Land tax for individual entrepreneurs in 2020: main changes
All changes made to the Tax Code (including paragraph 1 of Article 398 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and Article 2 of the Federal Law dated November 4, 2014 No. 347-FZ came into force on January 1, 2020.
Starting from 2020, individual entrepreneurs do not need to submit land tax returns.
The tax for land (which is owned by an individual entrepreneur) will now be paid by individual entrepreneurs based on the requirement of a tax notification until October 1 of the year following the reporting year, that is, by October 1, 2020, individual entrepreneurs must pay the land tax for 2020.
The deadline for paying land tax for ordinary individuals is set by local authorities and indicated in the tax notice.
Unlike individual entrepreneurs, legal entities still have the obligation to submit a land tax return. The deadline for filing a declaration for 2020 is February 1, 2020.
The deadline for payment of land tax by legal entities is set by local authorities; in some regions, land tax must be paid quarterly.
In 2020, the tax authorities plan to calculate land tax and send the relevant data to individual entrepreneurs and individuals for payment for 2020.
The tax base for determining the amount of land tax for 2017 is the cadastral value of the land plot as of January 1, 2020 (clause 1 of Article 391 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This calculation applies if during 2020 the following did not change:
- category of land;
- type of permitted use.
If during the year changes were made to the USRN according to the above indicators, then:
From January 1, 2020, when calculating land tax, the cadastral value is taken, which was determined on the date of registration of its change in the Unified State Register.
Taking into account this new procedure, the tax amount is determined based on the ownership coefficient (Q).
- Kv = Km/Kpm;
- Km - the number of full months from the date of entering information about the cadastral value into the Unified State Register of Real Estate;
- Kpm - The number of calendar months in the tax (reporting) period.
The BCC for paying land tax depends on the location of the land plot.
The following BCCs have been determined for 2020:
182 1 06 0603X XX 1000 110, where the indicator X XX depends on the location of the site:
for a land plot located within the boundaries of intra-city municipalities of the cities of Moscow, St. Petersburg and Sevastopol:
- tax 18210606031031000110
- penalties 182 1 06 06 031 03 2100 110
- fine 182 1 06 06 031 03 3000 110
for a land plot located within the boundaries of urban districts:
- tax 18210606032041000110
- penalties 182 1 0600 110
- fine 182 1 0600 110
for a land plot located within the boundaries of urban districts with intra-city division:
- tax 18210606032111000110
- penalties 182 1 0600 110
- fine 182 1 0600 110
for a land plot located within the boundaries of intracity districts:
- tax 18210606032121000110
- penalties 182 1 0600 110
- fine 182 1 0600 110
for a land plot located within the boundaries of intersettlement territories:
- tax 18210606033051000110
- penalties 182 1 0600 110
- fine 1 82 1 0600 110
for a land plot located within the boundaries of rural settlements:
- tax 18210606033101000110
- penalties 182 1 0600 110
- fine 182 1 0600 110
for a land plot located within the boundaries of urban settlements:
- tax 18210606033131000110
- penalties 182 1 0600 110
- fine 182 1 0600 110
CONFIRMATION OF THE RIGHT TO LAND TAX BENEFITS IN 2018
The right to apply land tax benefits is determined by Article 395 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In addition to the categories listed in this article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the legislation gives the right to municipal authorities to independently decide which categories of citizens to provide benefits for paying land tax.
Law No. 286-FZ dated September 30, 2017 amended the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in terms of confirming the right to land tax benefits. From January 1, 2018, to receive the benefit, there is no need to submit documents to the Federal Tax Service confirming the ability to apply this benefit.
Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation No. ММВ-7-21/897 dated November 14, 2017, which entered into force on January 1, 2020, approved a new form of application for land tax benefits.
Thanks to this form, the owner of the land plot has the right to choose whether to provide the Federal Tax Service with title documents for the plot and to receive benefits, or indicate the details of these documents in the application.
If you indicate the details of title documents without attaching them to the application, employees of the Federal Tax Service will independently send a request to the authorities that issued these documents. Further, if you are registered in the taxpayer’s personal account, then information on the consideration of an application for a benefit can be obtained by logging into your personal account.
If you still do not have an account in your personal account on the Federal Tax Service website, then you will receive a response in one of the following ways:
- in person at the tax office or at the MFC;
- by mail.
Tax payment procedure for individual entrepreneurs and organizations
Legal entities using the simplified tax system and individual entrepreneurs who use the simplified tax system pay tax in different ways. The reporting procedure for organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified regime is also different.
