent of the financial penalty or other type of punishment.
Every employee or employee who violates discipline at work can be punished by the employer. He may be reprimanded, fined, or suspended from office for a short time. But the violator also has the right to appeal the employer’s decision.
To do this, all such employees are given time to appeal - 3 months. But first they turn to the GIT (State Labor Inspectorate), and if nothing works out, then only to the judicial authorities.