Let's start with entrepreneurs. If you have registered an individual entrepreneur and own land, then you do not need to worry about calculating taxes and submitting documents. According to the changes that came into force on 01/01/15, entrepreneurs pay tax on the basis of a notification. The simplified procedure provides for the following conditions:
- You do not need to calculate the tax amount yourself. The fiscal service authority will send you a notification by mail, which will provide a full calculation of the payment amount;
- Along with the notification, a receipt is sent by mail, which contains all the necessary details for payment. All you need is to go to the nearest bank branch along with the receipt to transfer funds;
- For individual entrepreneurs, the obligation to file a tax return has been canceled, that is, there is no extra reason to visit the Federal Tax Service.
Individual entrepreneurs pay land taxes in the current year for the previous year (until December 31). The law stipulates that you must receive the notification no later than November 1 of the year (for 2020 - before 11/01/17).
The situation is a little more complicated with legal entities - “simplified”. They have a complete procedure for calculating tax, paying it and submitting reports.
Let's start with the documents: before February 1 of the next year, the “simplified” organization submits a declaration in which it indicates the full calculation of the tax in accordance with the established norm. You can submit your declaration in the way that is most convenient for you:
- Personal visit to the Federal Tax Service (receiving a form and filling out the form on the spot);
- Russian postal services (sending a letter with a notification and a list of attachments);
- Transfer of papers through a representative (you must first contact a notary to draw up a power of attorney);
- Using the electronic resource of the Federal Tax Service (the website of the fiscal service offers users the service of filing reports via the Internet).
By filing your return on time, ensure that your tax is paid on time. The law regulates the advance payment system for land taxes. Payments are made quarterly, their amount is determined as ¼ of the annual one. The payment deadline for each amount is until the end of the month following the quarter. Full payment of land tax must be made no later than October 1 (until 10/01/17 for 2016).
Example No. 3.
The accountant of Fontan LLC calculated the amount of land tax for 2016 in the amount of 2,104 rubles. Quarterly payments were:
RUB 2,104 / 4 sq. = 526 rub.
When submitting a declaration at the end of the year, the Fontana accountant indicated the annual amount of 2,205 rubles. (including recalculation). The final calculation of the land tax was made by Fountain on January 10, 2017. The last payment amount was calculated as follows:
RUB 2,205 – (526 rub. * 4 sq.) = 101 rub.
This might also be useful:
Is the information useful? Tell your friends and colleagues
By clicking on the “Submit” button you confirm that your comment does not contain personal data in any combination.
Questions and answers in the comments are provided by site users and are not in the nature of legal advice. If you need legal advice, we recommend that you obtain it by calling the numbers listed above or using this form
The simplified taxation system was created specifically to make life easier for entrepreneurs, and not complicate it. In fact, often, everything happens exactly the opposite: a payer who has recently switched to the simplified tax system is lost and does not understand either how to calculate the single tax or how to reflect it in accounting. The result is a lot of errors, and the Internet is full of messages “help me calculate the simplified tax system.”
We have collected all the most common mistakes when calculating a single tax, read the questions and advice from regulars, and prepared a cheat sheet for you: how to correctly reflect the tax under the simplified tax system using transactions?
Individual entrepreneur on the simplified tax system: notifications on land tax
If legal entities can independently calculate the amount of land tax, then individual entrepreneurs must wait for a special tax notification.
For your information! Previously, before 2014, both individuals and legal entities had to submit tax returns. But since 2015, individual entrepreneurs have been exempted from this obligation - now they receive tax notices with a pre-calculated amount of land tax.
It happens that the notification for some reason does not reach the addressee, then the taxpayer himself must appear at the tax authority and report the plot of land he owns. You must have all registration documents with you.
As the Tax Code states, representatives of the tax inspectorate must send notifications with the tax amount 30 days before the deadline for paying the land tax. From 2020, for individual entrepreneurs this deadline is December 1. This means that it will be necessary to take care of providing the tax authorities with the necessary information in the absence of notification in November.
Important! Starting from 2020, in cases where an individual entrepreneur-taxpayer who owns land has not received notification of the amount of land tax and has not voluntarily contacted the tax office in order to have the amount of tax payment calculated and assigned to him, he is obliged will incur administrative liability. In particular, he will be fined 20% of the unpaid tax and penalties.
In this article, we tried to talk about all the nuances of land tax relating to organizations and individual entrepreneurs who are on a simplified taxation system. However, to obtain more accurate information for each specific region of the Russian Federation, you should contact the tax office at the place of registration, since land tax rates, as well as the timing and procedure for its payment, are determined by the regions of the Russian Federation at the local level.
Land tax under the simplified tax system is paid by taxpayers on a general basis, as well as under the OSNO. The Tax Code does not provide for exemption from paying land tax under the simplified tax system (clause 2 of Article 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation lists all cases of tax exemption for organizations working under the simplified tax system).
What do you need to know about the single tax?
Entrepreneurs who apply the “simplified tax” pay one instead of three main taxes (profit, property and value added):
- or 6% of total income for 12 months;
- or 15% of the difference between income and expenses, but not less than 1% of total income.
The percentage charged under the “income” taxation scheme is unchanged. But for legal entities and individual entrepreneurs who have determined the “income-expenses” scheme as the basis, regional laws may establish a reduced tariff.
Also from 01/01/15. for individual entrepreneurs who carry out business activities in the following areas:
- education,
- the science,
- production,
For two years in a row, a zero (0%) single tax tariff is established if the individual entrepreneur meets the following requirements:
- 70% of income from economic activities relates to income in one of the areas indicated above;
- The individual entrepreneur complies with the requirements of regional law in terms of the average number of employees and the amount of total income received.
For tax purposes, all incoming and expended funds from the business or other activities of a legal entity or individual entrepreneur must be reflected in the KUDiR.
Next, on the basis of the formed KUDiR, from the beginning of the year until the end of the corresponding payment period, either the amount of income or the difference between income and expenses is calculated.
Advance periods for the Unified Tax Code on the simplified tax system are 3,6 and 9 months, while the tax period is considered to be one calendar year. Accordingly, the single tax must be calculated and paid four times a year - at the end of each quarter and within 3 months after the end of the tax period. The transfer of tax for the entire period is carried out simultaneously with the submission of a tax return, which reflects the amounts of payments already made and the remaining amount of debt.
Remember that from 01/01/2013 all entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system are required to maintain not only KUDiR, but also organize full-fledged accounting, as well as generate accounting and tax reporting. Accordingly, your task, as a payer, is not only to calculate and transfer tax to the budget, but also to correctly calculate and write it off using accounting entries.
Simplified betting
| Object of taxation | Bid, % |
| Income | 6 |
| Income minus expenses | 15 |
| Object of taxation | Minimum rates established by a constituent entity of the Russian Federation |
| Income | 1 |
| Income minus expenses | 5 |
So, for example, the Law of Moscow dated October 7, 2009 No. 41 reduced the simplified tax rate for the object “income minus expenses” to 10% for certain types of activities, provided that the revenue from this “preferential” type of activity is 75% or more for reporting (tax) period.
Calculating the base
If you apply the “income” scheme, then based on the completed KUDiR from the beginning of the year you need to summarize (taking into account the provisions of Articles 250, 254, 284 and 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- income from sales;
- other non-operating income.
From the resulting amount you can subtract the following value:
- actual contributions made to the Social Insurance Fund, Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund and Pension Fund;
- sick leave benefits paid to employees;
- contributions under voluntary insurance contracts for employees;
In this case, the amount of EH payable after the calculations made cannot decrease by more than half.
Enterprises and individual entrepreneurs paying the unified tax according to the “income-expenses” scheme, from the beginning of the period, sum up their income according to KUDiR, and then subtract from them the expenses determined in accordance with the provisions of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Remember that for the “income-expenses” scheme there is an approved procedure for confirming transactions (Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), which must be strictly adhered to. If you are not sure of the integrity of your counterparties, think several times before choosing “income-expenses” as the basis for the simplified tax system.
Also remember that there are some special conditions when defining a base:
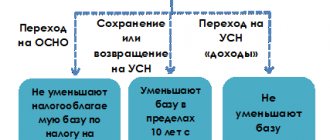
- Individual entrepreneurs working without hiring employees have the right to reduce the base under the simplified tax system “income” by the entire amount of fixed contributions from the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund and the Social Insurance Fund. At the same time, additional contributions (1% of the amount exceeding the minimum annual income) cannot be taken into account in the UN base.
- Entrepreneurs using the income-expenses scheme can carry forward losses incurred in the current year to periods in the future (within 10 years). At the same time, in the declaration and when making accounting entries for calculating the single tax, the amount of the loss must be shown and documents confirming it are reflected. Otherwise, it will be impossible to exercise the right to reduce the future simplified tax base. This rule is valid even if you have just started your business and only have expenses for now.
Tax notices for individual entrepreneurs
Tax returns for 2014 were submitted by both legal entities and individuals. Starting from 2020, individuals are freed from the obligation to report to the tax office - instead, they will receive tax notices with the amount of land tax to be paid already calculated by the fiscal authorities.
If the taxpayer has not received a tax notice, he must himself contact the tax authority at the location of the land plot and report the existing object of taxation. You will also need to submit title and registration documents for the land.
This obligation arose due to the introduction into Art. 23 Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 2.1. This means that if an individual or individual entrepreneur does not receive a tax notice about the payment of land tax by the end of 2020, then he must contact the fiscal department himself, filling out a special message about the availability of real estate.
The message form can be downloaded here.
In paragraph 2 of Art. 52 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that the Federal Tax Service sends notifications with tax calculations 30 days before the deadline for paying land tax. For individuals, this deadline from 2020 is December 1. That is, taxpayers can take care of submitting information to the Federal Tax Service in connection with failure to receive notifications as early as November 2020.
For failure to fulfill the obligation to independently contact the tax authority due to failure to receive a notification, a fine of 20% of the unpaid amount of tax and penalties will be charged (clause 3 of Article 129.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). These sanctions began to apply at the beginning of 2020.
We calculate and pay taxes
You have calculated the tax base for a certain period of time. What's next?
Next, we calculate the amount of EUR to be paid to the budget (line 110 of the declaration). To do this, we multiply the base by the corresponding tax rate and subtract the amount of tax contributions already paid from the resulting value. The resulting amount is a tax or advance payment, which you need to reflect in accounting for accrual or payment in an accounting program, for example 1C.
If you have a 1C version younger than 8.3.0.31.11, you will have to enter transactions for the single tax simplified tax system manually or use semi-automatic filling. For semi-automatic filling you need:
- Go to the main page of the program;
- Enter the section “Correspondence of invoices”;
- To calculate tax, select account “99” in the drop-down list for debit, and subaccount “12” for credit “68”.
- In the “Documents” column we find the hyperlink “Operation BU and NU” and follow it. Fill in the empty fields and indicate the amount.
- We press Enter and we can see the completed operation in the log.
In the same way, the posting for the payment of EN with the correspondence of accounts “Dt 68.12 Kt.51” is carried out, and we indicate the document - “write-off from the account” on the “Bank and Cash Office” tab. By the way, in later versions of 1C, the calculation and payment of tax according to the simplified tax system are fully automated.
>Recording of land plots under “simplified”
O.E. Shpilevaya, D.V.
Payment of land tax on the simplified tax system if the land has been owned for less than a year
As with any other types of taxes, the calculation and payment of land tax has its own characteristics. In particular, taxpayers often have questions in cases where the right to use a plot of land arose within a year. How to calculate tax in such situations?
It’s simple: the cadastral value of the plot must be taken on the date when the cadastral registration took place. At the same time, the amount of tax must be calculated taking into account a special coefficient, which you need to calculate yourself. To do this, you need to look at how many full months of the year the land plot was owned. Then the resulting number must be divided by 12 - the result will be the desired coefficient.
5/12 (5 months: 12 months) Next we calculate:
6250 rub. – 2500 rub. = 3750 rubles - this is exactly how much money this enterprise must pay to the state budget as land tax.
Land tax under the simplified tax system: payment procedure, deadlines
Ignatiev, experts from the Legal Consulting Service GARANT
The organization applies the simplified tax system with the object of taxation “income minus expenses”. The organization has several land plots on its balance sheet at purchase price; the acquired land plots are not intended for further resale. Land plots are not depreciated. How to write off the cost of land in accounting?
According to paragraph 3 of Article 4 of the Federal Law of November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ “On Accounting”, organizations that have switched to the simplified tax system are exempt from the obligation to maintain accounting records, except for accounting for fixed assets and intangible assets.
This means that an organization using the simplified tax system must keep records of fixed assets in accordance with PBU 6/01 “Accounting for fixed assets” (hereinafter referred to as PBU 6/01).
Land plots for accounting purposes are accounted for as part of fixed assets (clauses 4, 5 of PBU 6/01).
Fixed assets are accepted for accounting at their original cost (clause 7 of PBU 6/01). The initial cost of fixed assets acquired for a fee is recognized as the amount of the organization's actual costs for acquisition, construction and production, with the exception of VAT and other refundable taxes (except for cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation) (clause 8 of PBU 6/01).
As a general rule, the cost of fixed assets is repaid through depreciation (clause 17 of PBU 6/01).
At the same time, fixed assets whose consumer properties do not change over time, including land plots, are not subject to depreciation (clause 17 of PBU 6/01).
Consequently, the value of land plots can be written off from accounting only in the event of their disposal, which occurs in cases of sale, transfer in the form of a contribution to the authorized (share) capital of another organization, a mutual fund, transfer under an agreement of exchange, gift, deposit contribution under a joint activity agreement and in other cases (clause 29 of PBU 6/01).
Income and expenses from writing off fixed assets from accounting are reflected in accounting in the reporting period to which they relate and are subject to credit to the profit and loss account as other income and expenses (clause 31 of PBU 6/01).
According to paragraph 11 of PBU 10/99 “Expenses of the organization,” other expenses include, among other things, expenses associated with the sale, disposal and other write-off of fixed assets and other assets other than cash (except foreign currency), goods, and products.
For your information
Organizations applying the simplified tax system and choosing income reduced by the amount of expenses as an object of taxation can take into account for the purposes of forming the tax base only those expenses that are listed in the closed list contained in paragraph 1 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, provided that they meet the criteria specified in paragraph 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 2 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In accordance with subparagraph 1 of paragraph 1 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when determining the object of taxation, the taxpayer reduces the income received by expenses for the acquisition, construction and production of fixed assets (taking into account the provisions of paragraphs 3 and 4 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, fixed assets for the purpose of applying Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation include fixed assets that are recognized as depreciable property in accordance with Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 4 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Since, in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, land is not subject to depreciation and the list of expenses taken into account when determining the tax base under the simplified tax system, established by paragraph 1 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, does not provide for expenses for the acquisition of land plots, the organization does not have the right to take into account expenses in the form the cost of land plots when forming the tax base for the tax paid in connection with the application of the simplified tax system (see, for example, letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 30, 2011 No. 03-11-06/2/101, dated September 16, 2010 No. 03-11-06 /2/145).
How to calculate tax
Simplified tax is defined as the product of the tax base and the tax rate.
Under the simplified tax system, the tax base is the monetary expression of the object of taxation according to a simplified system.
For the object “income”, the tax base is the monetary expression of the income of an organization or individual entrepreneur (Clause 1 of Article 346.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
If the object of taxation is “income minus expenses,” then the tax base under the simplified tax system in this case will be the monetary expression of income reduced by the amount of expenses (clause 2 of article 346.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Which object to choose depends on the amount of expenses for the simplified tax system, because if there are no expenses under the simplified system or they are insignificant, then using the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” is inappropriate.
The object must be selected when switching to the simplified tax system. Subsequently, it can be changed at least every year.
How much and when?
To calculate land tax, data on the cadastral value of the plot is required. It is determined either at the beginning of the year or at the time of registration of the object. If the site is located on the territory of several subjects, then the cadastral value is determined for each within the established boundaries.
The tax period is one year. If during this period there is a change in the value of the site, the taxpayer will still calculate the tax base based on the assessment as of January 1. This requirement does not apply to the adjustment of value in the event of an error by the body carrying out cadastral valuation and accounting.
In case of shared ownership, the amount of land tax is set in proportion to the share of ownership. The taxpayer himself calculates the tax using information from the cadastral register.
Tax rates for land tax are determined by local authorities. But the legislation regulates the maximum sizes:
- 0.3% - for agricultural land, gardening, animal breeding, construction of residential buildings.
- 1.5 – for all other categories of land.
In certain situations, it is necessary to use ratios to calculate taxes.
Tax rate
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation positions land tax as a local tax. Rates for calculating land tax are set at the municipal level.
The maximum tax rates are set within the following limits (clause 1 of Article 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- 0.3% for agricultural land and for maintaining personal subsidiary plots (including gardening, vegetable farming, livestock farming), as well as for housing plots and lands with limited circulation;
- 1.5% for other categories of land.
These maximum values are applicable for calculating land tax throughout the Russian Federation. At the same time, the establishment by the legislator of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation of tax rates within the above framework does not conflict with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Current legislation allows for the establishment of different tax rates depending on the purpose of the land, permitted use and location of the site (clause 2 of Article 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Municipal legislation also has the right to regulate land tax benefits and the conditions for their application (clause 2 of Article 387 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Postings for land tax accounting
Land tax is reflected in the accounts depending on the use of the site. If the land is intended for production (performance of work/services), then Credit 68 of the Land Tax sub-account will correspond with the Debit of account 20 (and auxiliary 23,25,26,29) or 44.
If a plot of land is leased to generate income, an entry is made Debit 91.2 Credit 68 “Land Tax”.
When constructing an object on a site, tax is calculated: Debit 08 Credit 68 “Land Tax”.
To transfer tax to the budget, use posting Debit 68 “Land tax” Credit 51.
Example
purchased a plot of land in 2014. As of January 1, 2020, its cadastral value was RUB 2,755,926. The tax rate in this subject is 1.5%. You need to calculate advance payments for the first and second quarters. In the first quarter, the site was used as a parking lot for the company's vehicles. In the second quarter, the land was leased.
First quarter = 2,755,926 x 1.5% x ¼ = 10334.72
Second quarter = 2,755,926 x 1.5% x ¼ = 10334.72
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| 20.01 | 68.06 | Advance payment for land tax for the first quarter has been accrued | 10334,72 | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 68.06 | 51 | Advance payment for land tax for the first quarter was transferred to the budget | 10334,72 | Original payment order |
| 91.02 | 68.06 | Advance on land tax for the second quarter accrued | 10334,72 | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 68.06 | 51 | Advance payment of land tax for the second quarter has been paid | 10334,72 | Original payment order |
>What are the entries when calculating land tax (accounting)
How to do this correctly to avoid conflicts with the tax office?
Land tax as part of the “simplified” expenses
If you or your organization uses the simplified tax system, then you need to know that the amount of paid land tax can be taken into account as part of the expenses incurred. This condition applies if you use the “income minus expenses” scheme. By accounting for taxes as expenses, you can reduce the taxable base of personal income tax, and, consequently, the amount of tax payable. To do this, you need to indicate the amount of land tax transferred to the budget in the corresponding line of the declaration.
Example No. 2.
Auto Plus LLC provides vehicle parking services and uses the simplified tax system (income minus expenses). At the end of 2016, Auto Plus included in its expenses:
- 605 rub. – salary for the watchman and other service employees;
- 540 rub. – payment of utilities (electricity, water, gas supply);
- 610 rub. – land tax transferred to the budget.
The income of Auto Plus in 2020 amounted to 702,800 rubles.
When calculating personal income tax, the accountant indicated the revenue received and expenses incurred:
(RUB 702,800 – RUB 104,605 – RUB 88,540 – RUB 2,610) * 15% = RUB 76,057
In total, Auto Plus transferred personal income tax in the amount of 76,057 rubles.
What are the entries in budget accounting?
Every year, funds are allocated from budgets of all levels for the payment of land tax by budgetary organizations.
How to reflect the accrual and payment of land tax by budgetary organizations is indicated in the Instructions for Budget Accounting.
Depending on which taxation system the enterprise uses, accounting for accrual and payment of land tax will occur differently.
| Tax system | Land tax accounting |
| OSN | Land tax is included in expenses when taxing profits. This is stated in paragraph 1.1 of Art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| simplified tax system | If an enterprise applies the simplified tax system “Income”, then the paid land tax does not in any way affect the size of the tax base for the single tax. If an enterprise applies the “STS “Income minus expenses”, then the paid land tax should be included in the expenses of the enterprise, which reduce the tax base for the single tax. This is stated in paragraph 1. 22 of Art. 346. 16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| UTII | In Art. 346. 29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that paid land tax is not taken into account when calculating the tax base for “imputed” tax |
| Combination of UTII and OSN | If an enterprise uses both SST and UTII in its activities, and uses a land plot for both types of activities, then the amount of accrued land tax must be divided in proportion to the profit from each type of activity in the total profit of the company. This is due to the fact that with OSN the land tax is taken into account, but with UTII it is not. |
Land tax
According to the Instructions for Budget Accounting, land tax accounting in budgetary organizations depends on:
- use of land in budgetary activities
| Debit | Credit | |
| Land tax accrued | 1 401 012 90 “Other expenses” | 1 303 057 30 “Increase in accounts payable for other payments to the budget” |
| Land tax paid to the budget | 1 303 058 30 “Reduction of other debt on other payments to the budget” | 1 304 052 90 “Settlements for payments from the budget with bodies organizing the execution of budgets for other expenses” |
- and activities of the organization that generate income
| Debit | Credit | |
| Land tax accrued | 2 106 043 40 “Increase in the cost of manufacturing materials, finished products (works, services)” | 2 303 057 30 “Increase in accounts payable for other payments to the budget” |
| Land tax transferred to the budget | 2 303 058 30 “Reduction of accounts payable for other payments to the budget” | 2 201 016 10 “Disposal of institution funds from bank accounts” |
| Simultaneous reflection on the off-balance sheet account according to KOSGU 290 “Other expenses” | 18 “Retirement of funds from bank accounts of the institution” |
When calculating land tax under the simplified tax system, the transactions are exactly the same as in other taxation systems.
Regardless of the taxation system, the entries for the calculation and payment of land tax to the budget of the subject of the federation will be as follows:
The calculation of land tax and its reflection on one of the cost accounts depends on the intended purpose of the site.
To account for land tax, subaccount 9 “Land tax” is opened in account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”.
Land tax must be calculated and paid from the moment of registration of land rights. After registration, the land plot is accepted on the balance sheet of the enterprise in account 01 “Fixed assets” under the subaccount “Land plot”.
A plot of land is accounted for at its original cost. To calculate the initial amount of land tax, the cadastral value of the plot at the time of registration of real rights to it is taken.
Depreciation is not charged on land, so the tax can be reduced only if the cadastral value decreases.
For tax accounting purposes, the amount of accrued land tax is credited to account 91 “Other income and expenses” to subaccount 2 “other expenses”.
Thus, if the land plot is not used for the main activity, then the entries for the calculation and payment of land tax will be as follows:
Advance payment calculation
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that all taxpayers must make advance payments for land tax.
But, if the authorities of the constituent entities of the federation have not established such an obligation at the legislative level of the subject, then taxpayers should not accrue and pay advance payments.
Budgetary organizations are taxpayers of land tax, and charge and pay land tax on a general basis.
Budgetary organizations must pay land tax and advance payments from their own funds that business activities bring them.
If they do not conduct such activities, then they need to write a letter to the territorial department of the Federal Tax Service to grant them a deferment in paying this tax.
The calculation and payment of advance payments occurs in the same way as the main tax. The accounting entries are made exactly the same.
How to calculate the amount for paying land tax, read the article: calculation of land tax.
What benefits are provided to combat veterans?
For tax purposes, advance payments are taken into account in the same way as annual taxes. Such records are kept if the land plot is used for the main activity.
The basis for the calculation and payment of the advance payment, as well as the main tax, is an accounting certificate.
All accrued and paid advance payments are included in other expenses from ordinary or operating activities.
The management of the company decides how to account for advance payments. This decision must be reflected in the company's accounting policies.
The company chooses the list of indirect and direct expenses independently. They independently determine which expenses include land tax.
Such records are kept if the site is not used for the main activity.
Fine and penalty
Often, after a desk or field audit, tax authorities impose fines and penalties on taxes on taxpayers. Land tax is no exception.
If tax authorities have imposed fines and penalties, then the following entries should be made in accounting:
Even if the company is going to defend the illegality of accruing penalties and fines, it is still necessary to make an entry for the accrual of these amounts.
In 1C, transactions for calculating land tax are generated automatically.
If the company wins the case, and the accrual of fines and penalties is declared unlawful by the court, then based on the court decision, a “reversal” entry will be made.
All tax sanctions, including land tax, are not taken into account in tax accounting.
That is, when calculating the tax base for income tax, penalties are not included in the expenses that reduce this base.
The same applies to “simplified” people who use “income minus expenses”. Sanctions do not reduce the tax base for the single tax on the simplified tax system. The same state of affairs is with the “imputed” people.
Expenses for rent in case of rental agreement – when there are not enough funds for your own property
However, if the salary of an ordinary employee is not legally limited to the maximum, then the remuneration of managers, his deputies and chief accountants has corresponding limits. We will talk about this in the article. May 30, 2020 Commentary on the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 15, 2018 No. 09 01 09/16085 about advance payments Based on clause 3.11-1 of Art. 2 of the Federal Law of November 3, 2006 No. 174-FZ “On Autonomous Institutions”, autonomous institutions, when concluding contracts (agreements) for the supply of goods, performance of work, provision of services that require advance payments, comply with the requirements specified by regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, regulatory legal acts subjects of the Russian Federation, municipal legal acts regulating budget legal relations for recipients of funds from the corresponding budget of the budget system of the Russian Federation.
The department publishes an answer to a question frequently asked by taxpayers: “The organization leases a plot of land. What is the procedure for writing off rent as an expense if more is paid per month than the lessor invoiced? In accordance with paragraphs. 4 paragraphs 1 art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), when determining the object of taxation, the taxpayer reduces the income received by rental, including leasing, payments for rented, including leased, property.
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses of a taxpayer are recognized as expenses after their actual payment. In this case, expenses must meet the criteria established in paragraph 1 of Art. 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 2 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Clause 1 of Art.
Are certificates of service provision required? According to the recommendations of the Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service, expenses when renting a simplified tax system do not have to be confirmed by monthly acts on the provision of services (Letters of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-03-04/1/742 dated 09.11.2006, Federal Tax Service No. 02-1-07/81 dated 09.05.2005 G.). However, if such acts are absent, then the remaining documents must contain all the mandatory details in accordance with the Federal Law “On Accounting”. Otherwise, documents will not be able to confirm tax expenses.
Therefore, many tenants are forced to play it safe and negotiate with the landlord to provide certificates of service provision at the end of the month or quarter. Terms of the contract It is necessary to monitor compliance with the terms of the contract. If the lease agreement has expired, but the organization still uses the leased property, then an agreement on a new term should be signed.
The rent is paid upon delivery: expenses are written off immediately when the money is transferred to the lessor. If the lessor is a VAT payer, then the paid “input” VAT on rent can be taken into account as expenses under a separate item. How to confirm expenses? There is no specific list of documents that can be used to justify rental expenses in the Tax Code.
According to the recommendation of the Ministry of Finance (letter No. 03-03-06/1/559 dated 06.10.2008), it is important that during the inspection an organization or individual entrepreneur can provide: - a lease agreement; — act of acceptance and transfer of leased property; — rental payment schedule; — payment documents confirming payment of rent. Payment In this case, payment for goods (work, services) and (or) property rights is recognized as the termination of the obligation of the taxpayer - purchaser of goods (work, services) and (or) property rights to the seller, which is directly related to the supply of these goods (performance of work, provision of services ) and (or) transfer of property rights. Payment in advance However, the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation emphasized in letter dated March 30, 2012 No. 03-11-06/2/49, if the taxpayer makes rental payments for property used in business activities in advance (that is, he actually makes an advance payment services not provided by the lessor under the lease agreement), these payments must reduce the tax base evenly (as specified in the lease agreement) upon receipt of the above-mentioned services.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when provided on the territory of the Russian Federation by state authorities and local governments for lease of federal property, property of constituent entities of the Russian Federation and municipal property, the VAT tax base is determined as the amount of rent including tax. In this case, the tax base is determined by the tax agent separately for each leased property. Tax agents - tenants In this case, tax agents are the tenants of the specified property.
These persons are required to calculate, withhold from income paid to the lessor, and pay the appropriate amount of tax to the budget.
- Electronic reporting
- Online accounting
Salary, Timesheet, Personnel!!! Download and Run! 1838 rubles, including 2NDFL, persuchet
Nuances
The calculation and payment of land tax, like any other tax, has its own nuances. To avoid getting into trouble, you need to know a few important points.
If a land plot is provided for a fee for temporary use under a lease agreement?
The use of land in our country is paid. Owners pay land tax, and tenants pay rent according to the agreement.
Land leased under a lease agreement is not subject to land tax.
This is clearly stated in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The owner of the land must pay taxes on the plot of land.
The tenant, by paying a fee under the agreement, compensates the owner for all costs associated with the use of the land by the tenant, including land tax.
For an enterprise that has provided a plot of land for rent, the accrual of land tax will be reflected in account 91 of subaccount 2, since renting land is not the main activity of the enterprise.
The wiring will be as follows:
If the provision of land for rent is the main activity of the enterprise, then the accrual of land tax is taken into account on one of the cost accounts, usually on account 25 or 26.
Which entry reflects the transfer of land tax to the budget?
Every quarter, enterprises transfer advance payments to the budget, and at the end of the year - the main tax. During the year, the amount of accrued tax is accumulated in account 68 in subaccount 9 “Land tax”.
The tax is transferred from the company's current account. Payments must be made every quarter so that the amount of non-payment does not accumulate on account 68-9.
The transfer of land tax to the budget is reflected by the following entry:
How to pay property tax with a tax system in 2017-2018?
In most cases, “simplified” people who own a plot of land and use it for a retail outlet, warehouse, production, office, etc., calculate the tax based on this value. In rare cases, tax may be paid at a reduced rate of 0.3%. You have the right to use this indicator for calculation if you use the land for agricultural purposes, as well as for gardening, vegetable farming, livestock farming (for example, you grow crops for sale).
Rates may be reduced at the discretion of local authorities. In order to clarify what rate applies to a particular plot in your region, we advise you to contact the Federal Tax Service at your place of residence (registration).
Taxpayers
Land tax is paid by firms and entrepreneurs who own land plots by right:
- property;
- permanent (unlimited) use;
- lifelong inheritable ownership.
The status of land owner, landowner or land user must be confirmed with appropriate documents, for example, an act of state registration of ownership of a land plot.
note
Companies are not payers of land tax in relation to those plots of land that:
- or they have the right of free use, including the right of free fixed-term use;
- or transferred to them under a lease agreement.
What if you are already using a plot of land, but have not yet received the relevant documents? In such a situation, the tax office requires you to pay tax.
The position of the tax authorities in this case is supported by a letter from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 11, 2006 No. 03-06-02-02/37. It says that organizations and citizens who do not have title and title documents for actually used land plots should be held administratively liable for evading the registration of relevant rights to real estate, as provided for in Article 19.21 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
By virtue of this article, failure by the owner, tenant or other user to comply with the established procedure for state registration of rights to real estate or transactions with it shall entail the imposition of an administrative fine:
– for citizens in the amount of 1,500 to 2,000 rubles; – for officials – from 3,000 to 4,000 rubles; – for legal entities – from 30,000 to 40,000 rubles.
If you refuse to pay land tax, be prepared to defend your position in court. However, judicial practice on this issue is extremely contradictory. It is not a fact that the court's decision will be in your favor.
Thus, the opinion of officials is supported, in particular, by the FAS of the Central District in a resolution dated April 1, 2009 in case No. A68-3899/2008-174/5 and by the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation in a resolution dated July 12, 2006 No. 11991/05 in case No. A65-20581/2004-SA1-29. At the same time, the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court indicated that the absence of title documents for land plots cannot serve as a basis for exempting the actual land owner and land user from paying taxes, since the execution of such documents depends on the will of the latter.
Read about who must pay land tax and who is exempt from paying it in the “STS in practice” guide.